Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (23): 6030-6039.doi: 10.12307/2026.371
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association between sarcopenia and osteoporosis: a genome-wide data analysis in European populations
Yin Xingxiao1, Jiang Yang1, Song Yanping2, Yao Na2, Shen Zhen2, Li Yanqi1, Song Yueyu1, Peng Hao1, Chen Qigang2
- 1School of Physical Education, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2025-07-09Accepted:2025-09-07Online:2026-08-18Published:2025-12-31 -
Contact:Chen Qigang, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China Corresponding author: Peng Hao, PhD candidate, School of Physical Education, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Yin Xingxiao, MS candidate, School of Physical Education, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82360943 (to SZ); Yunnan Province Youth Talent Special Project - “Xingdian Talent Support Program,” No. XDYC-QNRC-2022-0609 (to SZ); Traditional Chinese Medicine Joint Special Project of Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology, Nos. 202101AZ070001-257 and 202101AZ070001-123 (both to SZ); Basic Research Special Project of Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 202201AU070120 (to SZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yin Xingxiao, Jiang Yang, Song Yanping, Yao Na, Shen Zhen, Li Yanqi, Song Yueyu, Peng Hao, Chen Qigang. Association between sarcopenia and osteoporosis: a genome-wide data analysis in European populations[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6030-6039.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
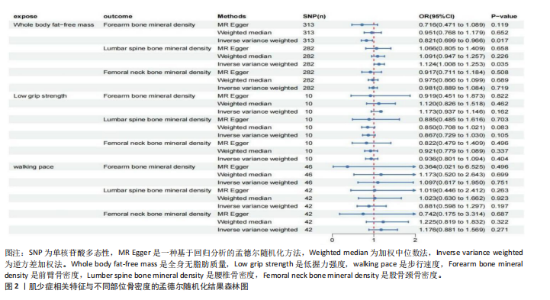
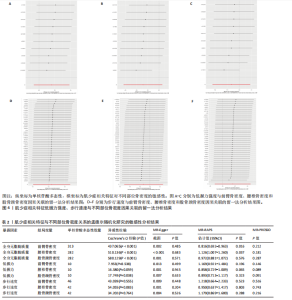
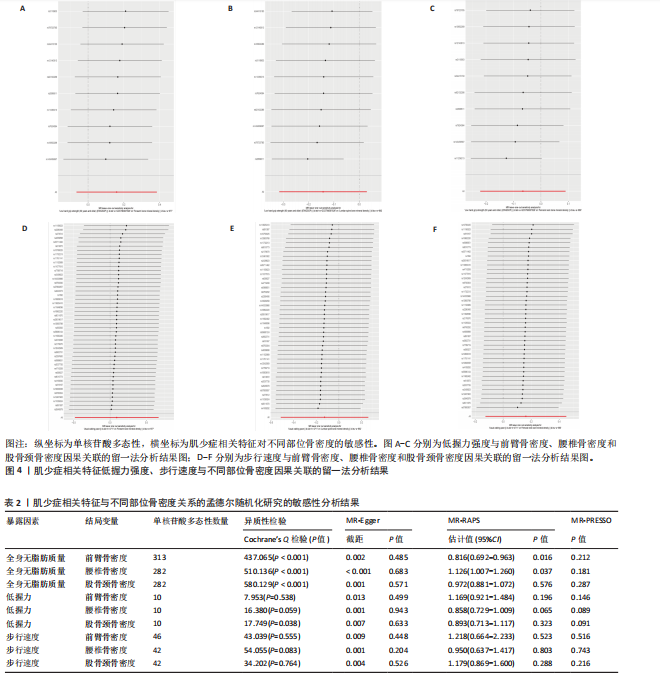
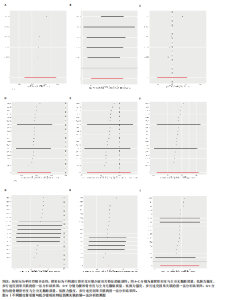
2.1 肌少症相关特征对不同部位骨密度的影响 逆方差加权法分析结果显示,全身无脂肪质量与前臂骨密度(OR=0.821,95%CI:0.699-0.966,P=0.017)及腰椎骨密度(OR=1.124,95%CI:1.008-1.253,P=0.035)存在显著因果关联,但全身无脂肪质量与股骨颈骨密度无显著因果关联(P=0.719)。尽管MR-Egger回归和加权中位数法的估计结果未达统计学显著性,但MR-RAPS方法的验证结果进一步支持全身无脂肪质量对前臂/腰椎骨密度具有稳健的因果效应。此外,低握力强度及步行速度与各部位骨密度均未表现出显著相关性(所有P > 0.05),见图2。敏感性分析表明,MR-Egger截距检验和MR-PRESSO全局检验均未检测到显著的水平多效性(P > 0.05),Cochran’s Q检验提示研究间不存在异质性(P > 0.05),见表2。留一法分析结果证实,无单一单核苷酸多态性位点对整体因果效应估计产生显著影响,见图3,4。 "

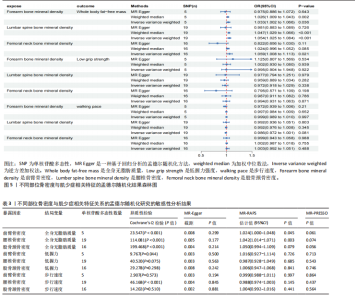
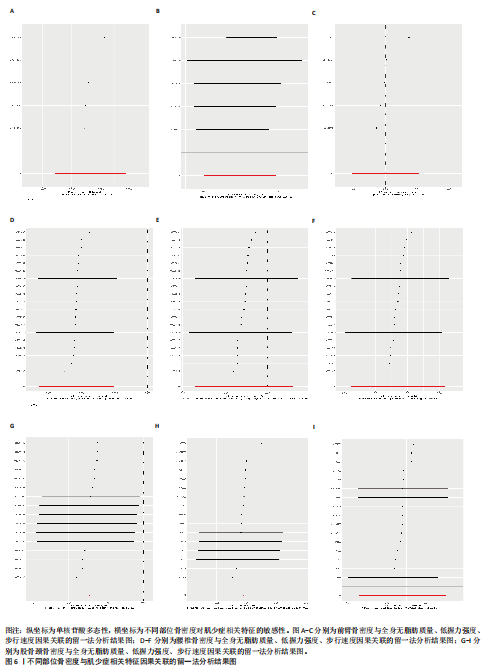
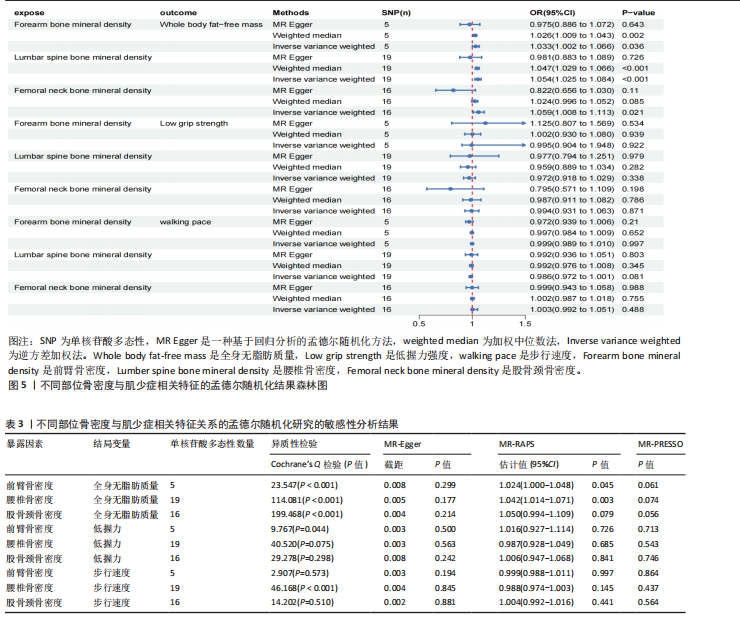
2.2 不同部位骨密度对肌少症相关特征的影响 基于逆方差加权法的分析结果表明,前臂骨密度(OR=1.033,95%CI:1.002-1.066,P=0.036)、腰椎骨密度(OR=1.054,95%CI:1.025-1.084,P 0.05),但其效应方向与逆方差加权法保持一致。值得注意的是,研究未发现各部位骨密度与握力强度及步行速度存在显著因果关联(均P > 0.05),详见图5、表3。 敏感性分析结果显示,MR-Egger截距检验和MR-PRESSO全局检验均未检测到显著的水平多效性(均P > 0.05),Cochran’s Q检验提示研究不存在异质性(P > 0.05),见表3。 此外,留一法分析结果证实,在逐步排除单个单核苷酸多态性后的因果效应估计值均保持稳定,表明此次研究结果具有较高的可靠性,详见图6。"
| [1] LASKOU F, FUGGLE NR, PATEL HP, et al. Associations of osteoporosis and sarcopenia with frailty and multimorbidity among participants of the Hertfordshire Cohort Study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1): 220-229. [2] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, SAYER AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191):2636-2646. [3] PAPADOPOULOU SK, TSINTAVIS P, POTSAKI G, et al. Differences in the prevalence of sarcopenia in community-dwelling, nursing home and hospitalized individuals. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr Health Aging. 2020;24(1):83-90. [4] YEUNG SSY, REIJNIERSE EM, PHAM VK, et al. Sarcopenia and its association with falls and fractures in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019;10(3):485-500. [5] FOESSL I, DIMAI HP, OBERMAYER-PIETSCH B. Long-term and sequential treatment for osteoporosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(9): 520-533. [6] SALARI N, GHASEMI H, MOHAMMADI L, et al. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16:1-20. [7] MARTINIAKOVA M, MONDOCKOVA V, KOVACOVA V, et al. Interrelationships among metabolic syndrome, bone-derived cytokines, and the most common metabolic syndrome-related diseases negatively affecting bone quality. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024;16(1):217. [8] ZHU Y, ZENG Q, SHI Y, et al. Association between sarcopenia and osteoporosis: the cross-sectional study from NHANES 1999-2020 and a bi-directions Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol. 2024;15:1399936. [9] YU C, DU Y, PENG Z, et al. Research advances in crosstalk between muscle and bone in osteosarcopenia. Exp Ther Med. 2023;25(4): 189. [10] YANG YJ, KIM DJ. An overview of the molecular mechanisms contributing to musculoskeletal disorders in chronic liver disease: osteoporosis, sarcopenia, and osteoporotic sarcopenia. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2604. [11] KIRK B, PROKOPIDIS K, DUQUE G. Nutrients to mitigate osteosarcopenia: the role of protein, vitamin D and calcium. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2021;24(1):25-32. [12] POLITO A, BARNABA L, CIARAPICA D, et al. Osteosarcopenia: a narrative review on clinical studies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5591. [13] CLYNES MA, GREGSON CL, BRUYÈRE O, et al. Osteosarcopenia: where osteoporosis and sarcopenia collide. Rheumatology. 2021;60(2): 529-537. [14] ROBERTO B, SONIA GG, IDA C, et al. Osteosarcopenia and pain: do we have a way out? Biomedicines. 2023;11(5):1285. [15] ZHAN Z, ZHANG Y, WU J, et al. Predictive efficacy of different diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia in osteoporosis and fractures. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):9473. [16] 靳丹,代新宇,刘淼,等.肌肉骨骼减少症发病机制及其运动防治效果[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2024,51(5):1105-1118. [17] ZHU L, RUAN X, ZOU Y, et al. The causal relationship between circulating inflammatory proteins, gut microbiotas, immune cells and leukemia: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Discov Oncol. 2025; 16(1):1-14. [18] PEI YF, LIU YZ, YANG XL, et al. The genetic architecture of appendicular lean mass characterized by association analysis in the UK Biobank study. Commun Biol. 2020;3(1):608. [19] JONES G, TRAJANOSKA K, SANTANASTO AJ, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of muscle weakness identifies 15 susceptibility loci in older men and women. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):654. [20] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAEYENS JP, BAUER JM, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412-423. [21] KARLSSON M, LJUNGREN Ö, AMIN N, et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture. Nature. 2015;525(7570):260-263. [22] XIANG M, WANG Y, GAO Z, et al. Exploring causal correlations between inflammatory cytokines and systemic lupus erythematosus: A Mendelian randomization. Front Immunol. 2023;13:985729. [23] YANG H, CHEN L, LIU Y. Novel causal plasma proteins for hypothyroidism: a large-scale plasma proteome Mendelian randomization analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;108(2): 433-442. [24] ZHOU S, TAO B, GUO Y, et al. Integrating plasma protein-centric multi-omics to identify potential therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):557. [25] ZHAO Q, WANG J, HEMANI G, et al. Statistical inference in two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization using robust adjusted profile score. Ann Stat. 2020;48(3): 1742-1768. [26] LIN Z, PAN I, PAN W. A practical problem with Egger regression in Mendelian randomization. PLoS Genet. 2022;18(5):e1010166. [27] LEE JE, LEE SR, SONG HK. Muscle mass is a strong correlation factor of total hip BMD among Korean premenopausal women. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2016;2(2):99-102. [28] LASKOU F, PATEL H, COOPER C, et al. Functional capacity, sarcopenia, and bone health. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2022;36(3):101756. [29] HE H, LIU Y, TIAN Q, et al. Relationship of sarcopenia and body composition with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(1): 473-482. [30] LIU C, LIU N, XIA Y, et al. Osteoporosis and sarcopenia-related traits: A bi-directional Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:975647. [31] MA XY, LIU HM, LV WQ, et al. A bi-directional Mendelian randomization study of the sarcopenia-related traits and osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(14):5681-5694. [32] 赵常红,王菲菲,连红强,等.骨肌串扰防治骨肌共减症的作用及机制[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2024,51(11):2936-2946. [33] 徐帅,赵常红,徐道明,等.肌骨交互视阈下肌骨共减综合症的生物学机制及其运动干预研究进展[J]. 中国体育科技,2022,58(5):75-83. [34] AHSAN M, GARNEAU L, AGUER C. The bidirectional relationship between AMPK pathway activation and myokine secretion in skeletal muscle: How it affects energy metabolism. Front Physiol. 2022;13:1040809. [35] CARIATI I, SCIMECA M, BONANNI R, et al. Role of myostatin in muscle degeneration by random positioning machine exposure: an in vitro study for the treatment of sarcopenia. Front Physiol. 2022;13:782000. [36] GIRARDI F, LE GRAND F. Wnt signaling in skeletal muscle development and regeneration. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018;153:157-179. [37] 赵常红,李世昌,孙朋,等.不同方式运动对生长期大鼠FGF、IGF信号及软骨内成骨的影响[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2021,14(6):628-637. [38] CHEN LY, WU YH, LIU LK, et al. Association among serum insulin-like growth factor-1, frailty, muscle mass, bone mineral density, and physical performance among community-dwelling middle-aged and older adults in Taiwan. Rejuvenation Res. 2018;21(3):270-277. [39] DENG Z, LUO P, LAI W, et al. Myostatin inhibits eEF2K-eEF2 by regulating AMPK to suppress protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;494(1-2):278-284. [40] ZHAO Z, YAN K, GUAN Q, et al. Mechanism and physical activities in bone-skeletal muscle crosstalk. Front Endocrinol. 2024;14:1287972. [41] KIRK B, MILLER S, ZANKER J, et al. A clinical guide to the pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of osteosarcopenia. Maturitas. 2020;140:27-33. [42] 苏洋洋,李杭远,吴秀琴.鸢尾素(Irisin):运动诱导骨骼肌自噬的新靶点[J].体育科技文献通报,2022,30(3):235-242. [43] HU X, WANG Z, WANG W, et al. Irisin as an agent for protecting against osteoporosis: A review of the current mechanisms and pathways. J Adv Res. 2024;62:175-186. [44] KAWAO N, MORITA H, IEMURA S, et al. Roles of Dkk2 in the linkage from muscle to bone during mechanical unloading in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2547. [45] COLAIANNI G, NOTARNICOLA A, SANESI L, et al. Irisin levels correlate with bone mineral density in soccer players. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2017;31(4 Suppl 1):21-28. [46] MERA P, LAUE K, FERRON M, et al. Osteocalcin signaling in myofibers is necessary and sufficient for optimum adaptation to exercise. Cell Metab. 2016;23(6):1078-1092. [47] LIU S, GAO F, WEN L, et al. Osteocalcin induces proliferation via positive activation of the PI3K/Akt, P38 MAPK pathways and promotes differentiation through activation of the GPRC6A-ERK1/2 pathway in C2C12 myoblast cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):1100-1112. [48] XIE X, HU L, MI B, et al. SHIP1 activator AQX-1125 regulates osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis through PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signaling. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:826023. [49] ESCRICHE-ESCUDER A, FUENTES-ABOLAFIO IJ, ROLDAN-JIMENEZ C, et al. Effects of exercise on muscle mass, strength, and physical performance in older adults with sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis according to the EWGSOP criteria. Exp Gerontol. 2021; 151:111420. [50] KITSUDA Y, WADA T, NOMA H, et al. Impact of high-load resistance training on bone mineral density in osteoporosis and osteopenia: a meta-analysis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39(5):787-803. |
| [1] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [2] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [3] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [4] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [5] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [6] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [7] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [8] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [9] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [10] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [11] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [12] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [13] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [14] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [15] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||