Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (2): 393-401.doi: 10.12307/2025.233
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of low-load blood flow restriction exercise and high-intensity resistance exercise on the thigh microcirculation function of athletic young men
Peng Yong1, Hu Jiangping2, Zhu Huan1
- 1School of Physical Education, Hubei Minzu University, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China; 2School of Physical Education, Guangxi Normal University for Nationalities, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-12-15Accepted:2024-01-31Online:2025-01-18Published:2024-05-25 -
Contact:Hu Jiangping, PhD candidate, Associate professor, School of Physical Education, Guangxi Normal University for Nationalities, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Peng Yong, PhD candidate, Lecturer, School of Physical Education, Hubei Minzu University, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:Philosophy and Social Science Research Project of Hubei Provincial Department of Education, No. 22Q145 (to PY); Science and Technology Program Project of Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, No. E20220009 (to PY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Peng Yong, Hu Jiangping, Zhu Huan. Effects of low-load blood flow restriction exercise and high-intensity resistance exercise on the thigh microcirculation function of athletic young men[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 393-401.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
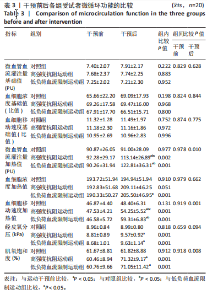
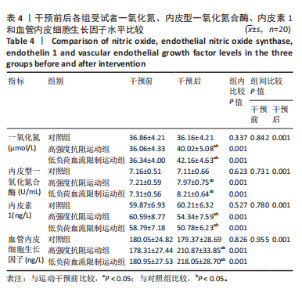
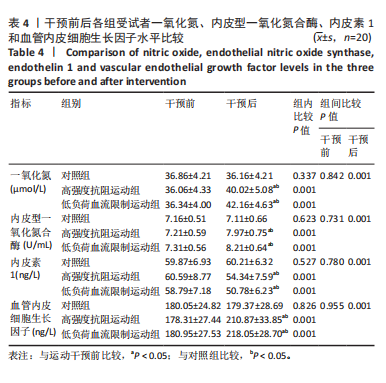
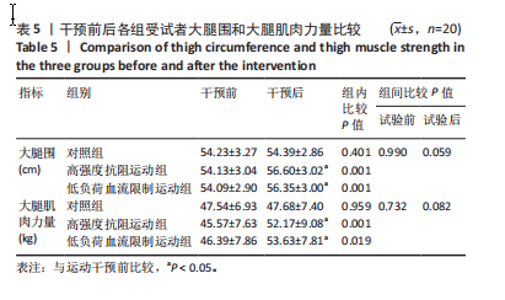
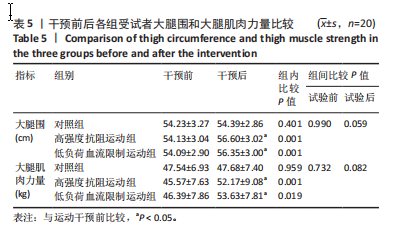
2.4 干预前后各组受试者微循环功能变化 见表3。组间比较结果显示:运动干预前各组各指标相互间差异无显著性意义;运动干预后高强度抗阻运动组和低负荷血流限制运动组的微血管血流灌注量加热值、血细胞移动速度加热值与对照组相比均有显著差异(P < 0.05);干预后低负荷血流限制运动组微血管血流灌注量加热值、血细胞移动速度加热值显著高于高强度抗阻运动组(P < 0.05)。组内比较结果显示:运动干预后高强度抗阻运动组和低负荷血流限制运动组的微血管血流灌注量加热值、血细胞移动速度加热值、经皮氧分压和肌氧饱和度与干预前相比均有显著差异(P < 0.05),低负荷血流限制运动组的血细胞浓度与干预前相比有显著差异(P < 0.05);干预前后对照组各指标差异无显著性意义。 2.5 干预前后各组受试者血液细胞因子水平的变化 见表4。组间比较结果显示:运动干预前各组各指标相互间差异无显著性意义;运动干预后高强度抗阻运动组和低负荷血流限制运动组的一氧化氮、内皮型一氧化氮合酶、内皮素1、血管内皮细胞生长因子水平与对照组相比均有显著差异(P < 0.05);干预后高强度抗阻运动组和低负荷"

| [1] TSCHAKOVSKY ME, SHERIFF DD. Immediate exercise hyperemia: contributions of the muscle pump vs. rapid vasodilation. J Appl Physiol. 2004;97(2):739-747. [2] 刘超杰.六周高强度力量训练对体育教育专业男子大学生肌力、围度、微循环的影响及三者之间关系的研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2021. [3] 冯燕.有氧、抗阻运动对衰老小鼠骨骼肌毛细血管生成和卫星细胞的影响研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2019. [4] 潘颖,赵彦,马晓缓,等.血流限制伴小强度抗阻运动对低体质量女性骨骼肌微循环、神经肌肉激活及主观疲劳的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(8):677-684. [5] KAMBIČ T. Blood flow restriction training: you can occlude your veins, but not your oxygen transport. J Physiol. 2020;598(18):3825-3826. [6] MOUSER JG, MATTOCKS KT, BUCKNER SL, et al. High-pressure blood flow restriction with very low load resistance training results in peripheral vascular adaptations similar to heavy resistance training. Physiol Meas. 2019;40(3):035003. [7] DA CUNHA NASCIMENTO D, SCHOENFELD BJ, PRESTES J. Potential implications of blood flow restriction exercise on vascular health: a brief review. Sports Med. 2020;50(1):73-81. [8] 钱洲曜,王勇平.血管内皮生长因子有望成为加速骨折愈合的全新治疗手段[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17):2759-2769. [9] 朱欢,高炳宏.有氧运动对人体微血管反应性的作用及机制研究进展[J].生命科学,2020,32(8):855-863. [10] 胡国鹏,王人卫,王振,等.12周循环抗阻训练对男子大学生心血管动力学参数的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(2):205-207. [11] KILGAS MA, MCDANIEL J, STAVRES J, et al. Limb blood flow and tissue perfusion during exercise with blood flow restriction. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019;119(2):377-387. [12] GRØNFELDT BM, LINDBERG NIELSEN J, MIERITZ RM, et al. Effect of blood-flow restricted vs heavy-load strength training on muscle strength: systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30(5):837-848. [13] 王艺璇,蔡军.剪切力和拉伸应力对血管内皮细胞的影响[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2012,4(8):38-41. [14] COOK SB, LAROCHE DP, VILLA MR, et al. Blood flow restricted resistance training in older adults at risk of mobility limitations. Exp Gerontol. 2017;99:138-145. [15] COOK SB, CLEARY CJ. Progression of blood flow restricted resistance training in older adults at risk of mobility limitations. Front Physiol. 2019;10:738. [16] LOENNEKE JP, THIEBAUD RS, FAHS CA, et al. Blood flow restriction does not result in prolonged decrements in torque. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(4):923-931. [17] LOENNEKE JP, KIM D, FAHS CA, et al. Effects of exercise with and without different degrees of blood flow restriction on torque and muscle activation. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51(5):713-721. [18] ERCAN M, KOKSAL C. The relationship between shear rate and vessel diameter. Anesth Analg. 2003;96(1):307. [19] TSCHAKOVSKY ME, ROGERS AM, PYKE KE, et al. Immediate exercise hyperemia in humans is contraction intensity dependent: evidence for rapid vasodilation. J Appl Physiol. 2004;96(2):639-644. [20] CLARK BC, MANINI TM, HOFFMAN RL, et al. Relative safety of 4 weeks of blood flow-restricted resistance exercise in young, healthy adults. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011;21(5):653-662. [21] 朱欢,万利,刘尧峰,等.低氧适应与低氧运动对慢性病患者微血管反应性的干预效应及机制研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2021,40(6):490-495. [22] 朱欢,高炳宏.微血管反应性在耐力性运动员训练中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(10):907-914. [23] Agarwal SC, Allen J, Murray A, et al. Comparative reproduc-ibility of dermal microvascular blood flow changes in response to acetylcholineiontophoresis,hyperthermia and reactive hyperaemia.Physiol Meas. 2010;31(1):1-11. [24] Agarwal SC, Allen J, Murray A, et al. Laser Doppler assess-ment of dermal circulatory changes in people with coronary artery disease. Microvasc Res. 2012;84(1):55-59. [25] 徐菲菲,郭渝成,刘秀华.皮肤微血管功能检测的研究进展[J].微循环学杂志,2014,24(3):71-76. [26] 朱欢,高炳宏,梁世雷,等.我国赛艇运动员肱二头肌微循环血流储备能力的研究[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2015,31(1):61-65. [27] KIM J, LANG JA, PILANIA N, et al. Effects of blood flow restricted exercise training on muscular strength and blood flow in older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2017;99:127-132. [28] EVANS C, VANCE S, BROWN M. Short-term resistance training with blood flow restriction enhances microvascular filtration capacity of human calf muscles. J Sports Sci. 2010;28(9):999-1007. [29] PATTERSON SD, FERGUSON RA. Increase in calf post-occlusive blood flow and strength following short-term resistance exercise training with blood flow restriction in young women. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010; 108(5):1025-1033. [30] PATTERSON SD, FERGUSON RA. Enhancing strength and postocclusive calf blood flow in older people with training with blood-flow restriction. J Aging Phys Act. 2011;19(3):201-213. [31] HUNT JE, GALEA D, TUFFT G, et al. Time course of regional vascular adaptations to low load resistance training with blood flow restriction. J Appl Physiol. 2013;115(3):403-411. [32] FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, LOENNEKE JP. Effect of different types of lower body resistance training on arterial compliance and calf blood flow. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2012;32(1):45-51. [33] SHIMIZU R, HOTTA K, YAMAMOTO S, et al. Low-intensity resistance training with blood flow restriction improves vascular endothelial function and peripheral blood circulation in healthy elderly people. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016;116(4):749-757. [34] 杨明明,朱欢,王丹.血流限制训练对不同性别跆拳道运动员经皮氧分压及经皮二氧化碳分压的影响[C].第十二届全国体育科学大会论文摘要汇编——墙报交流(体能训练分会),2022:22-23. [35] 肖哲,朱欢,胡江平,等.10周有氧运动和有氧结合抗阻运动对肥胖大学生微循环功能的影响及机制研究[J].中国全科医学,2022, 25(19):2349-2355, 2362. [36] 孙宇斌,杨紫强,林文杰,等.加压训练对肌氧饱和度的影响[J].体育科技文献通报,2021,29(8):198-199,208. [37] CHRISTIANSEN D, EIBYE K, HOSTRUP M, et al. Training with blood flow restriction increases femoral artery diameter and thigh oxygen delivery during knee-extensor exercise in recreationally trained men. J Physiol. 2020;598(12):2337-2353. [38] SCOTT BR, PEIFFER JJ, THOMAS HJ, et al. Hemodynamic responses to low-load blood flow restriction and unrestricted high-Load resistance exercise in older women. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1324. [39] TAN Z, ZHAO Y, ZHENG Y, et al. The effect of blood flow-restricted low resistance training on microvascular circulation of myocardium in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Front Physiol. 2022;13:829718. [40] TAKANO H, MORITA T, LIDA H, et al. Hemodynamic and hormonal responses to a short-term low-intensity resistance exercise with the reduction of muscle blood flow. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2005;95(1):65-73. [41] LARKIN KA, MACNEIL RG, DIRAIN M, et al. Blood flow restriction enhances postresistance exercise angiogenic gene expression. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(11):2077-2083. [42] HUNT JE, WALTON LA, FERGUSON RA. Brachial artery modifications to blood flow-restricted handgrip training and detraining. J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(6):956-961. [43] ZHAO Y, LIN A, JIAO L. Eight weeks of resistance training with blood flow restriction improve cardiac function and vascular endothelial function in healthy young Asian males. Int Health. 2021;13(5):471-479. [44] 马晓缓,赵彦,郑玉婵.加压训练对高血压患者血管内皮功能的影响[J].湖北体育科技,2021,40(4):341-344,354. [45] 谭朝文,赵彦,俞莹莹,等.低负荷加压训练改善自发性高血压大鼠的血压效果及机制研究[J].体育科学,2020,40(3):46-53,63. [46] 徐菲菲,郭渝成,刘秀华.皮肤微血管功能检测的研究进展[J].微循环学杂志,2014,24(3):71-76. [47] 高丽君,王军,周红艳,等.自发性高血压大鼠左心室肥厚与ACE-AngⅡ-AT1R轴/ACE2-Ang(1-7)-MasR轴变化[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016,30(6):568-571. [48] MACHADO MJC, BOARDMAN R, RIU F, et al. Enhanced notch signaling modulates unproductive revascularization in response to ni- tric oxide-angiopoietin signaling in a mouse model of peripheral ischemia. Microcirculation. 2019;26(6):e12549. [49] SCHAAF MB, HOUBAERT D, MECE O, et al. Lysosomal pathways and autophagy distinctively control endothelial cell behavior to affect tumor vasculature. Front Oncol. 2019;9:171. [50] TANG X, WANG JJ, WANG J, et al. Endothelium-specific deletion of Nox4 delays retinal vascular development and mitigates pathological angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 2021;24(2):363-377. [51] PITULESCU ME, SCHMIDT I, GIAIMO BD, et al. Dll4 and Notch signalling couples sprouting angiogenesis and artery formation. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(8):915-927. |
| [1] | Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713. |
| [2] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [3] | Zhou Lina, , Li Yun, , Liu Xixia, . Effects of different concentrations of hypertonic glucose in the repair of tendon injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6885-6892. |
| [4] | Jiang Siqi, Huang Huanhuan, Yu Xinyu, Peng Ying, Zhou Wei, Zhao Qinghua. Meta-analysis of dose-effect of exercise on improving muscle health in community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6295-6304. |
| [5] | Ding Yuan, Gong Jianbao, Zhang Jie, Qiao Yuan, Xu Wenlong. Characteristic analysis of isometric muscle strength of knee joint in patients after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5833-5838. |
| [6] | Wang Xia, Xue Boshi, Yang Chen, Zhou Zhipeng, Zheng Liangliang. Influence of neuromuscular function on the risk of biomechanical injury in landing manoeuvres in patients undergoing anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5556-5562. |
| [7] | Zhu Tianrui, Shi Jipeng, Sun Jiahe, Wang Luyi, Zhang Chen, Xu Hongqi, Quan Helong. Effectiveness of different exercise regimens to reduce fall risks in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5662-5672. |
| [8] | Zhao Yuhan, Li Yamei, Yan Shifang, Jiang Huabei. Immediate effects of different stretching methods on knee joint muscle strength and vertical jump performance of healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3784-3790. |
| [9] | Hong Jintao, Wang Jingjing, Li Yansong, Wang Chen, Mi Shouling. Sedentary behavior and lower-limb muscle strength in community-dwelling older adults: the mediating and moderating effects of fear of falling and age [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3566-3571. |
| [10] | Jia Yuexin, Tian Saisai, Qi Xiaohong, Zhang Suqin. Effects of 12 weeks of low-intensity resistance training combined with blood flow restriction training on body composition, muscle strength, and arterial elastic function in young adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2521-2527. |
| [11] | Chen Wenhan, Men Jie, Yang Wei, Zhao Xiaoyu. Effect of vibration therapy combined with suspension training on movement and knee joint function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2225-2230. |
| [12] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [13] | Shan Jiaxin, Zhang Yilong, Wu Hongtao, Zhang Jiayuan, Li Anan, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng, Zhao Chuanxi. Changes in muscle strength and pain in patients receiving Jianpi Yiqi Huoxue Formula after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1378-1382. |
| [14] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [15] | Wang Juan, Wang Ling, Zuo Huiwu, Zheng Cheng, Wang Guanglan, Chen Peng. Rehabilitative efficacy of kinesio taping following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 651-656. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||