Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (32): 6885-6892.doi: 10.12307/2025.942
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of different concentrations of hypertonic glucose in the repair of tendon injury in rats
Zhou Lina1, 3, Li Yun1, 3, Liu Xixia2, 3
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3The People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Joint Training Base of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine), Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-11-04Accepted:2024-12-12Online:2025-11-18Published:2025-04-26 -
Contact:Liu Xixia, MD, Associate chief physician, The People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Joint Training Base of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine), Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Guangxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhou Lina, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; The People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Joint Training Base of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine), Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, Nos. 2022GXNSFBA035519 and 2023GXNSFAA026175 (both to LXX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Lina, , Li Yun, , Liu Xixia, . Effects of different concentrations of hypertonic glucose in the repair of tendon injury in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6885-6892.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
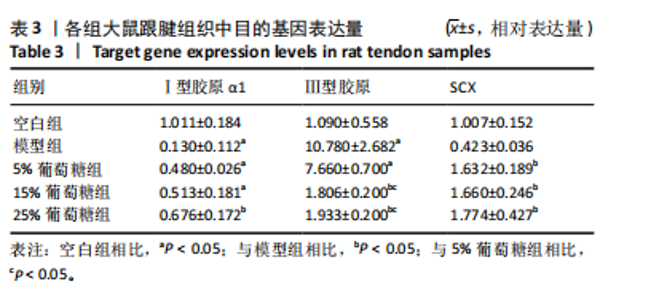
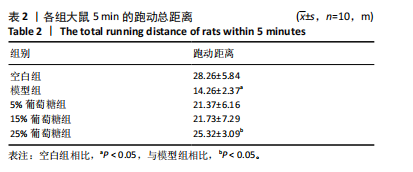
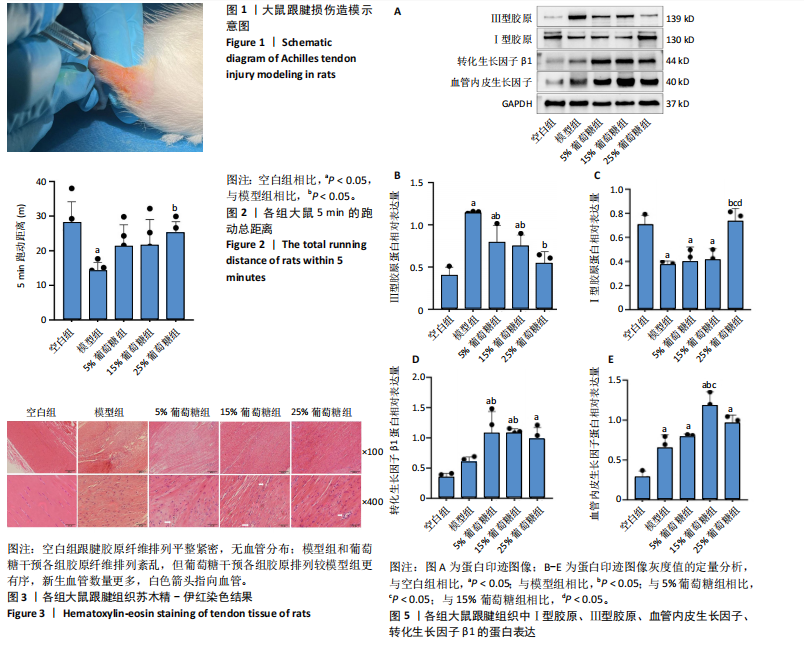
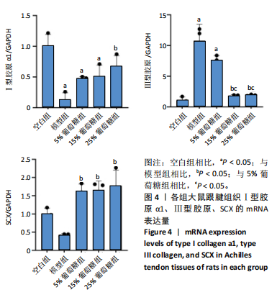
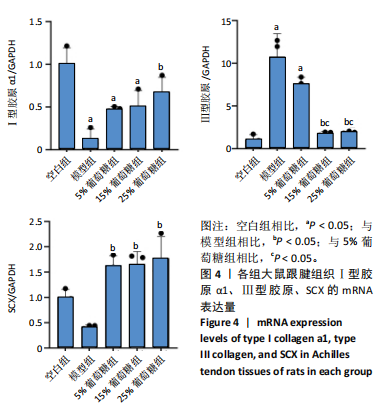
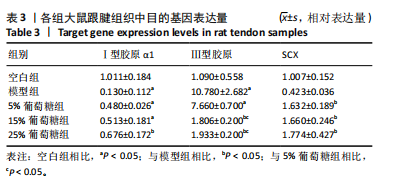
2.3 病理学变化 治疗3周后苏木精-伊红染色显示,空白组肌腱组织胶原纤维排列平整紧密,肌腱细胞呈纺锤形并平行于纤维,腱周组织少且几乎无血管;其他各组跟腱组织均有不同程度的细胞增多、炎性细胞浸润、胶原纤维排列紊乱,模型组跟腱组织出现脂肪浸润,葡萄糖干预的各组胶原纤维排列较模型组更加有序紧密,新生血管数量增加,见图3。 2.4 跟腱组织中Ⅰ型胶原α1、Ⅲ型胶原、SCX mRNA表达 RT-qPCR 检测结果显示,与空白组相比,模型组、5%葡萄糖组、15%葡萄糖组Ⅰ型胶原α1 mRNA表达量均降低(P < 0.05);5%葡萄糖组、15%葡萄糖组Ⅰ型胶原α1的mRNA表达量与模型组相比均有上升趋势,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);25%葡萄糖组Ⅰ型胶原α1的mRNA表达量与模型组相比增加 (P < 0.05)。与空白组相比,模型组Ⅲ型胶原的mRNA表达量升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,15%葡萄糖组、25%葡萄糖组Ⅲ型胶原的mRNA表达量均下降 (P < 0.05);与模型组相比,各剂量葡萄糖组SCX的mRNA表达量均增加(P < 0.05),见表3,图4。"
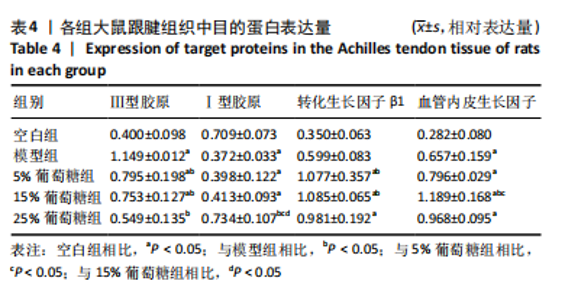
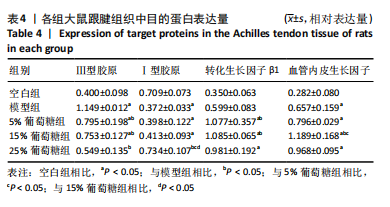
2.5 跟腱组织中Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原、转化生长因子β1、血管内皮生长因子的蛋白表达 Western blot 检测跟腱细胞外基质成分发现,与空白组相比,经造模的模型组、5%葡萄糖组、15%葡萄糖组损伤肌腱中的Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,25%葡萄糖组Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达量明显增加(P < 0.05),而5%葡萄糖组和15%葡萄糖组Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达量与模型组并无明显差异(P > 0.05)。与空白组相比,模型组、5%葡萄糖组、15%葡萄糖组Ⅲ型胶原蛋白均有所增加(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,各剂量葡萄糖组Ⅲ型胶原蛋白水平降低(P < 0.05),且葡萄糖浓度越高Ⅲ型胶原蛋白水平越低,见表4。"
| [1] MILLAR NL, SILBERNAGEL KG, THORBORG K, et al. Tendinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):1. [2] FLINT JH, WADE AM, GIULIANI J, et al. Defining the terms acute and chronic in orthopaedic sports injuries: A systematic review. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(1):235-241. [3] GARZÓN M, BALASCH-BERNAT M, COOK C, et al. How long does tendinopathy last if left untreated? Natural history of the main tendinopathies affecting the upper and lower limb: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2024;72:103103. [4] DE VOS RJ, VAN DER VLIST AC, ZWERVER J, et al. Dutch multidisciplinary guideline on Achilles tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2021;55(20): 1125-1134. [5] DARRIEUTORT-LAFFITE C, SOSLOWSKY LJ, LE GOFF B. Molecular and structural effects of percutaneous interventions in chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7000. [6] CHENG L, ZHENG Q, QIU K,et al. Mitochondrial destabilization in tendinopathy and potential therapeutic strategies. J Orthop Translat. 2024;49:49-61. [7] KENYON M, DRIVER P, MALLOWS A, et al. Characteristics of patients seeking National Health Service (NHS) care for Achilles tendinopathy: A service evaluation of 573 patients. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2024; 74:103156. [8] RIEL H, LINDSTRØM CF, RATHLEFF MS, et al. Prevalence and incidence rate of lower-extremity tendinopathies in a Danish general practice: A registry-based study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):239. [9] TOGNOLO L, SCANU A, VARGIU C, et al. Dextrose prolotherapy for chronic tendinopathy: A scoping review. Eur J Integr Med. 2022;45(3): 123-130. [10] HAGGAG MA, AL-BELASY FA, SAID AHMED WM. Dextrose prolotherapy for pain and dysfunction of the TMJ reducible disc displacement: A randomized, double-blind clinical study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2022;50(5):426-431. [11] CORTEZ VS, MORAES WA, TABA JV, et al. Comparing dextrose prolotherapy with other substances in knee osteoarthritis pain relief: A systematic review. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022;77:100037. [12] ZHU M, RABAGO D, CHUNG VC, et al. Effects of hypertonic dextrose injection (prolotherapy) in lateral elbow tendinosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2022;103(11):2209-2218. [13] AKCAY S, GUREL KANDEMIR N, KAYA T, et al. Dextrose prolotherapy versus normal saline injection for the treatment of lateral epicondylopathy: A randomized controlled trial. J Altern Complement Med. 2020;26(12):1159-1168. [14] APAYDIN H, BAZANCIR Z, ALTAY Z. Injection therapy in patients with lateral epicondylalgia: Hyaluronic acid or dextrose prolotherapy? A single-blind, randomized clinical trial. J Altern Complement Med. 2020; 26(12):1169-1175. [15] YELLAND M, RABAGO D, RYAN M, et al. Prolotherapy injections and physiotherapy used singly and in combination for lateral epicondylalgia: A single-blinded randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):509. [16] LIN CL, CHEN YW, WU CW, et al. Effect of hypertonic dextrose injection on pain and shoulder disability in patients with chronic supraspinatus tendinosis: A randomized double-blind controlled study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2022;103(2):237-244.
[17] CIFTCI YGD, TUNCAY F, KOCAK FA, et al. Is Low-Dose Dextrose Prolotherapy as Effective as High-Dose Dextrose Prolotherapy in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis? A Double-Blind, Ultrasound Guided, Randomized Controlled Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(2): 179-187. [18] 王卓琳. 不同浓度高渗葡萄糖对兔跟腱病模型Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原及IL-1β表达影响的实验研究[D]. 成都:成都体育学院,2021. [19] MARTINS CA, BERTUZZI RT, TISOT RA, et al. Dextrose prolotherapy and corticosteroid injection into rat Achilles tendon. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(10):1895-1900. [20] JOHNSTON E, KOU Y, JUNGE J, et al. Hypertonic dextrose stimulates chondrogenic cells to deposit collagen and proliferate. Cartilage. 2021; 13(2_suppl):213S-224S. [21] SCHULZE-TANZIL GG, CÁCERES MD, STANGE R, et al. Tendon healing: A concise review on cellular and molecular mechanisms with a particular focus on the Achilles tendon. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(8):561-574. [22] SUBRAMANIAN A, SCHILLING TF. Tendon development and musculoskeletal assembly: Emerging roles for the extracellular matrix. Development. 2015;142(24):4191-4204. [23] HAN DC, ISONO M, HOFFMAN BB, et al. High glucose stimulates proliferation and collagen type I synthesis in renal cortical fibroblasts: Mediation by autocrine activation of TGF-beta.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10(9):1891-1899. [24] SIADAT AH, ISSEROFF RR. Prolotherapy: Potential for the treatment of chronic wounds? Adv Wound Care. 2019;8(4):160-167. [25] LI H, LUO S, WANG H, et al. The mechanisms and functions of TGF-β1 in tendon healing. Injury. 2023;54(11):111052. [26] MILLAR NL, MURRELL GAC, MCINNES IB. Alarmins in tendinopathy: Unravelling new mechanisms in a common disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52(5):769-779. [27] BEST KT, LEE FK, KNAPP E, et al. Deletion of NFKB1 enhances canonical NF-κB signaling and increases macrophage and myofibroblast content during tendon healing. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10926. [28] LI J, LIU ZP, XU C, et al. TGF-β1-containing exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote proliferation, migration and fibrotic activity in rotator cuff tenocytes. Regen Ther. 2020;15:70-76. [29] ZHANG H, YANG L, HAN Q, et al. Antifibrotic effects of quercetin on TGF-β1-induced vocal fold fibroblasts. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(12): 8552-8561. [30] CHEN CH, LIN YH, CHEN CH, et al. Transforming growth factor beta 1 mediates the low-frequency vertical vibration enhanced production of tenomodulin and type I collagen in rat Achilles tendon. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0205258. [31] MAJEWSKI M, HEISTERBACH P, JAQUIÉRY C, et al. Improved tendon healing using bFGF, BMP-12 and TGFβ1 in a rat model. Eur Cell Mater. 2018;35:318-334. [32] SHI Z, YAO C, SHUI Y, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of angiogenesis in wound repair and regeneration. Front Physiol. 2023;14: 1284981. [33] KUMAR I, STATON CA, CROSS SS, et al. Angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in human surgical wounds. Br J Surg. 2009;96(12):1484-1491. [34] LIU X, ZHU B, LI Y, et al. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in tendon healing. Front Physiol. 2021;12:766080. [35] DE GIROLAMO L, MORLIN AMBRA LF, PERUCCA ORFEI C, et al. Treatment with human amniotic suspension allograft improves tendon healing in a rat model of collagenase-induced tendinopathy. Cells. 2019;8(11):1411. [36] 朱斌. 离心运动上调Scx提高Ⅰ型胶原合成促进慢性跟腱病修复的机制研究[D]. 泸州:西南医科大学,2022. [37] ZHANG T, WANG Y, DING L, et al. Efficacy of hypertonic dextrose proliferation therapy in the treatment of rotator cuff lesions: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):297. [38] LIANG W, ZHOU C, DENG Y, et al. The Current Status of Various Preclinical Therapeutic Approaches for Tendon Repair. Ann Med. 2024; 56(1):2337871. [39] FULLERTON BD. Prolotherapy for the Thoracolumbar Myofascial System. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2018;29(1):125-138. [40] MAO AS, MOONEY DJ. Regenerative Medicine: Current Therapies and Future Directions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(47):14452-14459. [41] HOU J, YANG R, VUONG I, et al. Biomaterials Strategies to Balance Inflammation and Tenogenesis for Tendon Repair. Acta Biomater. 2021;130:1-16. [42] DARRIEUTORT-LAFFITE C, BLANCHARD F, SOSLOWSKY LJ, et al. Biology and Physiology of Tendon Healing. Joint Bone Spine. 2024;91(5): 105696. [43] SUBRAMANIAN A, KANZAKI LF, GALLOWAY JL, et al. Mechanical Force Regulates Tendon Extracellular Matrix Organization and Tenocyte Morphogenesis through TGFbeta Signaling. Elife. 2018;7:e38069. [44] DOCHEVA D, MÜLLER SA, MAJEWSKI M, et al. Biologics for Tendon Repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;84:222-239. [45] MAFFULLI N, MOLLER HD, EVANS CH. Tendon Healing: Can It Be Optimised? Br J Sports Med. 2002;36(5):315-316. [46] ZHAO AT, CABALLERO CJ, NGUYEN LT, et al. A Comprehensive Update of Prolotherapy in the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Knee.Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2022;14(4):33921. [47] VOLETI PB, BUCKLEY MR, SOSLOWSKY LJ. Tendon Healing: Repair and Regeneration. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;14:47-71. [48] 刘雪丽, 沈丽, 毕文光,等. 低强度脉冲超声对大鼠急性肌腱损伤早期血管生成的影响及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(32): 5097-5103. [49] GUERQUIN MJ, CHARVET B, NOURISSAT G, et al. Transcription Factor EGR1 Directs Tendon Differentiation and Promotes Tendon Repair. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(8):3564-3576. [50] FERRARA N, ADAMIS AP. Ten Years of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15(6):385-403. [51] HUANG Y, PAN M, SHU H, et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Enhances Tendon‐bone Healing by Activating Yes‐associated Protein for Angiogenesis Induction and Rotator Cuff Reconstruction in Rats. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(3):2343-2353. [52] AHADI T, CHAM MB, MIRMOGHTADAEI M, et al. The Effect of Dextrose Prolotherapy versus Placebo/Other Non-Surgical Treatments on Pain in Chronic Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. J Foot Ankle Res. 2023;16(1):5. [53] DA RÉ GUERRA F, VIEIRA CP, OLIVEIRA LP, et al. Low-Level Laser Therapy Modulates Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines after Partial Tenotomy. Lasers Med Sci. 2016;31(4):759-766. [54] LI Y, LIU X, LIU X, et al. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signalling Pathway in Tendon Healing. Growth Factors. 2022;40(3-4):98-107. [55] INOUE M, NAKAJIMA M, OI Y, et al. The Effect of Electroacupuncture on Tendon Repair in a Rat Achilles Tendon Rupture Model. Acupunct Med. 2015;33(1):58-64. [56] FERRARI G, COOK B, TERUSHKIN V, et al. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta 1 (Tgf-β1) Induces Angiogenesis through Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (Vegf)-Mediated Apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219(2):449-458. [57] PAN PJ, WANG JC, TSAI CC, et al. Identification of Early Response to Hypertonic Dextrose Prolotherapy Markers in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients by an Inflammation-Related Cytokine Array. J Chin Med Assoc. 2022;85(4):525-531. [58] YUAN H. Collagen and Chondroitin Sulfate Functionalized Bioinspired Fibers for Tendon Tissue Engineering Application.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;170:248-260. [59] HILLEGE MMG, GALLI CARO RA, OFFRINGA C, et al. TGF-β Regulates Collagen Type I Expression in Myoblasts and Myotubes via Transient Ctgf and Fgf-2 Expression: 2. Cells. 2020;9(2):375. [60] VARRICCHIO L, IANCU-RUBIN C, UPADHYAYA B, et al. TGF-β1 protein trap AVID200 beneficially affects hematopoiesis and bone marrow fibrosis in myelofibrosis. JCI Insight. 2021;6(18):e145651. |
| [1] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [2] | Zhao Jianwei, Li Xunsheng, Lyu Jinpeng, Zhou Jue, Jiang Yidi, Yue Zhigang, Sun Hongmei. Deer antler stem cell exosome composite hydrogel promotes the repair of burned skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7344-7352. |
| [3] | Yi Xiaoding, Zhang Di, Guo Hong, Qing Liang, Zhao Tianyu. Decellularized tendon scaffold: a biomedical material for tendon injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7385-7392. |
| [4] | Wang Wanchun, , Yi Jun, Yan Zhangren, Yang Yue, Dong Degang, Li Yumei. 717 Jiedu Decoction remodels homeostasis of extracellular matrix and promotes repair of local injured tissues in rats after Agkistrodon halys bite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6457-6465. |
| [5] | Sun Yahui, Wang Yufeng, Guo Chao, Yao Junjie, Ji Yuanyuan, Li Zhongxu, Lou Huijuan, Jiang Jinglei, Sun Yiping, Xu Jing, Cong Deyu. Effect of massage on extracellular matrix collagen deposition in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5549-5555. |
| [6] | Wang Lian, Xie Na, Zhao Peiling, Chen Hao, Li Duyou, Wang Yuping. Effects of cannabidiol on hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrosis induced by transforming growth factor beta1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4965-4974. |
| [7] | Xu Jie, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Zhao Bin. Bio-3D printed bionic scaffold promotes healing after rotator cuff injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4761-4770. |
| [8] | Yang Shuo, Zhang Zhen, Bai Shuo, Sheng Li, Shen Liang, Sun Qingfeng, Gao Beiyao, Ge Ruidong, Jiang Shan. Mitochondrial dysfunction in tendinopathy: possibility of mitochondria-targeting therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4276-4285. |
| [9] | Peng Yong, Hu Jiangping, Zhu Huan. Effects of low-load blood flow restriction exercise and high-intensity resistance exercise on the thigh microcirculation function of athletic young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 393-401. |
| [10] | Chen Jiahui, Dai Xiaoqi, Xu Yangang, Li Yuanchao, Huang Mei, Zhan Yifei, Du Yuxuan, Li Liuqiang, Guo Yaochuan, Bian Jun, Lai Dehui. Isolation, culture and differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells into smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(19): 4076-4082. |
| [11] | Yu Yangyi , Song Zhuoyue, Lian Qiang, Ding Kang, Li Guangheng . AAV-mediated expression of p65shRNA and bone morphogenetic protein 4 synergistically enhances chondrocyte regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3537-3547. |
| [12] | Huang Chaolu, Huang Yi, Wu Changyan, Li Fangfei, Li Haiyan. Aerobic exercise mitigates liver fibrosis in db/db diabetes mice by regulating transforming growth factor beta/Smad pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 2951-2957. |
| [13] | Zhang Xingzhou, Wei Ming, Dong Guoqiang, Du Wei, Luo Yiwen, Zhang Nan . Mechanism of postoperative abdominal adhesion formation and therapeutic prospect of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 147-155. |
| [14] | Cheng Jie, Wang Jihong, Zhang Pei. Functional exercise for tendon adhesion in a model of deep flexor tendon II injury of the third toe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1161-1167. |
| [15] | Shen Jiangyong, He Xi, Tang Yuting, Wang Jianjun, Liu Jinyi, Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Xinyi, Liu Tong, Sun Haoyuan. RAS-selective lethal small molecule 3 inhibits the fibrosis of pathological scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1168-1173. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||