Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (23): 6040-6050.doi: 10.12307/2026.312
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a visual analysis of current status and emerging trends
Qu Bolin1, Ciren Lunzhu2, Guo Jinyang1, 3, Meng Hanlu4, Ding Guanxiang1, 5, Sang Hongpeng1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Chifeng University, Chifeng 024000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Shannan People's Hospital, Shannan 856000, Tibet Autonomous Region, China; 3Inner Mongolia Minzu University, Tongliao 028000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 4Tongliao People’s Hospital, Tongliao 028000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 5Baotou Medical College, Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, Baotou 014000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-04-22Accepted:2025-06-05Online:2026-08-18Published:2025-12-31 -
Contact:Sang Hongpeng, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Chifeng University, Chifeng 024000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Qu Bolin, MS, Attending physician, Affiliated Hospital of Chifeng University, Chifeng 024000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Shannan Science and Technology Program Project, No. SNSBJKJJHXM2023015 (to CL); Public Hospital Scientific Research Joint Fund Project of Inner Mongolia Academy of Medical Sciences, No. 2024GLLH1015 (to SHP); Chifeng Natural Science Research Project, No. SZR2022144 (to SHP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qu Bolin, Ciren Lunzhu, Guo Jinyang, Meng Hanlu, Ding Guanxiang, Sang Hongpeng. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a visual analysis of current status and emerging trends[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6040-6050.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
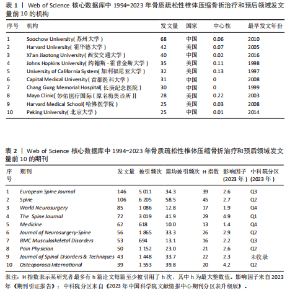
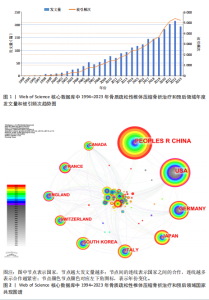
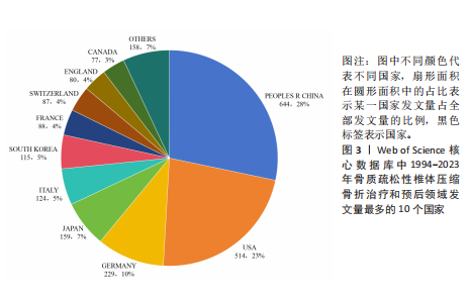
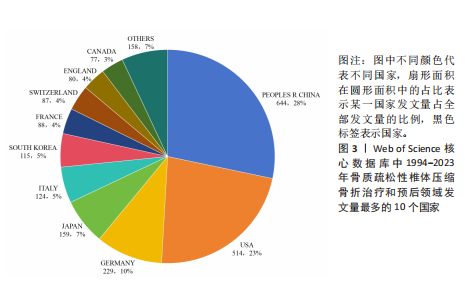
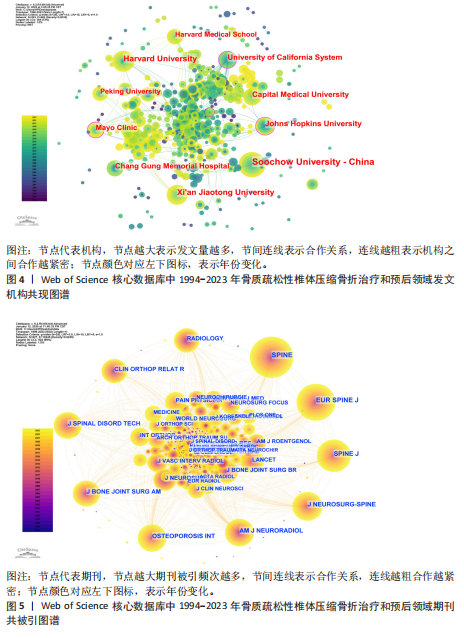
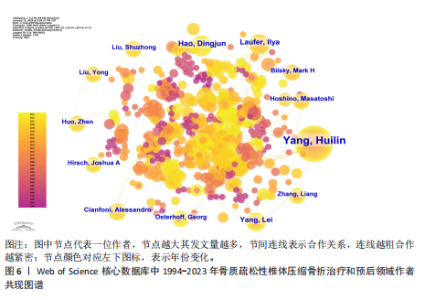
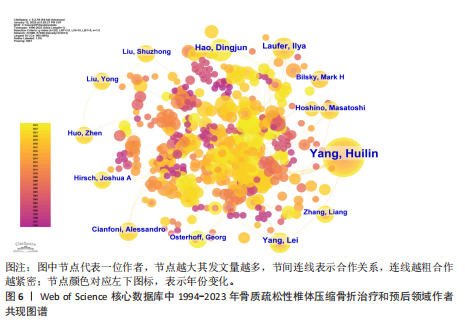
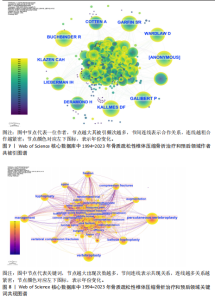
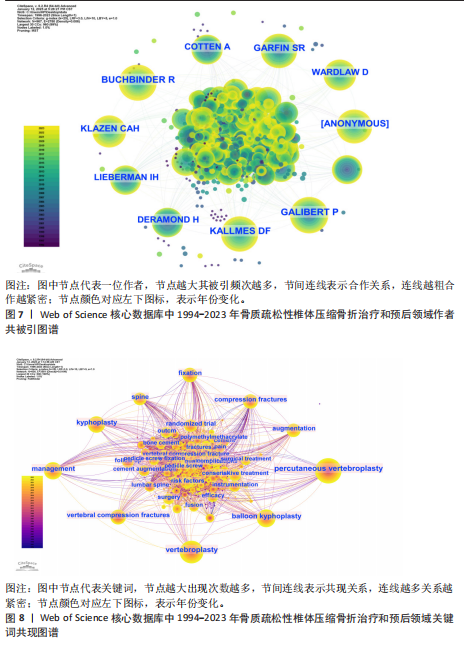
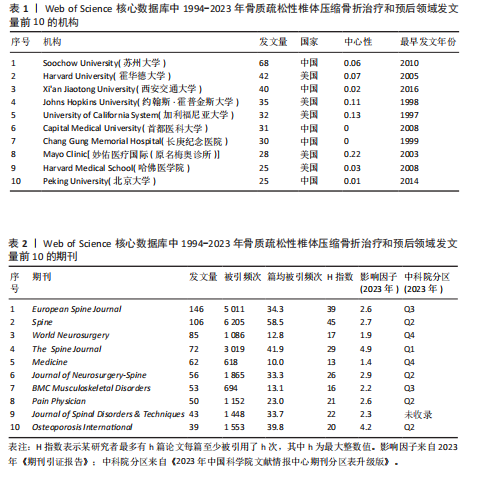
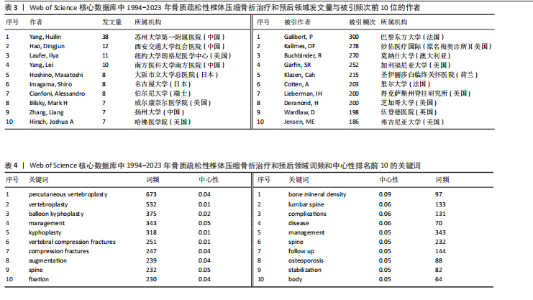
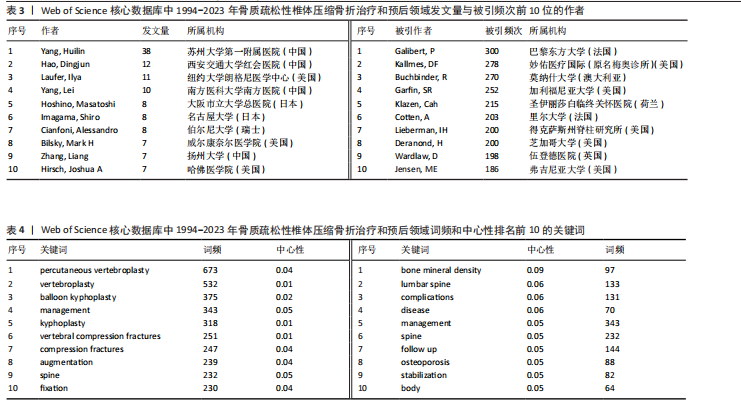
2.1 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折领域研究出版物和引用分析 年度发文量和被引频次变化可反映该领域的研究热度。经过文献筛选后,此次研究最终纳入2 275篇出版物,包括1 925篇论著和350篇综述。由图1可知,在1994-2023年期间,骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折领域相关文献的年发文量从0篇增加到215篇,年被引频次范围为0-5 386次,年发文量和被引频次总体呈持续上升趋势,受到学者们的持续关注。 2.2 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折领域研究国家分析 通过CiteSpace对国家进行共现分析(图2),共有68个国家参与骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折治疗和预后领域的研究。图3展示发文量最多的10个国家的发文量及其占比,其中中国共发表644篇文章,占总发文量的28%,是发文量最多的国家,其次是美国(n=514)和德国(n=229),分别占总发文量的23%与10%。中心性较高的前4个国家分别是美国(0.51)、法国(0.15)、英国(0.14)与德国(0.11),表明美国与其他国家/地区的之间紧密的合作关系。 2.3 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折领域研究机构分析 全球共有2 628个机构在骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折研究领域开展研究。表1展示发文量排名前10的机构,有5个机构来自美国,5个机构来自中国,其中苏州大学(约68篇)、霍华德大学(约42篇)和西安交通大学(约40篇)位列前3。 利用CiteSpace软件绘制机构可视化图谱,包括523个研究机构及机构间的1 473次合作关系(图4)。在这些机构中,相互之间的合作性是比较弱的,其中只有妙佑医疗国际(原名梅奥诊所)(中心性0.22)、加利福尼亚大学(中心性0.13)与约翰斯·霍普金斯大学(中心性0.11)具有较高的相关性。 2.4 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折领域研究期刊分析 在1994-2023年之间,有466种期刊发表了关于骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折治疗和预后的文献,期刊共被引网络知识图谱见图5,选择被引频次达到200次及以上的期刊进行可视化。表2展示了发文量前10的期刊,其中《European Spine Journal》的发文量最多(n=146),其次是《Spine》(n=106)与《World Neurosurgery》(n=85)。被引频次最多的期刊是《Spine》(n=6 205),其次是《European Spine Journal》(n=5 011)与《The?Spine Journal》(n=3 019)。篇均被引次数最多的期刊是《Spine》(58.5),H指数最高的期刊同样为《Spine》(45)。 2.5 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折领域研究作者分析 作者共现图谱共包括918个节点,形成10 255条合作关系,见图6。苏州大学第一附属医院的Yang, Huilin以38篇论文的发文量位居首位,西安交通大学红会医院的Hao, Dingjun(n=12)和纽约大学朗格尼医学中心的Laufer, Ilya(n=11)紧随其后,见表3。作者共被引图谱共包括967个节点和8 097条连线,见图7。法国医生Galibert, P(n=300)的被引频次最高,其次为来自美国妙佑医疗国际(原名梅奥诊所)的Kallmes, DF(n=278)与来自澳大利亚莫纳什大学的Buchbinder, R(n=270),见表3。 2.6 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折领域研究关键词和热点分析 关键词能够概括和反映文章的主要内容及核心思想,关键词共现分析可帮助读者更深入地理解该领域的研究重点。通过CiteSpace对文献关键词进行可视化分析并绘制关键词共现图谱(图8),词频排名前10的关键词为:“percutaneous vertebroplasty(经皮椎体成形术)”“vertebroplasty(椎体成形术)”“balloon kyphoplasty(球囊扩张椎体成形术)”“management(管理)”“kyphoplasty(椎体后凸成形术)” “vertebral compression fractures(椎体压缩性骨折)”“compression fractures (压缩性骨折)”“augmentation(强化)”“spine(脊柱)”“fixation(固定)”。而中心性排名前10的关键词为:“bone mineral density(骨密度)” “lumbar spine(腰椎)”“complications (并发症)”“disease(疾病)”“management(管理)”“spine(脊柱)” “follow up(随访)”“osteoporosis(骨质疏松症)”“stabilization(稳定)” “body(椎体)”“screw fixation(螺钉固定)”,见表4。"
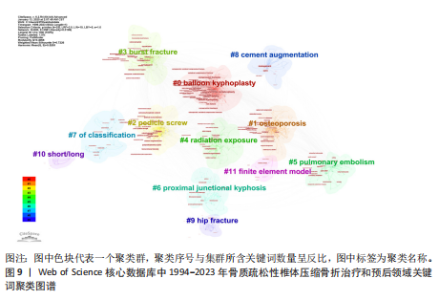
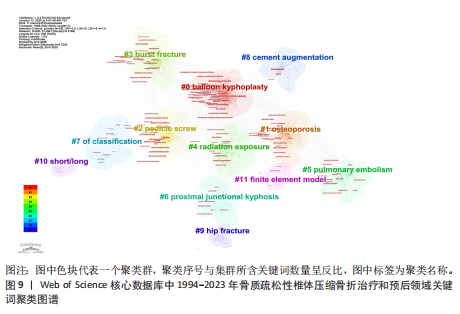
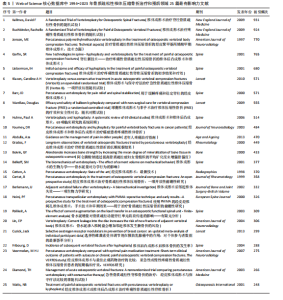
关键词聚类可以展示特定研究领域内不同研究方向之间的关联性及其内在逻辑。关键词聚类图谱中包括12个聚类(图9),分别为:#0 balloon kyphoplasty(球囊扩张椎体成形术)、#1 osteoporosis(骨质疏松症)、#2 pedicle screw(椎弓根螺钉)、#3 burst fracture(爆裂骨折)、#4 radiation exposure(射线照射)、#5 pulmonary embolism(肺栓塞)、#6 proximal junctional kyphosis(近端交界性后凸)、#7 of classification(分类)、#8 cement augmentation(水泥强化)、#9 hip fracture(髋骨折)、#10 short/long(短节段/长节段)、#11 finite element model(有限元模型)。 使用VOSviewer提取关键词,并将关键词阈值设定为38,绘制关键词时间线图谱(图10)。关键词突现是指在特定时间段内某一关键词的使用频率显著增加,通过分析关键词突现的起始时间、持续时长及其突现强度,判断该领域的研究热点及未来研究发展趋势,关键词的时间线图能够从时间维度直观呈现各阶段的研究热点和方向。利用CiteSpace 进行关键词突现分析,绘制关键词突现图谱(图11)。关键词突现图谱中,早期突现的关键词是“polymethylmethacrylate(聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯)”“metastases(转移瘤)”“cement(骨水泥)”“pulmonary embolism(肺栓塞)”“biomechanical evaluation(生物力学评估)”“screw fixation(螺钉固定)”。随着研究的继续,突现的关键词成为“surgical management(手术治疗)” “nonoperative treatment(非手术治疗)”“randomized trial(随机试验)”。近年来,突现的关键词改变为“safety(安全性)”“percutaneous vertebroplasty(经皮椎体成形术)”“risk factors(危险因素)”、“kummells disease(Kummell病)”。"
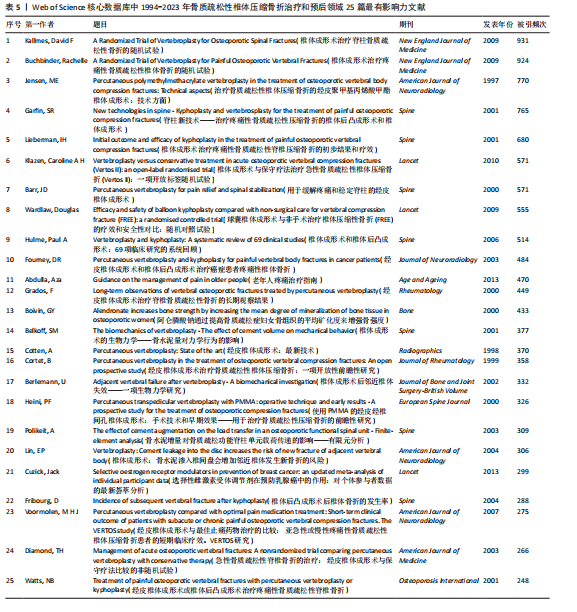
2.7 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折领域最有影响力文献分析 被引用次数更高的文献通常更有影响力,此次研究使用WoSCC中“创建引用报告”功能整理了25篇最有影响力文献(表5)。研究过程大致分为3个阶段:2000年之前、2000-2010年和2010年之后。在第一阶段,“Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects”是在1997年由Jensen, ME等在《American Journal of Neuroradiology》上发表的文献,这篇文献被引用了770次,是第一阶段被引用最多的文献[25]。在第二阶段,“A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures”是由Kallmes, David F等于2009年在《The New England Journal of Medicine》上发表的被引用次数最多的文献,引用次数为931次[26]。在第三阶段,“ertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial”是由Klazen, Caroline A-H等于2010年在《The Lancet》上发表的被引用次数最多的文献,引用次数为571次[27]。"
| [1] GLASER DL, KAPLAN FS. Osteoporosis. Definition and clinical presentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(24 Suppl):12S-16S. [2] STRÖM O, BORGSTRÖM F, KANIS JA, et al. Osteoporosis: burden, health care provision and opportunities in the EU: a report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA). Arch Osteoporos. 2011;6:59-155. [3] KARMAKAR A, ACHARYA S, BISWAS D, et al. Evaluation of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Management of Symptomatic Osteoporotic Compression Fracture. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(8):RC07-RC10. [4] BEALL DP, OLAN WJ, KAKAD P, et al. Economic Analysis of Kiva VCF Treatment System Compared to Balloon Kyphoplasty Using Randomized Kiva Safety and Effectiveness Trial (KAST) Data. Pain Physician. 2015;18(3):E299-306. [5] 中华医学会骨科学分会.骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南(2022年版)[J].中华骨科杂志, 2022,42(22):1473-1491. [6] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等.中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南(全文)(骨质疏松性骨折诊断及治疗原则)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(6):117-120. [7] GARFIN SR, BUCKELY RA, LEDLIE J, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty for symptomatic vertebral body compression fractures results in rapid, significant, and sustained improvements in back pain, function, and quality of life for elderly patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19):2213-2220. [8] BURTON AW, MENDEL E. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Pain Physician. 2003;6(3):335-341. [9] GALIBERT P, DERAMOND H, ROSAT P, et al. Note préliminaire sur le traitement des angiomes vertébraux par vertébroplastie percutanée. Neurochirurgie. 1987;33:166-168. [10] ZHANG L, LIU Z, WANG J, et al. Unipedicular versus bipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective randomized study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:145. [11] BALKARLI H, DEMIRTAS H, KILIC M, et al. Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty under local anesthesia: clinical and radiological results. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(9):16287-16293. eCollection 2015. [12] LONG Y, YI W, YANG D. Advances in Vertebral Augmentation Systems for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:3947368. [13] LI J, XU L, LIU Y, et al. Open Surgical Treatments of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2023; 15(11):2743-2748. [14] 姜宇,郭昭庆,陈仲强,等.陈旧性骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折继发胸腰椎后凸畸形的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2023, 43(7):465-470. [15] HSIEH JY, WU CD, WANG TM, et al. Reduction of the domino effect in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures through short-segment fixation with intravertebral expandable pillars compared to percutaneous kyphoplasty: a case control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:75. [16] NORIEGA D, MAESTRETTI G, RENAUD C, et al. Clinical Performance and Safety of 108 SpineJack Implantations: 1-Year Results of a Prospective Multicentre Single-Arm Registry Study. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:173872. [17] LAREDO JD, HAMZE B. Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty and their prevention. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2005; 26(2):65-80. [18] MATHIS JM. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: complication avoidance and technique optimization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24(8):1697-1706. [19] KIM YY, RHYU KW. Recompression of vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(11):1907-1912. [20] FREEDMAN BA, HELLER JG. Kummel Disease: A Not-So-Rare Complication of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009;22(1):75-78. [21] LIAO H, TANG M, LI L, et al. A Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization of Medical Big Data Research. Sustainability. 2018;10:166. [22] CHENG K, GUO Q, YANG W, et al. Mapping Knowledge Landscapes and Emerging Trends of the Links Between Bone Metabolism and Diabetes Mellitus: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2000 to 2021. Front Public Health. 2022;10:918483. [23] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538. [24] SYNNESTVEDT MB, CHEN C, HOLMES JH. CiteSpace II: visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2005;2005:724. [25] JENSEN ME, EVANS AJ, MATHIS JM, et al. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18(10):1897-1904. [26] KALLMES DF, COMSTOCK BA, HEAGERTY PJ, et al. A Randomized Trial of Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Spinal Fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(6):569-579. [27] KLAZEN CA, LOHLE PN, DE VRIES J, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2010; 376(9746):1085-1092. [28] 张毅,李唯,邵杰,等.骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折PVP/PKP术后二次骨折的危险因素分析及预测模型建立[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(9):785-792. [29] SUTIPORNPALANGKUL W, ZAMBRANA L, GIANAKOS A, et al. Comparison of Sagittal Balance between Radiofrequency Targeted Vertebral Augmentation and Balloon Kyphoplasty in Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Retrospective Study. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016;99(9):1025-1032. [30] VOORMOLEN MHJ. Kyphoplasty. Neuroradiology. 2011;53 Suppl 1(S1):S203-205. [31] CAO Z, WANG G, HUI W, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures improves spino-pelvic alignment and global sagittal balance maximally in the thoracolumbar region. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0228341. [32] YOKOYAMA K, KAWANISHI M, YAMADA M, et al. Postoperative change in sagittal balance after Kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(4):744-749. [33] BOHNER M, SANTONI BLG, DÖBELIN N. beta-tricalcium phosphate for bone substitution: Synthesis and properties. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:23-41. [34] 栾伟,陈家瀚,滕勇,等.新型可吸收骨水泥的制备及其应用于小牛椎体标本压缩性骨折椎体成形术的生物力学研究[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2022,27(10):721-728. |
| [1] | Chen Qiuhan, Yang Long, Yuan Daizhu, Wu Zhanyu, Zou Zihao, Ye Chuan. Peri-knee osteotomy for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: optimization of treatment strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2303-2312. |
| [2] | Liu Jinlong, Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Bai Zhen, Su Danyang, Miao Xin, Li Fei, Yang Xiaopeng. Efficacy of different nonsurgical treatments for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2370-2379. |
| [3] | Xinjiang Branch of China Trauma Rescue & Treatment Association. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of brucellar osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2403-2412. |
| [4] | Yang Qiongqiong, Liu Wei. Comparison of performance and clinical effects of zirconia and titanium implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2063-2071. |
| [5] | Fan Yongjing, Jin Wulong, Bai Haoyu, Ma Ping, Wang Shu. Role and mechanism of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth in tissue regeneration and disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1850-1857. |
| [6] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [7] | Wang Zhipeng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Hongwei, Zhao Xiyun, Li Yuanzhen, Guo Chenglong, Qin Daping, Ren Zhen. A systematic review of application value of machine learning to prognostic prediction models for patients with lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 740-748. |
| [8] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [9] | Li Yiguang, Guo Haonan, Ding Xiaotao, Yuan Mengyao, Jiang Lijin, Fan Xinfeng, Feng Yan. Visual analysis of research hotspots in the field of gut microbiota in the elderly at home and abroad [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6071-6080. |
| [10] | Huang Yushan, Wang Rongrong, Li Xiangmiao, Bai Jinzhu. Prostaglandin E1 pretreatment inhibits ferroptosis in endothelial cells in a rat model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5716-5727. |
| [11] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [12] | Zhang Qian, Wang Fuxia, Wang Wen, Zhang Kun. Characteristic analysis of nanogel composite system and its application strategies in visualization of diagnostic imaging and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 480-488. |
| [13] | Cheng Yanan, Yu Jiazhi, Liu Yinchang, Wu Jie, Yu Tong, Wang Lu, Li Xiaoguang. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of molar distalization with clear aligners with different thicknesses and edges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 310-318. |
| [14] | Meng Zhuo, Zhao Renghao, Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Wang Zicheng, Xu Yingtian, Tong Peijian. Literature visualization analysis of brain-computer interface applications in stroke rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4802-4813. |
| [15] | Li Ruiying, Xia Hong. Visual analysis of cuproptosis research: global landscape of hotspots and frontiers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4529-4541. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||