Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 3171-3181.doi: 10.12307/2026.663
Druggable genome-wide prediction of therapeutic target genes for lumbar spinal stenosis: data analysis based on DgiDB and FinnGen databases
Li Hanyu1, Wang Chaoyi1, Yang Jingyan1, Huang Renjun1, Zhao Yuyang1, Hao Huatao2, Yu Dong2
- 1The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 2The Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2025-02-20Accepted:2025-08-04Online:2026-04-28Published:2025-09-30 -
Contact:Yu Dong, PhD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Li Hanyu, MS candidate, The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China Wang Chaoyi, MS candidate, The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China Li Hanyu and Wang Chaoyi contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:Orthopedics and Traumatology of Traditional Chinese Medicine (OCTCM) - First-Class Discipline Construction Project of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (BUCM) (to YD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Hanyu, Wang Chaoyi, Yang Jingyan, Huang Renjun, Zhao Yuyang, Hao Huatao, Yu Dong. Druggable genome-wide prediction of therapeutic target genes for lumbar spinal stenosis: data analysis based on DgiDB and FinnGen databases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3171-3181.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
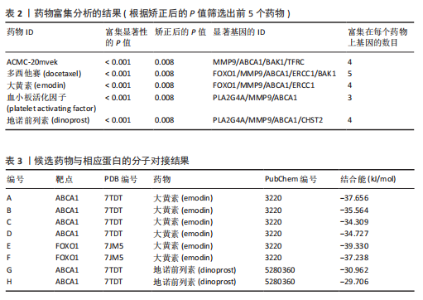
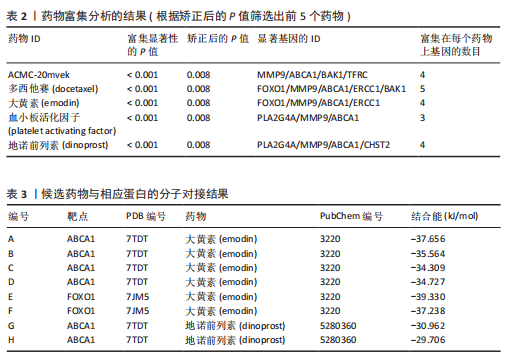
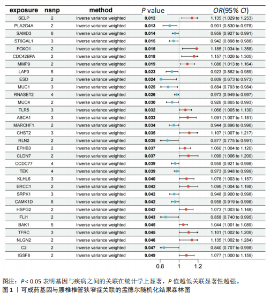
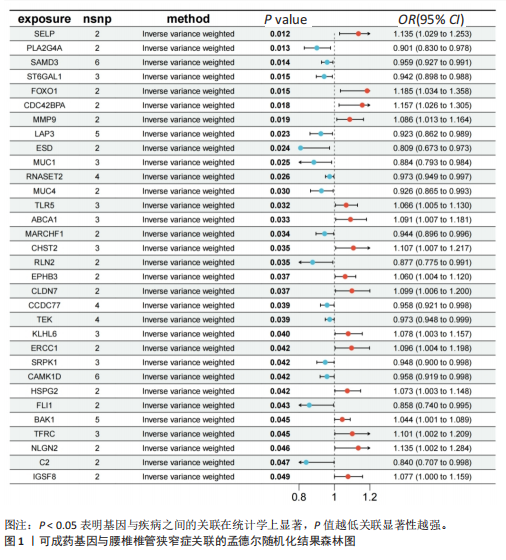
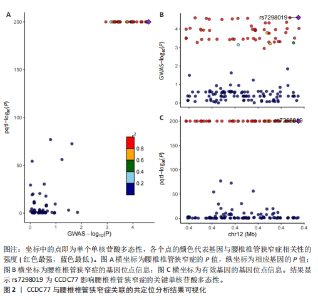
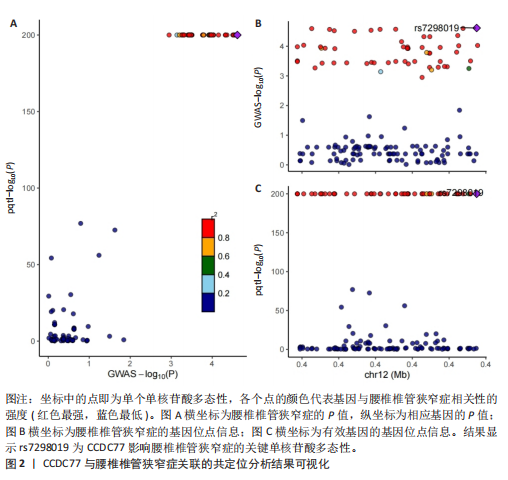
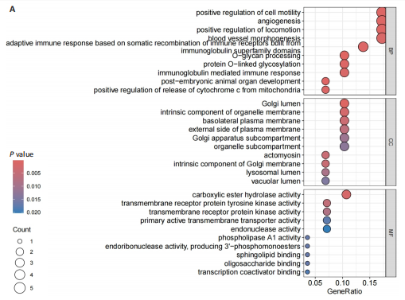
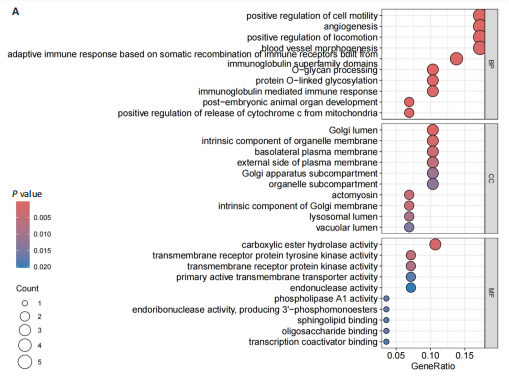
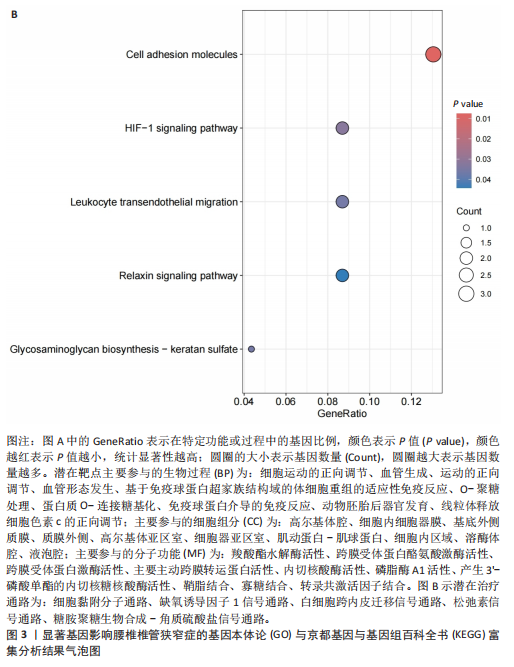
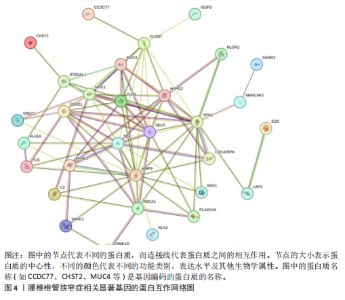
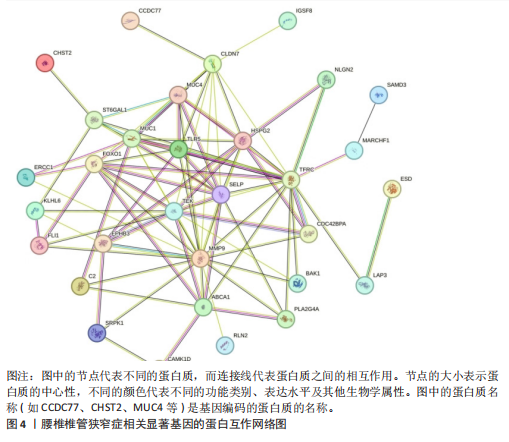
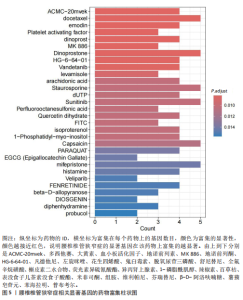
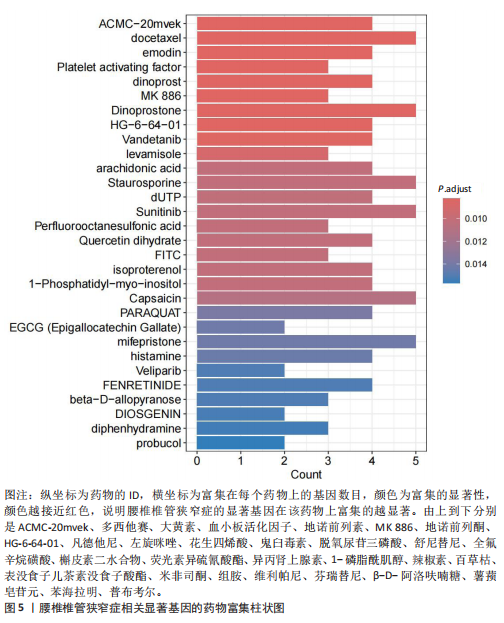
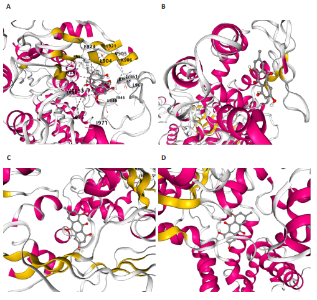
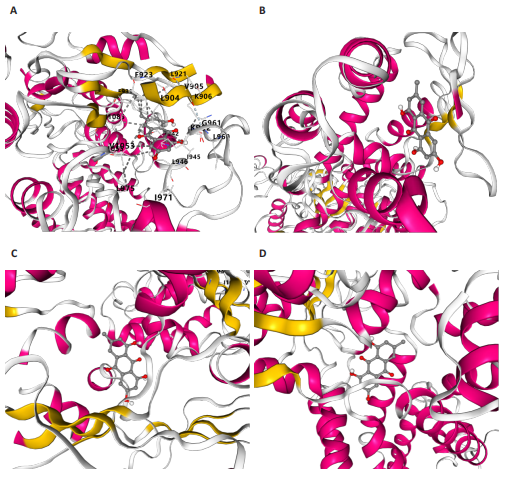
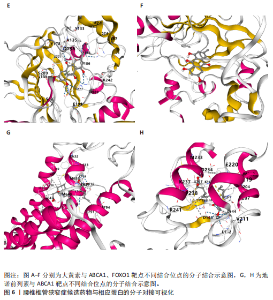
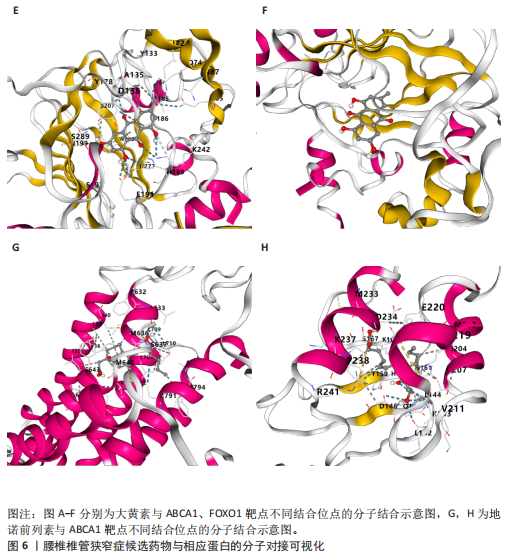
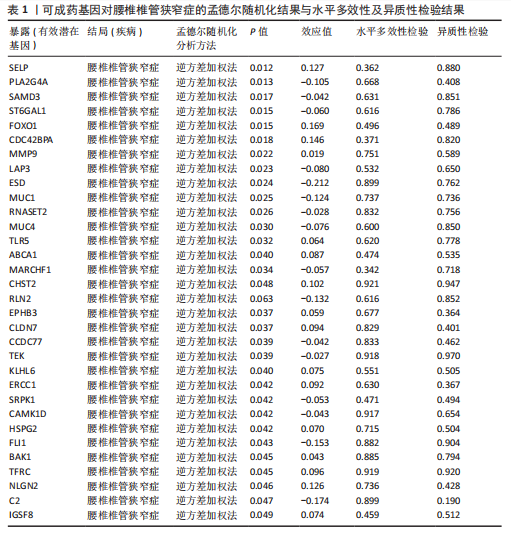
2.1 孟德尔随机化分析及有效基因的筛选 此次研究共筛选出来32个显著潜在基因,具体数据细节见表1,将其进行可视化(图1)。 2.2 共定位分析结果 结果表明在32个显著基因中,CCDC77的PP.H4为0.859,CCDC77与腰椎椎管狭窄症均可被rs7298019驱动结果表明CCDC77与腰椎椎管狭窄症有着较强的关联性,将以上结果进行可视化(图2)。 2.3 显著基因功能分析 对32个潜在靶点进行GO富集分析,可以看出,这些靶点共参与319项生物学过程(BP),涉及27个细胞组分(CC),包括33个主要分子功能(MF)。其中主要参与的生物学过程有细胞运动的正向调节(GO2000147、GO0040017)、血管生成(GO0001525、GO0048514)及与适应性免疫应答相关的生物代谢过程(GO0002460、GO0002250);主要细胞组分有高尔基体相关组分(GO0005796、GO0098791)、细胞器膜(GO0031300)、基底外侧质膜(GO0016323)、细胞器亚区(GO0031984)、肌动球蛋白(GO0042641);主要分子功能包括羧酸酯水解酶活性(GO0052689)、跨膜受体蛋白激酶活性(GO0004714、GO0019199)及核酸内切酶活性(GO0004519),见图3A。 KEGG通路富集展示了腰椎椎管狭窄症相关的显著可用药基因的5条潜在治疗通路,根据富集在每个药物上基因的数目及显著性,排名前3的是细胞黏附分子通路、缺氧诱导因子1信号通路、白细胞跨内皮迁移信号通路(图3B)。 2.4 蛋白互作网络分析 在将32个显著基因构建蛋白互作网络后,隐藏网络中断开的网络节点,共得到32个节点和91个边缘,平均节点度为5.69,预期边数为44,蛋白互作网络富集P值=0.045 3。将结果导出并进行可视化,见图4。 2.5 药物富集结果 将32个显著基因与DSigDB下载的数据进行富集分析后,得到182个药物,将以上结果进行可视化(图5),以矫正后的P值筛选出前5个药物为例,见表2。 2.6 分子对接结果 使用CB-Dock2在线工具分析与相应基因编码蛋白质亲和力强的前2种候选药物与相应基因编码蛋白质之间的结合位点和相互作用,相互作用产生结合能,结合能越低,结合效果越好,亲和力越高。获得了8个蛋白质与药物之间的有效对接结果(表3),由A-H编号,将结果可视化,见图6。"
| [1] KATZ JN, ZIMMERMAN ZE, MASS H, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Review. JAMA. 2022;327(17):1688-1699. [2] 库提鲁克·守克尔,艾克拜尔江·艾赛提,沙拉依丁·艾尔西丁,等.腰椎椎管狭窄症治疗现状的文献计量学研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2024,22(3):189-194. [3] ARABMOTLAGH M, SELLEI RM, VINAS-RIOS JM, et al. Klassifikation und Diagnostik der lumbalen Spinalkanalstenose [Classification and diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis]. Orthopade. 2019;48(10):816-823. [4] KIM M, CHO S, NOH Y, et al. Changes in pain scores and walking distance after epidural steroid injection in patients with lumbar central spinal stenosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(24):e29302. [5] YANG F, WANG Y, MA Y, et al. Single-segment central lumbar spinal stenosis: Correlation with lumbar X-ray measurements. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021;34(4):581-587. [6] SCHROEDER GD, KURD MF, VACCARO AR. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: How Is It Classified? J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(12):843-852. [7] 张晗,孙超,刘新晖.腰椎黄韧带纤维化的研究进展[J].临床骨科杂志,2022, 25(3):450-453. [8] LEE JY, CHOI HY, PARK CS, et al. Inhibition of COX-2 alleviates lumbar spinal stenosis-induced chronic mechanical allodynia in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105738. [9] ZHANG G, ZHANG W, HOU Y, et al. Detection of miR 29a in plasma of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis and the clinical significance. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(1):223-229. [10] WAWROSE RA, OYEKAN AA, TANG YM, et al. MicroRNA-29a: a novel target for non-operative management of symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2024; 33(3):892-899. [11] MA Q. Pharmacological Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome: Structure, Molecular Activation, and Inhibitor-NLRP3 Interaction. Pharmacol Rev. 2023;75(3):487-520. [12] NABA A. Mechanisms of assembly and remodelling of the extracellular matrix. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(11):865-885. [13] ZHANG J, ZHAO H. eQTL studies: from bulk tissues to single cells. J Genet Genomics. 2023;50(12):925-933. [14] 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; AUTON A, BROOKS LD, DURBIN RM, et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526(7571):68-74. [15] FINAN C, GAULTON A, KRUGER FA, et al. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(383): eaag1166. [16] TIN A, MARTEN J, HALPERIN KUHNS VL. Target genes, variants, tissues and transcriptional pathways influencing human serum urate levels. Nat Genet. 2019;51(10): 1459-1474. [17] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014; 10(5):e1004383. [18] LIU Z, YAN W, LIU S, et al. Regulatory network and targeted interventions for CCDC family in tumor pathogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2023;565:216225. [19] VIOREL VI, PASTORELLO Y, BAJWA N, et al. p38-MAPK and CDK5, signaling pathways in neuroinflammation: a potential therapeutic intervention in Alzheimer’s disease? Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1649-1650. [20] 郭云山,郝定均,王晓东,等.STIM1调控细胞运动促进骨肉瘤转移的研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2019,19(24):4601-4606. [21] 戴祝,彭嘉斌,廖瑛,等.成年关节软骨碎块化后MT1-MMP表达与软骨细胞迁移的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(28):4457-4462. [22] LA MENDOLA D, TRINCAVELLI ML, MARTINI C. Angiogenesis in Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10962. [23] 陈耀鑫,黎松波,方冠军,等.黄韧带中成纤维细胞生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子表达与腰椎管狭窄患者腰椎减压术后再狭窄的关系[J].实用医学杂志,2023, 39(18):2289-2293. [24] LIN W, XU L, ZWINGENBERGER S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells homing to improve bone healing. J Orthop Translat. 2017; 9:19-27. [25] HOSEINZADEH A, ESMAEILI SA, SAHEBI R, et al. Fate and long-lasting therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stromal/stem-like cells: mechanistic insights. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025;16(1):33. [26] FABREGAT I, HERRERA B, SÁNCHEZ A. Editorial Special Issue TGF-beta/BMP Signaling Pathway. Cells. 2020;9(11):2363. [27] WATTS E, WILLISON J, ARIENTI S, et al. Differential roles for the oxygen sensing enzymes PHD1 and PHD3 in the regulation of neutrophil metabolism and function. Wellcome Open Res. 2024;8:569. [28] COSTA RO, MARTINS H, MARTINS LF, et al. Synaptogenesis Stimulates a Proteasome-Mediated Ribosome Reduction in Axons. Cell Rep. 2019;28(4):864-876.e6. [29] ZHOU R, CHEN J, TANG Y, et al. Multi-omics uncovers immune-modulatory molecules in plasma contributing to resistance exercise-ameliorated locomotor disability after incomplete spinal cord injury. Genome Med. 2025;17(1):10. [30] MALIK KN, GIBERSON C, BALLARD M, et al. Pain Management Interventions in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Literature Review. Cureus. 2023;15(8):e44116. [31] SHI Y, GILKES DM. HIF-1 and HIF-2 in cancer: structure, regulation, and therapeutic prospects. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025;82(1):44. [32] 马瑗锾,石慧娟,温兰钰,等.组织化培养上调HIF-1α信号通路促进移植的间充质干细胞在脊髓损伤区存活的机制研究[C]//中国解剖学会.中国解剖学会2021年年会论文文摘汇编.中山大学中山医学院组织胚胎学教研室, 2021:1. [33] FANG J, CHEN Z, LAI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived HIF-1α-overexpressed extracellular vesicles ameliorate hypoxia-induced pancreatic β cell apoptosis and senescence through activating YTHDF1-mediated protective autophagy. Bioorg Chem. 2022;129:106194. [34] SCHIMMEL L, HEEMSKERK N, VAN BUUL JD. Leukocyte transendothelial migration: A local affair. Small GTPases. 2017;8(1):1-15. [35] DING H, LI A, SUN C, et al. Quantitative iTRAQ proteomics reveal the proteome profiles of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after cocultures with Schwann cells in vitro. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(18):962. [36] 吴丛宇,周悦,上官璐茜,等.大黄素的药理作用机制研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2023,54(5):634-643. [37] SAUNDERS IT, MIR H, KAPUR N, et al. Emodin inhibits colon cancer by altering BCL-2 family proteins and cell survival pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:98. [38] LI M, JIN S, CAO Y, et al. Emodin regulates cell cycle of non-small lung cancer (NSCLC) cells through hyaluronan synthase 2 (HA2)-HA-CD44/receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility (RHAMM) interaction-dependent signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):19. [39] 涂平华.芦荟大黄素介导的光动力诱导骨肉瘤MG63细胞自噬的研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2015. [40] 刘琳.大黄素对结肠癌细胞凋亡相关分子Caspase-3的作用[J].中国医药导刊,2013, 15(9):1532-1533. [41] 樊向文,张勇,席量,等.大黄素对人乳腺癌细胞MCF-7的促凋亡作用及其与JNK信号通路关系[J].中国肿瘤外科杂志, 2015,7(6):346-350+355. [42] MCDONALD SJ, VANDERVEEN BN, VELAZQUEZ KT, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Emodin for Gastrointestinal Cancers. Integr Cancer Ther. 2022;21: 15347354211067469. [43] ZHANG F, CUI D, WANG Z, et al. NOX4 Regulates NLRP3 by Inhibiting the Ubiquitination of LRRC8A to Promote Ferroptosis in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Inflammation. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s10753-025-02253-0. [44] 曾锦明,范成龙,邓姣,等.大黄素抑制背根神经节压迫小鼠模型STAT3、VEGFA、p-ERK蛋白表达及其镇痛作用研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2024, 44(9):1583-1591. [45] 曾欢欢,黄英如,李子健,等.大黄素对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后继发脊髓水肿的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018, 24(4):378-384. [46] GAHBAUER S, DELEON C, BRAZ JM, et al. Docking for EP4R antagonists active against inflammatory pain. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):8067. [47] HONG JY, KIM H, LEE J, et al. Epidural Injection Method for Long-Term Pain Management in Rats with Spinal Stenosis. Biomedicines. 2023;11(5):1390. [48] COHEN SP, BICKET MC, JAMISON D, et al. Epidural steroids: a comprehensive, evidence-based review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013;38(3):175-200. [49] 周若彤,庞倩倩,夏维波.前列腺素E2在骨形成中的作用机制[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2024,17(3):295-302. [50] TAKASHIMA H, TAKEBAYASHI T, YOSHIMOTO M, et al. The Difference in Gender Affects the Pathogenesis of Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018; 2(4):263-269. |
| [1] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [2] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [3] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [4] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [5] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [6] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [7] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [8] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [9] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [10] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [11] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [12] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| [13] | Liang Liang, Yan Yulu, Zheng Yang, Zhang Xiaoyun, Wang Lei, Qi Wen . Lactylation-related potential targets and Chinese herbal medicine active ingredients targeting treatment of spinal cord injury: GEO database screening analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3156-3170. |
| [14] | Gao Xinhai, Tan Huangsheng, He Shenghua. Carboxypeptidase M: unveiling a new therapeutic target for osteonecrosis based on eQTL Database and Finnish Genetic Big Data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2870-2876. |
| [15] | Yan Wenjian, Li Yinghui, Zhang Yong. Daily diet and structural damage of the knee joint: a large-scale genetic analysis based on UK and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2877-2885. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||