Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (14): 3011-3019.doi: 10.12307/2025.621
Previous Articles Next Articles
Collagen metabolism imbalance in intervertebral disc degeneration
Dong Yizhi1, Song Xinyue1, Yao Mingyu1, Zhu He1, Wu Ruixia1, Du Yaxin1, Zhu Yong2
- 1Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010107, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Peking University Cancer Hospital Inner Mongolia Hospital, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-06-11Accepted:2024-07-15Online:2025-05-18Published:2024-09-29 -
Contact:Zhu Yong, MD, PhD, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Peking University Cancer Hospital Inner Mongolia Hospital, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Dong Yizhi, Master candidate, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010107, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Higher Education Innovation Team Project, No. NMGIRT2229 (to ZY); Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Youth, No. YKD2022ZD003 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dong Yizhi, Song Xinyue, Yao Mingyu, Zhu He, Wu Ruixia, Du Yaxin, Zhu Yong . Collagen metabolism imbalance in intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 3011-3019.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
胶原蛋白代谢在椎间盘退变中作用研究的时间脉络见表1。 2.1 胶原蛋白在椎间盘退变中的意义 胶原蛋白(Collagen)是一种三股螺旋结构的纤维蛋白,是构成椎间盘的主要成分之一。在椎间盘中,胶原蛋白主要分布于纤维环和髓核,其中纤维环分为内层和外层纤维环,主要由Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白组成,而髓核则主要含有Ⅱ型胶原蛋白[13-15]。 胶原蛋白在椎间盘中起到维持椎间盘结构完整性、抵抗外力压缩、保持椎间盘弹性等重要作用。胶原蛋白的稳态维持对椎间盘的正常生理功能至关重要,当胶原蛋白合成与降解失衡时,可能导致椎间盘结构和功能受损,进而诱发腰椎间盘退行性疾病。 胶原蛋白的合成和降解过程主要由椎间盘(如成纤维细胞、软骨细胞等)通过合成前体分子、酶类和细胞因子等来调控。胶原蛋白合成过程包括前胶原蛋白的生成、成熟和纤维形成,其中涉及到脯氨酸羟化、酪氨酸酰胺化等一系列生化反应,这些反应由特异酶类如脯氨酸羟化酶和酪氨酸酰胺酶等催化进行[16-17]。椎间盘受到慢性炎症因子、氧化应激反应等多种因素的影响,引发胶原蛋白合成减少、降解增加,从而引发椎间盘结构损伤和功能障碍。研究发现,退行性椎间盘中胶原酶的表达和活性普遍升高,尤其是基质金属蛋白酶家族的表达呈现显著上升趋势。同时,炎症细胞因子如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α等水平也明显升高,这些因子可以进一步刺激胶原酶的产生,加速胶原蛋白的降解。 2.2 胶原代谢在椎间盘退变中的作用[18-20] 2.2.1 维持椎间盘的功能 生长因子、细胞因子和基质蛋白等胶原生成的代谢产物影响着椎间盘内细胞的增殖、分化、迁移,进而维持椎间盘内细胞的数量和功能,以保证椎间盘功能的稳定。"


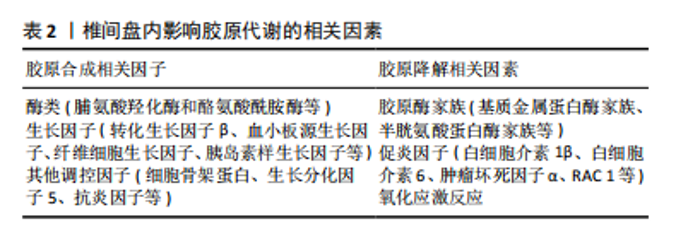
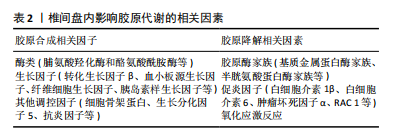
2.3.1 胶原合成相关因子 胶原合成相关因子在胶原蛋白生成过程中发挥重要作用,包括酶类、生长因子以及其他调控因子。这些因子共同参与胶原蛋白的合成和成熟过程,维持椎间盘的结构和功能。当胶原合成相关因子的活性受到抑制时,导致胶原蛋白合成减少,打破了椎间盘内胶原蛋白代谢的平衡,使椎间盘的抗剪切及抗拉伸功能降低,导致椎间盘发生退变。 (1)酶类:脯氨酸羟化酶和酪氨酸酰胺酶是胶原合成过程中的关键酶类。脯氨酸羟化酶催化前胶原蛋白中的脯氨酸残基羟化,形成羟脯氨酸,这一反应对于胶原蛋白的稳定性和抗拉伸强度至关重要[21-22]。酪氨酸酰胺酶则参与酪氨酸的磺酸化过程,有助于胶原蛋白分子间的交联和纤维形成。这些促进胶原合成的酶类在椎间盘退变疾病中的研究尚不充分,需要科研人员进一步研究探索其在椎间盘中发挥的作用机制,以期为椎间盘退变疾病的治疗提供新的方向。 (2)生长因子:生长因子是一种在生物体内广泛存在,对于细胞生长、分化和代谢等过程起关键作用的生物活性蛋白。在椎间盘中,一些重要的生长因子,如转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)、血小板源生长因子(platelet-derived growth factor,PDGF)、纤维细胞生长因子(fibroblast growth factor,FGF)和胰岛素样生长因子(insulin-like growth factor,IGF)等,在胶原蛋白的合成过程中发挥着重要的作用。 转化生长因子β是一种多效性生长因子,它在椎间盘中具有多种功能,包括细胞增殖、分化、胶原蛋白的合成和分泌以及炎症反应的调控等[23]。转化生长因子β通过与其特异性的受体结合,激活下游的Smad信号通路,进而调控胶原蛋白的合成。具体来说,转化生长因子β结合受体后,受体会磷酸化Smad2和Smad3,磷酸化的Smad2和Smad3与Smad4结合形成复合体,这个复合体进入细胞核,与特异的DNA序列结合,启动胶原蛋白基因的转录,从而促进胶原蛋白的合成。转化生长因子β1可以抑制椎间盘细胞凋亡并促进胶原代表合成,从而维持椎间盘稳态并延迟椎间盘退变的进展,还可以减轻炎症和氧化应激,以减少胶原蛋白的降解。SUN等[24]通过研究发现雷奈酸锶可以调节转化生长因子β1/核因子κB轴来减轻白细胞介素1β引起的髓核细胞功能障碍。CHEN等[11]通过研究发现转化生长因子β1通过激活转化生长因子β1/Smad信号通路,逆转Grem1诱导细胞凋亡、抑制细胞外基质合成代谢并促进分解代谢的作用。LIU等[25]通过研究发现M2c-Exoss通过miR-124/cilp/转化生长因子β轴改善椎间盘退变中细胞外基质的代谢失衡,增加了胶原蛋白的合成。转化生长因子β的研究始终是一个热门的话题,在各种疾病中都有着重要的作用,与椎间盘退变疾病的关系更是密不可分,需要继续从不同维度深入研究转化生长因子β与椎间盘退变疾病的关系,为椎间盘退变疾病提供新的治疗靶点。 血小板源生长因子是广泛存在于各种细胞中,特别是血小板中的生长因子。血小板源生长因子通过与其特异性的受体结合,激活下游的磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,AKT)和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)/细胞外调节蛋白激酶(extracellular-signalregu-latedkinase,ERK)信号通路,进而促进胶原蛋白的合成。血小板源生长因子还可以抑制胶原蛋白的降解,促进椎间盘的修复和再生[10,26]。ZHANG等[27]通过研究发现血小板源生长因子BB可以抑制髓核细胞的凋亡,并且可以抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的炎症和凋亡,从而促进椎间盘内胶原蛋白的合成,从而保护椎间盘的结构和功能。WEN等[28]发现血小板源生长因子可以促进软骨细胞增殖和蛋白聚糖的合成,并且可以抑制肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β,以减少胶原蛋白的降解。 纤维细胞生长因子是一种有多种生物活性的生长因子[29-30],它在椎间盘中主要参与细胞增殖、分化和代谢等过程。纤维细胞生长因子结合其特异性的受体,从而激活下游的MAPK/ERK信号通路,促进胶原蛋白合成。纤维细胞生长因子还可以通过调控椎间盘内细胞的生存和凋亡,以及调节其他生长因子如转化生长因子β和血小板源生长因子的作用,影响着椎间盘的健康和功能。MURUGAIYAN等[12]通过研究发现纤维细胞生长因子18可以与骨分化相关的基因,如RUNX 2、Ⅰ型胶原和骨形态发生蛋白4,进而促进胶原蛋白的合成。有研究发现纤维细胞生长因子21通过上调MAPK/pMAPK、下调STAT/pSTAT 3、上调PI3K/AKT抑制Caspase-3和骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡来减少胶原蛋白降解并促进骨新生血管的形成[31]。 胰岛素样生长因子是一种类似胰岛素的生长因子,它在椎间盘中主要参与细胞增殖、分化和代谢等过程。胰岛素样生长因子通过与其特异性的受体相结合,激活下游的PI3K/Akt和MAPK/ERK信号通路,促进胶原蛋白的合成[32]。胰岛素样生长因子还可以通过促进椎间盘的生存和抗氧化,抑制炎症反应并减少胶原蛋白的降解,进一步保护椎间盘的功能。LI等[33]通过研究发现胰岛素样生长因子1可以通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路促进胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的合成;ZHANG等[34]发现胰岛素样生长因子1可以抑制髓核细胞凋亡以维持椎间盘细胞的功能,以减少胶原蛋白的降解。 上述生长因子均能有效促进胶原蛋白的合成或是减少胶原蛋白的降解,从而促进椎间盘内胶原蛋白代谢平衡的稳定,但是因为生长因子的作用广泛且影响因素繁多,导致对椎间盘内生长因子与椎间盘内胶原蛋白代谢之间关系的研究较少,可以对此方向进行研究以制定治疗椎间盘退变疾病的新方法。 (3)其他调控因子:除了酶类和生长因子外,还有许多促进胶原蛋白合成的调控因子,它们在椎间盘的结构、功能以及与周围环境的互动中起着极其关键作用。 细胞骨架蛋白:细胞骨架蛋白是细胞内部的一种结构蛋白,主要包括微管蛋白、微丝蛋白和中间丝蛋白等。细胞骨架蛋白不仅构成了细胞的基本结构框架,维持细胞的形态和稳定性,而且也参与了多种细胞功能,如信号传导、物质运输和细胞分裂等。细胞骨架蛋白在椎间盘细胞中起到重要的结构骨架功能,具有维持细胞形态和稳定性的能力,可以通过激活相应的信号通路及影响细胞内的物质运输,从而在椎间盘退变起到重要作用。骨架蛋白F-actin可以抑制Hippo 信号通路的激活,从而降低对YAP的抑制作用,同时骨架蛋白F-actin聚集化导致 YAP 活化,使椎间盘内胶原合成增加,以维持椎间盘的稳定及功能[35-36]。细胞骨架蛋白还可以与生长因子和信号分子等相互作用,进而影响胶原蛋白的合成。如微丝蛋白可以与转化生长因子β等生长因子受体相结合,影响生长因子信号通路的激活,进而减少胶原蛋白的合成。 生长分化因子5(growth differentiation factor-5,GDF-5):又被称为软骨衍生形态发生蛋白1,在肌肉骨骼中发挥着重要作用,如软骨内骨化、关节形成及韧带维持[37]。CUI等[38]通过研究发现生长分化因子5可以抑制基质金属蛋白酶3的表达来减缓胶原蛋白的降解。还有研究发现生长分化因子5可以促进髓核细胞合成胶原蛋白,还可以上调Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的基因表达[39]。上述研究均说明生长分化因子5在椎间盘退变中起到至关重要的作用,作为治疗腰椎间盘退变的靶向药物具有较大的研究价值和广阔的应用前景。 抗炎因子:如白细胞介素10和白细胞介素4能够抑制炎症反应、减缓胶原蛋白的降解,这些抗炎因子通过抑制炎症因子的产生和释放,使胶原酶的活性降低,椎间盘内胶原降解减少,从而保护了椎间盘组织。在椎间盘退行性疾病中,抗炎因子水平往往较正常椎间盘组织中降低,这可能与炎症因子失衡有关。GE等[40]通过研究发现白细胞介素10可以通过抑制p38 MARK的激活来抑制炎症反应,并增加Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和Sox-9的mRNA表达,从而增加胶原蛋白的合成。有研究表明白细胞介素4可以诱导M0/M1型巨噬细胞向M2型巨噬细胞转化,从而减少促炎因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β)的分泌,增加抗炎因子(如白细胞介素10、白细胞介素3和转化生长因子β)的分泌,减轻炎症反应,从而促进组织修复,增加胶原蛋白合成[41]。 2.3.2 胶原降解相关因素 胶原降解相关因素在胶原蛋白降解过程中发挥重要作用,这些因子因素共同参与胶原蛋白的降解过程,并调节椎间盘细胞的功能,使椎间盘发生退变。 (1)胶原酶家族:胶原酶家族是一类具有特异性胶原降解活性的蛋白酶,主要包括基质金属蛋白酶家族(matrix metalloproteinases,MMPs)和半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族(Cysteine)[42]。胶原酶通过降解胶原蛋白,参与椎间盘组织的重建、修复以及疾病发生过程。 基质金属蛋白酶家族:基质金属蛋白酶是一类依赖锌离子的内肽酶,可降解细胞外基质中的各类蛋白质。在椎间盘中,基质金属蛋白酶通过特异性切割胶原蛋白分子,使其降解为较小的片段。在生理状态下,基质金属蛋白酶的活性受到严格调控,与其内源性抑制剂(组织抑制因子,TIMPs)的平衡关系密切。当椎间盘组织发生炎症或损伤时,基质金属蛋白酶的表达和活性会明显升高,导致胶原蛋白过度降解,进而影响椎间盘的结构和功能[43]。 MANKA等[44]发现基质金属蛋白酶家族的另一重要成员基质金属蛋白酶3的Cat结构域与血红素(HPX)结构域能与胶原蛋白的三维螺旋结构协同结合来参与胶原蛋白的降解。ZENG等[45]通过研究发现苦杏仁苷可以下调基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,从而降低Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的降解。LI等[46]通过研究发现肿瘤坏死因子α增强了髓核细胞中基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,从而降低了Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白的生成。以上这些研究均阐述了基质金属蛋白酶家族在胶原代谢中起到促进胶原戴白降解的作用,期待人们更加深入地了解其在椎间盘退变中的作用机制,以期为椎间盘的治疗提供新的靶点。 半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族:半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族是一类含有活性半胱氨酸残基的内肽酶。半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族在生理条件下主要参与细胞内的蛋白质降解和回收,但在炎症和组织损伤过程中,半胱氨酸蛋白酶的表达和活性会上升,从而参与胶原蛋白的降解[47]。尤其是组织蛋白酶K (Cathepsin K),其具有较高的胶原降解活性,可以有效降解胶原蛋白及蛋白聚糖,参与椎间盘退行性疾病的发生。有研究表明,组织蛋白酶K在破骨细胞中高度表达,并分泌到破骨细胞-骨细胞界面中,导致Ⅰ型胶原蛋白降解[48]。MORT等[49]通过研究发现组织蛋白酶K在关节软骨中对Ⅱ型胶原蛋白具有降解作用。半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶1 (caspase-1)是半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族的成员,也被称为白细胞介素1β转化酶(ICE),可以通过直接降解或激活炎症反应来降解胶原蛋白[50]。ZHOU等[51]通过研究发现硫氧还蛋白互作蛋白(TXNIP)可以通过NLPR3/Caspase-1/白细胞介素1β信号通路促进髓核细胞中Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的降解,从而加重椎间盘的退变。半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族的靶点明确,易于调控,但是其位于下游位置,容易受到各种促进和抑制信号的调节,因此很难精确调节半胱氨酸蛋白酶的浓度来抑制胶原蛋白的降解来减缓椎间盘退变的速度。虽然受到上述因素的制约,但是半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族仍然是治疗腰椎间盘退变的一个有前途的治疗靶点。 (2)促炎因子:促炎因子在胶原代谢中具有调控作用,当椎间盘承受异常的机械应力时,会释放促炎因子,它们可以刺激椎间盘产生胶原酶,促进胶原蛋白的降解。同时,炎症因子还能抑制胶原蛋白的合成,进一步加速椎间盘的退行性变。在腰椎间盘退行性疾病中,炎症因子水平显著升高,与胶原代谢失衡密切相关[52]。 白细胞介素1β:白细胞介素1β是白细胞介素1家族成员之一,在椎间盘退变中发挥重要作用。白细胞介素1β具有强烈的促炎活性,可诱导多种促炎递质,并通过参与炎症反应对周围组织造成损伤,同时还可以刺激髓核细胞产生基质金属蛋白酶1,3等金属基质蛋白酶来降解胶原蛋白。FANG等[53]通过研究发现白细胞介素1β可诱导基质金属蛋白酶1,3,13和解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶4的表达;SHI等[54]认为白细胞介素1β可以通过诱导核因子κB/MAPK的活化来降低miR-202-3P的表达,并诱导基质金属蛋白酶1的表达;ZHAN等[55]通过研究证明白细胞介素1β可以增加基质金属蛋白酶3,10,9的表达,这些研究都表明了白细胞介素1β可以增加胶原蛋白的降解。白细胞介素1β在免疫反应和炎症反应中都发挥着重要作用,需要更加深入地了解其特性和功能,从而更好地理解其在椎间盘退变过程中的作用机制,并为椎间盘退变的治疗提供新的思路和方法。 白细胞介素6:白细胞介素6是一种多功能的细胞因子,其在免疫调节、炎症反应、肿瘤进展等方面发挥着重要作用。CHEN等[56]发现白细胞介素6可以激活Yes相关蛋白1(YAP1),Yes相关蛋白1的过表达降低了SOX-9、Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达,并增加基质金属蛋白酶13的水平;ZHANG等[57]发现褪黑素可以减少炎症细胞的聚集和炎症因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的释放,从而使胶原蛋白的降解作用减弱,这些发现进一步证明了白细胞介素6在胶原代谢中的作用,为更加深入了解椎间盘退变机制提供了理论支持。 肿瘤坏死因子α:肿瘤坏死因子α是一种多效性促炎因子,属于肿瘤坏死因子配体超家族。在生理条件下,肿瘤坏死因子α在抗感染、抗肿瘤和免疫调节等方面发挥着重要作用,当肿瘤坏死因子α水平失调时,可能会导致一系列疾病的发生。肿瘤坏死因子α可以通过核因子κB/MAPK信号通路诱导多种基质金属蛋白酶和含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(ADAMTS)的表达,YANG等[58]发现肿瘤坏死因子α可以显著提高基质金属蛋白酶3和解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶5的表达;HUANG等[59]通过研究发现褪黑素可以抑制NLRP 3炎性小体的活性来抑制肿瘤坏死因子α介导的胶原蛋白降解,这可能与髓核细胞中的核因子κB/MAPK通路有关,这些研究都支持肿瘤坏死因子α在胶原蛋白降解中起到重要作用。 Ras相关C3肉毒毒素底物1(Rac family small GTPase 1,RAC 1):RAC 1是一种小的GTPase,是Rho GTPase家族的重要成员,在多种生物过程中起着关键作用,包括增殖、凋亡、迁移和侵袭运动。LONG等[60]发现软骨细胞中RAC 1引起基质金属蛋白酶13表达增加,使胶原蛋白降解增加;YANG等[61]通过研究发现,RAC 1通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路诱导髓核细胞变性,使胶原蛋白降解。以上这些研究均阐述了RAC 1可以促进胶原蛋白的降解,为椎间盘退变提供了一个新的治疗观点。 (3)氧化应激:氧化应激是指体内氧化作用和抗氧化作用之间的不平衡状态[62]。当椎间盘受到异常机械负荷、高氧张力等刺激时,椎间盘细胞中的线粒体功能出现障碍,并且刺激髓核和纤维环产生活性氧,过量的活性氧通过线粒体凋亡途径诱导髓核细胞凋亡[28]。H2O2是活性氧家族的一员,有研究表明H2O2可以显著下调人和大鼠椎间盘退变细胞中的Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖的表达[63]。还有研究表明,由抗炎因子或高氧诱导的活性氧显著抑制胶原蛋白的合成并调节椎间盘退变细胞中的基质金属蛋白酶的表达[64]。YANG等[65]发现氧化应激可诱导大鼠髓核细胞中的铁死亡,而抑制铁死亡可减缓胶原蛋白的降解速度,从而延缓腰椎间盘退变的速度,由此可以认为通过调节椎间盘细胞中的氧化还原平衡来改善氧化应激反应,以减缓椎间盘退变的发展。 椎间盘退行性疾病进展中,胶原蛋白降解相关因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β等)水平不断上升,加剧椎间盘炎症反应和氧化应激[66]。炎症反应和氧化应激不仅导致椎间盘凋亡,还能进一步促使胶原代谢失衡,形成恶性循环,加速椎间盘退行性疾病的发展,因此需要对这些因子进行更加深入的研究,了解其对椎间盘内胶原蛋白代谢平衡的作用机制,为椎间盘退变治疗提供更加有效的治疗方法。 2.4 胶原蛋白代谢产物的作用意义 胶原蛋白在各种水解酶的作用下被切割成碎片,经细胞外非特异性蛋白酶水解或被溶酶体进一步分解,形成小分子寡肽或游离氨基酸,主要包括胶原蛋白肽、胶原蛋白多肽和胶原蛋白活性肽等。这些代谢产物在各种疾病中都发挥着重要的作用,特别是作为标记物可以反应疾病的进展及治疗情况。胶原蛋白代谢产物的作用具体如下: 2.4.1 诱导炎症反应 胶原蛋白降解的某些产物可以刺激炎症因子的产生,从而在疾病的发生发展过程中发挥作用。LAMBERT等[67]通过研究发现Coll2-1(一种位于Ⅱ型胶原分子的肽)可以使滑膜细胞产生H2O2促进细胞的氧化状态,产生活性氧并刺激核因子κB依赖的促炎因子表达,并且可以刺激滑膜细胞产生白细胞介素8,刺激软骨细胞产生基质金属蛋白酶3,诱导大鼠关节炎。 2.4.2 调控细胞行为 胶原降解产物能够影响椎间盘内细胞的黏附、迁移和增殖等。LINDSEY等[68]通过研究发现,基质金属蛋白酶2和基质金属蛋白酶9切割位于Ⅰ型胶原蛋白α1的氨基酸1 158和1 159之间的C末端上游37个氨基酸处,通过切割该位点产生15个氨基酸的肽(氨基酸1 159-1 173),将其用于治疗心肌梗死的小鼠,发现小鼠心脏伤口的愈合程度加强,证明其在刺激细胞迁移过程和增强纤维细胞伤口中发挥作用。YASUDA等[69]发现T3是抗血管多肽(tumstatin)的一种生物活性肽,可通过与αvβ3和αvβ5整联蛋白受体结合来增强小鼠心脏成纤维细胞增殖和迁移的能力。有研究发现癌抑素(Canstatin)通过Rho/Rho相关蛋白酶(Rho/ROCK)途径增强成纤维细胞迁移,并增加成纤维细胞基质金属蛋白酶2的分泌介导ERK磷酸化,诱导成纤维迁移[70]。 2.4.3 生物标志物潜力 胶原降解产物在可以用来对某些疾病进行早期检测,以实现早期的干预及治疗。如COll2-1NO2可以反映氧化相关的Ⅱ型胶原降解,从而反映局部的炎症反应。有研究证明Coll2-1在患有退行性关节病的动物中更高,Coll2-1NO2的水平与马骨关节病变的程度呈正相关[71]。JOSEPH等[72]通过研究发现Coll2-1NO2可能是关节炎的一个重要的生物标志物。有研究表明Ⅰ型前胶原N-前肽(PINP)和β-C-端肽交联Ⅰ型胶原(β-CTX)是骨质疏松症中的骨形成和骨吸收标志物,可以通过这些指标对患者的疾病情况进行分析[73]。 胶原蛋白代谢产物在机体内的作用十分广泛,如在皮肤组织中可以改善皮肤的屏障功能从而诱导胶原蛋白和透明质酸的合成,从而减少皮肤的皱纹进而延缓皮肤衰老的过程,但对于其在椎间盘退变过程中具体的作用和功能目前研究尚不充分。在椎间盘退变疾病中,胶原蛋白代谢的平衡发挥着重要作用,因此,探究胶原蛋白代谢产物在退变椎间盘中的功能及作用机制也是很有必要的,希望通过更加深入的研究,为椎间盘退变的治疗提供新的策略和靶点。"

| [1] XIAO ZF, SU GY, HOU Y, et al. Mechanics and Biology Interact in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: A Novel Composite Mouse Model. Calcif Tissue Int. 2020;106(4):401-414. [2] LI XC, LUO SJ, FAN W, et al. Macrophage polarization regulates intervertebral disc degeneration by modulating cell proliferation, inflammation mediator secretion, and extracellular matrix metabolism. Front Immunol. 2022;13:922173. [3] LI H, WANG X, PAN H, et al. The mechanisms and functions of IL-1β in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Gerontol. 2023;177:112181. [4] CHAI Q, ZHANG B, DA Y, et al. Enhancement and Repair of Degenerative Intervertebral Disc in Rats Using Platelet-Rich Plasma/Ferulic Acid Hydrogel. Cartilage. 2023;14(4):506-515. [5] YANG X, LI F, ZHU Y, et al. Multiple variants in collagen genes are associated with the susceptibility to lumbar disc herniation in the Chinese population. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7):1709-1716. [6] 柴强,王文磊,祝勇,等. 椎间盘退变动物模型的研究进展[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(12):800-807. [7] TAHER F, ESSIG D, LEBL DR, et al. Lumbar degenerative disc disease: current and future concepts of diagnosis and management. Adv Orthop. 2012;2012:970752. [8] MANKA SW, BIHAN D, FARNDALE RW. Structural studies of the MMP-3 interaction with triple-helical collagen introduce new roles for the enzyme in tissue remodelling. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):18785. [9] 许刚,张长春,朱坤,等. 慢病毒介导的 IGF-1 与 PDGF 基因对人退变椎间盘髓核组织的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020, 34(7):907-914. [10] LO WC, CHANG CC, CHAN CH, et al. Platelet-Derived Biomaterials Exert Chondroprotective and Chondroregenerative Effects on Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Life (Basel). 2021; 11(10):1054. [11] CHEN S, LEI L, LI Z, et al. Grem1 accelerates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting TGF-β-mediated Smad2/3 phosphorylation. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(4):518-530. [12] MURUGAIYAN K, AMIRTHALINGAM S, HWANG NS, et al. Role of FGF-18 in Bone Regeneration. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(1):36. [13] RICARD-BLUM S. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011;3(1):a004978. [14] KESHARI KR, LOTZ JC, KURHANEWICZ J, et al. Correlation of HR-MAS spectroscopy derived metabolite concentrations with collagen and proteoglycan levels and Thompson grade in the degenerative disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(23):2683-2688. [15] LEE YC, ZOTTI MG, OSTI OL. Operative Management of Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(4):801-819. [16] WU X, LIU C, YANG S, et al. Glycine-Serine-Threonine Metabolic Axis Delays Intervertebral Disc Degeneration through Antioxidant Effects: An Imaging and Metabonomics Study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:5579736. [17] RAJASEKARAN S, SOUNDARARAJAN DCR, TANGAVEL C, et al. Uncovering molecular targets for regenerative therapy in degenerative disc disease: do small leucine-rich proteoglycans hold the key? Spine J. 2021;21(1):5-19. [18] MOHD ISA IL, TEOH SL, MOHD NOR NH, et al. Discogenic Low Back Pain: Anatomy, Pathophysiology and Treatments of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):208. [19] SHI S, KANG XJ, ZHOU Z, et al. Excessive mechanical stress-induced intervertebral disc degeneration is related to Piezo1 overexpression triggering the imbalance of autophagy/apoptosis in human nucleus pulpous. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):119. [20] KIBBLE MJ, DOMINGOS M, HOYLAND JA, et al. Importance of Matrix Cues on Intervertebral Disc Development, Degeneration, and Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):6915. [21] HU S, HE W, WU G. Hydroxyproline in animal metabolism, nutrition, and cell signaling. Amino Acids. 2022;54(4):513-528. [22] SALO AM, MYLLYHARJU J. Prolyl and lysyl hydroxylases in collagen synthesis. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30(1):38-49. [23] XIAO L, GAO D, ZHANG Y, et al. Codelivery of TGF-β1 and anti-miR-141 by PLGA microspheres inhibits progression of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):17. [24] SUN R, ZHU J, SUN K, et al. Strontium Ranelate Ameliorates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Regulating TGF-β1/NF-κB Axis. Int J Med Sci. 2023;20(13):1679-1697. [25] LIU Y, XUE M, HAN Y, et al. Exosomes from M2c macrophages alleviate intervertebral disc degeneration by promoting synthesis of the extracellular matrix via MiR-124/CILP/TGF-β. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023; 8(6):e10500. [26] LO WC, CHANG CC, CHAN CH, et al. Platelet-Derived Biomaterials Exert Chondroprotective and Chondroregenerative Effects on Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Life (Basel). 2021; 11(10):1054. [27] ZHANG W, GONG Y, ZHENG X, et al. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Inhibits Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Suppressing Pyroptosis and Activating the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12: 799130. [28] WEN P, ZHENG B, ZHANG B, et al. The role of ageing and oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:1052878. [29] KUMAR V, GOUTAM RS, PARK S, et al. Functional Roles of FGF Signaling in Early Development of Vertebrate Embryos. Cells. 2021;10(8):2148. [30] LU S, LIN CW. Lentivirus-mediated transfer of gene encoding fibroblast growth factor-18 inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(2):856. [31] TANG Y, ZHANG M. Fibroblast growth factor 21 and bone homeostasis. Biomed J. 2023;46(4):100548. [32] LIN H, TIAN S, PENG Y, et al. IGF Signaling in Intervertebral Disc Health and Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:817099. [33] LI H, KONG R, WAN B, et al. Initiation of PI3K/AKT pathway by IGF-1 decreases spinal cord injury-induced endothelial apoptosis and microvascular damage. Life Sci. 2020;263:118572. [34] ZHANG CC, ZHOU JS, HU JG, et al. Effects of IGF-1 on IL-1β-induced apoptosis in rabbit nucleus pulposus cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(2):441-444. [35] ZHANG C, WANG F, XIE Z, et al. The hippo pathway orchestrates cytoskeletal organisation during intervertebral disc degeneration. Acta Histochem. 2021;123(6):151770. [36] 张聪. 细胞骨架蛋白介导Hippo信号调控对椎间盘髓核细胞形态及增殖活性的效应机制研究[D].南京:东南大学,2020. [37] GUO S, CUI L, XIAO C, et al. The Mechanisms and Functions of GDF-5 in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(3): 734-741. [38] CUI M, WAN Y, ANDERSON DG, et al. Mouse growth and differentiation factor-5 protein and DNA therapy potentiates intervertebral disc cell aggregation and chondrogenic gene expression. Spine J. 2008;8(2): 287-95. [39] LUO XW, LIU K, CHEN Z, et al. Adenovirus-mediated GDF-5 promotes the extracellular matrix expression in degenerative nucleus pulposus cells. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17(1):30-42. [40] GE J, YAN Q, WANG Y, et al. IL-10 delays the degeneration of intervertebral discs by suppressing the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;147:262-270. [41] CHENG H, GUO Q, ZHAO H, et al. An Injectable Hydrogel Scaffold Loaded with Dual-Drug/Sustained-Release PLGA Microspheres for the Regulation of Macrophage Polarization in the Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):390. [42] ZHU Y, LI S, HUANG Z, et al. Association study between matrix metalloproteinase-3 gene (MMP3) polymorphisms and ankylosing spondylitis susceptibility. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019;7(7):e00752. [43] ZOU X, ZHANG X, HAN S, et al. Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications of matrix metalloproteinases in intervertebral disc degeneration: A comprehensive review. Biochimie. 2023;214(Pt B):27-48. [44] MANKA SW, BIHAN D, FARNDALE RW. Structural studies of the MMP-3 interaction with triple-helical collagen introduce new roles for the enzyme in tissue remodelling. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):18785. [45] ZENG Q, SUN Q, XU H, et al. Amygdalin Delays Cartilage Endplate Degeneration and Improves Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Inflammatory Response. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:3455-3468. [46] LI X, LIN F, WU Y, et al. Resveratrol attenuates inflammation environment-induced nucleus pulposus cell senescence in vitro. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(5):BSR20190126. [47] SOLBERG R, LUNDE NN, FORBORD KM, et al. The Mammalian Cysteine Protease Legumain in Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15983. [48] DRAKE MT, CLARKE BL, OURSLER MJ, et al. Cathepsin K Inhibitors for Osteoporosis: Biology, Potential Clinical Utility, and Lessons Learned. Endocr Rev. 2017;38(4):325-350. [49] MORT JS, BEAUDRY F, THÉROUX K, et al. Early cathepsin K degradation of type II collagen in vitro and in vivo in articular cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(8):1461-1469. [50] MAKONI NJ, NICHOLS MR. The intricate biophysical puzzle of caspase-1 activation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021;699:108753.
[51] ZHOU Y, CHEN Z, YANG X, et al. Morin attenuates pyroptosis of nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of the TXNIP/NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 20215;559:106-112. [52] TENG Y, HUANG Y, YU H, et al. Nimbolide targeting SIRT1 mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration by reprogramming cholesterol metabolism and inhibiting inflammatory signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13(5):2269-2280. [53] FANG W, ZHOU X, WANG J, et al. Wogonin mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration through the Nrf2/ARE and MAPK signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;65:539-549. [54] SHI C, WU L, LIN W, et al. MiR-202-3p regulates interleukin-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase 1 in human nucleus pulposus. Gene. 2019;687:156-165. [55] ZHAN S, WANG K, SONG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates intervertebral disc degenerative changes via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):201. [56] CHEN J, MEI Z, HUANG B, et al. IL-6/YAP1/β-catenin signaling is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5964-5971. [57] ZHANG Y, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin modulates IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(22):10499-10512. [58] YANG S, LI L, ZHU L, et al. Aucubin inhibits IL-1β- or TNF-α-induced extracellular matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cell through blocking the miR-140-5p/CREB1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8): 13639-13648. [59] HUANG Y, PENG Y, SUN J, et al. Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyl Transferase Controls NLRP3 Inflammasome Activity Through MAPK and NF-κB Signaling in Nucleus Pulposus Cells, as Suppressed by Melatonin. Inflammation. 2020;43(3):796-809. [60] LONG DL, WILLEY JS, LOESER RF. Rac1 is required for matrix metalloproteinase 13 production by chondrocytes in response to fibronectin fragments. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(6):1561-1568. [61] YANG X, SUN Y, LI X, et al. Rac1 regulates nucleus pulposus cell degeneration by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and promotes the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022;322(3):C496-C507. [62] HAJAM YA, RANI R, GANIE SY, et al. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells. 2022;11(3):552. [63] WEI A, BRISBY H, CHUNG SA, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 protects human intervertebral disc cells in vitro from apoptosis. Spine J. 2008;8(3):466-74. [64] SCHARF B, CLEMENT CC, YODMUANG S, et al. Age-related carbonylation of fibrocartilage structural proteins drives tissue degenerative modification. Chem Biol. 2013;20(7):922-34. [65] YANG RZ, XU WN, ZHENG HL, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced annulus fibrosus cell and nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021; 236(4):2725-2739. [66] WANG Y, CHENG H, WANG T, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(9):e13448. [67] LAMBERT C, BORDERIE D, DUBUC JE, et al. Type II collagen peptide Coll2-1 is an actor of synovitis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(11): 1680-1691. [68] LINDSEY ML, IYER RP, ZAMILPA R, et al. A Novel Collagen Matricryptin Reduces Left Ventricular Dilation Post-Myocardial Infarction by Promoting Scar Formation and Angiogenesis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66(12):1364-74. [69] YASUDA J, FUKUI K, OKADA M, et al. T3 peptide, a fragment of tumstatin, stimulates proliferation and migration of cardiac fibroblasts through activation of Akt signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017;390(11):1135-1144. [70] AIKIO M, ALAHUHTA I, NURMENNIEMI S, et al. Arresten, a collagen-derived angiogenesis inhibitor, suppresses invasion of squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51044. [71] VERWILGHEN DR, MARTENS A, BUSSCHERS E, et al. Coll2-1, Coll2-1NO2 and myeloperoxidase concentrations in the synovial fluid of equine tarsocrural joints affected with osteochondrosis. Vet Res Commun. 2011;35(7):401-8. [72] JOSEPH GB, NEVITT MC, MCCULLOCH CE, et al. Associations between molecular biomarkers and MR-based cartilage composition and knee joint morphology: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(8):1070-1077. [73] BROWN JP, DON-WAUCHOPE A, DOUVILLE P, et al. Current use of bone turnover markers in the management of osteoporosis. Clin Biochem. 2022;109-110:1-10. [74] WANG Y, WANG Z, DONG Y. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(3):1132-1150. [75] ANGEL PM, ZAMBRZYCKI SC. Predictive value of collagen in cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2022;154:15-45. [76] LIU L, WANG W, HUANG L, et al. Injectable pathological microenvironment-responsive anti-inflammatory hydrogels for ameliorating intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomaterials. 2024; 306:122509. |
| [1] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [2] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [3] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [4] | Huang Haina, Yu Yanrong, Bi Jian, Huang Miao, Peng Weijie. Epigenetic characteristics of hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7848-7855. |
| [5] | Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879. |
| [6] | Ji Long, Chen Ziyang, , Jin Pan, Kong Xiangkui, Pu Rui, . Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7611-7619. |
| [7] | Zhang Pulian, Liu Baoru, Yang Min . Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of aplastic anemia: inhibiting or activating relevant targets in its pathological evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6800-6810. |
| [8] | Yu Bingbing, Wang Tingting, Fang Junlin, Guo Yun, Huang Yingru. Acupuncture for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: meta-analysis, systematic evaluation and trial sequential analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6305-6316. |
| [9] | Wang Jiaru, Zhang Ying, Yang Yong, Qi Wen, Xiao Huaye, Ma Qiuping, Yang Lianzhao, Luo Ziwei, He Yaqing, Zhang Jiangyin, Wei Jiawen, Meng Yuan, Tan Silian. Systematic review of machine learning models for predicting functional recovery and prognosis in stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6317-6325. |
| [10] | Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Gulimire·Yilihamu, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Cellular biomechanisms of Wallerian degeneration in peripheral nerve axon injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5688-5694. |
| [11] | Geng Longyu, Sheng Li, Bai Shuo, Gao Beiyao, Ge Ruidong, Jiang Shan . Role and molecular mechanism of pyroptosis in motor system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5695-5703. |
| [12] | Jiang Qianping, Yang Dan, , , Wan Shilei, Xu Dandan, , , , Cao Lu, , Zhou Jing, , , . Role of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine glycosylation in neurodegenerative diseases and its clinical application prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5704-5712. |
| [13] | Yang Shuo, Zhang Zhen, Bai Shuo, Sheng Li, Shen Liang, Sun Qingfeng, Gao Beiyao, Ge Ruidong, Jiang Shan. Mitochondrial dysfunction in tendinopathy: possibility of mitochondria-targeting therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4276-4285. |
| [14] | Wang Wenchi, Xia Tian, Wu Ruiqi, Liang Haohan, Ni Zhenyang, Zhang Zhenhao, Li Zhenxing, Chen Guanghui, Su Han. Molecular mechanism of active ingredients of Ligustri Lucidi Fructus against osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3856-3867. |
| [15] | Wang Ke, Wang Lei, Li Wenshan, Gong Weijun . Application prospect of brain-computer interface technology in the rehabilitation of lower limb function in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 3027-3033. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||