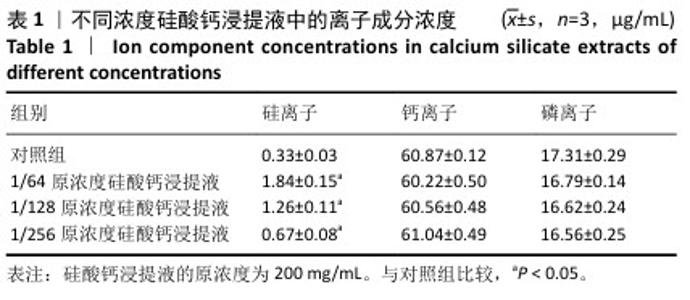
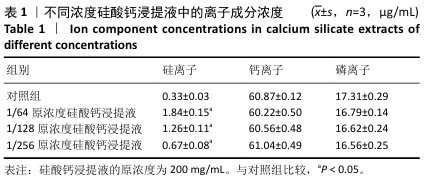
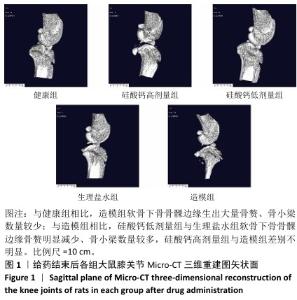
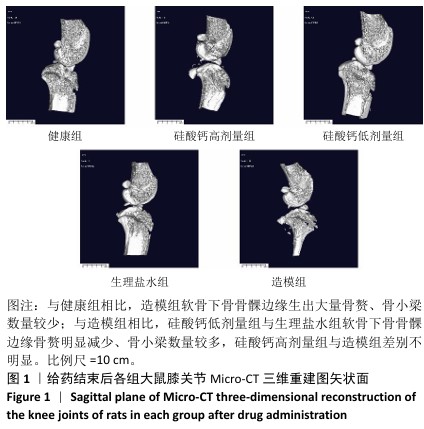
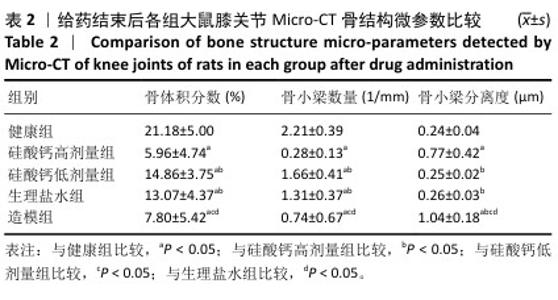
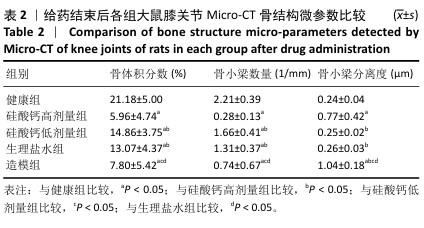
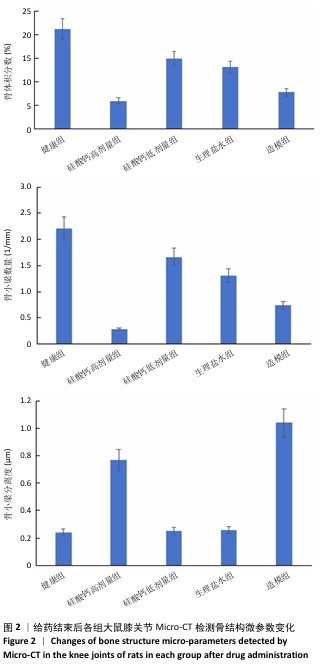
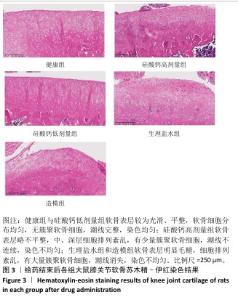
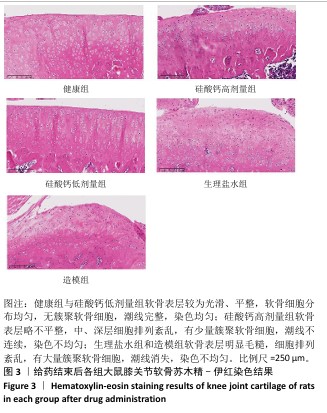
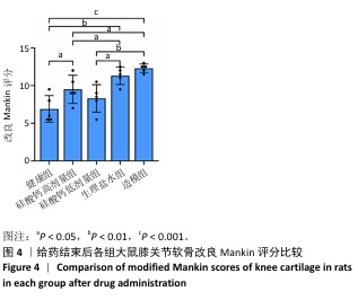
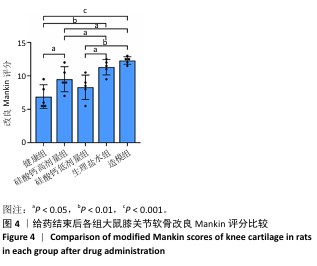
[1] BOWDEN JL, HUNTER DJ, DEVEZA LA, et al. Core and adjunctive interventions for osteoarthritis: efficacy and models for implementation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(8):434-447.
[2] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, SMITH E, et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):819-828.
[3] ROELOFS AJ, DE BARI C. Osteoarthritis year in review 2023: Biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024;32(2):148-158.
[4] LI XX, CAO F, ZHAO CN, et al. Global burden of osteoarthritis: Prevalence and temporal trends from 1990 to 2019. Int J Rheum Dis. 2024;27(8):e15285.
[5] PRIMORAC D, MOLNAR V, ROD E, et al. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review of Pathogenesis and State-Of-The-Art Non-Operative Therapeutic Considerations. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(8):854.
[6] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019; 393(10182):1745-1759.
[7] O’NEILL TW, MCCABE PS, MCBETH J. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors and disease outcomes of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(2):312-326.
[8] ARDEN NK, PERRY TA, BANNURU RR, et al. Non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis: comparison of ESCEO and OARSI 2019 guidelines. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(1):59-66.
[9] ZHU S, WANG Z, LIANG Q, et al. Chinese guidelines for the rehabilitation treatment of knee osteoarthritis: An CSPMR evidence-based practice guideline. J Evid Based Med. 2023;16(3):376-393.
[10] SOTO OCAÑA J, BAYARD NU, HART JL, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs sensitize epithelial cells to Clostridioides difficile toxin-mediated mitochondrial damage. Sci Adv. 2023;9(29):eadh5552.
[11] DOMPER ARNAL MJ, HIJOS-MALLADA G, LANAS A. Gastrointestinal and cardiovascular adverse events associated with NSAIDs. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022;21(3):373-384.
[12] CHEN T, BAO S, CHEN J, et al. Xiaojianzhong decoction attenuates aspirin-induced gastric mucosal injury via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/ULK1 and AMPK/ULK1 pathways. Pharm Biol. 2023;61(1):1234-1248.
[13] SUN W, WANG M, ZHAO J, et al. Sulindac selectively induces autophagic apoptosis of GABAergic neurons and alters motor behaviour in zebrafish. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):5351.
[14] KOMPEL AJ, ROEMER FW, MURAKAMI AM, et al. Intra-articular Corticosteroid Injections in the Hip and Knee: Perhaps Not as Safe as We Thought? Radiology. 2019;293(3):656-663.
[15] BOWMAN S, AWAD ME, HAMRICK MW, et al. Recent advances in hyaluronic acid based therapy for osteoarthritis. Clin Transl Med. 2018; 7(1):6.
[16] BENNELL KL, PATERSON KL, METCALF BR, et al. Effect of Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma vs Placebo Injection on Pain and Medial Tibial Cartilage Volume in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: The RESTORE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021;326(20):2021-2030.
[17] MORAN CJ, PASCUAL-GARRIDO C, CHUBINSKAYA S, et al. Restoration of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(4):336-344.
[18] 许鑫,胡小卫,金志旦,等.关节软骨损伤治疗进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(11):1021-1025.
[19] CHEN L, DENG C, LI J, et al. 3D printing of a lithium-calcium-silicate crystal bioscaffold with dual bioactivities for osteochondral interface reconstruction. Biomaterials. 2019;196:138-150.
[20] JAYACHANDRAN V, MURUGAN SS, DALAVI PA, et al. Alginate-based Composite Microspheres: Preparations and Applications for Bone Tissue Engineering. Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(13):1067-1081.
[21] GWON K, PARK JD, LEE S, et al. Injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel encapsulated with Si-based NiO nanoflower by visible light cross-linking: Its antibacterial applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;208:149-158.
[22] KÜÇÜKKAYA EREN S. Clinical applications of calcium silicate-based materials: a narrative review. Aust Dent J. 2023;68 Suppl 1:
S96-s109.
[23] HAN X, DENG F, ZHU R, et al. Osteoimmune reaction caused by a novel silicocarnotite bioceramic promoting osteogenesis through the MAPK pathway. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(11):2877-2891.
[24] DU L, QIN C, ZHANG H, et al. Multicellular Bioprinting of Biomimetic Inks for Tendon-to-Bone Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(21): e2301309.
[25] REIS G, CUBA GT, TARGA WHC, et al. S53P4 BIOACTIVE GLASS PUTTY IN THE LOCAL TREATMENT OF CAVITARY CHRONIC OSTEOMYELITIS. Acta Ortop Bras. 2023;31(1):e258453.
[26] XU N, LU D, QIANG L, et al. 3D-Printed Composite Bioceramic Scaffolds for Bone and Cartilage Integrated Regeneration. ACS Omega. 2023;8(41):37918-37926.
[27] ZHAO C, LIU W, ZHU M, et al. Bioceramic-based scaffolds with antibacterial function for bone tissue engineering: A review. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:383-398.
[28] WEE CY, LIM QRT, XU X, et al. Characterization and in-vitro assessment of silicon-based apatite microspheres for bone tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2024;112(1):e35349.
[29] DENG C, ZHOU Q, ZHANG M, et al. Bioceramic Scaffolds with Antioxidative Functions for ROS Scavenging and Osteochondral Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(12):e2105727.
[30] DENG C, QIN C, LI Z, et al. Diatomite-incorporated hierarchical scaffolds for osteochondral regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2024;38:305-320.
[31] LI CJ, PARK JH, JIN GS, et al. Strontium/Silicon/Calcium-Releasing Hierarchically Structured 3D-Printed Scaffolds Accelerate Osteochondral Defect Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(20):e2400154.
[32] KELLAR K, PANDILLAPALLI NR, MOREIRA AG. Calcium and Phosphorus: All You Need to Know but Were Afraid to Ask. Clin Perinatol. 2023; 50(3):591-606.
[33] DANG W, WANG X, LI J, et al. 3D printing of Mo-containing scaffolds with activated anabolic responses and bi-lineage bioactivities. Theranostics. 2018;8(16):4372-4392.
[34] YU B, LI H, ZHANG Z, et al. Extracellular vesicles engineering by silicates-activated endothelial progenitor cells for myocardial infarction treatment in male mice. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):2094.
[35] LIN TL, LIN YH, LEE AK, et al. The exosomal secretomes of mesenchymal stem cells extracted via 3D-printed lithium-doped calcium silicate scaffolds promote osteochondral regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2023;22:100728.
[36] KIM SJ, KIM JE, CHOE G, et al. Self-assembled peptide-substance P hydrogels alleviate inflammation and ameliorate the cartilage regeneration in knee osteoarthritis. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):40.
[37] MARTÍN-MILLÁN M, CASTAÑEDA S. Estrogens, osteoarthritis and inflammation. Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(4):368-373.
[38] LINN S, MURTAUGH B, CASEY E. Role of sex hormones in the development of osteoarthritis. PM R. 2012;4(5 Suppl):S169-173.
[39] GENG R, LI J, YU C, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: Current status and research progress in treatment (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2023; 26(4):481.
[40] QIAN JJ, XU Q, XU WM, et al. Expression of VEGF-A Signaling Pathway in Cartilage of ACLT-induced Osteoarthritis Mouse Model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):379.
[41] SADRI B, HASSANZADEH M, BAGHERIFARD A, et al. Cartilage regeneration and inflammation modulation in knee osteoarthritis following injection of allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: a phase II, triple-blinded, placebo controlled, randomized trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):162.
[42] SZWEDOWSKI D, SZCZEPANEK J, PACZESNY Ł, et al. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on the Intra-Articular Microenvironment in Knee Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5492.
[43] SALTZMAN BM, LEROUX T, MEYER MA, et al. The Therapeutic Effect of Intra-articular Normal Saline Injections for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-analysis of Evidence Level 1 Studies. Am J Sports Med. 2017; 45(11):2647-2653.
[44] LEWIS E, MERGHANI K, ROBERTSON I, et al. The effectiveness of leucocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma injections on symptomatic early osteoarthritis of the knee: the PEAK randomized controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2022;104-b(6):663-671.
[45] BANNURU RR, MCALINDON TE, SULLIVAN MC, et al. Effectiveness and Implications of Alternative Placebo Treatments: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of Osteoarthritis Trials. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163(5):365-372.
[46] TAMBIAH JRS, SIMSEK I, SWEARINGEN CJ, et al. Comparing Patient-Reported Outcomes From Sham and Saline-Based Placebo Injections for Knee Osteoarthritis: Data From a Randomized Clinical Trial of Lorecivivint. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(3):630-636.
[47] ABHISHEK A, DOHERTY M. Mechanisms of the placebo response in pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(9):1229-1235.
[48] HARADA H, TAGASHIRA S, FUJIWARA M, et al. Cbfa1 isoforms exert functional differences in osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274(11):6972-6978.
[49] LEE KS, HONG SH, BAE SC. Both the Smad and p38 MAPK pathways play a crucial role in Runx2 expression following induction by transforming growth factor-beta and bone morphogenetic protein. Oncogene. 2002;21(47):7156-7163.
[50] KAWATO Y, HIRAO M, EBINA K, et al. Nkx3.2 promotes primary chondrogenic differentiation by upregulating Col2a1 transcription. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34703.
[51] FERGUSON C, ALPERN E, MICLAU T, et al. Does adult fracture repair recapitulate embryonic skeletal formation? Mech Dev. 1999;87(1-2): 57-66.
[52] PFANDER D, CRAMER T, SCHIPANI E, et al. HIF-1alpha controls extracellular matrix synthesis by epiphyseal chondrocytes. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 9):1819-1826.
[53] KOMATSU DE, HADJIARGYROU M. Activation of the transcription factor HIF-1 and its target genes, VEGF, HO-1, iNOS, during fracture repair. Bone. 2004;34(4):680-688.
[54] 吴成铁,常江.硅酸盐生物活性陶瓷用于骨组织修复及再生的研究[J].无机材料学报,2013,28(1): 29-39.
[55] LEE CY, NEDUNCHEZIAN S, LIN SY, et al. Bilayer osteochondral graft in rabbit xenogeneic transplantation model comprising sintered 3D-printed bioceramic and human adipose-derived stem cells laden biohydrogel. J Biol Eng. 2023;17(1):74. |