Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (14): 3675-3686.doi: 10.12307/2026.055
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects and mechanisms of natural polyphenol-based hydrogels in promoting bone repair
Gong Yukang1, Ye Gaoqi1, Wang Chenhao2, Chen Dejin1, Gao Wenshan1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 2School of Basic Medicine, Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-21Accepted:2025-04-23Online:2026-05-18Published:2025-09-12 -
Contact:Gao Wenshan, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Gong Yukang, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:2024 In-Hospital Fund Project of Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, No. 2024ZA01 (to GWS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gong Yukang, Ye Gaoqi, Wang Chenhao, Chen Dejin, Gao Wenshan. Effects and mechanisms of natural polyphenol-based hydrogels in promoting bone repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3675-3686.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 天然多酚概述 2.1.1 天然多酚的来源与提取方法 天然多酚是一类具有多个酚羟基的天然分子,是植物的次生代谢物,普遍存在于水果、蔬菜、茶叶、植物种子和药草等中,特别是水果、叶子和种子。天然多酚在自然界普遍存在且极具多样化,现已在不同的植物中发现和鉴定了8 000多种不同的酚类化合物[3]。 植物中含有较高含量的酚类物质[4],不溶性酚类物质存在于细胞壁中,而可溶性酚类物质存在于植物细胞液泡中。收获期间的成熟程度、土壤气候条件、加工和储存方式都会影响多酚含量[5],在提取之前,植物的预处理(例如清洁、洗涤、研磨、干燥)同样至关重要。从干燥、冷冻或新鲜的植物样品中都能提取多酚,提取技术可以采用传统方法(例如渗滤、浸渍),也可以采用现代方法(例如超声波或微波),现代方法应用更为广泛。但在这两种提取方式下,萃取效率也取决于多种因素,例如溶剂与固体的比例、溶剂的性质,如渗滤萃取使用水作为溶剂,获得待浓缩的纯提取物需要很长时间[6]。浸渍是固液萃取方法,根据目标化合物的物理和化学性质使用不同的溶剂,较高的固体/溶剂比可提高多酚回收率,该法与超声辅助提取相比的效率和提取率较低,并且需要使用大量溶剂。热回流萃取是在恒温状态下反复进行溶剂蒸发和冷凝的固液萃取方法,与渗滤或浸渍相比需要的提取时间和溶剂少,并且提取率更高。超声波是生物技术中常用的破壁方式,可加速细胞壁的破裂,提高提取率。微波辅助提取是一种环保技术,与超声辅助提取和浸渍等提取方法相比从废物中回收多酚的效率更高。 "

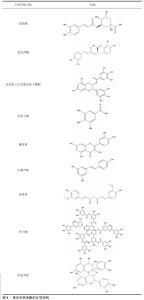
2.1.2 天然多酚的分类、化学结构 多酚因具有多个酚基团而得名,并具有多个酚环,根据酚环的数量和这些环的共轭元素数量,多酚又可分为酚酸、黄酮类、芪类和木脂素类。该文对常见用于骨修复领域的天然多酚结构进行了总结,见图3。随着对天然多酚研究的深入,发现多酚具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗炎、抗肿瘤等多功能活性。由于多酚具有氧化还原特性,使得它们能够在氧化反应中充当还原剂;此外,多酚的氧化醌形式还可以与官能团发生席夫碱反应或迈克尔加成。 在化学结构方面,多酚含有丰富的酚羟基,可作为氢键的供体,多酚含有的芳香环可以通过疏水相互作用与底物分子上的疏水位点相互作用。另外,芳香羟基中氧原子的电负性或芳香羟基的解离可以使多酚参与与带正电分子的静电相互作用,而去质子化的芳香羟基具有高电荷密度,可以与金属螯合生成酸碱度(pH值)响应性金属多酚配位化合物;此外,芳香族羟基也可以发生共价相互作用,例如通过酯化作用与羧酸反应、通过醚化作用与烷基卤化物/环氧化物反应。 "

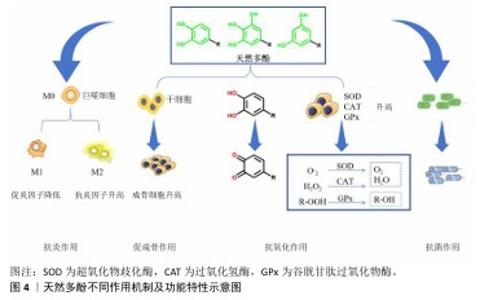
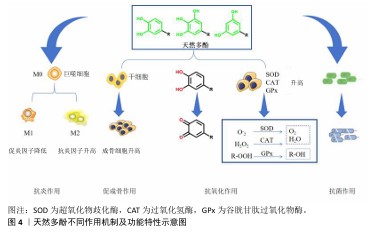
2.1.3 天然多酚的生物性能及作用机制 (1)天然多酚的抗氧化机制:多酚可以作为有效的抗氧化剂在体内外清除自由基(图4)。由于特殊的化学结构,多酚可以通过氢原子转移清除自由基,形成稳定的醌结构。电子转移、质子转移是多酚自由基清除活性的另一反应途径,它们可以通过向自由基传递或转移电子来清除自由基,从而稳定活性物质。核因子E2相关因子2可以调控抗氧化酶(超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶等)[7],而多酚可以调节核因子E2相关因子2通路,由此来提高细胞抗氧化活性。多酚化合物通过核因子E2相关因子2-抗氧化应答元素途径上调编码抗氧化酶的基因,调节氧化还原敏感转录因子(核因子κB)和过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体发挥抗氧化作用[8]。由于天然多酚结构的复杂性及多样性,有研究发现,单宁酸的抗氧化保护作用可能归因于核因子κB信号通路对过氧化氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶表达水平的提高[9]。也有研究发现单宁酸可以抑制活性氧自由基的产生[10]。同时有研究表明,单宁酸也可以通过激活过氧化物酶体增殖受体γ辅激活因子α和核因子E2相关因子2信号通路来减少氧化损伤[11]。另外,原花青素通过激活核因子E2相关因子2通路并上调成骨细胞中抗氧化酶的表达,保护成骨细胞免受氧化应激、线粒体功能障碍和成骨损伤[12-13]。 天然多酚优异的抗氧化性能已被大量研究证实,如ZHANG等[14]将水溶性差的天然抗氧化剂白藜芦醇封装在硫醇化泊洛沙姆胶束中开发了一种具有成骨能力的抗氧化水凝胶,水凝胶溶解度提高了50倍以上,在脂多糖暴露下该水凝胶可以清除小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞(RAW264.7细胞)中的细胞内活性氧自由基,表现出优异的抗氧化能力。 (2)天然多酚抗炎、抗菌机制:天然多酚具有极好的抗炎、抗菌能力(图4),它们可以抑制促炎递质的合成与释放改变类二十烷酸的合成,比如通过核因子κB或激活蛋白1阻碍环氧合酶2和一氧化氮合酶的活性。一些酚酸(例如迷迭香酸)可以在基因和蛋白质水平上减少白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的产生[15]。作为一种典型的植物源多酚,原花青素可以抑制炎症细胞的附着。白藜芦醇可以抑制促炎细胞因子(肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β)的基因表达,发挥抗炎能力[14]。槲皮素通过抑制核因子κB通路显著降低巨噬细胞M1极化标记物(如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α)的表达,激活AMP活化蛋白激酶和蛋白激酶B信号通路增强巨噬细胞M2极化水平,产生抗炎作用[16-18]。研究证明多酚-壳聚糖接枝共聚物具有良好的抗菌特性,可调节巨噬细胞的功能、抑制炎症反应关键调节因子(包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6)来改善骨微环境[19-20]。 由于天然多酚的结构多种多样,其抗菌机制主要如下:①多酚与细菌细胞壁成分和细菌细胞膜相互作用;②预防和抑制生物膜的形成;③抑制微生物酶活性;④干扰蛋白质调节;⑤剥夺细菌细胞酶的底物和金属离子。绿原酸对革兰阴性菌和革兰阳性菌均具有优异的抗菌活性[21]。单宁酸对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抑制作用取决于酚羟基含量,因此单宁酸浓度越高抗菌作用越强,抗菌活性持续时间越长。PANG等[22]开发了一种受贻贝启发的矿物水凝胶,没食子酸接枝提高了水凝胶系统的抗菌性能,可有效抑制金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的生长,定量分析显示该水凝胶对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抑制率均在90%以上。 (3)天然多酚促成骨作用机制:天然多酚结构的多样性使其促成骨作用机制也不尽相同。没食子酸的高分子量聚合物通过经典的Wnt信号通路(Wnt/β-catenin)显著增强成骨作用[23]。槲皮素通过核因子κB受体激活因子配体途径抑制破骨细胞形成、促进骨再生[24]。白藜芦醇通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/糖原合成酶激酶3β)信号通路增强成骨作用[25]。目前的研究已证明多酚具有促成骨作用(图4),但对于不同天然多酚促成骨作用的具体机制仍需研究人员的不断探索。 "
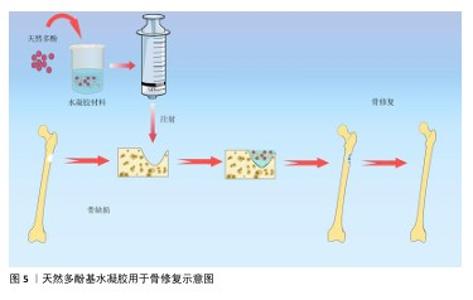
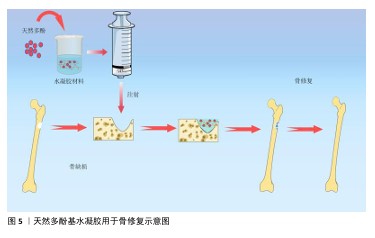
2.2 天然多酚基水凝胶的构建 2.2.1 天然多酚基水凝胶的生物相容性和机械性能 近年来研究人员研发了大量的骨材料,如生物活性玻璃、生物陶瓷、骨水泥、水凝胶等,这些材料修复骨缺损具有良好的效果。水凝胶材料具有天然的生物相容性,其多孔结构特性有利于营养物质和氧气的交换、新生血管网络的重建和新骨的长入。不同的交联方式还会赋予水凝胶独特的性能,比如席夫碱和氢键等交联能赋予水凝胶自愈性能。水凝胶因可注射性可以设计成不同的尺寸和形状,适合用于不规则骨缺损的治疗,见图5。另外,水凝胶具有多个修饰位点,易于物理/化学掺杂各种复合材料,以此来创建一个理想的骨再生环境。 骨重建是骨形成和骨吸收的稳态系统,需要成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间的微妙协调[26],如果这种平衡被打破就会导致骨质流失、骨密度降低等骨代谢疾病。天然多酚是植物提取物中的活性成分,具有良好的生物相容性且不良反应少,可协调骨形成和骨吸收的作用。LIU等[27]通过单宁酸与聚乙烯醇分子之间动态氢键形成凝胶,增强了水凝胶得机械性能并赋予其自愈能力,当单宁酸质量浓度从 0 mg/mL增加到250 mg/mL时,水凝胶的含水量明显下降,并且随着单宁酸质量浓度的增加,形成的氢键明显增多、自愈合性能随之增强。CHOI等[28]使用天然聚合物甲基丙烯酰化明胶制备了紫外单交联和单宁酸氢键以及紫外双交联的水凝胶,证实单宁酸双交联水凝胶具有更高的机械强度和更好的细胞相容性。 AMIRYAGHOUBI等[29]通过席夫碱反应使明胶和氧化藻酸盐形成凝胶,合成了负载姜黄素的壳聚糖微球并将其整合到明胶/氧化藻酸盐基质中,形成了坚固的复合凝胶框架,该凝胶具有溶胀率低和降解性更持久的特点,具备良好的压缩弹性与缓释能力,表现出卓越的生物相容性。WEI等[30]将固体脂质纳米粒子负载白藜芦醇并封装在甲基丙烯酰化明胶中,制备出具有良好的生物相容性、骨传导和骨诱导作用的支架。 "
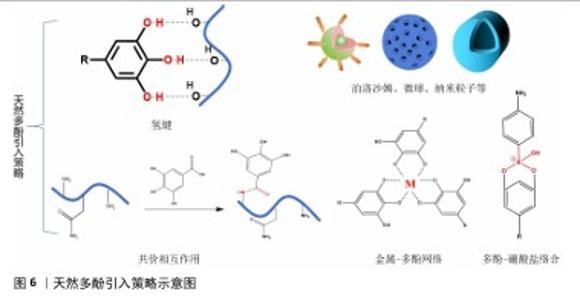
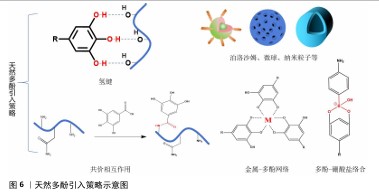
2.2.2 天然多酚基水凝胶的引入原因及其策略 活性氧自由基参与了复杂细胞信号,这些信号涉及增殖、炎症和衰老。正常活性氧自由基水平有助于正常的细胞稳态和功能,但如果活性氧自由基水平不能保持正常水平,则会启动细胞死亡,包括促凋亡的级联反应和细胞坏死。在骨材料植入的早期阶段,骨缺损部位的炎症反应和缺氧环境会导致大量的活性氧自由基产生;创伤和手术也可能引起强烈的炎症反应,并伴随着大量活性氧自由基的产生;损伤后的缺血再灌注过程也会释放更多的活性氧自由基;新毛细血管的形成增加了受伤部位的血管形成并促进炎症细胞的流入,导致活性氧自由基的增加。过度的细胞内活性氧自由基可以直接与蛋白质、脂肪、碳水化合物和核酸反应并在骨组织中散布,导致更多的损伤。过多的活性氧自由基也会扩散到周围的骨组织和骨材料中,损害蛋白质、脂质、碳水化合物和核酸,从而严重影响植入材料内部和周围细胞的存活、增殖和分化,改变骨重塑过程,导致破骨细胞和成骨细胞活性之间的不平衡、抑制成骨基因表达、影响细胞外基质合成和矿化,从而导致骨修复困难[31]。因此,及时调控骨缺损部位的微环境对于骨修复至关重要。 天然多酚在空气中很容易被氧化,并且部分天然多酚的溶解度低,导致生物利用度差。持续且长期局部药物释放系统能将所需药物剂量直接输送到作用部位,减轻全身毒性作用和不良反应,为此,人们开发了各种先进的水凝胶支架药物递送系统。天然多酚在骨修复材料中常见的反应/相互作用引入模式有:氢键、金属-多酚网络、共价相互作用(酯化、醚化、酰胺化)、多酚-硼酸盐络合及泊洛沙姆胶束、介孔粒子、纳米粒子等。可逆氢键通常可以在材料内提供交联网络,从而赋予材料自修复能力并改善机械性能。不同的金属有着不同的生物性能,比如铁具有抗菌活性、锌促血管生成等,金属-多酚网络简单快速、绿色化学,可以将多酚和金属离子本身的性质结合起来,然后相互修饰或协同增强彼此的功能。共价相互作用、泊洛沙姆胶束和介孔粒子、纳米粒子等通过化学或物理封装来达到缓释效果并改善材料的机械性能,具体反应/相互作用模式见图6。 骨修复过程通常分为炎症期、修复期和重塑期。在炎症期,引入天然多酚缓释凝胶系统可以通过缓释改善高活性氧自由基水平、促进M1表型巨噬细胞向M2表型巨噬细胞极化、减轻炎症反应并减少活性氧的积累,将活性氧自由基维持在相对正常水平以刺激骨再生。在修复期,天然多酚水凝胶系统的缓释性也可以通过继续少量释放天然多酚来促进成骨细胞、成骨基因以及碱性磷酸酶和钙结节的表达,进一步促进骨再生。在骨重塑阶段,天然多酚基水凝胶交联位点天然多酚的崩解释放协同多孔结构促进新骨的长入,加快骨的重塑。因此,引入天然多酚基水凝胶缓释系统来调控骨缺损部位的微环境对于骨修复至关重要。 "

2.3 天然多酚基水凝胶在骨修复中的应用 根据酚环的数量和这些环的共轭元素数量,天然多酚常被分为四类,包括酚酸、黄酮类、芪类和木脂素类。该文选择了几种常见用于骨修复领域的天然多酚以及相关专利进行了总结阐述分析。 2.3.1 槲皮素 槲皮素是一种低成本、低风险、不良反应少的植物提取药物,因具有抗炎和免疫调节作用逐渐被学者所关注。有研究表明,槲皮素通过核因子κB受体激活因子配体途径抑制破骨细胞形成、促进骨再生[24];此外,槲皮素也可以抑制核因子κB通路显著降低巨噬细胞M1极化标记物(如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α)水平,通过激活AMP活化蛋白激酶和蛋白激酶B信号通路增强M2极化水平,发挥抗炎作用[16-18]。然而,槲皮素是一种水溶性差的黄酮类化合物[32],使其生物利用度显著降低。 骨缺损修复治疗是临床实践中长期存在的挑战,尽管基于组织工程材料的修复疗法在骨再生中发挥着至关重要的作用,但目前针对临界尺寸骨缺损的治疗方法仍存在一些局限性。ZHOU等[33]将槲皮素固体脂质纳米颗粒封装在水凝胶中,将温度响应性聚(ε-己内酯-丙交酯)-b聚(乙二醇)-b-聚(ε-己内酯-丙交酯)修饰物偶联到透明质酸水凝胶的主链上,构建免疫调节水凝胶支架,发现这种骨免疫调节支架通过降低巨噬细胞M1极化、提高M2极化形成抗炎微环境,协同血管生成和抗破骨细胞分化,为大尺寸骨缺损修复提供了新的方法。 慢性骨髓炎需要一个有效的系统来消除感染和促进骨修复。JAFARBEGLOU等[34]开发了一种使用丝素蛋白和壳聚糖硫脲的天然水凝胶支架,并掺入万古霉素和槲皮素负载的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米颗粒,发现万古霉素和槲皮素从水凝胶支架中持续释放超过20 d,可促进成骨细胞黏附且无细胞毒性。 以上研究表明,槲皮素通过纳米颗粒等封装于水凝胶中达到了药物缓释并发挥抗氧化和抗炎能力,为骨再生提供理想的免疫微环境,从而促进骨再生。 "


2.3.2 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 儿茶素包括表儿茶素、表儿茶素没食子酸酯、表没食子儿茶素和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯。表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯占绿茶的50%,被认为是一种产生生物活性作用的多酚,具有优异的抗氧化、抗炎、促进成骨和抗菌特性,在骨修复领域中得到广泛研究。 HONDA等[35]通过水性化学合成制备表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯共轭明胶凝胶,表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯的羟基与凝胶基材的羧基产生交联,与未交联的凝胶和具有未结合表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯的交联凝胶相比,表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯共轭明胶凝胶表现出显著的成骨能力。为了调节多酚的智能按需释放,DING等[36]通过表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、3-丙烯酰胺基苯基硼酸的交联制备了一种活性氧自由基清除水凝胶,体内研究表明该水凝胶可以显著促进骨整合、清除积累的活性氧自由基、抑制炎症细胞因子的表达、诱导巨噬细胞极化为M2表型,促进成骨。为了构建骨再生理想的促成骨微环境,JING等[37]通过海藻酸钠和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯之间的氢键和物理缠结形成初级水凝胶,再引入Zn2+,该水凝胶模仿了天然细胞外基质,并表现出对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌良好的抗菌性能;随着表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯含量的增加,自由基清除效率更高,增强了小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞的增殖分化和成骨基因表达。 以上研究表明,表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯改性改善了凝胶的降解及释放性能,在抗氧化、成骨、抗炎和抗菌等生物性能方面发挥重要作用,展示了含表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯材料优异的发展潜力。"


2.3.3 没食子酸 没食子酸是在植物中发现的一种天然多酚化合物,具有多个羟基,可以有效减少活性氧自由基;此外,没食子酸的高分子量聚合物通过经典的Wnt信号通路显著增强成骨作用[23],但它在体内的吸收率较低且容易氧化。 金属离子的配位可以增强天然多酚在体内的稳定性和吸收性。多酚和金属离子的配位可通过加速电子转移,增强多酚清除活性氧自由基的能力。LUO等[38]通过集成羧甲基壳聚糖、右旋糖酐和4-甲酰基苯基硼酸的智能响应水凝胶系统,探索了一种金属有机框架(包含镁离子和没食子酸),结果表明该金属有机框架具有出色的活性氧自由基清除能力,显著上调Runx2、碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨桥蛋白和骨保护素的mRNA表达水平,促进碱性磷酸酶和钙结节的生成。 DONG等[39]通过使用紫外线接枝方法在磺化长碳纤维增强聚醚醚酮植入物表面构建多功能刺激响应金属有机框架水凝胶,该水凝胶由纳米羟基磷灰石核、没食子酸和镁离子金属有机框架以及甲基丙烯酰化壳聚糖组成,体外和体内研究结果表明,该水凝胶可以释放足够的抗炎药物没食子酸和营养元素镁离子,释放的没食子酸可减轻早期炎症反应,创造促进骨再生的骨免疫微环境;释放的镁离子可促进种植体周围的血管生成,为新骨形成阶段提供足够的氧气和营养;在骨修复后期,钙离子的长期持续释放保证了细胞外骨基质的钙化,促进新骨形成。WAN等 [40]通过没食子酸的羧基和明胶的氨基交联以及和磷酸锌锶金属配位制作复合水凝胶,结果显示该复合水凝胶可上调碱性磷酸酶表达、促进钙沉积物的形成与人脐静脉内皮细胞的管形成。 以上研究表明没食子酸具有优异的金属螯合能力和独特的化学性质,金属-多酚网络作为一项成熟的技术,可以将多酚和许多金属离子稳定地附着在不同材料表面,同时发挥多酚和金属离子的功能。没食子酸改性水凝胶通过发挥抗氧化能力和调节免疫微环境和巨噬细胞表型促进碱性磷酸酶和钙结节的生成,为骨再生构建理想的微环境。 "


2.3.4 白藜芦醇 白藜芦醇普遍存在于葡萄、浆果和红酒中,拥有促进成骨分化、血管生成及抗氧化、抗炎特性[41-42]。但是白藜芦醇的水溶性较低,口服后生物利用度较差,它还容易在热、光和氧气环境下降解。为了提高白藜芦醇的生物利用度,LI等[43]成功开发了一种可进行免疫调节和促进成骨分化的多功能热敏水凝胶复合系统(包含地塞米松、白藜芦醇、介孔羟基磷灰石微球),结果显示该水凝胶复合系统具有更强的抗氧化性能和抗炎性能,为骨的再生提供了一个良好的免疫微环境。 时空免疫紊乱是导致骨组织愈合失败的关键因素,在损伤后24-48 h内准确抑制过度的免疫反应峰值、调节骨骼的时空骨免疫紊乱至关重要。HAN等[44]将明胶-甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸水凝胶制备而成超声控制“爆炸”水凝胶,该水凝胶负载有通过缩合反应双重乳化产生的白藜芦醇纳米气泡,创新性地实现了超声控制的白藜芦醇释放,从而精确调节时空骨免疫疾病,加速骨修复进程。 以上研究表明,白藜芦醇改性水凝胶有着出色的抗氧化能力和调节免疫微环境、巨噬细胞表型能力。"


2.3.5 原花青素 原花青素是葡萄皮中丰富的有效自由基清除剂,以抗炎、抗衰老、抗氧化和抗菌作用而闻名[45]。有研究表明,原花青素通过激活核因子E2相关因子2通路上调成骨细胞中抗氧化酶的表达,保护成骨细胞免受氧化应激、线粒体功能障碍和成骨损伤[12-13]。 长期炎症会导致活性氧自由基过度积累,进一步加重病情、降低局部pH值,对骨缺损愈合产生不利影响,传统的药物输送支架材料难以满足这种复杂且动态的微环境的需求。QI等[13]基于硼酸盐复合物独特的pH值和活性氧自由基响应性合成了一种智能甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶,用于原花青素和阿米卡星的双重递送,保护小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞(MC3T3-E1)免受氧化应激并促进其成骨分化;此外,该水凝胶还对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌表现出高效的抗菌作用。WANG等[46]开发了泊洛沙姆@多西环素/藻酸盐微球@原花青素热敏复合水凝胶,可分级释放多西环素和原花青素,多西环素表现出爆发释放特性,从而实现优异的抗菌性能,而原花青素的释放在早期相对缓慢,从而依次发挥免疫调节和促成骨作用;该复合水凝胶可诱导小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞(RAW264.7细胞)从M1到M2的极化,促进炎症微环境中MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨。 各种金属离子和酚类分子之间的相互作用形成金属酚类络合物,已成为构建药物递送平台的策略。如镁离子与原花青素的螯合保留了原花青素的生物效应,同时使镁离子和原花青素协同缓慢释放。LI等[47]通过自组装过程合成了镁离子-原花青素配位的金属多酚纳米粒子,并将其负载于由多巴胺修饰的透明质酸和泊洛沙姆组成的水凝胶中,水凝胶持续释放的镁离子(Mg2+)和原花青素可减轻炎症并促进巨噬细胞极化向M2表型,增强胶原蛋白的合成和矿化,促进肌腱-骨界面的修复。有效整合感染控制和成骨以促进感染骨修复也是目前骨修复的一大难点。WANG等[48]通过将抗菌和抗氧化原花青素配位氧化锌微球与硫醚接枝海藻酸钠以及氯化钙复合,开发了注射可编程原花青素配位锌基复合水凝胶,该水凝胶可响应感染骨缺损中的高活性氧自由基微环境,引发复合水凝胶的崩解和氧化锌的快速释放,显著提高超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的活性,抑制金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的生长,降低细胞内活性氧自由基水平,下调巨噬细胞促炎细胞因子表达和上调巨噬细胞抗炎细胞因子表达,促进成骨。 以上研究表明,原花青素改性水凝胶具有显著的抗氧化能力、抗菌能力和抗炎能力,极大地促进了骨再生。 "


2.3.6 姜黄素 虽然姜黄素有很多好处,但存在代谢快、吸收能力差、水溶性低等局限性。克服姜黄素局限性的常见方法是将姜黄素与水凝胶、脂质体、纳米颗粒等结合使用。 CHEN等[49]通过动态席夫碱键合反应制备了季铵化壳聚糖/泊洛沙姆水凝胶,再将姜黄素负载到泊洛沙姆胶束中,显著提高了姜黄素的溶解度,该水凝胶通过释放姜黄素达到抗炎和抗氧化作用,在愈合过程中为干细胞提供保护环境。骨肉瘤切除后复发和骨缺损对临床医生来说是重大挑战。YU等[50]开发了姜黄素/壳聚糖纳米颗粒-丝素蛋白/甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸水凝胶,用于骨肉瘤治疗和骨再生,与姜黄素/壳聚糖纳米颗粒相比,姜黄素/壳聚糖纳米颗粒-丝素蛋白/甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸水凝胶具有可持续的药物释放,发挥抗癌和促进成骨细胞增殖的作用。 以上研究表明,姜黄素以不同的方式负载于水凝胶可发挥抗氧化、抗炎和促进骨再生的作用。值得注意的是,姜黄素被应用于骨肉瘤骨再生并取得了良好的效果,为骨肉瘤治疗提供了潜在的方向。 "


2.3.7 单宁酸 单宁酸是一种天然的多酚化合物,广泛存在于多种树木和高等植物中,具有良好的抗氧化活性,可抑制细胞过度积累的活性氧自由基,保护干细胞免受氧化应激损伤,促进成骨分化[51]。然而,人们对单宁酸保护细胞的抗氧化机制仍在探索。有研究发现,单宁酸可通过核因子κB信号通路提高过氧化氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的水平,发挥抗氧化作用[9]。也有研究发现,单宁酸可以抑制活性氧自由基的产生,通过抑制表皮生长因子受体-蛋白激酶B-雷帕霉素靶蛋白和表皮生长因子受体-Ras原癌基因-Raf激酶-细胞外调节蛋白激酶-细胞外信号调节激酶-信号转录和转录激活因子3通路来调节细胞凋亡[10]。另有研究表明,单宁酸可以通过激活过氧化物酶体增殖受体γ辅激活因子1α和核因子E2相关因子2/抗氧化应答元素信号通路来减少氧化损伤[11]。 由于单宁酸具有多个酚类基团,可以通过氢键、配位键等多种相互作用来交联大分子。CHEN等[52]用单宁酸作为明胶的交联剂与明胶分子链中的伯胺基反应形成凝胶,在一定范围内,单宁酸浓度的增加可显著提高水凝胶的弹性模量、缩短凝胶化时间。由此可见,单宁酸交联的水凝胶具有许多优点,包括快速的凝胶形成能力和可调的机械性能等。 单宁酸可以很容易地与各种金属离子偶联形成动态的金属-多酚网络,赋予凝胶更出色的抗炎、抗氧化、抗菌能力。JEONG等[53]将单宁酸和镁离子通过金属-多酚网络自组装并加入明胶冷冻凝胶中,释放的纳米颗粒通过活性氧的消除来减少M1巨噬细胞的生成,降低破骨细胞成熟程度。 以上研究表明,单宁酸改性水凝胶可以改善凝胶的机械性能,通过发挥抗氧化能力和调节免疫微环境、巨噬细胞表型显著增强骨再生,为治疗骨缺损提供了新的视角。 "


2.3.8 绿原酸 多酚-壳聚糖接枝共聚物由于较强的生物活性激发了很多研究者的兴趣。绿原酸是一种从咖啡酸和奎宁酸中提取的肉桂酸,具有有效的抗菌特性和调节巨噬细胞的功能,通过抑制炎症反应的关键调节因子(包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6)来改善骨微环境[19-20]。 骨缺损愈合涉及免疫调节、血管生成和成骨分化,并且修复过程因细菌感染而变得复杂,因此,临床迫切需要综合治疗策略以获得满意的治疗结果。DUAN等[54]开发了由羧甲基绿原酸昆虫壳聚糖、甲基丙烯酸酐-硫酸软骨素氧化物和Sr2+形成的三交联网络水凝胶,该水凝胶可显著减轻炎症、促进巨噬细胞向M2极化、促进骨髓间充质干细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖和迁移,从而加速血管生成、成骨分化和生物矿化过程。HE等[21]构建了磺化聚醚醚酮表面支撑的载绿原酸/接枝肽水凝胶系统,对革兰阴性菌和革兰阳性菌均具有优异的抗菌活性。 "


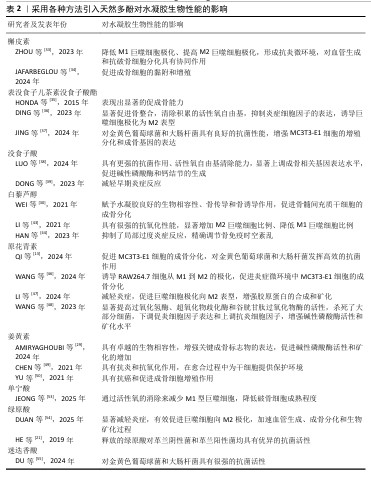
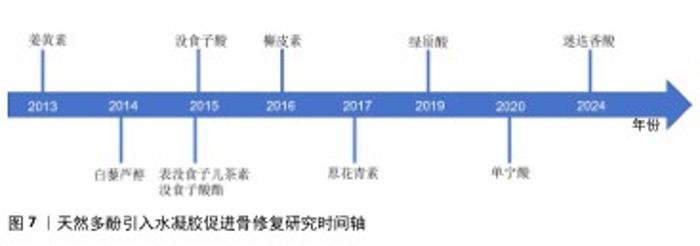
2.3.10 专利 潘晓丽团队发明了一种以绿原酸为基材的治疗感染性骨缺损的天然多糖/多酚/金属可注射水凝胶(专利号CN202411249982.8),该水凝胶具备良好的可注射性、抗炎、抗菌、促血管生成、成骨分化等生物活性。Carlo BermesJoerg Eppelmann等 发明了一种含有透明质酸和天然多酚抗氧化剂的药物,该药物可通过口服来治疗关节和骨骼疾病(专利号US201816630184)。俞豪杰团队利用多酚-硼酸盐络合发明了由单宁酸、没食子儿茶素或表没食子茶素没食子酸酯组成的抗炎小分子(专利号CN202310319220.X),实现了活性氧响应性释放抗炎药物,可以快速清除多种自由基。由此可见天然多酚在骨修复中的应用研究在不断得到关注,并且也取得了一定的成果。 表1总结归纳了在水凝胶中引入天然多酚的方法汇总,可见表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、没食子酸、原花青素、单宁酸、绿原酸均可构建金属-多酚网络,协同金属离子的各种性能(如锌、锶促血管生成,铁抗菌等)促进成骨,是目前构建最多的方式;而多酚-硼酸盐络合可以智能响应活性氧自由基水平,通过活性氧自由基响应来控制多酚的释放,也得到了广大研究者的运用;另外,氢键、共价相互作用的构建方式也取得极大的运用,通过共价键的交联可以增强材料的机械性能。表2总结了采用各种方法引入天然多酚对水凝胶生物性能的影响,可见天然多酚的抗氧化、抗菌、抗炎、促成骨功能性能均已得到证明。不同天然多酚引入水凝胶促进骨修复的研究时间轴,见图7,白藜芦醇在2014年被引入水凝胶[56],绿原酸在2019年被引入水凝胶[21],槲皮素在2016年被引入水凝胶[57],迷迭香酸在2024年被引入水凝胶[55],单宁酸在2020年被引入水凝胶[58],没食子酸在2015年被引入水凝胶[59],姜黄素在2013年被引入水凝胶[60],原花青素在2017被引入水凝胶[61],表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯在2015年被引入水凝胶[35]。由图可见,因为天然多酚的多功能特性,研究人员探索天然多酚的种类也在不断增加,极大促进了天然多酚基材料的应用进展。"

| [1] ARAI Y, PARK H, PARK S, et al. Bile acid-based dual-functional prodrug nanoparticles for bone regeneration through hydrogen peroxide scavenging and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Control Release. 2020;328:596-607. [2] XU J, ZE X, ZHAO L, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles oral exposure induce osteoblast apoptosis, inhibit osteogenic ability and increase lipogenesis in mouse. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024;277:116367. [3] EDELMANN S, LUMB JP. A para- to meta-isomerization of phenols. Nat Chem. 2024;16(7):1193-1199. [4] TZIMA K, BRUNTON NP, LYNG JG, et al. The effect of Pulsed Electric Field as a pre-treatment step in Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of phenolic compounds from fresh rosemary and thyme by-products. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. 2021;69:102644. [5] PINO C, SEPúLVEDA B, TAPIA F, et al. The Impact of Mild Frost Occurring at Different Harvesting Times on the Volatile and Phenolic Composition of Virgin Olive Oil. Antioxidants. 2022;11(5):852. [6] SRIDHAR A, PONNUCHAMY M, KUMAR PS, et al. Techniques and modeling of polyphenol extraction from food: a review. Environ Chem Lett. 2021;19(4): 3409-3443. [7] LUO J, SI H, JIA Z, et al. Dietary Anti-Aging Polyphenols and Potential Mechanisms. Antioxidants. 2021;10(2):283. [8] TRINDADE LR, DA SILVA DVT, BAIÃO DDS, et al. Increasing the Power of Polyphenols through Nanoencapsulation for Adjuvant Therapy against Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules. 2021;26(15):4621. [9] ZHANG J, SONG Q, HAN X, et al. Multi-targeted protection of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice by tannic acid. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;47: 95-105. [10] NAG S, MANNA K, SAHA M, et al. Tannic acid and vitamin E loaded PLGA nanoparticles ameliorate hepatic injury in a chronic alcoholic liver damage model via EGFR-AKT-STAT3 pathway. Nanomedicine. 2019;15(3):235-257. [11] SALMAN M, TABASSUM H, PARVEZ S. Tannic Acid Provides Neuroprotective Effects Against Traumatic Brain Injury Through the PGC-1α/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(6):2870-2885. [12] CHEN L, HU S-L, XIE J, et al. Proanthocyanidins-Mediated Nrf2 Activation Ameliorates Glucocorticoid-Induced Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Osteoblasts. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:1-14. [13] QI H, WANG B, WANG M, et al. A pH/ROS-responsive antioxidative and antimicrobial GelMA hydrogel for on-demand drug delivery and enhanced osteogenic differentiation in vitro. Int J Pharm. 2024; 657:124134. [14] ZHANG W, ZHENG L, YAN Y, et al. Facile Preparation of Multifunctional Hydrogels with Sustained Resveratrol Release Ability for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Gels. 2024; 10(7):429. [15] RAHMAN MM, RAHAMAN MS, ISLAM MR, et al. Role of Phenolic Compounds in Human Disease: Current Knowledge and Future Prospects. Molecules. 2021;27(1):233. [16] LU H, WU L, LIU L, et al. Corrigendum to “Quercetin ameliorates kidney injury and fibrosis by modulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization” [Biochem. Pharmacol. 154 (2018) 203–212]. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;198:114936. [17] WONG RWK, RABIE ABM. Effect of quercetin on bone formation. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(8):1061-1066. [18] WANG Y, LI C, WAN Y, et al. Quercetin‐Loaded Ceria Nanocomposite Potentiate Dual‐Directional Immunoregulation via Macrophage Polarization against Periodontal Inflammation. Small. 2021; 17(41):e2101505. [19] NAVEED M, HEJAZI V, ABBAS M, et al. Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:67-74. [20] LIU J, PU H, LIU S, et al. Synthesis, characterization, bioactivity and potential application of phenolic acid grafted chitosan: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2017; 174:999-1017. [21] HE X, DENG Y, YU Y, et al. Drug-loaded/grafted peptide-modified porous PEEK to promote bone tissue repair and eliminate bacteria. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces. 2019;181:767-777. [22] PANG Y, GUAN L, ZHU Y, et al. Gallic acid-grafted chitosan antibacterial hydrogel incorporated with polydopamine-modified hydroxyapatite for enhancing bone healing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1162202. [23] OH Y, AHN CB, MARASINGHE MPCK, et al. Insertion of gallic acid onto chitosan promotes the differentiation of osteoblasts from murine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;183:1410-1418. [24] WONG SK, CHIN KY, IMA-NIRWANA S. Quercetin as an Agent for Protecting the Bone: A Review of the Current Evidence. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6448. [25] LIU Z, MAO J, LI W, et al. Smart glucose-responsive hydrogel with ROS scavenging and homeostasis regulating properties for diabetic bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2024;497:154433. [26] ZHAO Z, WU C, HUANGFU Y, et al. Bioinspired Glycopeptide Hydrogel Reestablishing Bone Homeostasis through Mediating Osteoclasts and Osteogenesis in Periodontitis Treatment. ACS Nano. 2024; 18(43):29507-29521. [27] LIU Y, XIONG D. A tannic acid-reinforced PEEK-hydrogel composite material with good biotribological and self-healing properties for artificial joints. J Mat Chem B. 2021;9(38):8021-8030. [28] CHOI JB, KIM YK, BYEON SM, et al. Characteristics of Biodegradable Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogel Designed to Improve Osteoinduction and Effect of Additional Binding of Tannic Acid on Hydrogel. Polymers. 2021;13(15):2535. [29] AMIRYAGHOUBI N, FATHI M, SAFARY A, et al. In situ forming alginate/gelatin hydrogel scaffold through Schiff base reaction embedded with curcumin-loaded chitosan microspheres for bone tissue regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;256(Pt 2):128335. [30] WEI B, WANG W, LIU X, et al. Gelatin methacrylate hydrogel scaffold carrying resveratrol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for enhancement of osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and effective bone regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(5): 1-14. [31] ZHOU H, HE Z, CAO Y, et al. An injectable magnesium-loaded hydrogel releases hydrogen to promote osteoporotic bone repair via ROS scavenging and immunomodulation. Theranostics. 2024; 14(9):3739-3759. [32] HAN X, XU T, FANG Q, et al. Quercetin hinders microglial activation to alleviate neurotoxicity via the interplay between NLRP3 inflammasome and mitophagy. Redox Biol. 2021;44:102010. [33] ZHOU P, YAN B, WEI B, et al. Quercetin-solid lipid nanoparticle-embedded hyaluronic acid functionalized hydrogel for immunomodulation to promote bone reconstruction. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad025. [34] JAFARBEGLOU M, MEIMANDI-PARIZI A, DERAKHSHANDEH A, et al. Silk fibroin/chitosan thiourea hydrogel scaffold with vancomycin and quercetin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for treating chronic MRSA osteomyelitis in rats. Int J Pharm. 2024;666:124826. [35] HONDA Y, TANAKA T, TOKUDA T, et al. Local Controlled Release of Polyphenol Conjugated with Gelatin Facilitates Bone Formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(6): 14143-14157. [36] DING W, ZHOU Q, LU Y, et al. ROS-scavenging hydrogel as protective carrier to regulate stem cells activity and promote osteointegration of 3D printed porous titanium prosthesis in osteoporosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1103611. [37] JING H, WU Y, LIN Y, et al. A Zn2+ cross-linked sodium alginate/epigallocatechin gallate hydrogel scaffold for promoting skull repair. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces. 2024;239:113971. [38] LUO Q, YANG Y, HO C, et al. Dynamic hydrogel–metal–organic framework system promotes bone regeneration in periodontitis through controlled drug delivery. J Nanobiotechnol. 2024; 22(1):287. [39] DONG W, ZHAO S, WANG Y, et al. Stimuli-responsive metal–organic framework hydrogels endow long carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone with enhanced anti-inflammatory and angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Mater Des. 2023;225:111485. [40] WAN J, WU L, LIU H, et al. Incorporation of Zinc–Strontium Phosphate into Gallic Acid–Gelatin Composite Hydrogel with Multiple Biological Functions for Bone Tissue Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024;10(8):5057-5067. [41] MENG T, XIAO D, MUHAMMED A, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Action and Mechanisms of Resveratrol. Molecules. 2021;26(1):229. [42] MENG X, ZHOU J, ZHAO CN, et al. Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms of Resveratrol: A Narrative Review. Foods. 2020;9(3):340. [43] LI J, LI L, WU T, et al. An Injectable Thermosensitive Hydrogel Containing Resveratrol and Dexamethasone‐Loaded Carbonated Hydroxyapatite Microspheres for the Regeneration of Osteoporotic Bone Defects. Small Methods. 2023;8(1):e2300843. [44] HAN X, SHEN J, CHEN S, et al. Ultrasonic-controlled “explosive” hydrogels to precisely regulate spatiotemporal osteoimmune disturbance. Biomaterials. 2023;295:122057. [45] HUANG X, YE Y, ZHANG J, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Functional Hydrogel Delivers Procyanidins for the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022; 14(29):33756-33767. [46] WANG XY, LI QL, LIU Z, et al. Thermosensitive composite hydrogel with antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and osteogenic properties promotes periodontal bone regeneration via staged release of doxycycline and proanthocyanidin. Mater Today Chem. 2024;38:102052. [47] LI J, KE H, LEI X, et al. Controlled-release hydrogel loaded with magnesium-based nanoflowers synergize immunomodulation and cartilage regeneration in tendon-bone healing. Bioact Mater. 2024;36:62-82. [48] WANG Y, ZHAO Y, MA S, et al. Injective Programmable Proanthocyanidin-Coordinated Zinc-Based Composite Hydrogel for Infected Bone Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;13(6): e2302690. [49] CHEN B, LIANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Synergistic enhancement of tendon-to-bone healing via anti-inflammatory and pro-differentiation effects caused by sustained release of Mg2+/curcumin from injectable self-healing hydrogels. Theranostics. 2021;11(12): 5911-5925. [50] YU Q, MENG Z, LIU Y, et al. Photocuring Hyaluronic Acid/Silk Fibroin Hydrogel Containing Curcumin Loaded CHITOSAN Nanoparticles for the Treatment of MG-63 Cells and ME3T3-E1 Cells. Polymers. 2021;13(14):2302. [51] YANG J, LIANG J, ZHU Y, et al. Fullerol-hydrogel microfluidic spheres for in situ redox regulation of stem cell fate and refractory bone healing. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4801-4815. [52] CHEN S, LI M, MICHÁLEK M, et al. Cross-linking of mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticle incorporated gelatin hydrogels by tannic acid with enhanced mechanical performance and stability. Materialia. 2024;36: 102165. [53] JEONG H, BYUN H, LEE J, et al. Enhancement of Bone Tissue Regeneration with Multi‐Functional Nanoparticles by Coordination of Immune, Osteogenic, and Angiogenic Responses. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025;14(5):e2400232. [54] DUAN Y, LI Y, WANG Y, et al. An all-in-one “multifunctional hydrogel”: Through antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and angiogenic to promoting MRSA-infected bone defect repair. Chem Eng J. 2025;503: 158132. [55] DU J, CHU Y, HU Y, et al. A multifunctional self-reinforced injectable hydrogel for enhancing repair of infected bone defects by simultaneously targeting macrophages, bacteria, and bone marrow stromal cells. Acta Biomater. 2024;189:232-253. [56] WANG W, SUN L, ZHANG P, et al. An anti-inflammatory cell-free collagen/resveratrol scaffold for repairing osteochondral defects in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(12): 4983-4995. [57] GOGOI S, MAJI S, MISHRA D, et al. Nano-Bio Engineered Carbon Dot-Peptide Functionalized Water Dispersible Hyperbranched Polyurethane for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2016;17(3):1-15. [58] SAREETHAMMANUWAT M, BOONYUEN S, ARPORNMAEKLONG P. Effects of beta‐tricalcium phosphate nanoparticles on the properties of a thermosensitive chitosan/collagen hydrogel and controlled release of quercetin. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2020;109(7):1147-1159. [59] LIŠKOVÁ J, DOUGLAS TEL, BERANOVÁ J, et al. Chitosan hydrogels enriched with polyphenols: Antibacterial activity, cell adhesion and growth and mineralization. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;129:135-142. [60] ORELLANA BR, THOMAS MV, DZIUBLA TD, et al. Bioerodible calcium sulfate/poly (β-amino ester) hydrogel composites. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013;26: 43-53. [61] LUO H, ZHANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Constructing three-dimensional nanofibrous bioglass/gelatin nanocomposite scaffold for enhanced mechanical and biological performance. Chem Eng J. 2017;326: 210-221. |
| [1] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [2] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [3] | Guo Yuchao, Ni Qianwei, Yin Chen, Jigeer·Saiyilihan, Gao Zhan . Quaternized chitosan hemostatic materials: synthesis, mechanism, and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [4] | Liu Dawei, Cui Yingying, Wang Fanghui, Wang Zixuan, Chen Yuhan, Li Yourui, Zhang Ronghe. Epigallocatechin gallate-mediated bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species and its application in nanomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2101-2112. |
| [5] | Lai Yu, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Research hotspots and frontier trends of bioactive materials in treating bone infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2132-2144. |
| [6] | Zhou Hongli, Wang Xiaolong, Guo Rui, Yao Xuanxuan, Guo Ru, Zhou Xiongtao, He Xiangyi. Fabrication and characterization of nanohydroxyapatite/sodium alginate/polycaprolactone/alendronate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [7] | Wang Songpeng, Liu Yusan, Yu Huanying, Gao Xiaoli, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Min. Bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanomaterials: from tumor therapy and antibacterial activity to cytoprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2033-2013. |
| [8] | . Effect of mussel-derived antimicrobial peptide-coated modified prosthesis on prevention of early periprosthetic joint infection and regulation of bone transfer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 278-287. |
| [9] | Guo Jingwen, Wang Qingwei, He Zijun, Hu Zihang, Chen Zhi, Zhu Rong, Wang Yuming, Liu Wenfei, Luo Qinglu. Intra-articular injection of different concentrations of silicon-based bioceramics in treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 288-295. |
| [10] | Xu Wenhe, Li Xiaobing, Liu Fang. Functionalized biomimetic mineralized collagen modified orthopedic implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 516-527. |
| [11] | Zhou Shibo, Yu Xing, Chen Hailong, Xiong Yang. Nanocrystalline collagen-based bone combined with Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction repairs bone defects in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 354-361. |
| [12] | Liu Xiaohong, Zhao Tian, Mu Yunping, Feng Wenjin, Lyu Cunsheng, Zhang Zhiyong, Zhao Zijian, Li Fanghong. Acellular dermal matrix hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [13] | Yuan Qian, Zhang Hao, Pang Jie. Characterization and biological properties of naringin-loaded chitosan/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [14] | Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei. Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| [15] | Kong Xiaojuan, Tan Zhenyu, Lei Lei. Repair of rat endometrial injury by using miR-424-5p modified exosome/Poloxam 407 hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3626-3635. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||