Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (22): 3490-3495.doi: 10.12307/2024.443
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hot spots in study of vascular stent effect and problems in medical quality management: health economics evaluation
Li Jialu1, Li Xiaomeng2
- 1Department of Operation and Management, First Affiliated Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China; 2Liaoning Academy of Social Sciences, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2023-06-21Accepted:2023-07-23Online:2024-08-08Published:2024-01-20 -
Contact:Li Jialu, Master, Department of Operation and Management, First Affiliated Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Li Jialu, Master, Department of Operation and Management, First Affiliated Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Liaoning Provincial Social Science Foundation, No. L17CSH004 (to LXM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jialu, Li Xiaomeng. Hot spots in study of vascular stent effect and problems in medical quality management: health economics evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3490-3495.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

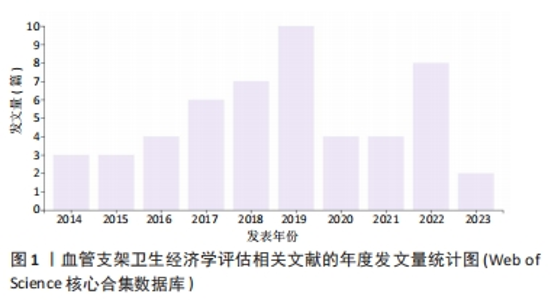
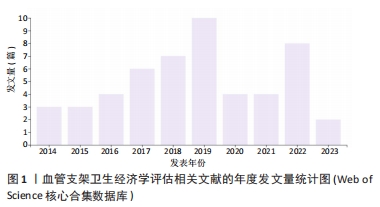
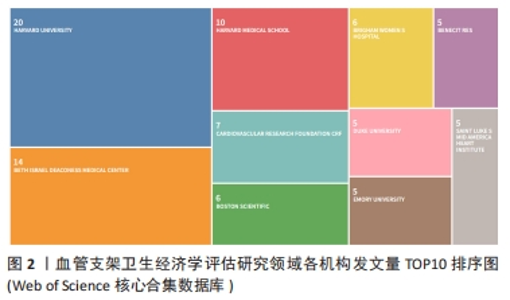
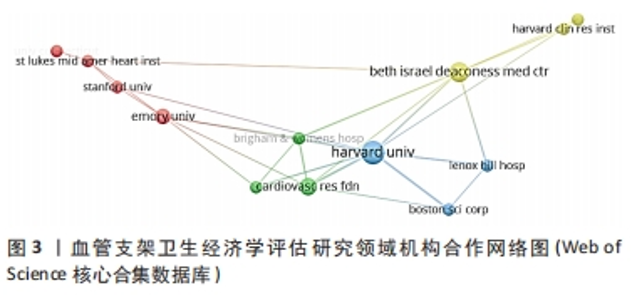
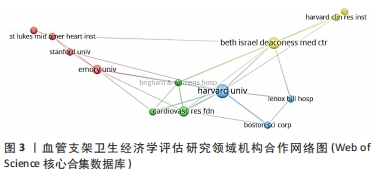
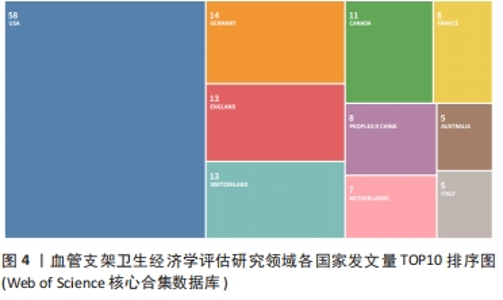
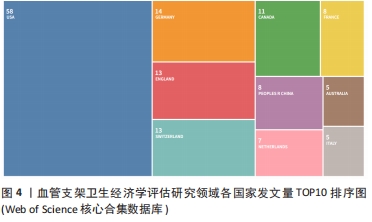
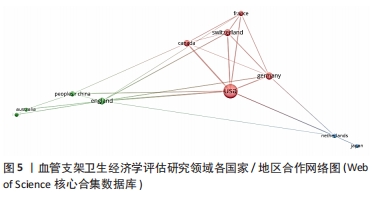
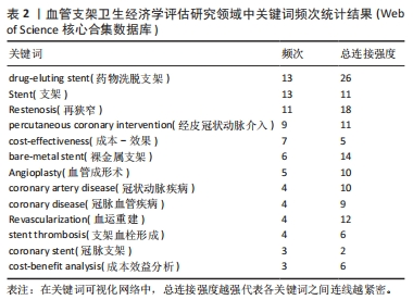
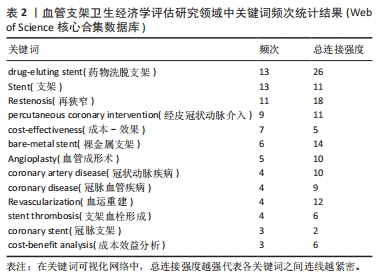
2.5 高被引文献分析 将纳入的120篇文献按被引次数排序,选择具有代表性的高被引文献进行该领域的研究热点分析。被引频次最高的研究原著文献为“Cost-effectiveness of sirolimus-eluting stents for treatment of complex coronary stenoses-Results from the sirolimus-eluting balloon expandable stent in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery lesions (SIRIUS) trial西罗莫司洗脱支架治疗复杂冠状动脉狭窄的成本效益-西罗莫司洗脱球囊扩张支架治疗新生原发性冠状动脉病变患者(SIRIUS)试验的结果”[22],被引173次。通过文献内容深度分析发现,以下研究的经济学分析结果较为经典,各研究结果所推荐的支架成本效果较好被引次数较高,被同行学者认可[22-27](被引173次),见表3。"


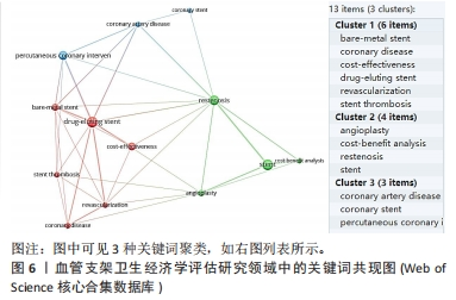
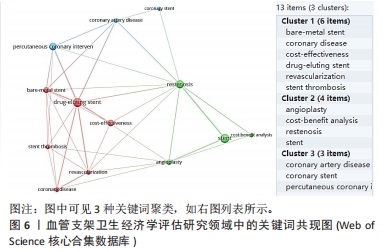
COHEN等[22]研究发现,对于接受复杂冠状动脉狭窄的患者来说,在美国医疗体系的背景下,西罗莫司洗脱支架的成本效益似乎是合理的。尽管西罗莫司洗脱支架初始费用更高,但由于减少了复发性冠脉狭窄的需求,总体而言,西罗莫司洗脱支架可能是一个经济上可接受的选择。SHIREMAN等[24](被引95次)研究了急性缺血性脑卒中患者接受血管内取栓(SST)加组织型纤溶酶原激活物(tPA)治疗相对于单独接受tPA治疗的效果和经济性发现,尽管SST+阿替普酶治疗的初始费用较高,但是在一生的时间范围内,相对于阿替普酶治疗,SST+阿替普酶治疗可以提高生活质量调整年限并降低总体医疗费用。WEAVER等[25]研究(被引76次)表明,对接受单血管冠状动脉成形术患者而言,在与初始气球扩张术加临时支架策略相比较时,常规支架植入策略在急性和长期的临床效果上更好,而且其成本与初始气球扩张术加临时支架策略相当。这意味着常规支架策略在医疗成本和患者临床结果方面可能更具有经济性和实用性。 2.6 不同血管支架或支架治疗方法的成本效果总结 针对文章纳入的120篇文献研究结果分析归纳如下: 药物洗脱支架:大部分研究显示药物洗脱支架相对于裸金属支架在防止再狭窄和进一步的血管疾病方面具有更好的效果,并且在长期效果方面也表现出较好的成本效果。然而,药物洗脱支架的初始费用较高,并且可能增加晚期血栓形成和全身性药物反应的风险。 裸金属支架:这是早期的支架,通常比药物洗脱支架便宜,但在某些情况下存在再狭窄的风险较高。裸金属支架相对于药物洗脱支架来说成本较低,但在防止再狭窄和进一步的血管疾病方面效果较差。因此,在选择支架类型时,需要权衡成本和效果。 生物降解支架:该支架治疗的目标是结合药物洗脱支架和裸金属支架的优点,即避免长期的支架存在和减少再狭窄的风险。但是,它们的成本可能会更高,而且短期内可能会有一些并发症。生物可吸收支架是介入心脏病学治疗冠状动脉疾病的一个新领域,引入这项技术是为了克服目前金属药物洗脱支架的局限性,如支架内晚期再狭窄和永久性封闭血管。生物降解支架的概念是在被人体降解和吸收之前,在愈合过程中为血管提供临时支持,促进血管运动的恢复[28]。目前,有几种生物降解支架正在开发中或已在市场上销售,而些支架最终会被人体吸收。 血管支架的具体效果在不同疾病情况下可能存在差异。例如,在颅内动脉瘤的治疗中,目前研究明确了使用管道栓塞装置相对于支架辅助卷曲术的经济效益优势。而在颈动脉狭窄的治疗中,颈动脉内膜剥脱术相对于颈动脉支架植入具有更好的经济效益。经皮冠状动脉介入是一种常见的治疗冠心病的方法,多个研究显示此治疗在改善患者生活质量和降低心血管事件的发生上具有较好的成本效益。然而,经皮冠状动脉介入是否优于其他治疗方法如药物治疗和搭桥手术,仍然需要根据患者的具体情况进行综合评估。 需要注意的是,不同血管支架研究的结果可能存在差异,这取决于研究的设计、病例的选择、区域和社会背景等因素。在实际临床决策中,需要综合考虑患者的具体情况和资源分配的可行性。因此,针对不同类型的支架和不同疾病情况下的血管支架的经济评估结果,需要进一步研究具体的实证研究来支持决策。"

| [1] D’ORIA M, WANHAINEN A, DEMARTINO RR, et al. A scoping review of the rationale and evidence for cost-effectiveness analysis of fenestrated-branched endovascular repair for intact complex aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72(5):1772-1782. [2] KOSHY SKG, GEORGE LK, DAS P. Cost-effectiveness and outcomes with early or same-day discharge after elective percutaneous coronary intervention. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020;22(6):42. [3] ULLAH M, WAHAB A, KHAN SU, et al. Stent as a Novel technology for coronary artery disease and their clinical manifestation. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023;48(1):101415. [4] WU X, LI L, HE L. Drug-coated balloon versus drug-eluting stent in patients with small-vessel coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cardiol Res Pract. 2021;2021:1647635. [5] 吴丹枫,沈蔺.快速康复外科卫生经济学效益分析[J].中国医院,2021,25(3):48-51. [6] 高艳,周泓羽,赵庆华,等.医院感染的卫生经济学研究现状及启示[J].中国卫生资源,2021,24(5):520-524. [7] 安思兰,王泠.国外护理服务的卫生经济学评价研究进展[J].护士进修杂志,2022, 37(14):1300-1304. [8] 马冰,王晓春,黄求进,等.压力性损伤防治的卫生经济学评价研究进展[J].护理学杂志,2021,36(1):25-29. [9] 孙利强,李晶,刘航,等.CT-血流储备分数指导稳定性冠心病患者的治疗观察[J].中华实验外科杂志,2023,40(1):153-156. [10] 马云通,马慧慧,赵欣,等.定量血流分数在冠状动脉多支临界病变治疗中的价值[J].济宁医学院学报,2022,45(1):11-15. [11] 孙明敏,王连生,赵俊.冠心病患者介入治疗应用进口和国产药物洗脱支架的成本-效果分析[J].江苏医药,2013,39(8):944-946. [12] WILLICH SN, MÜLLER-RIEMENSCHNEIDER F, MCBRIDE D, et al. Health economic evaluation of the use of drug-eluting stents: first results from the drug-eluting stent registry (DES.de). Herz. 2012. doi: 10.1007/s00059-012-3581-5. [13] 祁方家,冯莎,吴伟栋,等.药物洗脱支架火鹰(Firehawk)与XIENCE V治疗单支单处冠状动脉病变的卫生经济学评价[J].中国卫生资源,2015,18(4):283-286. [14] ZBINDEN R, VON FELTEN S, WEIN B, et al. Impact of stent diameter and length on in-stent restenosis after DES vs BMS implantation in patients needing large coronary stents-A clinical and health-economic evaluation. Cardiovasc Ther. 2017;35(1):19-25. [15] MATTKE S, HANSON M, DALLMANN AC, et al. Health economic evaluation of an ultrathin, bioresorbable-polymer sirolimus-eluting coronary stent compared to a thin, durable-polymer everolimus-eluting stent. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2019;20(9):752-757. [16] ZHOU J, LIEW D, DUFFY SJ, et al. Intravascular ultrasound versus angiography-guided drug-eluting stent implantation: a health economic analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2021;14(5):e006789. [17] 刘畅,陶立波,王芳旭,等.血流导向密网支架(PED)对比支架辅助弹簧圈技术治疗颅内大型动脉瘤的卫生经济学评价[J].中国医疗保险,2022(3):61-67. [18] 刘洪章,杜炎秋,刘瑾瑜,等.颈动脉内膜剥脱术与支架植入术治疗颈动脉狭窄的卫生经济学评价[J].中国卫生经济,2023,42(5):80-85. [19] 潘希丁,周峰,荆莉,等.阿替普酶静脉溶栓桥接支架取栓对比直接支架取栓治疗急性缺血性卒中的卫生经济学评价[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2023,20(7):464-471. [20] SRIVASTAVA R, SRIVASTAVA S. Bibliometric analysis of indian journal of palliative care from 1995 to 2022 using the VOSviewer and bibliometrix software. Indian J Palliat Care. 2022;28(4):338-353. [21] ARRUDA H, SILVA ER, LESSA M, et al. VOSviewer and bibliometrix. J Med Libr Assoc. 2022;110(3):392-395. [22] COHEN DJ, BAKHAI A, SHI C, et al. Cost-effectiveness of sirolimus-eluting stents for treatment of complex coronary stenoses: results from the sirolimus-eluting balloon expandable stent in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery lesions (SIRIUS) trial. Circulation. 2004;110(5):508-514. [23] PARISE H, MAEHARA A, STONE GW, et al. Meta-analysis of randomized studies comparing intravascular ultrasound versus angiographic guidance of percutaneous coronary intervention in pre-drug-eluting stent era. Am J Cardiol. 2011;107(3):374-382. [24] SHIREMAN TI, WANG K, SAVER JL, et al. Cost-effectiveness of solitaire stent retriever thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: results from the SWIFT-PRIME Trial (Solitaire With the Intention for Thrombectomy as Primary Endovascular Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke). Stroke. 2017;48(2):379-387. [25] Weaver WD, Reisman MA, Griffin JJ, et al. Optimum percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty compared with routine stent strategy trial (OPUS-1): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;355(9222):2199-2203. [26] COHEN DJ, TAIRA DA, BEREZIN R, et al. Cost-effectiveness of coronary stenting in acute myocardial infarction: results from the stent primary angioplasty in myocardial infarction (stent-PAMI) trial. Circulation. 2001;104(25):3039-3045. [27] COLBY GP, LIN LM, PAUL AR, et al. Cost comparison of endovascular treatment of anterior circulation aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device and stent-assisted coiling. Neurosurgery. 2012;71(5):944-948; discussion 948-950. [28] ANG HY, BULLUCK H, WONG P, et al. Bioresorbable stents: current and upcoming bioresorbable technologies. Int J Cardiol. 2017;228:931-939. [29] 姜英,王乃东.颅内外血管狭窄术后支架内再狭窄的研究进展[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2022,19(2):130-135. [30] 何钰,王建波,王武.颅内动脉粥样硬化性狭窄支架植入术后再狭窄机制及治疗新进展[J].介入放射学杂志,2021,30(11):1184-1189. [31] 赵霞,左洪炜,藤碧云,等.支架置入在人工血管内瘘回流静脉狭窄中应用的长期效果分析[J].中国血液净化,2023,22(7):546-550. [32] 马金阳,汪雷,董元训,等.Willis覆膜支架治疗复杂颈内动脉病变的临床应用[J].介入放射学杂志,2022,31(12):1185-1189. [33] 赵铮,丁文飞,邵淑馨,等.西罗莫司-聚三亚甲基碳酸酯改性镁合金的降解和药物释放行为[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30):4836-4843. [34] 王江平,焦勇,许志斌,等.腹腔镜3D打印血管外支架植入术治疗胡桃夹综合征的安全性和有效性[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2018,39(3):200-204. [35] 方振威,石秀锦,赵紫楠,等.CYP2C19基因指导急性冠状动脉综合征或经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者P2Y12受体拮抗剂个体化治疗的长期疗效与安全性Meta分析[J].临床药物治疗杂志,2022,20(1):43-52. [36] 崔耀刚,吕小宁,庞然.冠心病PCI术后SICAM-1、RDW及vWF水平与支架内再狭窄的关系[J].分子诊断与治疗杂志,2022,14(3):426-429. [37] TEPE G, BRODMANN M, MICARI A, et al. 5-year outcomes of drug-coated balloons for peripheral artery in-stent restenosis, long lesions, and CTOs. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2023;16(9):1065-1078. [38] YI Y, WANG B, LI C. Sensors-based monitoring and treatment approaches for in-stent restenosis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2023;111(2):490-498. [39] 胡仁杰,张磊,张文,等.术中置入肺动脉分支血管支架的镶嵌技术治疗肺动脉分支狭窄[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2017,33(1):25-27. [40] BERTOGLIO L, MELLONI A, BUGNA C, et al. In-hospital cost-effectiveness analysis of open versus staged fenestrated/branched endovascular elective repair of thoracoabdominal aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2023;78(2):300-312.e3. [41] D’ORIA M, WANHAINEN A, DEMARTINO RR, et al. A scoping review of the rationale and evidence for cost-effectiveness analysis of fenestrated-branched endovascular repair for intact complex aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72(5):1772-1782. [42] 李洪坤,王新生,李江峰,等.冠心病经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者住院费用影响因素分析[J].精准医学杂志,2022,37(4):332-336,341. [43] 周力,李宇能,朱仕文,等.一期减张内固定与延迟手术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折合并筋膜间隔综合征的比较研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(5):394-399. [44] 丁轶.脑血管金属支架植入脑动脉血管血栓形成的风险评估[J].血栓与止血学, 2020,26(5):789-791. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Lei, Wu Fangting, Wang Jiahui, Duan Xuelin, Zhao Tiejian, Zhao Bin, Zheng Yang. Bibliometric analysis of researches on liver organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104. |
| [2] | Sun Yukang, Song Lijuan, Wen Chunli, Ding Zhibin, Tian Hao, Ma Dong, Ma Cungen, Zhai Xiaoyan. Visualization analysis of stem cell therapy for myocardial infarction based on Web of Science in recent ten years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1143-1148. |
| [3] | Li Yan, Liu Ning, Wang Xiaoyang, Xiao Xiangyu, Liu Ping, Zhang Yili, Jiang Hongjiang, Zhu Liguo, Wei Xu. Bibliometric and visual analysis of postmenopausal osteoporosis based on highly cited SCI papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5681-5687. |
| [4] | Luo Weidong, Zou Lihua, Huang Da. Visual analysis of hot topics in concussion field by finite element method: Improvements in brain injury models, test methods and protective devices [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5487-5493. |
| [5] | Xu Yi, Deng Yubin. Exoskeleton-assisted walking rehabilitation for spinal cord injury: CiteSpace analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5403-5412. |
| [6] | Yan Jie, Zhou Jing, Zhao Jingpu, Zhang Qingfang, Zhou Mingchao, Wang Yulong. Visual analysis of high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5110-5115. |
| [7] | Tao Guangyi, Wang Linzi, Yang Bin, Huang Junqing. Research hotspots of artificial intelligence in the field of spinal deformity: visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4915-4920. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhilong, Yang Shengping, Chen Tianxin, Zhu Yuqi. Research hotspots and trends in the field of articular cartilage repair: a visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4306-4311. |
| [9] | Duan Yanzhe, Hua Jianlin, Ding Zhibin, Jiang Nan, Song Lijuan, Yan Yuqing, Ma Cungen. Visual analysis of the effect of apoptosis on ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4145-4150. |
| [10] | Hou Zhaomeng, Su Shaoting, Chen Longhao, Wei Guikang, Zhou Honghai. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and trends in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3424-3430. |
| [11] | Xie Enli, Tao Huimin. Application trends of blood flow restriction training in clinical rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 258-262. |
| [12] | Fang Yuan, Kang Zhijie, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe, Zhang Kai. Visualization analysis of vascular stimulating scaffolds in bone tissue engineering#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2708-2715. |
| [13] | Hong Jing, Lu Congfei, Huang Chenbin, Jiang Qian, Liu Jingxiong. Visualization analysis of hot spots and trends in material biomechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2358-2363. |
| [14] | Zheng Ying, Huang Kemin. Bibliometrics and visualization-based analysis of research landscape of exosomes and foresight [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2126-2132. |
| [15] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Research hot spots and trends of exosomes in theranostic application for chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 86-92. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||