Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 1028-1035.doi: 10.12307/2025.972
Previous Articles Next Articles
Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations
Rong Xiangbin1, 2, Zheng Haibo1, Mo Xueshen1, Hou Kun1, Zeng Ping1, 3
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530222, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-11-13Accepted:2024-12-31Online:2026-02-08Published:2025-05-22 -
Contact:Zeng Ping, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530222, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Rong Xiangbin, MD candidate, Associate chief physician, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530222, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160913 (to ZP); Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Doctoral Student Innovation Project, No. YCBZ2023155 (to RXB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
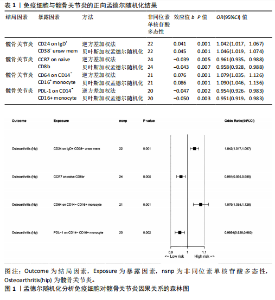
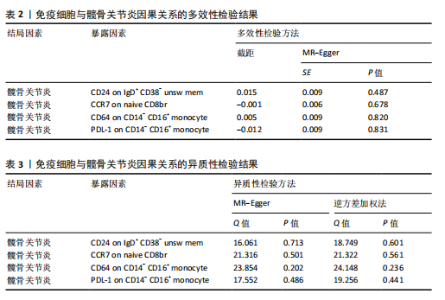
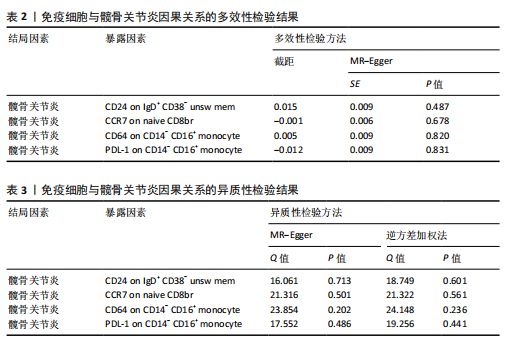
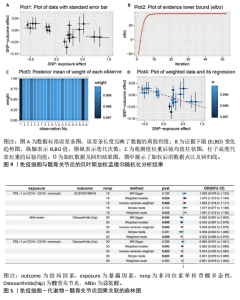
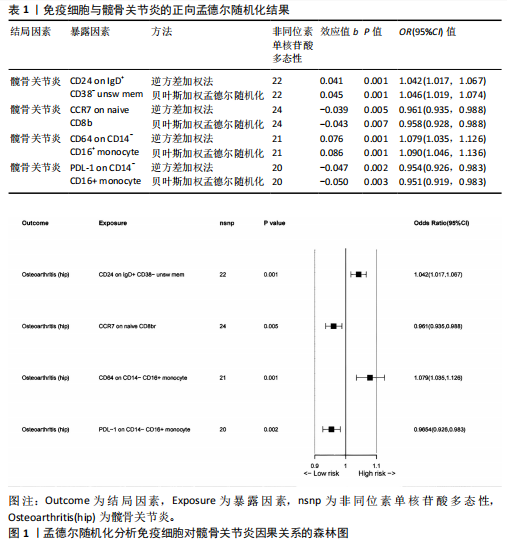
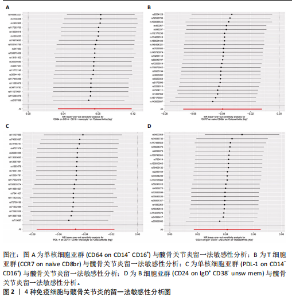
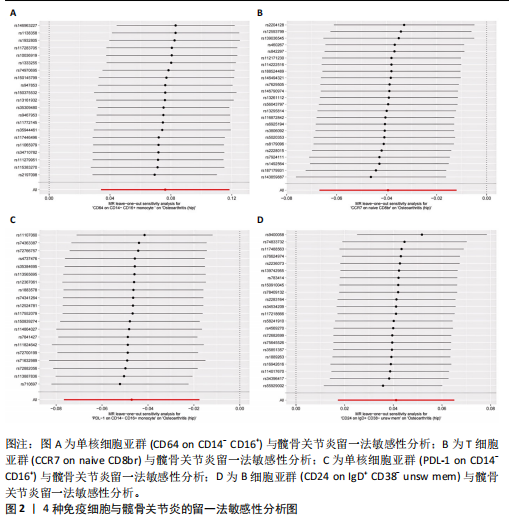
2.1 双样本孟德尔随机化和贝叶斯加权孟德尔随机化分析结果 逆方差加权分析结果显示,有4种免疫细胞满足筛选条件与髋骨关节炎存在潜在关联,见表1、图1。贝叶斯加权孟德尔随机化分析结果表明这4种免疫细胞仍满足显著相关的条件,见表1。 逆方差加权法和贝叶斯加权孟德尔随机化法的P均< 0.05,并且得到B细胞亚群CD24 on IgD+ CD38- unsw mem和单核细胞亚群CD64 on CD14- CD16+与髋骨关节炎呈正相关;T细胞亚群CCR7 on naive CD8br和单核细胞PDL-1 on CD14- CD16+与髋骨关节炎呈负相关。敏感性分析结果表明,这些单核苷酸多态性之间没有异质性和水平多效性。留一法敏感性分析结果表明,去除单个单核苷酸多态后未对效应估计值产生较大影响,即因果关系具一定的稳健性。水平多效性、异质性检验结果见表2,3,留一法敏感性分析检验结果见图2。"
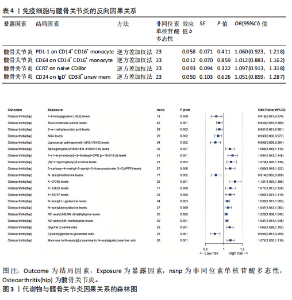
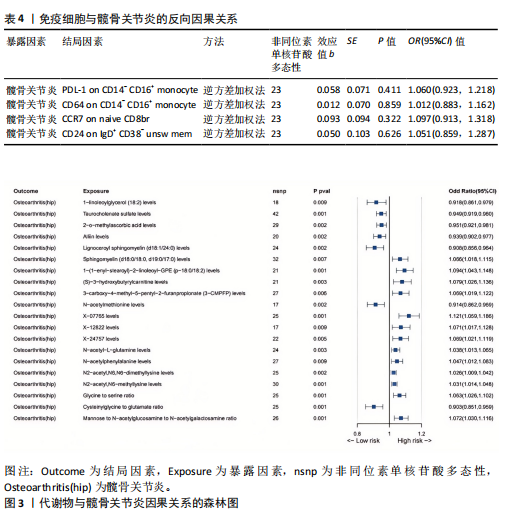
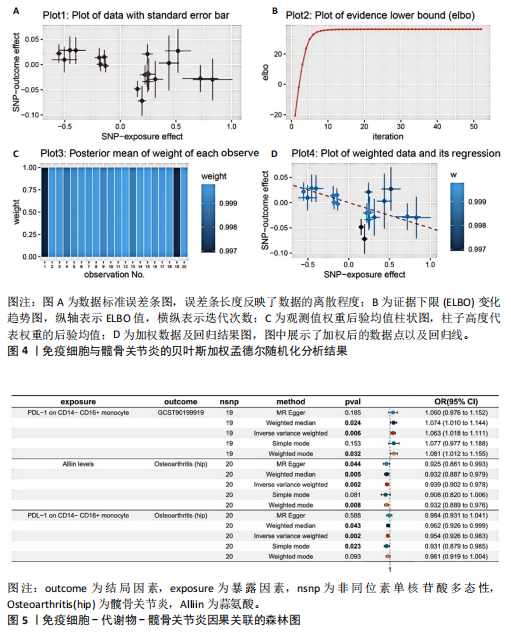
2.2 反向孟德尔随机化分析结果 髋骨关节炎和免疫细胞之间的反向孟德尔随机化分析结果,见表4。逆方差加权方法显示,髋骨关节炎与所选择的4种免疫细胞之间的P均> 0.05。在其他4种补充算法中也得到相同的结论,即作为暴露的髋骨关节炎与作为结局的4种免疫细胞之间无反向因果关系(P > 0.05)。 2.3 两步孟德尔随机化分析结果 以血浆代谢物作为中介,探究免疫细胞对髋骨关节炎的效应是否受到其介导。筛选得到与髋骨关节炎具强相关的代谢物有20种,见图3。 在此基础上,通过逆方差加权法进行免疫细胞到代谢物的孟德尔随机化分析,设置P < 0.05,且所有方法效应量为OR和效应值b方向一致,发现仅有一种单核细胞亚群(PDL-1 on CD14- CD16+)满足筛选条件,且与1种血浆代谢物蒜氨酸(Alliin levels)强相关。同时对该免疫细胞进行贝叶斯加权孟德尔随机化验证,以确定该免疫细胞与结局的稳健性,结果见图4。故采用单核细胞亚群(PDL-1 on CD14- CD16+)作为暴露因素,髋骨关节炎作为结局因素,蒜氨酸作为中间变量进行中介效应分析。 2.4 中介效应分析 通过逆方差加权方法得出单核细胞(PDL-1 on CD14- CD16+)对髋骨关节炎的总效应值为-0.047,反映了该免疫细胞对髋骨关节炎风险的总体影响为负相关。中介分析进一步揭示了其中的作用机制,蒜氨酸的中介效应值为-0.004,中介效应占比8.5%。直接效应值为-0.043,表示控制中介变量的影响后,该免疫细胞对髋关节骨关节炎仍产生负向影响。最终结果表明,蒜氨酸可能是因果效应的中介因素,见图5。"
| [1] DAMERAU A, KIRCHNER M, PFEIFFENBERGER M, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of synovial fibroblasts in osteoarthritis by inhibition of pathologically overexpressed pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases. Metab Eng. 2022;72:116-132. [2] BOER CG, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Deciphering osteoarthritis genetics across 826,690 individuals from 9 populations. Cell. 2021;184(18):4784-4818.e4717. [3] GBD 2021 Osteoarthritis Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990-2020 and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(9):e508-e522. [4] 潘炳,周颖芳,方芳,等.骨性关节炎的国内外研究现状及治疗进展[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2021,27(5):861-865. [5] CHI HB, PEPPER M, THOMAS PG. Principles and therapeutic applications of adaptive immunity. Cell. 2024;187(9):2052-2078. [6] CUI A, HUANG T, LI SQ, et al. Dictionary of immune responses to cytokines at single-cell resolution. Nature. 2024;625(7994): 377-384. [7] XIA SY, CHEN ZH, SHEN C, et al. Higher-order assemblies in immune signaling: Supramolecular complexes and phase separation. Protein Cell. 2021;12(9):680-694. [8] 刘畅,卞华,许博.基于生物信息学探讨骨关节炎相关分子机制及免疫细胞浸润分析[J].中国医科大学学报,2023, 52(5):385-391+397. [9] BAUERMEISTER A, MANNOCHIO-RUSSO H, COSTA-LOTUFO LV, et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in microbiome investigations. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;20(3):143-160. [10] REINKE SN, CHALECKIS R, WHEELOCK CE. Metabolomics in pulmonary medicine: Extracting the most from your data. Eur Respir J. 2022;60(2):2200102. [11] WANG X, NING YJ, LI C, et al. Alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolite profiles of patients with Kashin-Beck disease, an endemic osteoarthritis in China. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(11):1015. [12] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization: The STROBE-MR statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621. [13] BURGESS S, DAVEY SMITH G, DAVIES NM, et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: Update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2019; 4:186. [14] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SMITH G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601. [15] ZHAO J, MING JS, HU XH, et al. Bayesian weighted Mendelian randomization for causal inference based on summary statistics. Bioinformatics. 2020;36(5):1501-1508. [16] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525. [17] CHEN YH, LU TY, PETTERSSON-KYMMER U, et al. Genomic atlas of the plasma metabolome prioritizes metabolites implicated in human diseases. Nat Genet. 2023;55(1):44-53. [18] 吕浩,张舸,胡芷苜,等.炎症、代谢物与骨质疏松症[J].中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(17):3697-3704. [19] 詹群璋,张钰玲,韩雨欣,等.肥胖和骨质疏松之间的关联:一项两样本双向孟德尔随机化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(27):4319-4324. [20] YE CJ, LIU D, CHEN ML, et al. Mendelian randomization evidence for the causal effect of mental well-being on healthy aging. Nat Hum Behav. 2024;8(9):1798-1809. [21] WOOTTON RE, LAWN RB, MILLARD LAC, et al. Evaluation of the causal effects between subjective wellbeing and cardiometabolic health: Mendelian randomisation study. BMJ. 2018;362:k3788. [22] CARTER AR, SANDERSON E, HAMMERTON G, et al. Mendelian randomisation for mediation analysis: Current methods and challenges for implementation. Eur J Epidemiol. 2021;36(5):465-478. [23] CHEN JH, LIU YD, ZHAN PQ, et al. Bayesian-based analysis of the causality between 731 immune cells and erectile dysfunction: A two-sample, bidirectional, and multivariable Mendelian randomization study. Sex Med. 2024;12(4):qfae062. [24] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-698. [25] 刘帅祎,赵晓璇,李奇,等.九十一种炎症蛋白与颈椎间盘退变的因果关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(17):3732-3740. [26] AU YEUNG SL, GILL D. Standardizing the reporting of Mendelian randomization studies. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):187. [27] CARTER AR, SANDERSON E, HAMMERTON G, et al. Mendelian randomisation for mediation analysis: current methods and challenges for implementation. Eur J Epidemiol. 2021;36(5):465-478. [28] SANDERSON E. Multivariable Mendelian Randomization and Mediation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021;11(2):a038984. [29] LIN ZT, XUE HR, PAN W. Robust multivariable Mendelian randomization based on constrained maximum likelihood. Am J Hum Genet. 2023;110(4):592-605. [30] COSTA F, VESCOVINI R, MARCHICA V, et al. PD-L1/PD-1 Pattern of Expression Within the Bone Marrow Immune Microenvironment in Smoldering Myeloma and Active Multiple Myeloma Patients. Front Immunol. 2020;11:613007. [31] DE LANGE-BROKAAR BJ, IOAN-FACSINAY A, VAN OSCH GJ, et al. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1484-1499. [32] ZHENG J, LIANG H, XU C, et al. An unbalanced PD-L1/CD86 ratio in CD14(++)CD16(+) monocytes is correlated with HCV viremia during chronic HCV infection. Cell Mol Immunol. 2014;11(3):294-304. [33] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257. [34] YANG J, LI S, LI Z, et al. Targeting YAP1-regulated Glycolysis in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Impairs Macrophage Infiltration to Ameliorate Diabetic Osteoarthritis Progression. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(5):e2304617. [35] LI H, XIE S, QI Y, et al. TNF-α increases the expression of inflammatory factors in synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway in a rat model of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(6):4737-4744. [36] BLANCO FJ, REGO I, RUIZ-ROMERO C. The role of mitochondria in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(3):161-169. [37] LI M, YIN H, YAN Z, et al. The immune microenvironment in cartilage injury and repair. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:23-42. [38] FAN Z, LIU Y, SHI Z, et al. MiR-155 promotes interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and catabolic activity by targeting PIK3R1-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(15):8441-8451. [39] ZHANG Q, SUN C, LIU X, et al. Mechanism of immune infiltration in synovial tissue of osteoarthritis: a gene expression-based study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):58. [40] LI Z, DAI A, YANG M, et al. p38MAPK Signaling Pathway in Osteoarthritis: Pathological and Therapeutic Aspects. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:723-734. [41] LIETMAN C, WU B, LECHNER S, et al. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling ameliorates osteoarthritis in a murine model of experimental osteoarthritis. JCI Insight. 2018;3(3):e96308. [42] CHEN Y, PAN X, ZHAO J, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis through PI3K/Akt/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):204. [43] PIETZNER M, STEWART ID, RAFFLER J, et al. Plasma metabolites to profile pathways in noncommunicable disease multimorbidity. Nat Med. 2021;27(3):471-479. [44] DENG Y, HO CT, LAN Y, et al. Bioavailability, Health Benefits, and Delivery Systems of Allicin: A Review. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(49):19207-19220. [45] SHANG A, CAO SY, XU XY, et al. Bioactive Compounds and Biological Functions of Garlic (Allium sativum L.). Foods. 2019; 8(7):246. [46] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072. [47] WRIGHT HL, LYON M, CHAPMAN EA, et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fluid Neutrophils Drive Inflammation Through Production of Chemokines, Reactive Oxygen Species, and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Front Immunol. 2020;11:584116. [48] ARELLANO-BUENDÍA AS, CASTAÑEDA-LARA LG, LOREDO-MENDOZA ML, et al. Effects of Allicin on Pathophysiological Mechanisms during the Progression of Nephropathy Associated to Diabetes. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(11):1134. [49] BORLINGHAUS J, ALBRECHT F, GRUHLKE MC, et al. Allicin: chemistry and biological properties. Molecules. 2014;19(8):12591-12618. [50] QUINTERO-FABIÁN S, ORTUÑO-SAHAGÚN D, VÁZQUEZ-CARRERA M, et al. Alliin, a garlic (Allium sativum) compound, prevents LPS-induced inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:381815. [51] ZOU L, GUO H, BERZUINI C. Bayesian mendelian randomization with study heterogeneity and data partitioning for large studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022;22(1):162. [52] CHEBIB J, GUILLAUME F. Pleiotropy or linkage? Their relative contributions to the genetic correlation of quantitative traits and detection by multitrait GWA studies. Genetics. 2021;219(4):iyab159. |
| [1] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [2] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [3] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [4] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [5] | Zhang Jiuxuan, Zhang Jinnan, Sui Xiaofan, Pei Xiaxia, Wei Jianhong, Su Qiang, Li Tian. Effects of ammonia poisoning on cognitive behavior and hippocampal synaptic damage in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1122-1128. |
| [6] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [7] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [8] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [9] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [10] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [11] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [12] | Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [13] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [14] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [15] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||