Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1782-1789.doi: 10.12307/2025.574
Previous Articles Next Articles
Sequence analysis and identification of novel human leukocyte antigen alleles DQB1*06:436 and DQB1*02:108
Wang Manni, Wang Xiaofang, Wang Tianju, Shang Lixia, Chen Le, Li Yuhui, Zhang Yuan, Qi Jun
- Xi’an Central Blood Station, Shaanxi Blood Center, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-01Revised:2025-02-25Accepted:2025-03-17Online:2026-03-08Published:2025-08-20 -
Contact:Qi Jun, MD, Chief technician, Xi’an Central Blood Station, Shaanxi Blood Center, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Wang Manni, MS, Associate chief technician, Xi’an Central Blood Station, Shaanxi Blood Center, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Shaanxi Provincial Key Research & Development Program (General Project), No. 2022SF-098 (to QJ); Shaanxi Provincial Health and Health High-level Talent Cultivation Program Project (to QJ); Shaanxi Province Key Research & Development Plan (General Project), No. 2023-YBSF-024 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Manni, Wang Xiaofang, Wang Tianju, Shang Lixia, Chen Le, Li Yuhui, Zhang Yuan, Qi Jun. Sequence analysis and identification of novel human leukocyte antigen alleles DQB1*06:436 and DQB1*02:108[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1782-1789.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
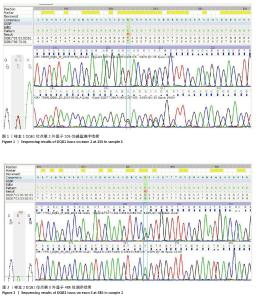
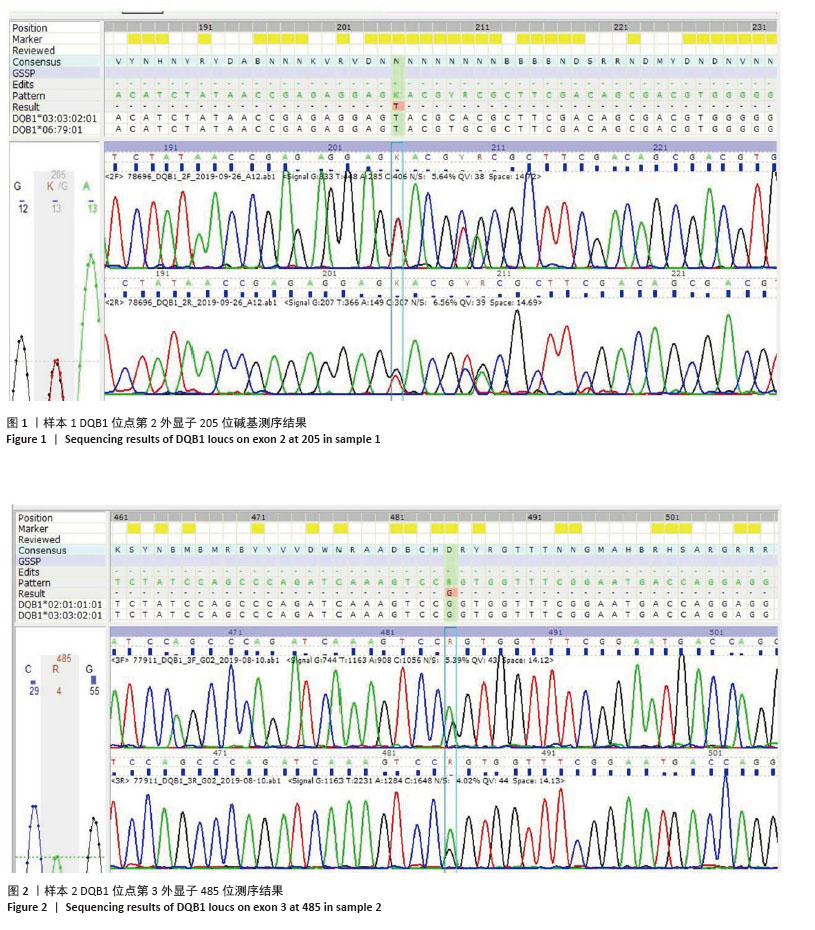
2.1 PCR-SBT实验结果 陕西地区2019年造血干细胞捐献者进行入库HLA分型,分型结果基本符合中国常见及确认的HLA等位基因表(CWD)2.4版中国人的基因型,发现2例样本DQB1位点无完全匹配基因分型。第1例先证者A、B、C、DRB1、DPB1位点分型结果分别为HLA-A*02:01,03:01;HLA-B*35:03,40:01;HLA-C*12:03,15:02;HLA-DRB1*07:01,15:01;HLA-DPB1*05:01:01G,13:01:01G。DQB1位点无完全匹配的分型结果,与其同源性最高的HLA-DQB1*03:03:02:01, 06:79:01的等位基因组合相比在第2外显子存在1个碱基差异,见图1,提示该位置可能存在碱基突变,故进一步应用单链测序和NGS测序进行确证。 第2例先证者A、B、C、DRB1、DPB1位点分型结果分别为HLA-A*24:02,33:03;HLA-B*57:01,58:01;HLA-C*01:02,03:02;HLA-DRB1*03:01,07:01;HLA-DPB1*04:02,15:01。DQB1位点无完全匹配的分型结果,与其同源性最高的HLA-DQB1*02:01:01:01, 03:03:02:01的等位基因组合相比在第3外显子有1个碱基差异,见图2,提示该位置可能存在碱基突变,故进一步应用NGS测序进行确证。"

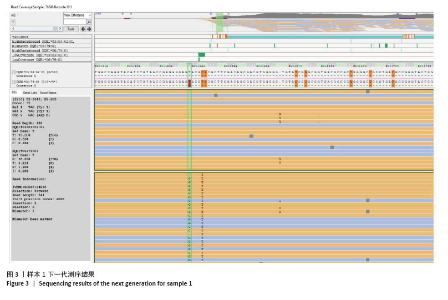
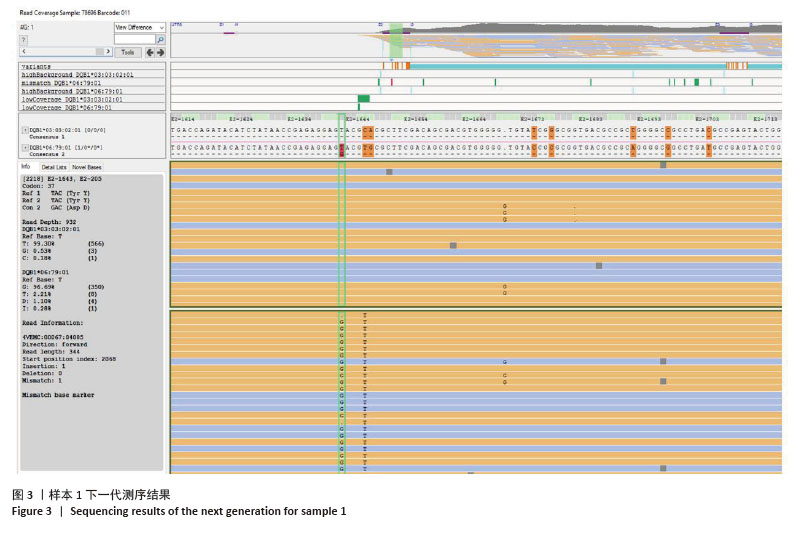
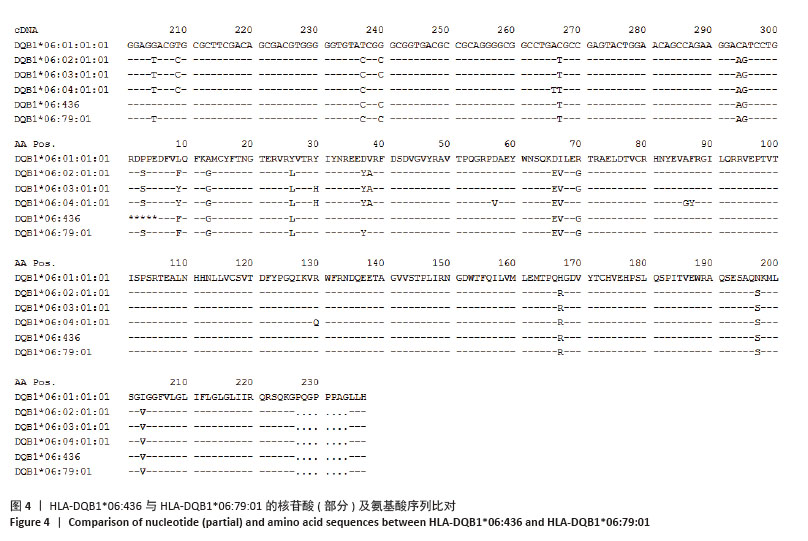
2.3 新等位基因与同源性最高的等位基因序列比对及命名 经BLAST比对,样本1与同源性最高的等位基因HLA-DQB1*06:79:01相比,在第2外显子205位碱基发生了T > G突变,导致位于第37位的酪氨酸(Tyr)变为天冬氨酸(Asp)。样本2与HLA-DQB1*02:01:01:01相比,在第3外显子485位存在一个碱基差异,发生了G > A突变,导致位于第130位的精氨酸(Arg)变为谷氨酰胺(Gln)。新等位基因与同源性最高等位基因对比见图4,5。将2例样本检测序列上传至Genbank后获得的Bankit ID及相关信息提交WHO HLA因子命名委员会,经审核后被正式命名为HLA-DQB1*06:436(HWS10064583)和HLA-DQB1*02:108(HWS10064279)。 "
| [1] TIMOFEEVA OA, PHILOGENE MC, ZHANG QJ. Current donor selection strategies for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hum Immunol. 2022;83(10):674-686. [2] TIERCY JM, CLAAS F. Impact of HLA diversity on donor selection in organ and stem cell transplantation. Hum Hered. 2013;76(3-4): 178-186. [3] BLANDIN L, DOUGÉ A, FAYARD A, et al. Platelet transfusion refractoriness and anti-HLA immunization. Transfusion. 2021;61(6): 1700-1704. [4] HAUFROID V, PICARD N. Pharmacogenetics Biomarkers Predictive of Drug Pharmacodynamics as an Additional Tool to Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Ther Drug Monit. 2019;41(2):121-130. [5] HORN PA, ELSNER HA, BLASCZYK R. Tissue typing for hematopoietic cell transplantation: HLA-DQB1 typing should be included. Pediatr Transplant. 2006;10(6):753-754. [6] 朱发明,毛伟,张志欣.人类白细胞抗原系统分型技术及其应用的现状分析和展望[J].中国输血杂志,2019,32(8):736-740. [7] GEO JA, AMEEN R, AL SHEMMARI S, et al. Advancements in HLA Typing Techniques and Their Impact on Transplantation Medicine. Med Princ Pract. 2024;33(3):215-231. [8] DUNN PP. Human leucocyte antigen typing: techniques and technology, a critical appraisal. Int J Immunogenet. 2011;38(6): 463-473. [9] YOHE S, THYAGARAJAN B. Review of Clinical Next-Generation Sequencing. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2017;141(11):1544-1557. [10] 董丽娜,陈男英,王炜,等.AllType NGS11位点测序试剂在HLA-DPB1基因分型中的模棱两可结果分析[J].中国输血杂志,2023, 36(1):1-7. [11] 武君华,王满妮,王天菊,等.下一代测序鉴定新等位基因HLA-DQB1*04:74和HLA-DRB1*07:01:23序列及家系调查[J].中国实验诊断学,2021,25(10):1489-1494. [12] 钟艳平,陈浩,周丹,等.应用二代测序技术排除PCR-SBT零错配的HLA-C基因型[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2022,30(4):1213-1218. [13] FERNANDES TA, FUKAI R, SOUZA CA, et al. Molecular identification of the HLA-DRB1-DQB1 for diagnosis and follow-up of acute leukemias. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2010;44(2):69-73. [14] 齐珺,王天菊,陈乐,等.HLA-DRB1,-DQB1,-DPB1等位基因及单体型多态性与北方汉族急性髓系白血病(非M3型)的关联性研究[J].中国输血杂志,2021,34(2):101-106. [15] KUTSZEGI N, YANG X, GÉZSI A, et al. HLA-DRB1*07:01-HLA-DQA1*02:01-HLA-DQB1*02:02 haplotype is associated with a high risk of asparaginase hypersensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2017;102(9):1578-1586. [16] GAGNÉ V, ST-ONGE P, BEAULIEU P, et al. HLA alleles associated with asparaginase hypersensitivity in childhood ALL: a report from the DFCI Consortium. Pharmacogenomics. 2020;21(8):541-547. [17] QI J, WANG TJ, LI HX, et al. Association of HLA class II (-DRB1,-DQB1,-DPB1) alleles and haplotypes on susceptibility to aplastic anemia in northern Chinese Han. Hum Immunol. 2020;81(12):685-691. [18] 黄雅琴,徐琳,艾竹,等.发作性睡病1型患者神经心理学、睡眠结构及HLA-DQB1基因型分布特征[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2023,23(8):730-737. [19] 王亮,费丽萍,杨凯,等.HLA-DQB1基因多态性与结核病易感性关系的Meta分析[J].实用预防医学,2020,27(26):641-645. [20] 杨志明.丙型肝炎病毒感染和HLA-DQB1基因多态性的相关性研究[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2018,28(9):1057-1059. [21] WANG T, SHEN C, QI J, et al. Haplotype-dependent HLA-DRB1-DQB1 susceptibility to occult HBV infection in Xi’an Han population. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023;11(4):e2102. [22] RAMANATHAN AS, SENGUTTUVAN P, CHINNIAH R, et al. Association of HLA-DR/DQ alleles and haplotypes with nephrotic syndrome. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016;21(9):745-752. [23] PODDIGHE D, CAPITTINI C, GAVIGLIO I, et al. HLA-DQB1*02 allele in children with celiac disease: Potential usefulness for screening strategies. Int J Immunogenet. 2019;46(5):342-345. [24] ZOU J, KONGTIM P, ORAN B, et al. Refined HLA-DPB1 mismatch with molecular algorithms predicts outcomes in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2022;107(4):844-856. [25] MALKI MMA, GENDZEKHADZE K, STILLER T, et al. Protective effect of HLA-DPB1 mismatch remains valid in reduced-intensity conditioning unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(2):409-418. [26] PETERSDORF EW, BENGTSSON M, DE SANTIS D, et al. Role of HLA-DP Expression in Graft-Versus-Host Disease After Unrelated Donor Transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(24):2712-2718. [27] FLEISCHHAUER K, SHAW BE. HLA-DP in unrelated hematopoietic cell transplantation revisited: challenges and opportunities. Blood. 2017;130(9):1089-1096. [28] DEHN J, SPELLMAN S, HURLEY CK, et al. Selection of unrelated donors and cord blood units for hematopoietic cell transplantation: guidelines from the NMDP/CIBMTR. Blood. 2019;134(12):924-934. [29] MANGUM DS, CAYWOOD E. A clinician’s guide to HLA matching in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Hum Immunol. 2022;83(10):687-694. [30] FUCHS EJ, MCCURDY SR, SOLOMON SR, et al. HLA informs risk predictions after haploidentical stem cell transplantation with posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Blood. 2022;139(10): 1452-1468. [31] PETERSDORF EW, ANASETTI C, MARTIN PJ, et al. Limits of HLA mismatching in unrelated hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2004;104(9):2976-2980. [32] PETERSDORF EW. Mismatched unrelated donor transplantation. Semin Hematol. 2016;53(4):230-236. [33] LOISEAU P, BUSSON M, BALERE ML, et al. HLA Association with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation outcome: the number of mismatches at HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, or -DQB1 is strongly associated with overall survival. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13(8):965-974. [34] MORISHIMA Y, KASHIWASE K, MATSUO K, et al. Biological significance of HLA locus matching in unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 2015;125(7):1189-1197. [35] FÜRST D, NEUCHEL C, TSAMADOU C, et al. HLA Matching in Unrelated Stem Cell Transplantation up to Date. Transfus Med Hemother. 2019; 46(5):326-336. [36] PETERSDORF EW, STEVENSON P, BENGTSSON M, et al. HLA-B leader and survivorship after HLA-mismatched unrelated donor transplantation. Blood. 2020;136(3):362-369. [37] AYUK F, BEELEN DW, BORNHÄUSER M, et al. Relative Impact of HLA Matching and Non-HLA Donor Characteristics on Outcomes of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018; 24(12):2558-2567. [38] FLEISCHHAUER K, TRAN TH, MEISEL R, et al. Donor Selection for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2023;120(15):261-268. |
| [1] | Chen Jinjie, Li Geng, Jiang Yefan. Role of Siblings protein family in cardiovascular diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5171-5178. |
| [2] | Mei Rigeng, Geng Shaohui, Lin Zhimin, Wu Jiapeng, Liu Xin, Lan Xinyi, Gao Yuruo, Huang Guangrui. Minipigs used in hydrogel wound repair research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4697-4702. |
| [3] | Shi Guangbo, Li Xiuting, Liu Xingcui, Guo Xianhu, Li Longfei, Wang Wenqing. Ability of medical wound dressings to resist penetration of bloodborne pathogens [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 3937-3941. |
| [4] | Shen Yong, Liu Shizhang. Research progress on antibacterial properties of medical copper-containing titanium alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3430-3437. |
| [5] | Wu Junhua, Wang Tianju, Wang Manni, Xu Hua, Qi Jun, Shang Lixia, Chen Le. Sequence analysis and identification of a new allele HLA-DRB1*12:02:10 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4857-4861. |
| [6] | Zhou Junli, Wang Xiaojun, Wang Haijiao, Li Chun. A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of new medical dressings for diabetic foot ulcers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2562-2569. |
| [7] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [8] | He Liumei, Chen Hao, Zhong Yanping, Quan Zhanrou, Zou Hongyan. Next-generation sequencing of identifying the human leukocyte antigen-A*24:353 and its gene frequency analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4009-4012. |
| [9] | Wei Zhongling, Jiang Yizhi, Huang Laiquan, Yan Jiawei, Yu Zhengzhi, Wang Nana, Huang Chen, Wang Ran, Huang Dongping. Severe aplastic anemia treated with unrelated cord blood combined with matched sibling allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2049-2054. |
| [10] | Zhong Yanping, Zou Hongyan, Quan Zhanrou, Deng Zhihui, Hong Wenxu. Analysis of full-length sequence and 18 point mutations of HLA-B in a leukemia patient and her family [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 77-82. |
| [11] | Yang Jinfeng, Ma Sanhui. Association between polymorphism of aggregate protein metabolic pathway gene and severity of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4939-4944. |
| [12] | Quan Zhanrou, He Liumei, Chen Hao, Hong Wenxu, Gao Suqing . Distribution characteristics of polymorphism of human leukocyte antigen C of hepatitis B virus carriers in patients from Shenzhen [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 482-486. |
| [13] | Xiong Chunxiang, , Wei Xiaochun, Yin Dong, Huang Yu, Du Chang, Mo Bingfeng. Susceptibility of ankylosing spondylitis early-onset hip ankylosis and human leukocyte antigen-B27 subtypes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3710-3715. |
| [14] | Huang Ruina, Huang Ruijia, Niu Caili, Qiu Wenbo, Wu Xiaowan, Wang Xiaojun, Wang Haijiao, Yang Chaojie. Effect of silver dressing on diabetic foot ulcer: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 323-328. |
| [15] | Gu Yingxuan, Hu Qu, Huang Linfeng, Hu Xiaohui, Quan Xiaoming, Wang Xiaojun, Wang Haijiao. Silver dressings for treating chronic infected wound: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2941-2946. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||