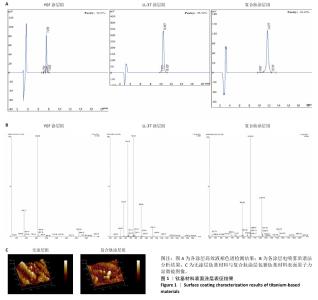
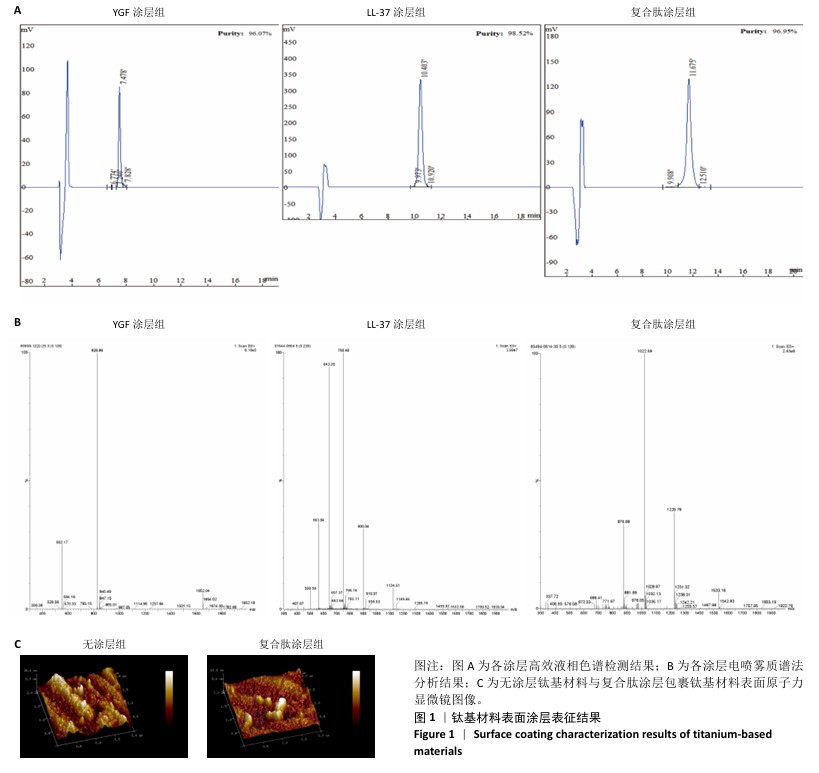
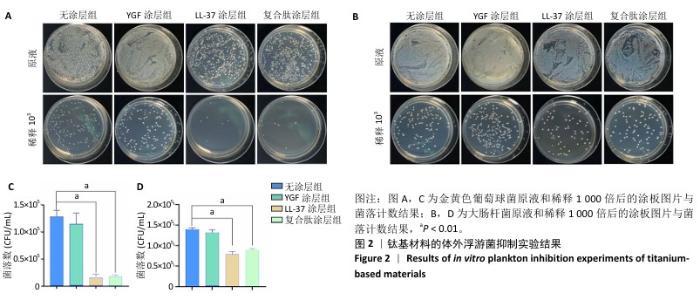
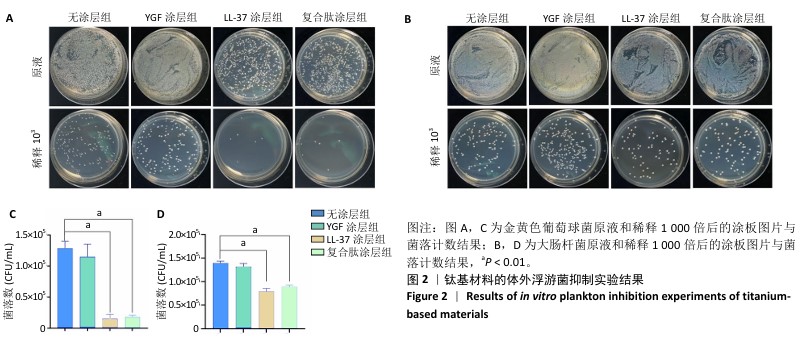
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 278-287.doi: 10.12307/2026.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of mussel-derived antimicrobial peptide-coated modified prosthesis on prevention of early periprosthetic joint infection and regulation of bone transfer
Liu Bo, Wuhuzi · Wulamu, Zhu Guangzhao, Guo Xiaobin, Song Ziyue, Meng Xingbu, Hu Junjie, Zhang Xiaogang
- Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-11-14Accepted:2025-02-20Online:2026-01-18Published:2025-06-10 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaogang, MS, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liu Bo, Master candidate, Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160421 (to ZXG); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82002276 (to GXB); Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2022D01D56 (to ZXG); “Tianshan Talents” Medical and Health High-level Talent Training Program Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. TSYC202301A008 (to ZXG); “Youth Scientific Research Sailing” Special Project of First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University and First Clinical Medical College, No. 2023YFY-QKMS-05 (to WW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
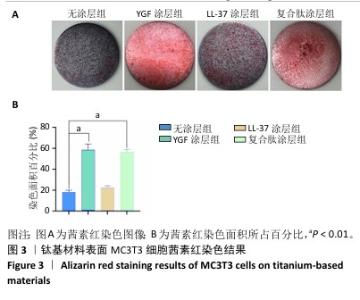
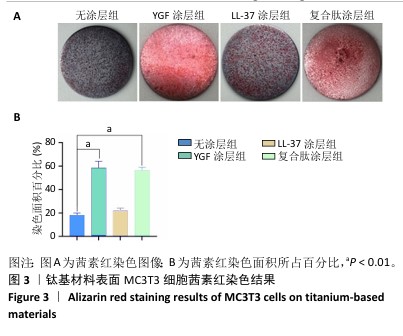
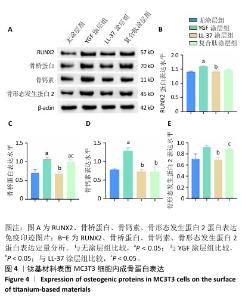
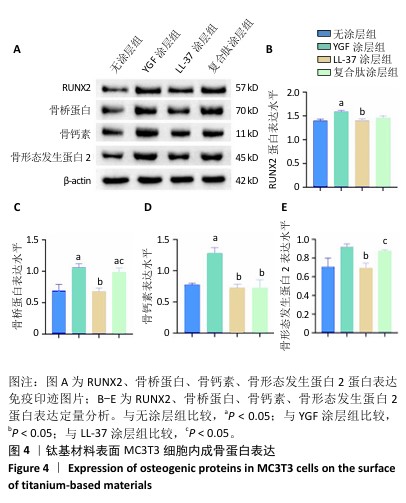
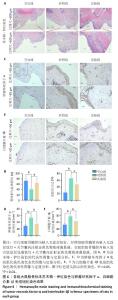
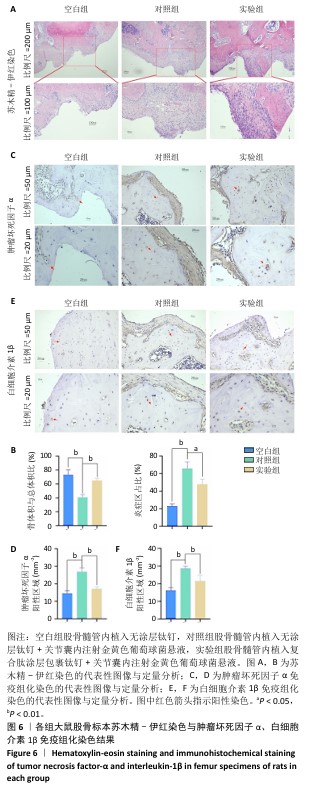
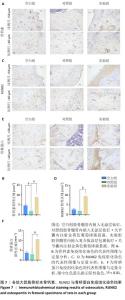
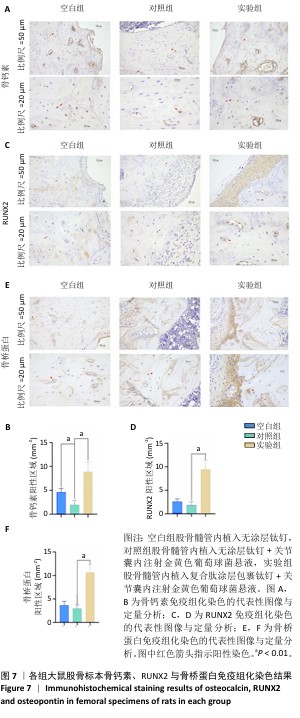
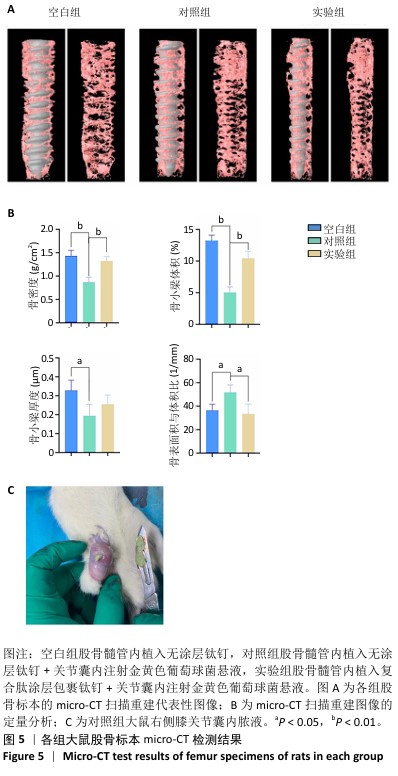
2.4 钛基材料的体内骨整合能力实验结果 2.4.1 实验动物数量分析 24只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.4.2 micro-CT扫描结果 为验证体外实验结果,此次研究利用SD大鼠构筑假体周围感染模型,对照组大鼠膝关节可见囊肿,处死取材后将肿块切开流出淡黄色脓液(图5)。micro-CT扫描重建结果显示,对照组骨量少于空白组、实验组;定量分析结果显示,对照组骨密度、骨小梁体积低于空白组、实验组(P < 0.01),骨表面积与骨体积比高于空白组、实验组(P < 0.05),骨小梁厚度低于空白组(P < 0.05),见图5。表明由于感染导致对照组骨矿物质与骨量流失明显,而实验组因复合肽涂层发挥作用使骨矿物质和骨量流失情况得到改善。"
| [1] VILLA JM, PANNU TS, THEEB I, et al. International Organism Profile of Periprosthetic Total Hip and Knee Infections. J Arthroplasty. 2021; 36(1):274-278. [2] BAERTL S, RUPP M, KERSCHBAUM M, et al. The PJI-TNM classification for periprosthetic joint infections. Bone Joint Res. 2024;13(1):19-27. [3] TANDE AJ, PATEL R. Prosthetic joint infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014; 27(2):302-345. [4] SUKHONTHAMARN K, STRONY JT, PATEL UJ, et al. Distal Femoral Replacement and Periprosthetic Joint Infection After Non-Oncological Reconstruction: A Retrospective Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(12): 3959-3965. [5] IANNOTTI F, PRATI P, FIDANZA A, et al. Prevention of Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI): A Clinical Practice Protocol in High-Risk Patients. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2020;5(4):186. [6] RUPP M, WALTER N, BÄRTL S, et al. Fracture-Related Infection-Epidemiology, Etiology, Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024;121(1):17-24. [7] TARABICHI S, PARVIZI J. Prevention of surgical site infection: a ten-step approach. Arthroplasty. 2023;5(1):21. [8] KAPADIA BH, BERG RA, DALEY JA, et al. Periprosthetic joint infection. Lancet. 2016;387(10016):386-394. [9] ZARDI EM, FRANCESCHI F. Prosthetic joint infection. A relevant public health issue. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(12):1888-1891. [10] ZHAO B, DONG Y, SHEN X, et al. Construction of multifunctional coating with cationic amino acid-coupled peptides for osseointegration of implants. Mater Today Bio. 2023;23:100848. [11] DE MEO D, CECCARELLI G, IAIANI G, et al. Clinical Application of Antibacterial Hydrogel and Coating in Orthopaedic and Traumatology Surgery. Gels. 2021;7(3):126. [12] ONORATO F, MASONI V, GAGLIARDI L, et al. What to Know about Antimicrobial Coatings in Arthroplasty: A Narrative Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(4):574. [13] GALLO J, HOLINKA M, MOUCHA CS. Antibacterial surface treatment for orthopaedic implants. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(8):13849-13880. [14] ROMANÒ CL, SCARPONI S, GALLAZZI E, et al. Antibacterial coating of implants in orthopaedics and trauma: a classification proposal in an evolving panorama. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:157. [15] CHEN Y, ZHOU L, GUAN M, et al. Multifunctionally disordered TiO2 nanoneedles prevent periprosthetic infection and enhance osteointegration by killing bacteria and modulating the osteoimmune microenvironment. Theranostics. 2024;14(15):6016-6035. [16] GIBON E, AMANATULLAH DF, LOI F, et al. The biological response to orthopaedic implants for joint replacement: Part I: Metals. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(7):2162-2173. [17] MEI S, WANG H, WANG W, et al. Antibacterial effects and biocompatibility of titanium surfaces with graded silver incorporation in titania nanotubes. Biomaterials. 2014;35(14):4255-4265. [18] FILIPOVIĆ U, DAHMANE RG, GHANNOUCHI S, et al. Bacterial adhesion on orthopedic implants. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020; 283:102228. [19] ARCIOLA CR, CAMPOCCIA D, MONTANARO L. Implant infections: adhesion, biofilm formation and immune evasion. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018;16(7):397-409. [20] GHIMIRE A, SONG J. Anti-Periprosthetic Infection Strategies: From Implant Surface Topographical Engineering to Smart Drug-Releasing Coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(18): 20921-20937. [21] CHOUIRFA H, BOULOUSSA H, MIGONNEY V, et al. Review of titanium surface modification techniques and coatings for antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater. 2019;83:37-54. [22] PIGOSSI SC, MEDEIROS MC, SASKA S, et al. Role of Osteogenic Growth Peptide (OGP) and OGP(10-14) in Bone Regeneration: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(11):1885. [23] RAPHAEL-MIZRAHI B, ATTAR-NAMDAR M, CHOURASIA M, et al. Osteogenic growth peptide is a potent anti-inflammatory and bone preserving hormone via cannabinoid receptor type 2. Elife. 2022;11: e65834. [24] GUO X, BAI J, GE G, et al. Bioinspired peptide adhesion on Ti implants alleviates wear particle-induced inflammation and improves interfacial osteogenesis. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;605:410-424. [25] ZAIOU M, GALLO RL. Cathelicidins, essential gene-encoded mammalian antibiotics. J Mol Med (Berl). 2002;80(9):549-561. [26] BOLOSOV IA, PANTELEEV PV, SYCHEV SV, et al. Dodecapeptide Cathelicidins of Cetartiodactyla: Structure, Mechanism of Antimicrobial Action, and Synergistic Interaction With Other Cathelicidins. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:725526. [27] BHATTACHARJYA S, ZHANG Z, RAMAMOORTHY A. LL-37: Structures, Antimicrobial Activity, and Influence on Amyloid-Related Diseases. Biomolecules. 2024;14(3):320. [28] GUERRA M, VIEIRA B, CALAZANS A, et al. Recent advances in the therapeutic potential of cathelicidins. Front Microbiol. 2024;15: 1405760. [29] YOON G, PUENTES R, TRAN J, et al. The role of cathelicidins in neutrophil biology. J Leukoc Biol. 2024;116(4):689-705. [30] SÁNCHEZ-PEÑA FJ, MLÁ R, TORRES-AGUILAR H, et al. LL-37 Triggers Antimicrobial Activity in Human Platelets. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3): 2816. [31] SU Y, SHARMA NS, JOHN JV, et al. Engineered Exosomes Containing Cathelicidin/LL-37 Exhibit Multiple Biological Functions. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(20):e2200849. [32] MAJEWSKA M, ZAMLYNNY V, PIETA IS, et al. Interaction of LL-37 human cathelicidin peptide with a model microbial-like lipid membrane. Bioelectrochemistry. 2021;141:107842. [33] ENGELBERG Y, LANDAU M. The Human LL-37(17-29) antimicrobial peptide reveals a functional supramolecular structure. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3894. [34] VAN DER SCHOT G, BONVIN AM. Performance of the WeNMR CS-Rosetta3 web server in CASD-NMR. J Biomol NMR. 2015;62(4): 497-502. [35] BAI J, WANG H, CHEN H, et al. Biomimetic osteogenic peptide with mussel adhesion and osteoimmunomodulatory functions to ameliorate interfacial osseointegration under chronic inflammation. Biomaterials. 2020;255:120197. [36] 贾麒钰,黄晓夏,郭建,等.整合素靶向肽促进SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(30): 4780-4786. [37] RAPHEL J, KARLSSON J, GALLI S, et al. Engineered protein coatings to improve the osseointegration of dental and orthopaedic implants. Biomaterials. 2016;83:269-282. [38] MEYERS SR, GRINSTAFF MW. Biocompatible and bioactive surface modifications for prolonged in vivo efficacy. Chem Rev. 2012;112(3): 1615-1632. [39] PAN G, GUO Q, MA Y, et al. Thermo-responsive hydrogel layers imprinted with RGDS peptide: a system for harvesting cell sheets. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013;52(27):6907-6911. [40] EHRENSBERGER MT, CLARK CM, CANTY MK, et al. Electrochemical methods to enhance osseointegrated prostheses. Biomed Eng Lett. 2020;10(1):17-41. [41] JALALI F, OVEISI H, MESHKINI A. Enhanced osteogenesis properties of titanium implant materials by highly uniform mesoporous thin films of hydroxyapatite and titania intermediate layer. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(12):114. [42] ZHAO H, HUANG Y, ZHANG W, et al. Mussel-Inspired Peptide Coatings on Titanium Implant to Improve Osseointegration in Osteoporotic Condition. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(7): 2505-2515. [43] PAN G, SUN S, ZHANG W, et al. Biomimetic Design of Mussel-Derived Bioactive Peptides for Dual-Functionalization of Titanium-Based Biomaterials. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(45):15078-15086. [44] SUN J, HUANG Y, ZHAO H, et al. Bio-clickable mussel-inspired peptides improve titanium-based material osseointegration synergistically with immunopolarization-regulation. Bioact Mater. 2022;9:1-14. [45] RODRIGUES LOPES I, ALCANTARA LM, SILVA RJ, et al. Microscopy-based phenotypic profiling of infection by Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates reveals intracellular lifestyle as a prevalent feature. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7174. [46] JEVON M, GUO C, MA B, et al. Mechanisms of internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by cultured human osteoblasts. Infect Immun. 1999;67(5):2677-2681. [47] WRIGHT JA, NAIR SP. Interaction of staphylococci with bone. Int J Med Microbiol. 2010;300(2-3):193-204. [48] JIN Y, LIU H, CHU L, et al. Initial therapeutic evidence of a borosilicate bioactive glass (BSG) and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle scaffold on implant-associated Staphylococcal aureus bone infection. Bioact Mater. 2024;40:148-167. [49] GUO HN, TONG YC, WANG HL, et al. Novel Hybrid Peptide Cathelicidin 2 (1-13)-Thymopentin (TP5) and Its Derived Peptides with Effective Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Anti-Adhesion Activities. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11681. [50] AGADI N, MAITY A, JHA AK, et al. Distinct mode of membrane interaction and disintegration by diverse class of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2022;1864(12):184047. [51] LIU H, LIU Z, DU J, et al. Thymidine phosphorylase exerts complex effects on bone resorption and formation in myeloma. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(353):353ra113. [52] MA Y, ZHANG Y, LIN Y, et al. Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model. Open Med (Wars). 2023;18(1):20230656. [53] POLICASTRO GM, LIN F, SMITH CALLAHAN LA, et al. OGP functionalized phenylalanine-based poly(ester urea) for enhancing osteoinductive potential of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16(4):1358-1371. [54] CHEN YC, BAB I, MANSUR N, et al. Structure-bioactivity of C-terminal pentapeptide of osteogenic growth peptide [OGP(10-14)]. J Pept Res. 2000;56(3):147-156. [55] LEE SJ, KANG SW, DO HJ, et al. Enhancement of bone regeneration by gene delivery of BMP2/Runx2 bicistronic vector into adipose-derived stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(21):5652-5659. [56] CHEN Z, WANG X, SHAO Y, et al. Synthetic osteogenic growth peptide promotes differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts via RhoA/ROCK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;358(1-2):221-227. [57] PING Z, WANG Z, SHI J, et al. Inhibitory effects of melatonin on titanium particle-induced inflammatory bone resorption and osteoclastogenesis via suppression of NF-κB signaling. Acta Biomater. 2017;62:362-371. [58] MIGUEL SM, NAMDAR-ATTAR M, NOH T, et al. ERK1/2-activated de novo Mapkapk2 synthesis is essential for osteogenic growth peptide mitogenic signaling in osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(45):37495-37502. [59] YU YL, WU JJ, LIN CC, et al. Elimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms on titanium implants via photothermally-triggered nitric oxide and immunotherapy for enhanced osseointegration. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):21. [60] LIU H, JIAO Y, ZHOU W, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells improve the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cell sheets on irradiated bone defect repair in a rat model. J Transl Med. 2018; 16(1):137. |
| [1] | Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei. Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| [2] | Zhou Shibo, Yu Xing, Chen Hailong, Xiong Yang. Nanocrystalline collagen-based bone combined with Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction repairs bone defects in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 354-361. |
| [3] | Yuan Qian, Zhang Hao, Pang Jie. Characterization and biological properties of naringin-loaded chitosan/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [4] | Guo Jingwen, Wang Qingwei, He Zijun, Hu Zihang, Chen Zhi, Zhu Rong, Wang Yuming, Liu Wenfei, Luo Qinglu. Intra-articular injection of different concentrations of silicon-based bioceramics in treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 288-295. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||