Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (14): 3576-3585.doi: 10.12307/2026.078
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effect of mesoporous ZLN005@polydopamine nanoparticles on chondrocytes in osteoarthritis
Wu Tianyi1, Miao Yiming2, Wan Kaichen1, Teng Yun1, Zou Jun1
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Changshu Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changshu 215500, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-14Accepted:2025-05-18Online:2026-05-18Published:2025-09-10 -
Contact:Zou Jun, MD, Chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wu Tianyi, Master candidate, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82172506 (to ZJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Tianyi, Miao Yiming, Wan Kaichen, Teng Yun, Zou Jun. Protective effect of mesoporous ZLN005@polydopamine nanoparticles on chondrocytes in osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3576-3585.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
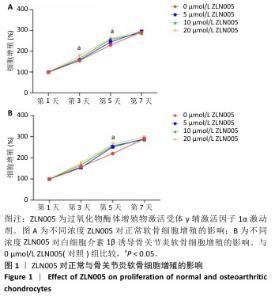
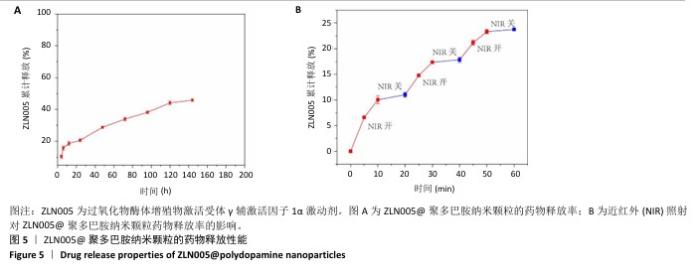
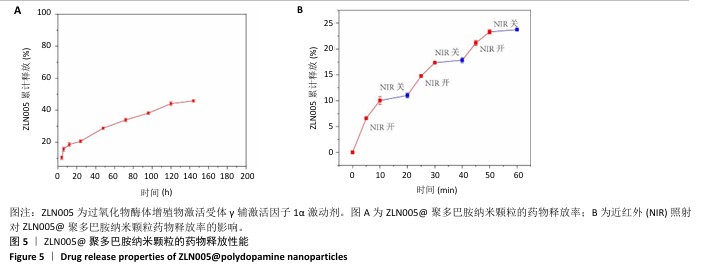
2.1 ZLN005对正常与骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖的影响 研究表明20 μmol/L ZLN005可有效激活过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅激活因子1α[21],因此实验选择20 μmol/L作为基准浓度,探讨ZLN005对小鼠软骨细胞增殖的影响。CCK-8检测结果显示,在正常培养第1天,不同浓度ZLN005对软骨细胞增殖未产生显著影响;正常培养第3,5天,20 μmol/L ZLN005组细胞增殖率显著高于对照组(P < 0.05);正常培养第7天,各组细胞增殖率趋于相似,均接近300%,见图1A。在白细胞介素1β诱导的骨关节炎模型下,培养第1,3天,各组细胞增殖率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养第5天,20 μmol/L ZLN005组细胞增殖率高于对照组(P < 0.05);培养第7天,各组细胞增殖率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图1B。"
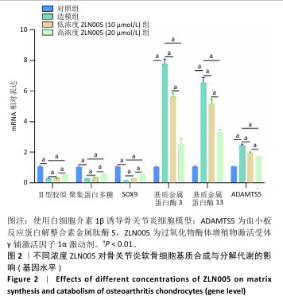
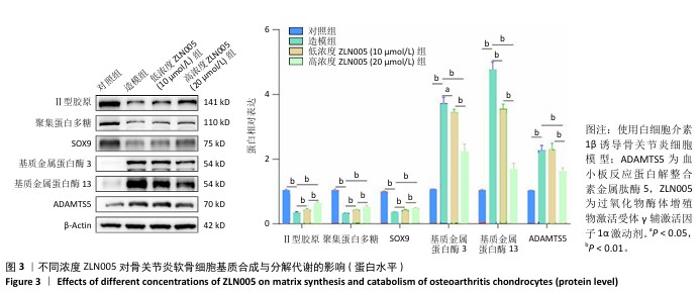
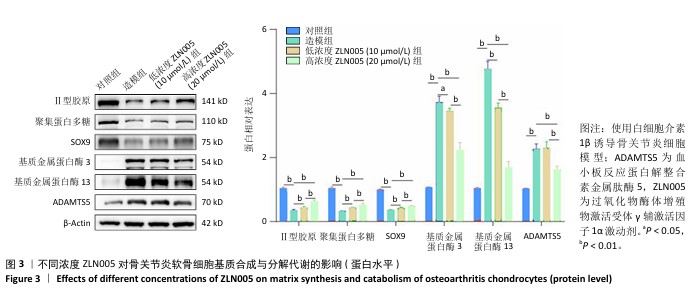
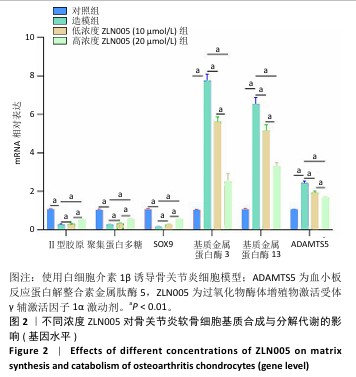
2.2 ZLN005对骨关节炎软骨细胞基质合成与分解代谢的影响 软骨细胞基质代谢功能对于骨关节炎进展有重要意义,因此实验对ZLN005处理后的骨关节炎软骨细胞基质合成与分解代谢功能进行检测。RT-qPCR检测结果显示,与对照组比较,造模组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3和ADAMTS5 mRNA表达升高(P < 0.01);与造模组比较,低浓度ZLN005组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9 mRNA表达升高(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3和ADAMTS5 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.01);与低浓度ZLN005组比较,高浓度ZLN005组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9 mRNA表达升高(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3和ADAMTS5 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.01),见图2。 Western Blot检测结果显示,与对照组比较,造模组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3和ADAMTS5蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01);与造模组比较,低浓度ZLN005组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.05);与低浓度ZLN005组比较,高浓度ZLN005组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3、ADAMTS5蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01),见图3。 "
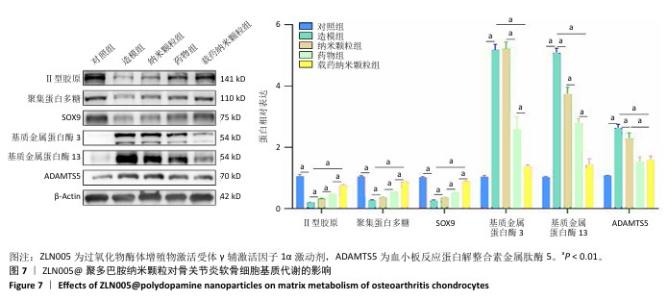
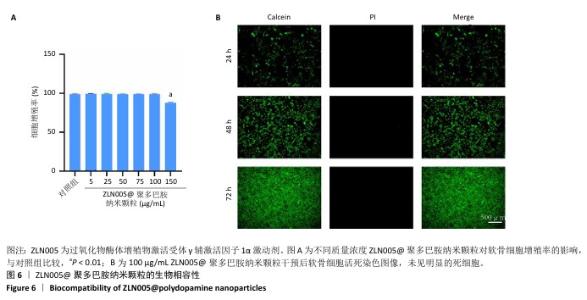
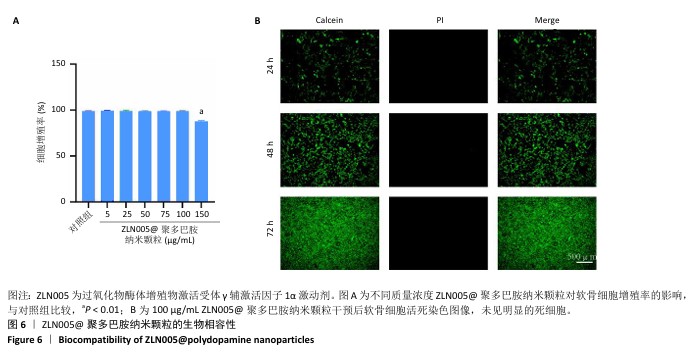
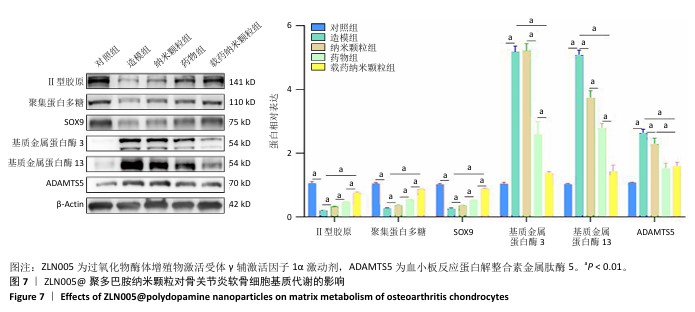
2.6 ZLN005@聚多巴胺纳米颗粒对骨关节炎软骨细胞基质代谢的影响 Western blot检测结果显示,与对照组比较,造模组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3和ADAMTS5蛋白表达升高 (P < 0.01);与造模组比较,纳米颗粒组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS5蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01);与纳米颗粒组比较,药物组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白与SOX9蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3、ADAMTS5蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01);与药物组比较,载药纳米颗粒组聚集蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、SOX9蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶3表达降低(P < 0.01),见图7。 "
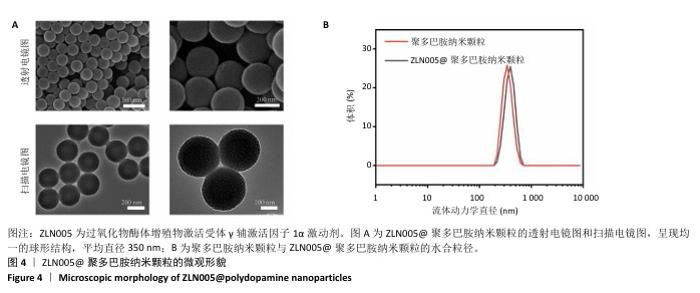
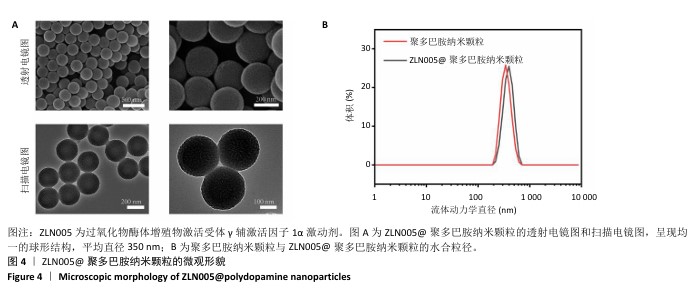
| [1] LEIFER VP, KATZ JN, LOSINA E. The burden of OA-health services and economics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(1):10-16. [2] YASUDA T. Effects of birth weight on body composition, physical fitness, and sarcopenia assessments in young Japanese women. PLoS One. 2024;19(9):e0297720. [3] FUKUI J, MATSUI Y, MIZUNO T, et al. Comparison of gait analysis before and after unilateral total knee arthroplasty for knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):506. [4] LI G, LIU S, CHEN Y, et al. An injectable liposome-anchored teriparatide incorporated gallic acid-grafted gelatin hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):3159. [5] YANG D, XU J, XU K, et al. Skeletal interoception in osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2024; 12(1): 22. [6] SILVERSTEIN FE, FAICH G, GOLDSTEIN JL, et al. Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: the CLASS study: A randomized controlled trial. Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study. JAMA. 2000; 284(10):1247-1255. [7] XIAO S, CHEN L. The emerging landscape of nanotheranostic-based diagnosis and therapy for osteoarthritis. J Control Release. 2020;328: 817-833. [8] YANG D, XU K, XU X, et al. Revisiting prostaglandin E2: A promising therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol. 2024;260:109904. [9] LI X, SHENG S, LI G, et al. Research Progress in Hydrogels for Cartilage Organoids. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(22):e2400431. [10] MAO X, FU P, WANG L, et al. Mitochondria: Potential Targets for Osteoarthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:581402. [11] ZHOU B, TIAN R. Mitochondrial dysfunction in pathophysiology of heart failure. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(9):3716-3726. [12] VILAS-BOAS EA, KOWALTOWSKI AJ. Mitochondrial redox state, bioenergetics, and calcium transport in caloric restriction: A metabolic nexus. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024;219:195-214. [13] LIU C, LIN JD. PGC-1 coactivators in the control of energy metabolism. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(4):248-257. [14] LIN J, HANDSCHIN C, SPIEGELMAN BM. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005;1(6): 361-370. [15] ZHANG LN, ZHOU HY, FU YY, et al. Novel small-molecule PGC-1α transcriptional regulator with beneficial effects on diabetic db/db mice. Diabetes. 2013;62(4):1297-1307. [16] ZHANG T, LIU CF, ZHANG TN, et al. Overexpression of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator 1-α Protects Cardiomyocytes from Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mitochondrial Damage and Apoptosis. Inflammation. 2020;43(5):1806-1820. [17] MORICI L, ALLÉMANN E, RODRÍGUEZ-NOGALES C, et al. Cartilage-targeted drug nanocarriers for osteoarthritis therapy. Int J Pharm. 2024;666:124843. [18] MIAO Y, YANG T, YANG S, et al. Protein nanoparticles directed cancer imaging and therapy. Nano Converg. 2022;9(1):2. [19] CHEN F, XING Y, WANG Z, et al. Nanoscale Polydopamine (PDA) Meets π-π Interactions: An Interface-Directed Coassembly Approach for Mesoporous Nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2016;32(46):12119-12128. [20] GENG N, FAN M, KUANG B, et al. 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid prevents osteoarthritis by targeting aspartyl β hydroxylase and inhibiting chondrocyte senescence in male mice preclinically. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):7712. [21] LINGYAN Z, YIHONG W, YOUHUA W, et al. Protective efficacy of Shenge San on mitochondria in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. J Tradit Chin Med. 2022; 42(6):892-899. [22] SANCHEZ-LOPEZ E, CORAS R, TORRES A, et al. Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(5):258-275. [23] BLANCO FJ, REGO I, RUIZ-ROMERO C. The role of mitochondria in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(3):161-169. [24] QIAN L, ZHU Y, DENG C, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 (PGC-1) family in physiological and pathophysiological process and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):50. [25] GODOY JA, MIRA RG, INESTROSA NC. Intracellular effects of lithium in aging neurons. Ageing Res Rev. 2024;99:102396. [26] RADAK Z, ZHAO Z, KOLTAI E, et al. Oxygen consumption and usage during physical exercise: the balance between oxidative stress and ROS-dependent adaptive signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013; 18(10):1208-1246. [27] BOST F, KAMINSKI L. The metabolic modulator PGC-1α in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9(2):198-211. [28] RUBALCAVA-GRACIA D, GARCÍA-VILLEGAS R, LARSSON NG. No role for nuclear transcription regulators in mammalian mitochondria? Mol Cell. 2023;83(6):832-842. [29] STEVENS RM, ERVIN J, NEZZER J, et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Intraarticular Trans-Capsaicin for Pain Associated With Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(9):1524-1533. [30] LV Z, HAN J, LI J, et al. Single cell RNA-seq analysis identifies ferroptotic chondrocyte cluster and reveals TRPV1 as an anti-ferroptotic target in osteoarthritis. EBioMedicine. 2022; 84:104258. [31] SAKATA S, KUNIMATSU R, TSUKA Y, et al. High-frequency near-infrared diode laser irradiation suppresses IL-1β-induced inflammatory cytokine expression and NF-κB signaling pathways in human primary chondrocytes. Lasers Med Sci. 2022;37(2): 1193-1201. [32] WU Z, YUAN K, ZHANG Q, et al. Antioxidant PDA-PEG nanoparticles alleviate early osteoarthritis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and angiogenesis in subchondral bone. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022; 20(1):479. [33] MA H, PENG J, ZHANG J, et al. Frontiers in Preparations and Promising Applications of Mesoporous Polydopamine for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2022;15(1):15. [34] KUTHATI Y, BUSA P, TUMMALA S, et al. Mesoporous Polydopamine Nanoparticles Attenuate Morphine Tolerance in Neuropathic Pain Rats by Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Restoration of the Endogenous Antioxidant System. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(2):195. |
| [1] | Min Changqin, Huang Ying. Construction of pH/near-infrared laser stimuli-responsive drug delivery system and its application in treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951. |
| [2] | Zhou Hongli, Wang Xiaolong, Guo Rui, Yao Xuanxuan, Guo Ru, Zhou Xiongtao, He Xiangyi. Fabrication and characterization of nanohydroxyapatite/sodium alginate/polycaprolactone/alendronate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [3] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [4] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [5] | . Effect of mussel-derived antimicrobial peptide-coated modified prosthesis on prevention of early periprosthetic joint infection and regulation of bone transfer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 278-287. |
| [6] | Guo Jingwen, Wang Qingwei, He Zijun, Hu Zihang, Chen Zhi, Zhu Rong, Wang Yuming, Liu Wenfei, Luo Qinglu. Intra-articular injection of different concentrations of silicon-based bioceramics in treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 288-295. |
| [7] | Zhou Shibo, Yu Xing, Chen Hailong, Xiong Yang. Nanocrystalline collagen-based bone combined with Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction repairs bone defects in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 354-361. |
| [8] | Wang Yuhang, Zhang Han, Zhang Chaojing, Kou Xurong, Jing Tongtong, Lin Rimei, Liu Xinyu, Lou Shilei, Yan Hui, Sun Cong. Curcumin extraction and preparation and optimization of curcumin nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 362-374. |
| [9] | Yuan Qian, Zhang Hao, Pang Jie. Characterization and biological properties of naringin-loaded chitosan/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [10] | Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei. Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| [11] | Wang Hao, He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Zhang Jun, Wu Zhilin. Deferoxamine-loaded strontium alginate hydrogel promotes the repair of skull injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3609-3617. |
| [12] | Li Liang, Yang Han, Suo Hairui, Guan Lu, Wang Zhenlin. 3D printed methacrylated gelatin/chitosan scaffolds: evaluation of antibacterial, mechanical properties and cytocompatibility [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3636-3642. |
| [13] | Gong Yukang, Ye Gaoqi, Wang Chenhao, Chen Dejin, Gao Wenshan. Effects and mechanisms of natural polyphenol-based hydrogels in promoting bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3675-3686. |
| [14] | Lu Yuchun, Zhu Zimo, Li Chaomeng, Liu Ju, Jiang Zixian, Li Xiufang, Wang Tao, Wang Wenjing. Effect and mechanism of dichloromethane extract of fresh Sambucus adnata Wall. in rat osteoarthritis models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3014-3028. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||