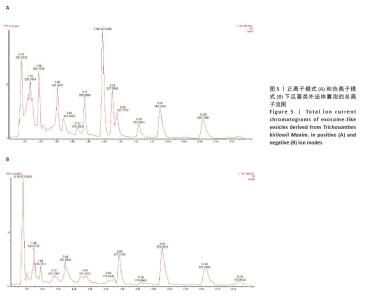
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1768-1781.doi: 10.12307/2026.118
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis
Chen Yulin1, 2, He Yingying1, 2, Hu Kai1, 2, Chen Zhifan1, 2, Nie Sha1, 2, Meng Yanhui1, 2, Li Runzhen1, 2, Zhang Xiaoduo1, 2, Li Yuxi2, Tang Yaoping1, 2, 3
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Faculty of International Education, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-01-11Revised:2025-06-20Accepted:2025-07-03Online:2026-03-08Published:2025-08-19 -
Contact:Tang Yaoping, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Faculty of International Education, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chen Yulin, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Science Fund Project), No. 82160856 (to TYP); Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Master Graduate Student Innovation Project, No. YCSW2024418 (to CYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Yulin, He Yingying, Hu Kai, Chen Zhifan, Nie Sha Meng Yanhui, Li Runzhen, Zhang Xiaoduo , Li Yuxi, Tang Yaoping. Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
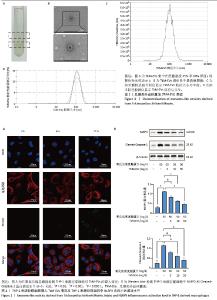
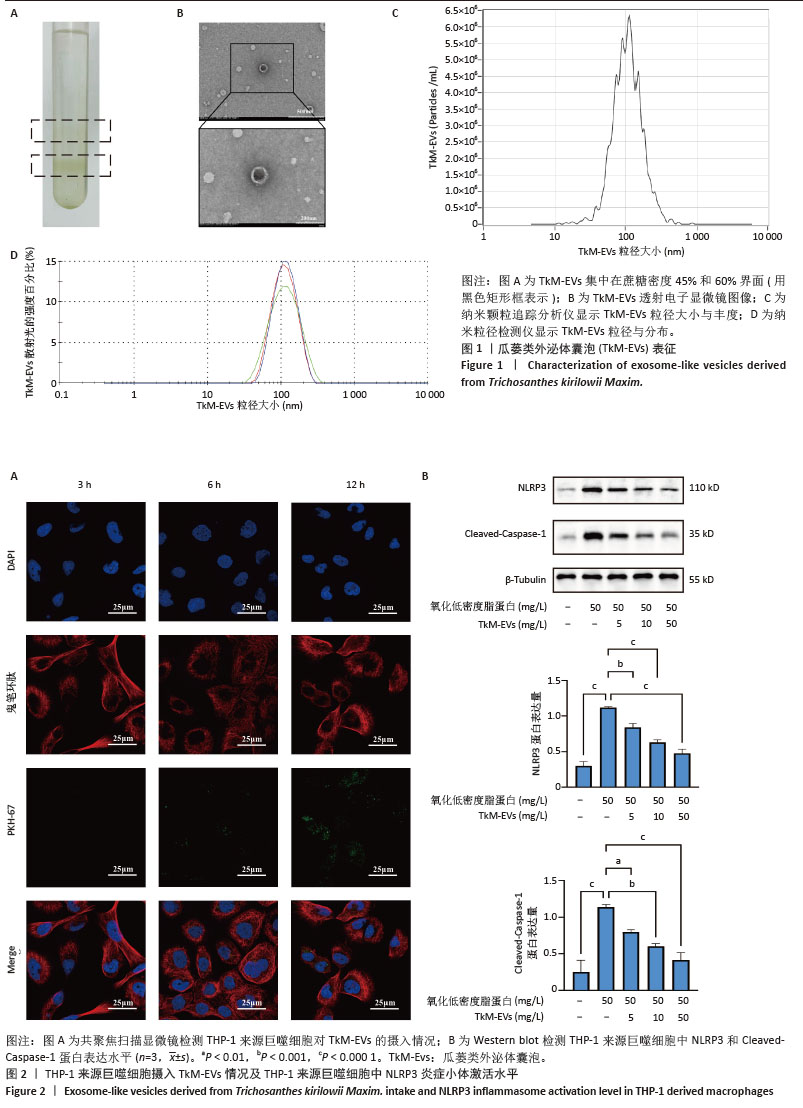
2.1 瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡表征 瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡集中在蔗糖梯度45%和60%界面(图1A),透射电子显微镜显示提取的瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡呈茶托状,粒径大小在50-150 nm之间(图1B),纳米颗粒追踪分析仪、纳米粒径检测仪与透射电子显微镜结果一致,均提示瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡粒径大小在50-150 nm之间,颗粒浓度约为1.4×1011/mL(图1C,D)。 2.2 瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡的细胞摄取情况 孵育3 h,在THP-1来源巨噬细胞中检测到瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡,表明瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡很快被THP-1来源巨噬细胞吸收。孵育12 h,大量THP-1来源巨噬细胞已内化瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡(图2A)。 2.3 THP-1来源巨噬细胞中NLRP3和Cleaved-Caspase-1蛋白表达水平 与空白组比较,模型组NLRP3和Cleaved-Caspase-1蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.000 1);与模型组比较,瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡低、中、高剂量组NLRP3和Cleaved-Caspase-1蛋白表达水平均减少,且呈浓度依赖性下降(图2B)。"
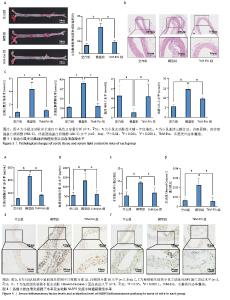
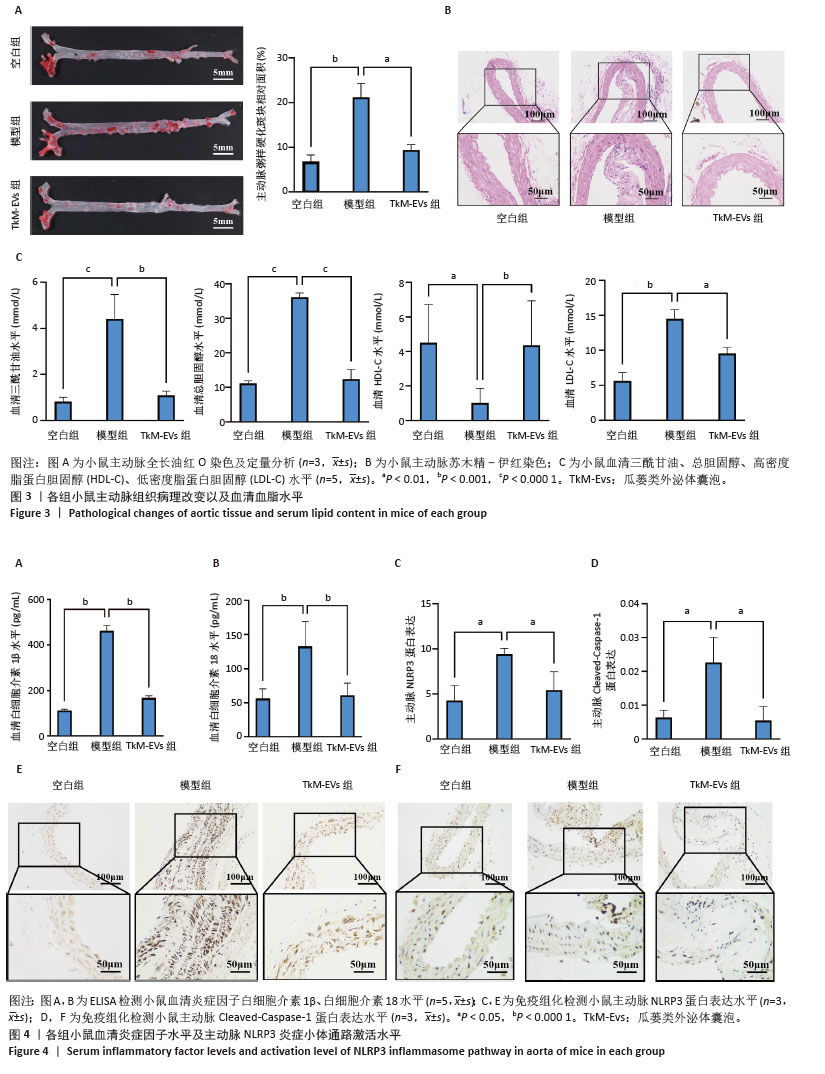
2.4 小鼠主动脉斑块面积 油红O染色显示,空白组斑块形成较少,模型组斑块形成较为广泛,主动脉斑块面积显著增加(P < 0.001);与模型组相比,瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡组主动脉斑块面积显著减少(P < 0.01)(图3A)。 2.5 小鼠主动脉病理形态 苏木精-伊红染色显示,空白组小鼠主动脉结构完整,管壁均匀,内膜光滑,平滑肌细胞排列规则,未见明显炎症细胞浸润或组织损伤;模型组小鼠主动脉管壁结构紊乱,内膜损伤,平滑肌细胞排列不规则,有明显的炎症细胞浸润现象;与模型组比较,瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡组主动脉管壁结构有所改善,内膜较为完整,平滑肌细胞排列较为规则,炎症细胞浸润程度减少(图3B)。 2.6 小鼠血脂水平 与空白组比较,模型组血清中三酰甘油、总胆固醇和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平明显上升,高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平明显下降;与模型组相比,瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡组血清中三酰甘油、总胆固醇和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平下降,高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平上升(图3C)。 2.7 小鼠血清炎症因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18水平 与空白组相比,模型组血清中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18水平显著升高(P < 0.000 1);与模型组相比,瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡组血清中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18水平显著下降(P < 0.000 1)(图4A,B)。 2.8 小鼠主动脉NLRP3和Cleaved-Caspase-1蛋白表达水平 与空白组相比,模型组NLRP3和Cleaved-Caspase-1蛋白表达水平显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡组NLRP3和Cleaved-Caspase-1蛋白表达水平显著下降(P < 0.05) (图4C-F)。"
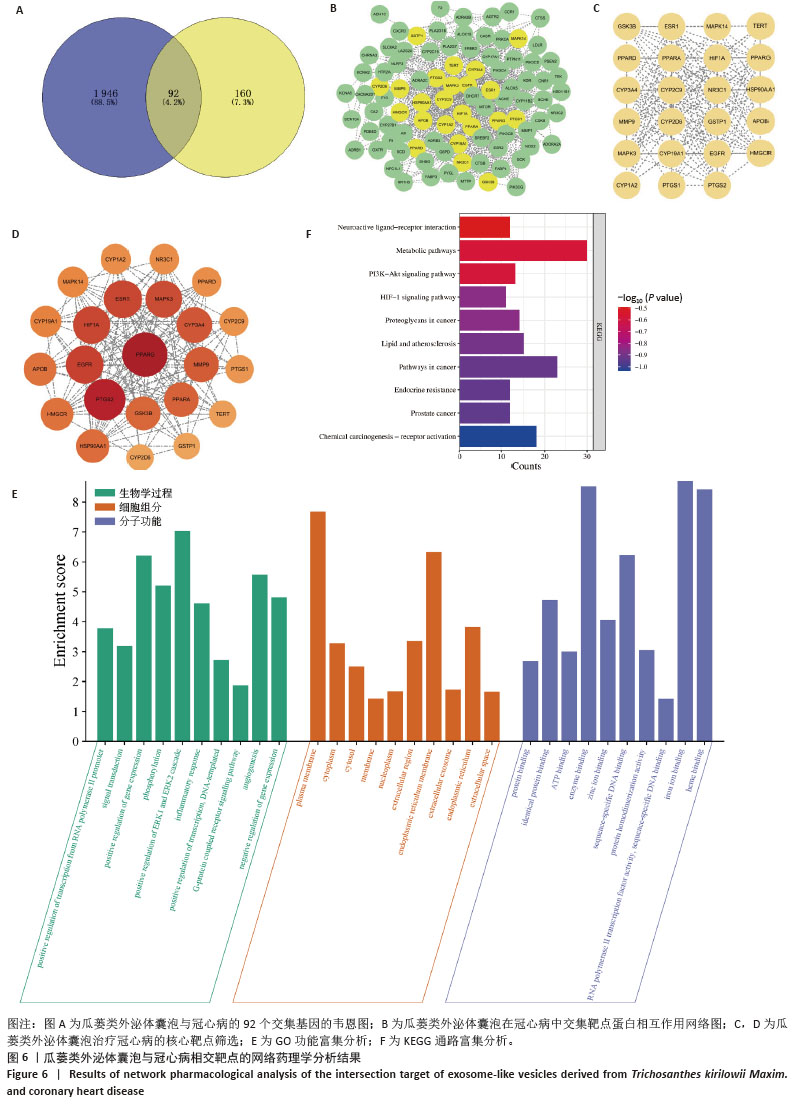
2.11 瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡治疗冠心病靶点预测 通过GeneCards、OMIM和DisGeNET数据筛选出1 946个与冠心病相关的疾病靶点,将疾病靶点与瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡靶点相交集,可得到92个共同靶点(图6A)。 2.12 交集靶点蛋白相互作用网络图 将92个共同靶点导入STRING数据库,下载tsv格式数据,然后导入Cytoscape软件构建成由92个节点和671条边组成的蛋白相互作用网络(图6B),利用CytoNCA插件筛选出23个中介中心性和接近中心性均大于中位数的核心靶点(图6C,D)。 2.13 GO功能富集分析和KEGG通路富集分析 GO功能富集分析显示瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡参与了多种生物学过程,如正向调控ERK1和ERK2连锁反应、血管生成以及炎症反应等(图6E);在细胞组分方面,瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡与内质网、质膜和细胞质相关(图6E);在分子功能方面,瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡主要涉及铁离子结合、血红素结合、酶结合、序列特异性DNA结合等(图6E)。KEGG通路显示瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡主要参与的信号通路包括脂质与动脉粥样硬化、低氧诱导因子1信号通路等相关通路(图6F)。"
| [1] RADDATZ MA, PERSHAD Y, PARKER AC, et al. Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential and Cardiovascular Health. Cardiol Clin. 2025;43(1):13-23. [2] GUSEV E, SARAPULTSEV A. Atherosclerosis and Inflammation: Insights from the Theory of General Pathological Processes. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):7910. [3] RUIZ-LEON AM, LAPUENTE M, ESTRUCH R, et al. Clinical Advances in Immunonutrition and Atherosclerosis: A Review. Front Immunol. 2019;10:837. [4] LIBBY P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021; 592(7855):524-533. [5] MACH F, BAIGENT C, CATAPANO AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(1):111-188. [6] HERNANDO-REDONDO J, NIÑO OC, FITÓ M. Atherogenic low-density lipoprotein and cardiovascular risk. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2025;36(1):8-13. [7] ITABE H, OBAMA T. The Oxidized Lipoproteins In Vivo: Its Diversity and Behavior in the Human Circulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5747. [8] LI Z, GUO J, BI L. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110542. [9] KELLEY N, JELTEMA D, DUAN Y, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3328. [10] FU JN, WU H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2023;41:301-316. [11] HA MT, PHAN TN, KIM JA, et al. Trichosanhemiketal A and B: Two 13,14-seco-13,14-epoxyporiferastanes from the root of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. Bioorg Chem. 2019;83:105-110. [12] HU XQ, SONG H, LI N, et al. Identification and analysis of miRNAs differentially expressed in male and female Trichosanthes kirilowii maxim. BMC Genomics. 2023;24(1):81. [13] ZHANG Y, WANG K, HUANG Q, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of an alpha-amylase inhibitor (TkAAI) gene from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. Biotechnol Lett. 2022;44(10):1127-1138. [14] HOU Z, ZHU L, MENG R, et al. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant activities of Trichosanthes kirilowii maxim seed oil and flavonoids in mice fed with a high-fat diet. J Food Biochem. 2020;44(8):e13272. [15] 鲍友利,曹寅,吴鸿飞. “瓜蒌-薤白”药对诱导自噬抑制NLRP3炎症小体激活减轻RAW264.7巨噬细胞炎症反应[J].中国中药杂志, 2023,48(10):2820-2828. [16] MU N, LI J, ZENG L, et al. Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:4987-5009. [17] CUI LS, PERINI G, PALMIERI V, et al. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Frontier in Cancer Therapeutics. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(16):1331. [18] BUZAS EI. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023;23(4):236-250. [19] ZHANG B, SIM WK, SHEN TL, et al. Engineered EVs with pathogen proteins: promising vaccine alternatives to LNP-mRNA vaccines. J Biomed Sci. 2024;31(1):9. [20] WU J, MA Y, CHEN Y. Extracellular vesicles and COPD: foe or friend? J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):147. [21] COLY PM, BOULANGER CM. Role of extracellular vesicles in atherosclerosis: An update. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;111(1):51-62. [22] SHARMA S, MAHANTY M, RAHAMAN SG, et al. Avocado-derived extracellular vesicles loaded with ginkgetin and berberine prevent inflammation and macrophage foam cell formation. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(7):e18177. [23] ZHANG S, XIA J, ZHU Y, et al. Establishing Salvia miltiorrhiza-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles and Elucidating Their Role in Angiogenesis. Molecules. 2024;29(7):1599. [24] NIU W, XIAO Q, WANG X, et al. A Biomimetic Drug Delivery System by Integrating Grapefruit Extracellular Vesicles and Doxorubicin-Loaded Heparin-Based Nanoparticles for Glioma Therapy. Nano Lett. 2021;21(3):1484-1492. [25] KIM J, LI S, ZHANG S, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(1):53-69. [26] MADRIGAL-MATUTE J, FERNANDEZ-GARCIA CE, BLANCO-COLIO LM, et al. Thioredoxin-1/peroxiredoxin-1 as sensors of oxidative stress mediated by NADPH oxidase activity in atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;86:352-361. [27] EL HADRI K, MAHMOOD DF, COUCHIE D, et al. Thioredoxin-1 promotes anti-inflammatory macrophages of the M2 phenotype and antagonizes atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(6):1445-1452. [28] KHARE HA, BINDERUP T, HAG AMF, et al. Longitudinal imaging of murine atherosclerosis with 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose and [18F]-sodium fluoride in genetically modified Apolipoprotein E knock-out and wild type mice. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):22983. [29] WANG LH, GU ZW, LI J, et al. Isorhynchophylline inhibits inflammatory responses in endothelial cells and macrophages through the NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023;23(1):80. [30] GUPTA D, ZICKLER AM, EL ANDALOUSSI S. Dosing extracellular vesicles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;178:113961. [31] FENG WJ, TENG YT, ZHONG QP, et al. Biomimetic Grapefruit-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Safe and Targeted Delivery of Sodium Thiosulfate against Vascular Calcification. Acs Nano. 2023;17(24):24773-24789. [32] LI M, HOU XF, ZHANG J, et al. Applications of HPLC/MS in the analysis of traditional Chinese medicines. J Pharm Anal. 2011;1(2):81-91. [33] 吴希泽,康健,李越,等.基于“浊气归心,淫精于脉”理论运用HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和网络药理学探讨抵挡汤防治动脉粥样硬化和高脂血症的作用机制[J].中国中药杂志,2023,48(5):1352-1369. [34] LIAN MQ, CHNG WH, LIANG J, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: Recent advancements and current challenges on their use for biomedical applications. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11(12):e12283. [35] NEMATI M, SINGH B, MIR RA, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: a novel nanomedicine approach with advantages and challenges. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):69. [36] CHEN Y, CUI FC, WU XY , et al. The expression and clinical significance of serum exosomal-long non-coding RNA DLEU1 in patients with cervical cancer. Ann Med. 2025;57(1):2442537. [37] ALDALI F, DENG CC, NIE MB, et al. Advances in therapies using mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes for treatment of peripheral nerve injury: state of the art and future perspectives. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(11):3151-3171. [38] ZHAO Y, ZHANG YD, LIU X, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of plasma exosomes reveals the functional contribution of N-acetyl-alpha-glucosaminidase to Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2025; 20(10):2998-3012. [39] YIN WJ, MA HY, QU Y, et al. Exosomes: the next-generation therapeutic platform for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(5):1221-1235. [40] WU GQ, SU TY, ZHOU P, et al. Engineering M2 macrophage-derived exosomes modulate activated T cell cuproptosis to promote immune tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials. 2025:315:122943. [41] JIANG MY, ZHANG K, MENG JF, et al. Engineered exosomes in service of tumor immunotherapy: From optimizing tumor-derived exosomes to delivering CRISPR/Cas9 system. Int J Cancer. 2025;156(5):898-913. [42] RAIMONDO S, URZÌ O, MERAVIGLIA S, et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of lemon-derived extracellular vesicles are achieved through the inhibition of ERK/NF-kappaB signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(15):4195-4209. [43] LI ZF, WANG HZ, YIN HR, et al. Arrowtail RNA for ligand display on ginger exosome-like nanovesicles to systemic deliver siRNA for cancer suppression. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14644. [44] QIAO ZZ, ZHANG K, LIU J, et al. Biomimetic electrodynamic nanoparticles comprising ginger-derived extracellular vesicles for synergistic anti-infective therapy. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7164. [45] KANG SJ, LEE JH, RHEE WJ. Engineered plant-derived extracellular vesicles for targeted regulation and treatment of colitis-associated inflammation. Theranostics. 2024;14(14):5643-5661. [46] WATABE N, SUBSOMWONG P, YAMANE K, et al. Exosome-like nanoparticles from Arbutus unedo L. mitigate LPS-induced inflammation via JAK-STAT inactivation. Food Funct. 2024;15(22):11280-11290. [47] BIAN YP, LI WZ, JIANG XQ, et al. Garlic-derived exosomes carrying miR-396e shapes macrophage metabolic reprograming to mitigate the inflammatory response in obese adipose tissue. J Nutr Biochem. 2023;113:109249. [48] AL-HAWARY SIS, JASIM SA, ROMERO-PARRA RM, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in atherosclerosis: Focusing on the therapeutic potential of non-coding RNAs. Pathol Res Pract. 2023;246:154490. [49] XUE Z, ZHANG Z, LIU H, et al. lincRNA-Cox2 regulates NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy mediated neuroinflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(1):130-145. [50] HAO H, CAO L, JIANG C, et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Underlies Cholestasis-Associated Sepsis. Cell Metab. 2017;25(4):856-867. e5. [51] CHEN Y, QIN X, AN Q, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Directly Promote Inflammation by Canonical NLRP3 and Non-canonical Caspase-11 Inflammasomes. EBioMedicine. 2018;32:31-42. [52] SHARMA BR, KANNEGANTI TD. NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(5):550-559. [53] TANASE DM, VALASCIUC E, GOSAV EM, et al. Portrayal of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Atherosclerosis: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):8162. [54] WU P, WU W, ZHANG S, et al. Therapeutic potential and pharmacological significance of extracellular vesicles derived from traditional medicinal plants. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1272241. [55] LIU X, LOU K, ZHANG Y, et al. Unlocking the Medicinal Potential of Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: current Progress and Future Perspectives. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:4877-4892. [56] KIM M, PARK JH. Isolation of Aloe saponaria-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Investigation of Their Potential for Chronic Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(9):1905. [57] 丁杨,胡容. NLRP3炎症小体激活及调节机制的研究进展[J].药学进展,2018,42(4):294-302. [58] LUCAFÒ M, GRANATA S, BONTEN EJ, et al. Hypomethylation of NLRP3 gene promoter discriminates glucocorticoid-resistant from glucocorticoid-sensitive idiopathic nephrotic syndrome patients. Clin Transl Sci. 2021;14(3):964-975. [59] JIAO Y, YAN Z, YANG A. Mitochondria in innate immunity signaling and its therapeutic implications in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1160035. [60] WU Y, NI T, ZHANG M, et al. Treatment with β-Adrenoceptor Agonist Isoproterenol Reduces Non-parenchymal Cell Responses in LPS/D-GalN-Induced Liver Injury. Inflammation. 2024;47(2):733-752. [61] LIAO X, CHANG E, TANG X, et al. Cardiac macrophages regulate isoproterenol-induced Takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy. JCI Insight. 2022;7(3):e156236. [62] RONG J, HAN C, HUANG Y, et al. Inhibition of xanthine oxidase alleviated pancreatic necrosis via HIF-1α-regulated LDHA and NLRP3 signaling pathway in acute pancreatitis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14(8): 3591-3604. [63] MA J, CHEN L, ZHU X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21a-5p promotes M2 macrophage polarization and reduces macrophage infiltration to attenuate atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(9):1227-1236. [64] AL-AHMADI W, WEBBERLEY TS, JOSEPH A, et al. Pro-atherogenic actions of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 serine 727 phosphorylation in LDL receptor deficient mice via modulation of plaque inflammation. FASEB J. 2021;35(10):e21892. [65] JAIPERSAD AS, LIP GY, SILVERMAN S, et al. The role of monocytes in angiogenesis and atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(1):1-11. [66] XIAO X, XU M, YU H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles mitigate oxidative stress-induced senescence in endothelial cells via regulation of miR-146a/Src. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):354. |
| [1] | Zhou Sirui, Xu Yukun, Zhao Kewei. Ideas and methods of anti-melanogenesis of Angelica dahurica extracellular vesicles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1747-1754. |
| [2] | Wang Zhenze, Liu Fende, Zhang Rui, Li Wujun. Mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of arteriosclerosis obliterans of lower extremities: systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1869-1876. |
| [3] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [4] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [5] | Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai. Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 43-49. |
| [6] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [7] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [8] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [9] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [10] | Fang Yuan, Qian Zhiyong, He Yuanhada, Wang Haiyan, Sha Lirong, Li Xiaohe, Liu Jing, He Yachao, Zhang Kai, Temribagen. Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528. |
| [11] | Jiang Qiyu, Zeng Huiyan. A novel analysis and prediction method for potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine based on artificial intelligence and omics data-driven approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7552-7561. |
| [12] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [13] | Wang Tong, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Yang Hu, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Action mechanism of Gegenmaqi prescription in treatment of periarthritis of shoulder combined with type 2 diabetes based on TCMSP database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7669-7678. |
| [14] | Zhang Xin, Guo Baojuan, Xu Huixin, Shen Yuzhen, Yang Xiaofan, Yang Xufang, Chen Pei. Protective effects and mechanisms of 3-N-butylphthalide in Parkinson’s disease cell models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
| [15] | Hu Shujuan, Liu Dang, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang. Ameliorative effect of walnut oil and peanut oil on atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6482-6488. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||