Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 3198-3216.doi: 10.12307/2026.701
Mechanisms of stroke therapy targeting inflammatory cytokines: a big data analysis based on the IEU Open GWAS
Cheng Le1, Zhu Caifeng1, 2, Zhou Bingyuan1, Gao Dahong3, Cui Xiaoya2, Li Jing4, Wang Xuewei1, Yang Gaoshang1, Chen Xiyang1
- 1Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China; 2Geriatrics Department III, 3Medical Affairs Department, 4Neurology Department IV, Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-16Accepted:2025-08-17Online:2026-04-28Published:2025-10-09 -
Contact:Zhu Caifeng, PhD, Chief physician, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China; Geriatrics Department III, Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Cheng Le, MS, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:Anhui Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation Research Project, No. 2024CCCX004 (to ZCF); Science and Technology Major Special Project of Anhui Huatuo Medical Research Institute - “Best Candidate Project,” No. BZKZ2402 (to ZCF); Anhui Province Natural Science Foundation, No. 2208085MH273 (to ZCF); National Key Specialty Project - Geriatrics Advantage Specialty Construction Project (to ZCF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Le, Zhu Caifeng, Zhou Bingyuan, Gao Dahong, Cui Xiaoya, Li Jing, Wang Xuewei, Yang Gaoshang, Chen Xiyang. Mechanisms of stroke therapy targeting inflammatory cytokines: a big data analysis based on the IEU Open GWAS[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3198-3216.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
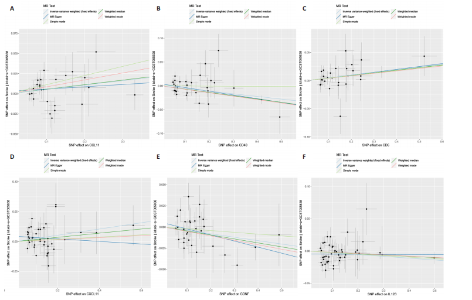
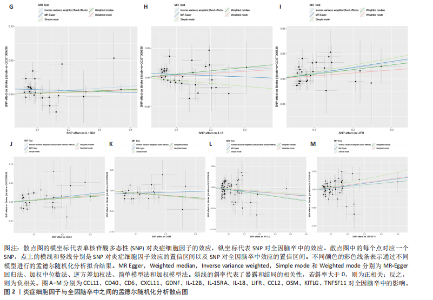
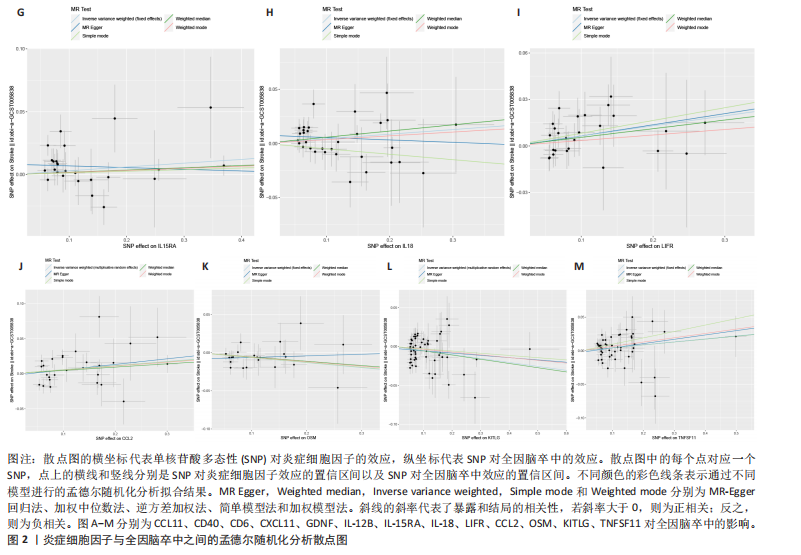
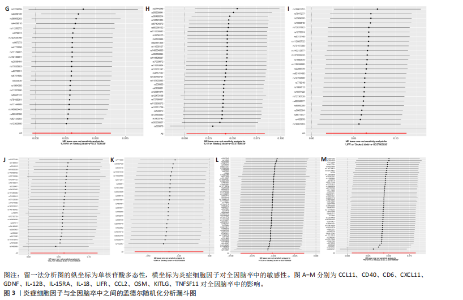
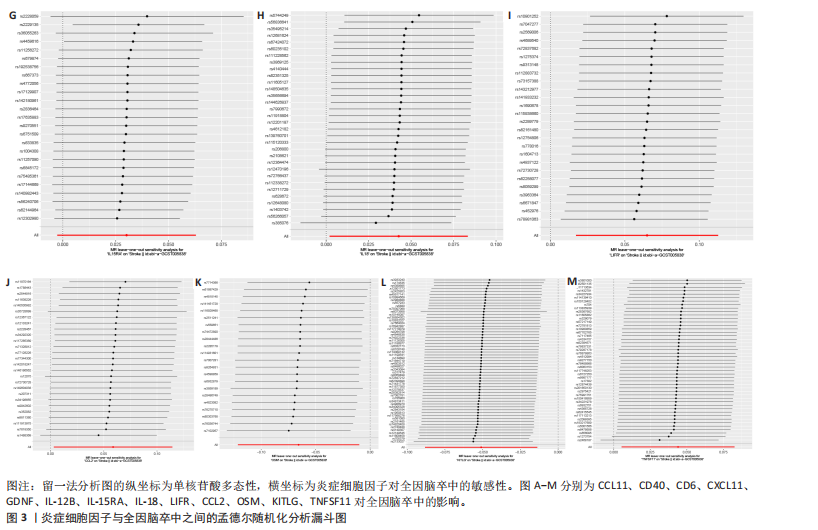
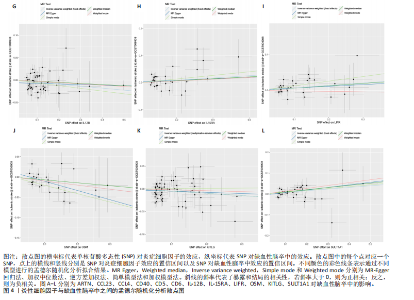
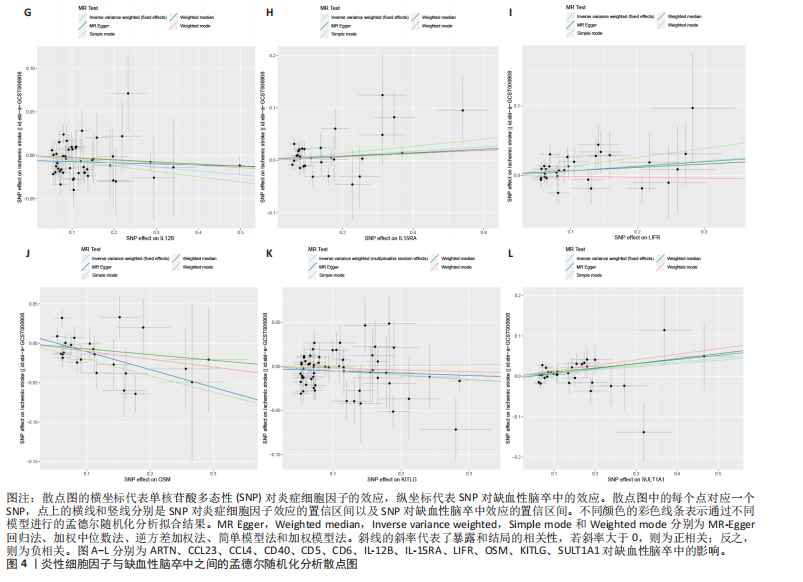
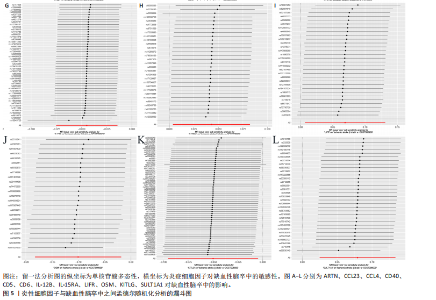
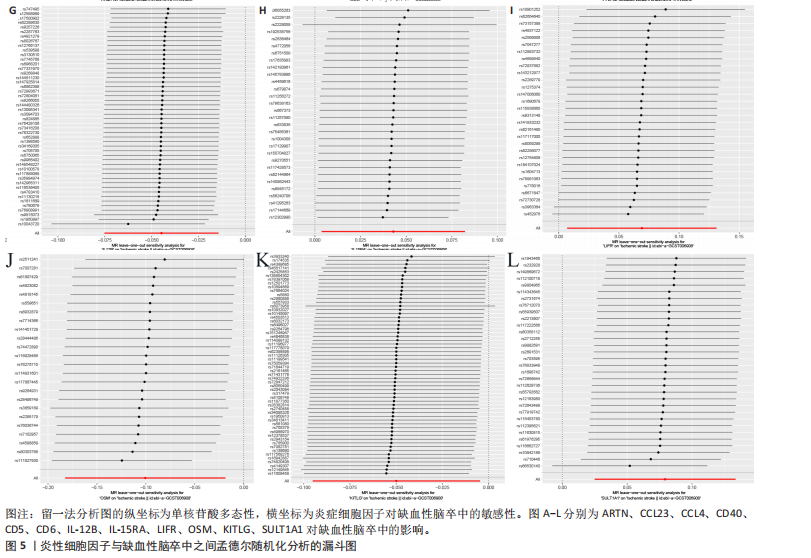
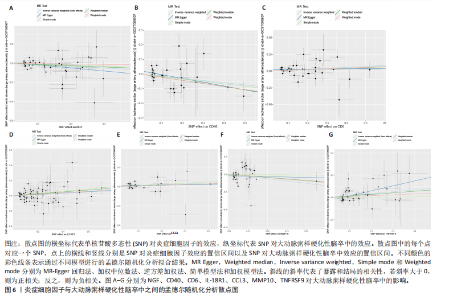
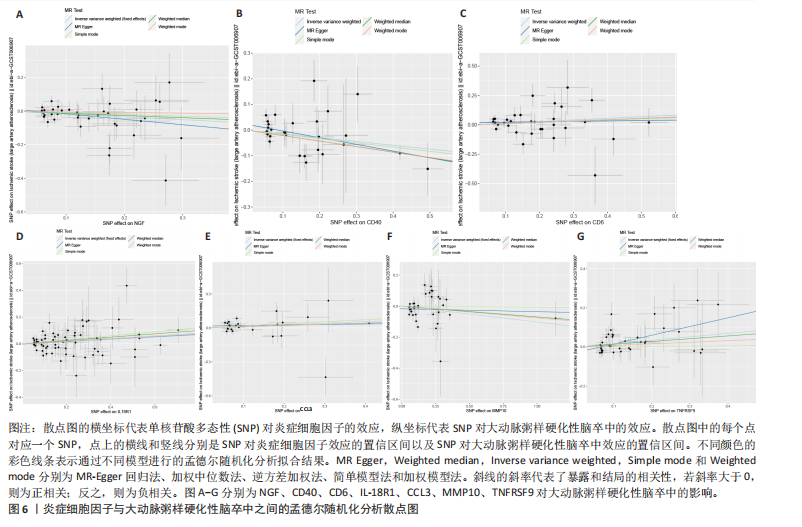
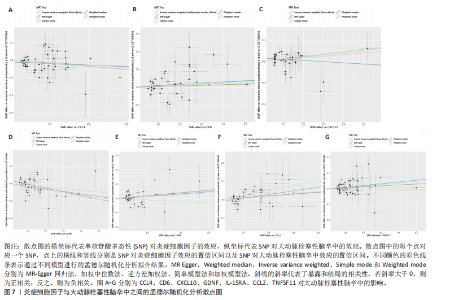
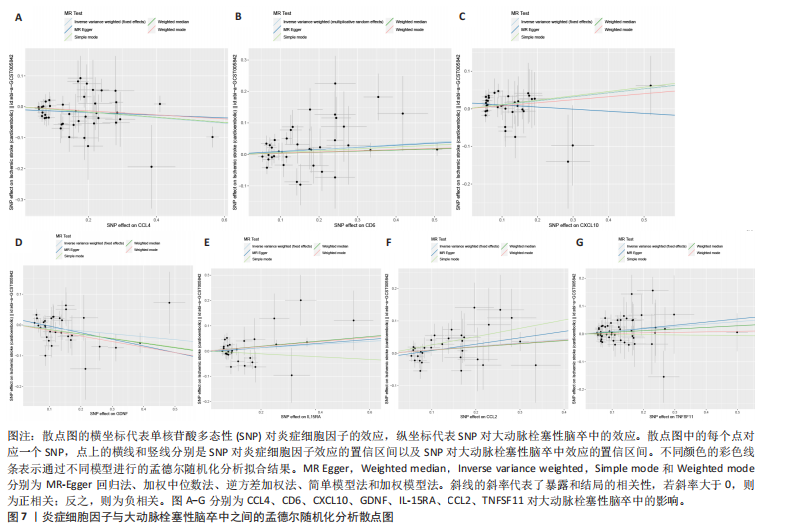
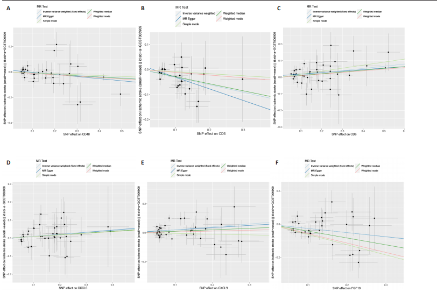
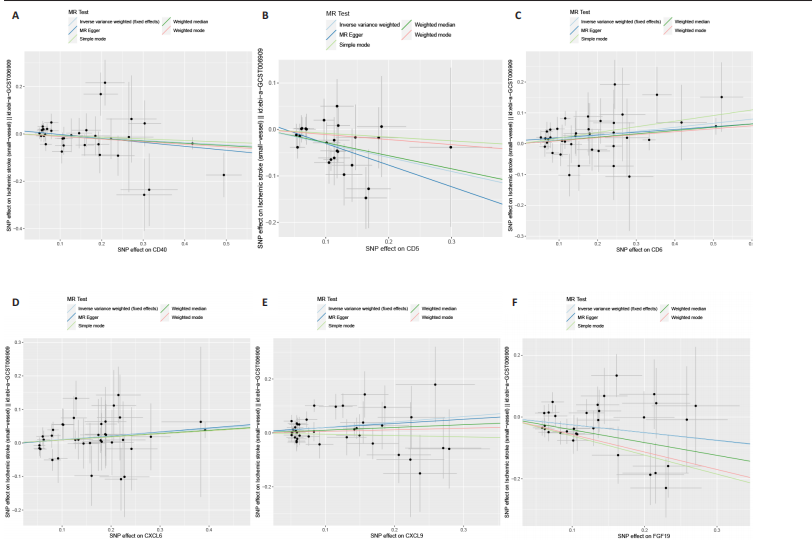
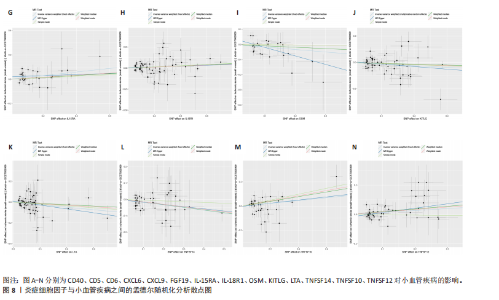
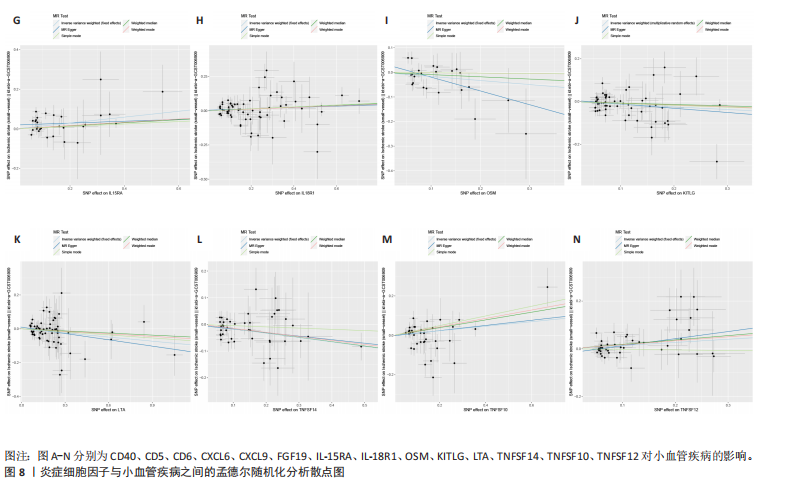
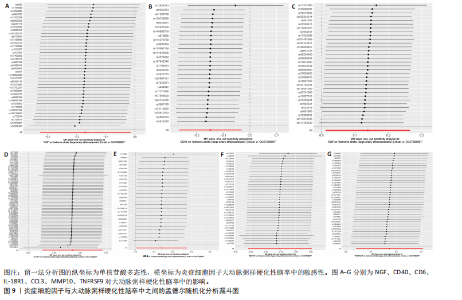
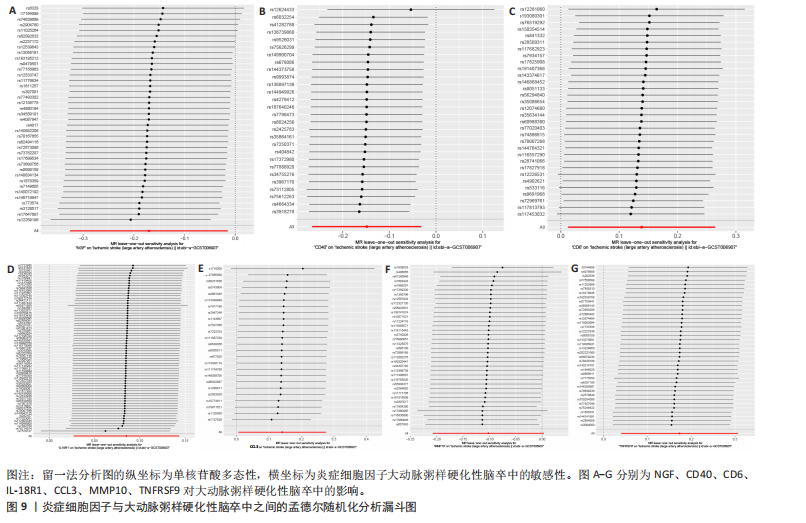
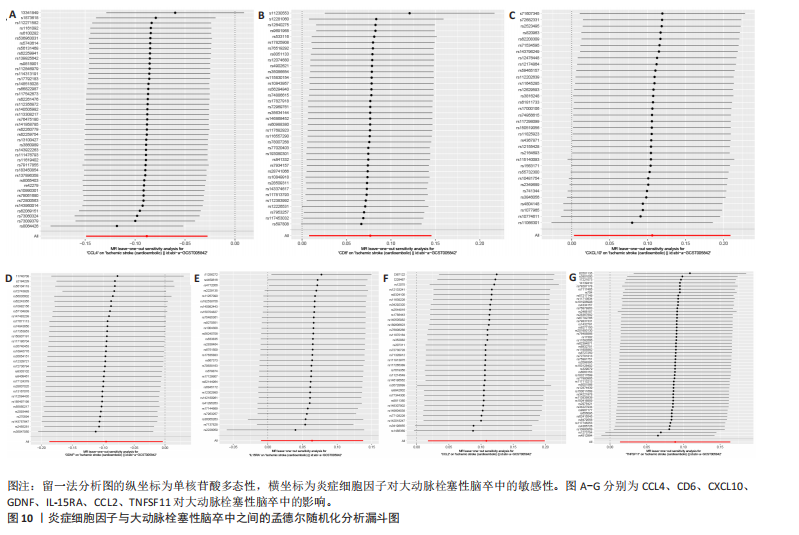
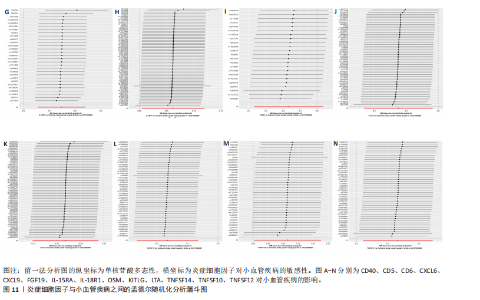
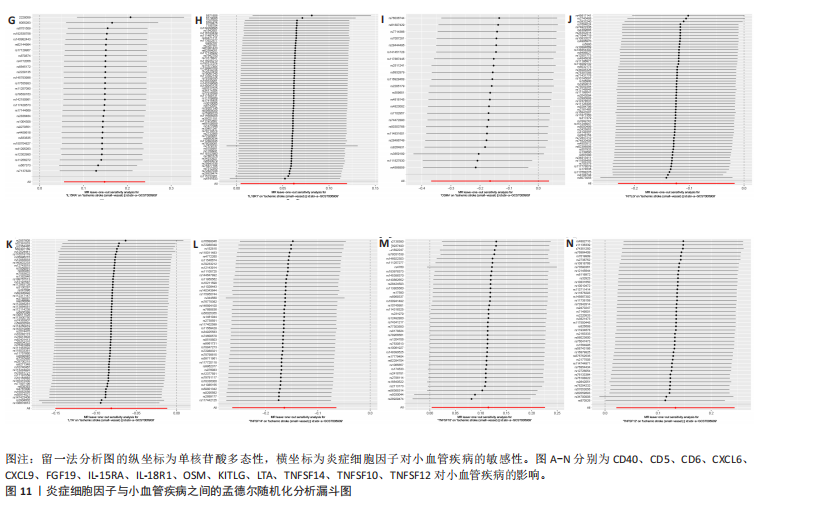
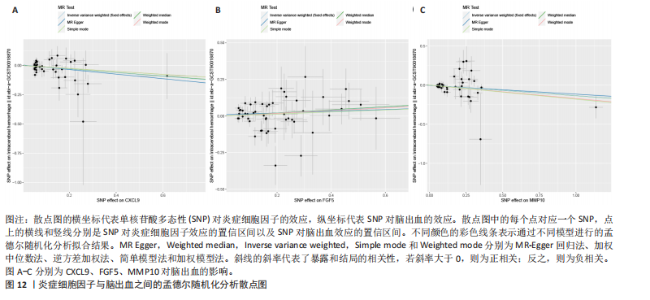
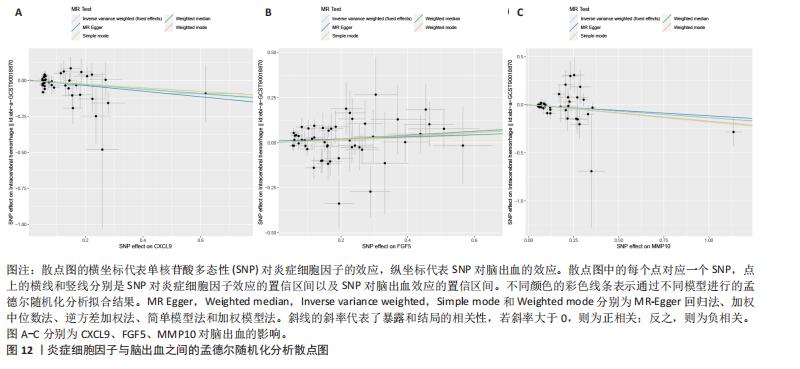
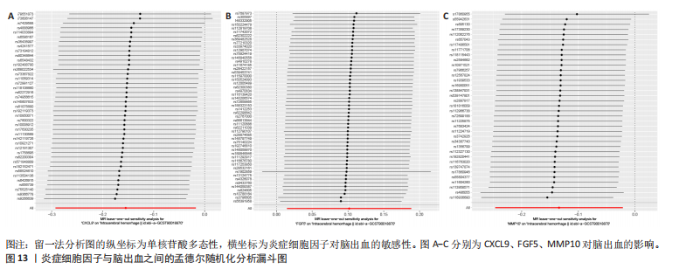
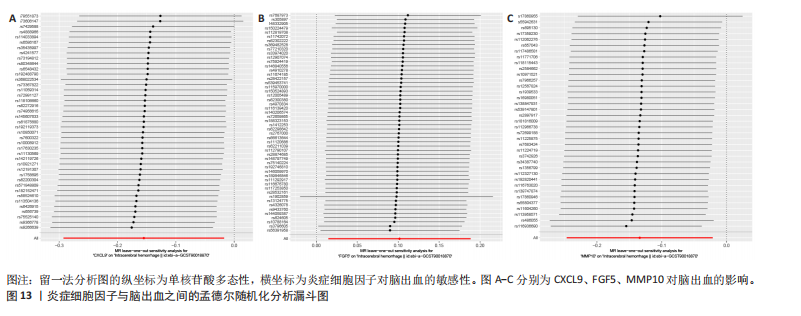
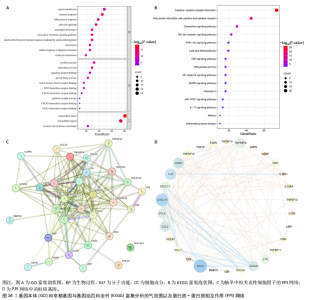
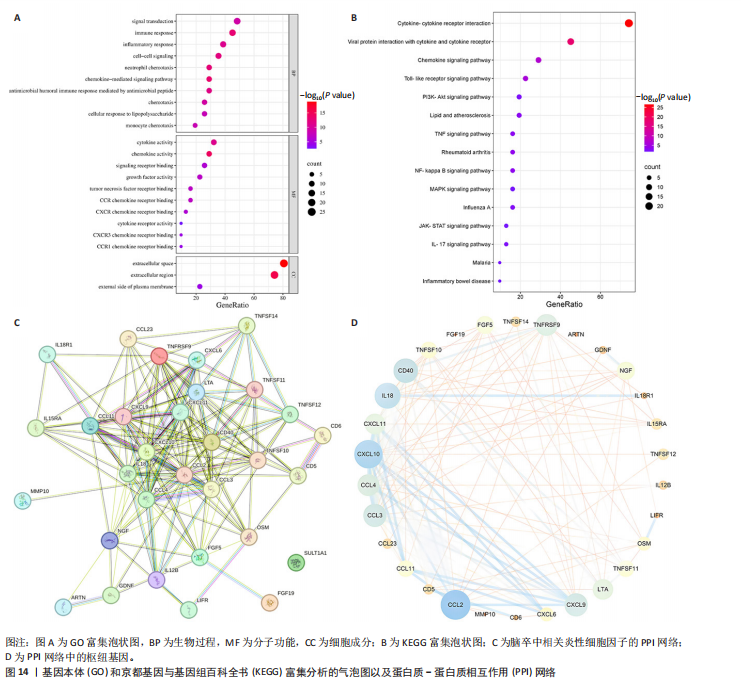
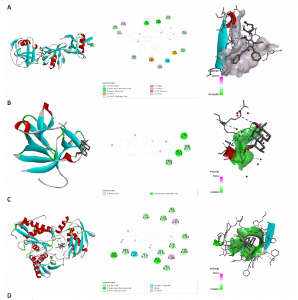
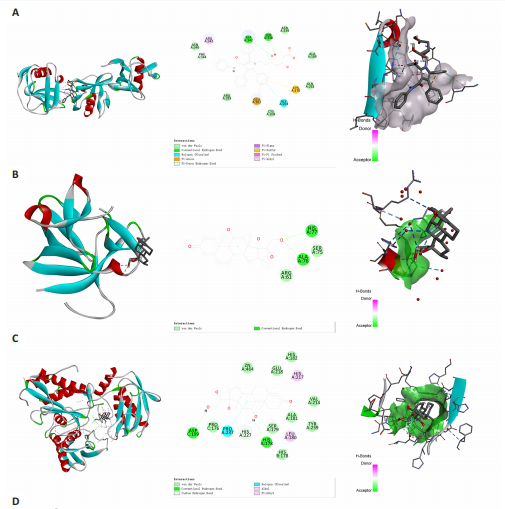
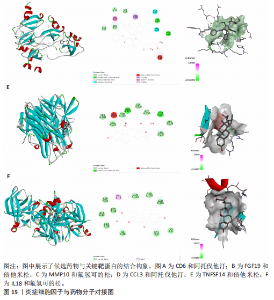
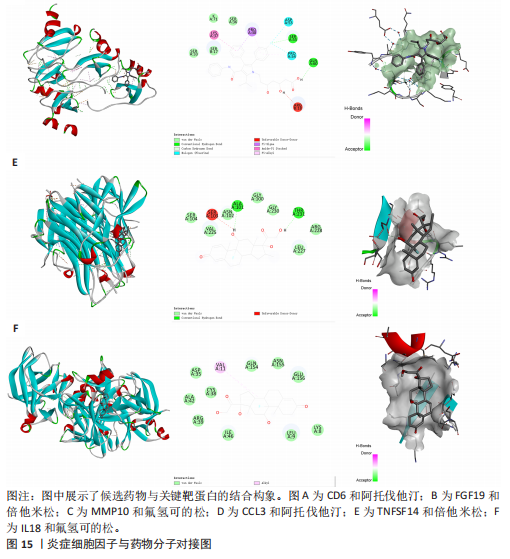
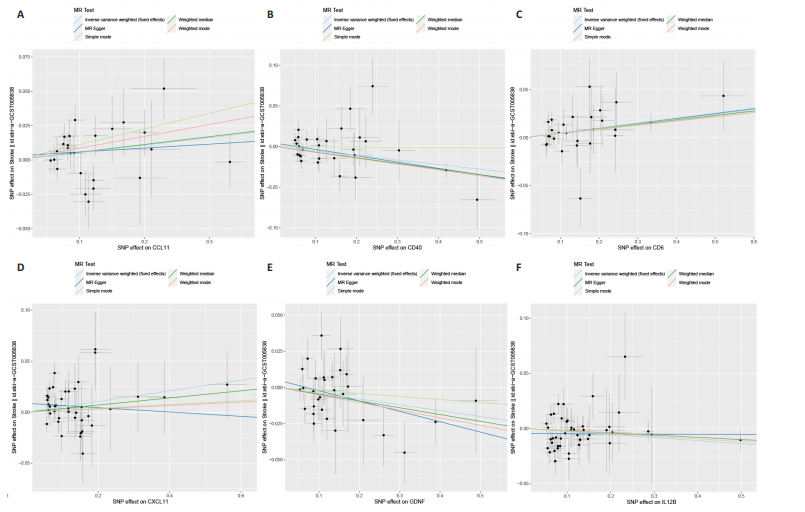
2.1 基因预测炎症细胞因子与脑卒中的关联 当使用P < 5×10-5作为全基因组显著性阈值时,所有炎症细胞因子在识别的SNP数量上均大于3。通过计算,所选SNP的F值均大于10(21.028-99.990),表明此次研究没有出现弱工具偏倚。采用逆方差加权方法进行初步的孟德尔随机化分析,包括91种炎症细胞因子与脑卒中、缺血性脑卒中、缺血性脑卒中亚型以及脑出血之间的关系。随后,进行Bonferroni校正生成森林图。 2.2 炎症细胞因子对全因脑卒中的因果效应 结果发现,13种炎症细胞因子与全因脑卒脑卒中险存在显著的因果关联。C-C介导的CCL11、CD6、CXCL11、IL-15RA、IL-18、LIFR、CCL2、TNFSF11这8种炎症细胞因子与脑卒中呈正相关,表明这8种炎症细胞因子可能增加脑卒中的风险。CD40、神经胶质细胞来源的GDNF、IL-12B、OSM和KITLG这5种炎症细胞因子与脑卒中呈负相关,表明它们对脑卒中症状有保护作用,见图2。 通过对相关SNPs进行leave-one-out分析,结果发现纳入的工具变量的效应值和总效应值大小较为接近,SNP对称分布,表明因果关系的潜在偏倚较小,见图3。为验证结果的可靠性,进行了敏感性分析,基于Cochran’s Q检验显示CCL2与KITLG与全因脑卒中的孟德尔随机化分析结果存在异质性(P < 0.05)。在MR-Egger回归分析中观察到截距P > 0.05,显示SNPs之间不存在水平多效性。 2.3 炎症细胞因子对缺血性脑卒中的因果效应 对于缺血性脑卒中,12种炎症细胞因子与缺血性脑卒中风险有显著的因果相关性。CD6、IL-15RA、LIFR、SULT1A1这4种炎症细胞因子可能增加了缺血性脑卒中的风险,ARTN、CCL23、CCL4、CD40、CD5、IL-12B、OSM、KITLG这8种炎症细胞因子可能降低了缺血性脑卒中的风险,如图4所示。 通过留一法分析进一步验证了主要结果的稳健性,见图5。敏感性分析显示,通过Cochran’s Q检验揭示了CCL4、CD40、KITLG与缺血性脑卒中之间的孟德尔随机化分析结果存在异质性(P < 0.05)。在MR-Egger回归分析中观察到截距P > 0.05,未发现水平多效性。 2.4 炎症细胞因子对缺血性脑卒中亚型的因果效应 在91种炎症细胞因子中,CD6、IL-18R1、CCL3、TNFRSF9可能与大动脉粥样硬化性脑卒中风险增加有关,NGF、CD40 和MMP10可能与大动脉粥样硬化性脑卒中风险降低有关,见图6。CD6、CXCL10、 IL-15RA、CCL2、TNFSF11与大动脉栓塞性脑卒中发生呈正相关,CCL4、GDNF与大动脉栓塞性脑卒中发生呈负相关,见图7。CD6、CXCL6、CXCL9、IL-15RA、IL-18R1、TNFSF10、TNFSF12这7种炎症细胞因子与小血管疾病发生呈正相关,CD40、CD5、FGF19、OSM、KITLG、LTA、TNFSF14这7种炎症细胞因子与小血管疾病发生呈负相关,见图8。 通过Cochran’s Q检验,发现CD6与大动脉粥样硬化性脑卒中之间的孟德尔随机化分析结果有异质性(P < 0.05),CD6与大动脉栓塞性脑卒中之间的孟德尔随机化分析结果发现异质性,KITLG与小血管疾病之间的孟德尔随机化分析结果发现异质性。在炎症细胞因子与小血管疾病的孟德尔随机化分析中,孟德尔随机化多效性试验检测到CD5相关工具变量的水平多效性(intercept=0.047,P=0.007),当剔除存在显著交叉的混杂工具变量后,逆方差加权结果表明CD5与小血管疾病无显著的因果关系,通过留一法分析也揭示了主要结果的稳健性,见图9-11。此次研究中KITLG与小血管疾病的孟德尔随机化分析存在显著异质性,可能源于多效性遗传变异与人群特异性效应。同时,尽管CD5的关联存在水平多效性,但加权中位数法与逆方差加权结果方向一致,显示敏感性分析一致性。此次研究通过严格工具变量筛选及多方法验证降低异质性与多效性的干扰,应用严格的LD阈值及F统计量> 10排除弱工具变量。结合MR-Egger、加权中位数法等互补方法,确保结果对方法假设的鲁棒性。 2.5 炎症细胞因子对脑出血的因果效应 在评估炎症细胞因子对脑出血的影响时,发现FGF5可能增加了脑出血的风险,CXCL9、MMP10可能降低了脑出血的风险,见图12。基于留一法分析揭示了主要结果的稳健性,见图13。未发现异质性及水平多效性。 2.6 基因本体、京都基因与基因组百科全书富集分析和蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络 基因本体功能注释结果显示,涉及19个生物过程功能、3种细胞成分功能和158种分子功能。前3个 GO_BPs是信号转导、免疫反应和炎症反应。前3个GO_MF是细胞因子活性、趋化因子活性和信号受体结合。在细胞成分方面,核心基因主要富集在质膜外侧、细胞外区域和细胞外空间,见图14A。 京都基因与基因组百科全书通路分析显示,炎症细胞因子通过调节TLR、PI3K/Akt、TNF、NF-κB、MAPK、JAK-STAT和IL-17信号通路在脑卒中中发挥作用,见图14B。这些通路与代谢、炎症和免疫反应有关。 通过蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络模块分析,确定脑卒中和炎症细胞因子的参与及其功能,筛选出核心子模块,见图14C,D。 2.7 药物预测和分子对接 基于DSigDB数据库的转录组特征,利用enrichment识别与炎症细胞因子相互作用的靶向候选药物。根据P值选择10种可用于脑卒中治疗和后续分析的潜在化合物,10种可能的药物分子包括和厚朴酚、阿托伐他汀、维生素D3、氟氢可的松、罗氟司特、辛伐他汀、米非司酮、巴马汀、倍他米松、吡格列酮,这些潜在的药物为推荐治疗脑卒中的常见化合物。 在蛋白质数据银行下载炎症细胞因子独立的三维结构,选取CD6、FGF19、IL18、MMP10、CCL3、TNFSF14这6个靶蛋白进行分子对接分析,预测其对脑卒中患者的潜在治疗效果。此文分子对接以原配体的结合位点作为参考结合位点,配体与受体结合的稳定能越低,作用的可能性越大。用均方根偏差评价对接准确性,分子对接结果的均方根偏差值始终保持在2以下,这表明药物分子与炎症细胞因子之间的相互作用很强,见表3,图15显示了与这7种炎症细胞因子靶点结合最好的药物分子。"
| [1] CAMPBELL BCV, KHATRI P. Stroke. Lancet. 2020;396(10244):129-142. [2] GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(10): 795-820. [3] TU WJ, ZHAO Z, YIN P, et al. Estimated Burden of Stroke in China in 2020. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(3):e231455. [4] LIU C, WANG G, HAN W, et al. Ferroptosis: a potential therapeutic target for stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(5):988-997. [5] BELLUT M, BIEBER M, KRAFT P, et al. Delayed NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition ameliorates subacute stroke progression in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):4. [6] SHAAFI S, SHARIFIPOUR E, RAHMANIFAR R, et al. Interleukin-6, a reliable prognostic factor for ischemic stroke. Iran J Neurol. 2014;13(2):70-76. [7] LUO Y, ZHOU Y, XIAO W, et al. Interleukin-33 ameliorates ischemic brain injury in experimental stroke through promoting Th2 response and suppressing Th17 response. Brain Res. 2015;1597:86-94. [8] GUO H, ZHANG W, WANG Z, et al. Dexmedetomidine post-conditioning protects blood-brain barrier integrity by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization via inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway in intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:977941. [9] CHEN W, GUO C, HUANG S, et al. MitoQ attenuates brain damage by polarizing microglia towards the M2 phenotype through inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome after ICH. Pharmacol Res. 2020;161:105122. [10] ZHANG T, FANG S, WAN C, et al. Excess salt exacerbates blood-brain barrier disruption via a p38/MAPK/SGK1-dependent pathway in permanent cerebral ischemia. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16548. [11] ARDISSINO M, SLOB EAW, RAJASUNDARAM S, et al. Safety of beta-blocker and calcium channel blocker antihypertensive drugs in pregnancy: a Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2022;20(1):288. [12] DENG MG, LIU F, LIANG YH, et al. Association between frailty and depression: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Science Advances. 2023;9(38): eadi3902. [13] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SMITH G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. Bmj. 2018;362:k601. [14] MALIK R, CHAUHAN G, TRAYLOR M, et al. Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nature Genetics. 2018;50(4):524-537. [15] SAKAUE S, KANAI M, TANIGAWA Y, et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nature Genetics. 2021;53(10):1415-1424. [16] ZHAO JH, STACEY D, ERIKSSON N, et al. Genetics of circulating inflammatory proteins identifies drivers of immune-mediated disease risk and therapeutic targets. Nature Immunol. 2023;24(9):1540-1551. [17] PIERCE BL, AHSAN H, VANDERWEELE TJ. Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2011;40(3):740-752. [18] PALMER TM, LAWLOR DA, HARBORD RM, et al. Using multiple genetic variants as instrumental variables for modifiable risk factors. Statistical Methods in Medical Research. 2012;21(3):223-242. [19] YANG H, SONG J, LI A, et al. Genetically predicted levels of folate, vitamin B(12), and risk of autoimmune diseases: A Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023; 14:1139799. [20] SU Y, HU Y, XU Y, et al. Genetic causal relationship between age at menarche and benign oesophageal neoplasia identified by a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1113765. [21] LV L, SUN X, LIU B, et al. Genetically Predicted Serum Albumin and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Clin Epidemiol. 2022;14:771-778. [22] WANG J, ZHUGE J, FENG D, et al. Mendelian randomization study of circulating lipids and biliary tract cancer among East Asians. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):273. [23] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nature Genetics. 2018;50(5):693-698. [24] YANG Z, MA W, WANG L, et al. Population genomics reveals demographic history and selection signatures of hazelnut (Corylus). Hortic Res. 2023;10(5):uhad065. [25] LIU M, SUN Q, CAO K, et al. Acetylated Proteomics of UV-B Stress-Responsive in Photosystem II of Rhododendron chrysanthum. Cells. 2023;12(3):478. [26] FENG ZW, TANG YC, SHENG XY, et al. Screening and identification of potential hub genes and immune cell infiltration in the synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis by bioinformatic approach. Heliyon. 2023; 9(1):e12799. [27] ZHANG Y, YU B, TIAN Y, et al. A novel risk score model based on fourteen chromatin regulators-based genes for predicting overall survival of patients with lower-grade gliomas. Front Genet. 2022;13:957059. [28] LU L, LIU LP, GUI R, et al. Discovering common pathogenetic processes between COVID-19 and sepsis by bioinformatics and system biology approach. Front Immunol. 2022;13:975848. [29] MOHAMMED ALI H. In-silico investigation of a novel inhibitors against the antibiotic-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022;29(10):103424. [30] XU S, LU J, SHAO A, et al. Glial Cells: Role of the Immune Response in Ischemic Stroke. Front Immunol. 2020;11:294. [31] XU Q, ZHAO B, YE Y, et al. Relevant mediators involved in and therapies targeting the inflammatory response induced by activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):123. [32] BATES KM, VATHIOTIS I, MACNEIL T, et al. Spatial characterization and quantification of CD40 expression across cancer types. BMC Cancer. 2023;23(1):220. [33] WEINSTEIN JR, ETTINGER RE, ZHANG M, et al. Thrombin regulates CD40 expression in microglial cells. Neuroreport. 2008;19(7):757-760. [34] MA Y, WANG SX, LIU Y, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism of CD40 in the 5’-untranslated region is associated with ischemic stroke. Gene. 2013;529(2):257-261. [35] ALSBROOK DL, DI NAPOLI M, BHATIA K, et al. Neuroinflammation in Acute Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2023;23(8):407-431. [36] LIU S, LIU YP, LV Y, et al. IL-18 Contributes to Bone Cancer Pain by Regulating Glia Cells and Neuron Interaction. J Pain. 2018; 19(2):186-195. [37] SLOWIK A, LAMMERDING L, HOFFMANN S, et al. Brain inflammasomes in stroke and depressive disorders: Regulation by oestrogen. J Neuroendocrinol. 2018;30(2). doi: 10.1111/jne.12482. [38] FANN DY, LEE SY, MANZANERO S, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin suppresses NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal death in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(9):e790. [39] CHEN C, CHU SF, LIU DD, et al. Chemokines play complex roles in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int. 2018;112:146-158. [40] COUGHLAN CM, MCMANUS CM, SHARRON M, et al. Expression of multiple functional chemokine receptors and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human neurons. Neuroscience. 2000;97(3):591-600. [41] XIA MQ, BACSKAI BJ, KNOWLES RB, et al. Expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 on neurons and the elevated expression of its ligand IP-10 in reactive astrocytes: in vitro ERK1/2 activation and role in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol. 2000;108(1-2):227-235. [42] KIM EK, CHOI EJ. Compromised MAPK signaling in human diseases: an update. Arch Toxicol. 2015;89(6):867-882. [43] TIAN S, CHEN X, WU W, et al. Nucleus pulposus cells regulate macrophages in degenerated intervertebral discs via the integrated stress response-mediated CCL2/7-CCR2 signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med. 2024;56(2):408-421. [44] MA K, SINGH G, WANG J, et al. Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors as a Therapeutic Strategy for Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(2):675-690. [45] CHE X, YE W, PANGA L, et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expressed in neurons and astrocytes during focal ischemia in mice. Brain Res. 2001;902(2): 171-177. [46] TEI N, TANAKA J, SUGIMOTO K, et al. Expression of MCP-1 and fractalkine on endothelial cells and astrocytes may contribute to the invasion and migration of brain macrophages in ischemic rat brain lesions. J Neurosci Res. 2013;91(5):681-693. [47] HUGHES PM, ALLEGRINI PR, RUDIN M, et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 deficiency is protective in a murine stroke model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22(3):308-317. [48] CHEN Y, HALLENBECK JM, RUETZLER C, et al. Overexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in the brain exacerbates ischemic brain injury and is associated with recruitment of inflammatory cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23(6):748-755. [49] WATTS TH. TNF/TNFR family members in costimulation of T cell responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:23-68. [50] Li XQ, Wang YY, Yang TT, et al. Increased Peripheral CD137 Expression in a Mouse Model of Permanent Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019;39(3):451-460. [51] FANN DY, NICKLES EP, POH L, et al. CD137 Ligand-CD137 Interaction is Required For Inflammasome-Associated Brain Injury Following Ischemic Stroke. Neuromolecular Med. 2020;22(4):474-483. [52] LV C, CHENG T, ZHANG B, et al. Triptolide protects against podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Ren Fail. 2023;45(1):2165103. [53] PENG C, DING Y, YI X, et al. Polymorphisms in CYP450 Genes and the Therapeutic Effect of Atorvastatin on Ischemic Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Chinese Population. Clin Ther. 2018;40(3):469-477.e2. [54] CHAN DY, CHAN DT, SUN TF, et al. The use of atorvastatin for chronic subdural haematoma: a retrospective cohort comparison study. Br J Neurosurg. 2017; 31(1):72-77. [55] HASAN D, LINDSAY KW, WIJDICKS EF, et al. Effect of fludrocortisone acetate in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 1989;20(9):1156-1161. |
| [1] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [2] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [3] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [4] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [5] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [6] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [7] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [8] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [9] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [10] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [11] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [12] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| [13] | Jiang Huanhuan, Mu Sheng, Ma Wenxin, Liu Chang, Liu Ziyu, Pu Jing, Zhu Xiangdong, Hui Hong, Ma Huiming. Mechanism of multi-target intervention of the active ingredient of Allii Tuberosi Semen in rats with oligoasthenozoospermia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3044-3057. |
| [14] | Liang Liang, Yan Yulu, Zheng Yang, Zhang Xiaoyun, Wang Lei, Qi Wen . Lactylation-related potential targets and Chinese herbal medicine active ingredients targeting treatment of spinal cord injury: GEO database screening analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3156-3170. |
| [15] | Li Hanyu, Wang Chaoyi, Yang Jingyan, Huang Renjun, Zhao Yuyang, Hao Huatao, Yu Dong. Druggable genome-wide prediction of therapeutic target genes for lumbar spinal stenosis: data analysis based on DgiDB and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3171-3181. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||