Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (16): 2550-2554.doi: 10.12307/2024.294
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and analysis of osteoarthritis diagnosis model based on artificial neural networks
Fan Yidong1, Qin Gang2, Su Guowei1, Xiao Shifu1, Liu Junliang1, Li Weicai1, Wu Guangtao1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Osteoarthropathy, Traumatic Orthopedics, and Femoral Head Necrosis Specialty, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-02-28Accepted:2023-05-08Online:2024-06-08Published:2023-07-31 -
Contact:Qin Gang, MD, Chief physician, Osteoarthropathy, Traumatic Orthopedics, and Femoral Head Necrosis Specialty, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Fan Yidong, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2020JJA140375 (to QG); Scientific Research Innovation Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. YCSY2022028 (to FYD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Yidong, Qin Gang, Su Guowei, Xiao Shifu, Liu Junliang, Li Weicai, Wu Guangtao. Establishment and analysis of osteoarthritis diagnosis model based on artificial neural networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2550-2554.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
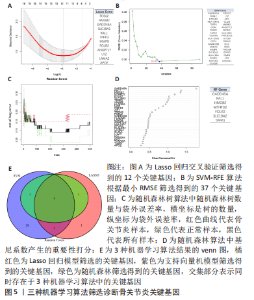
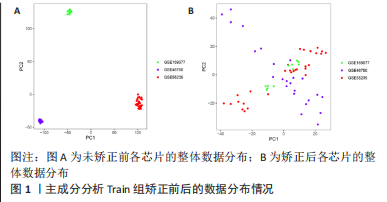
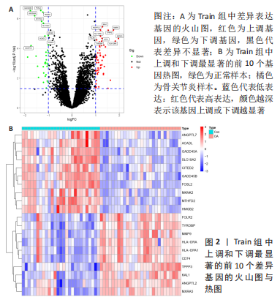
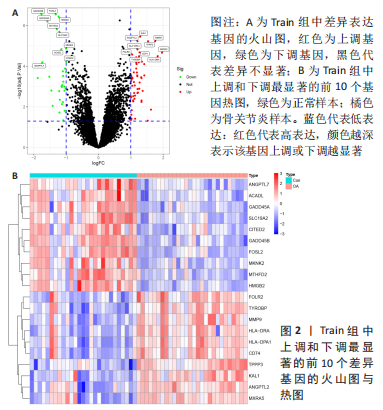
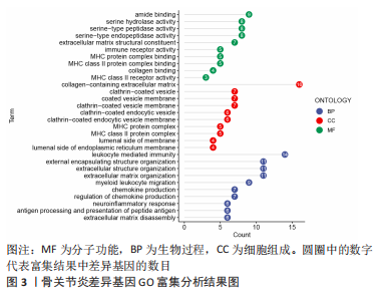
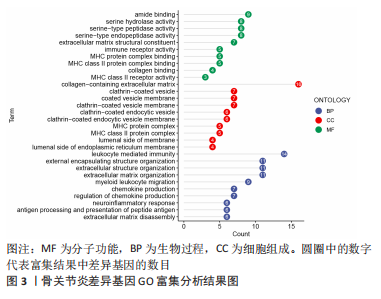
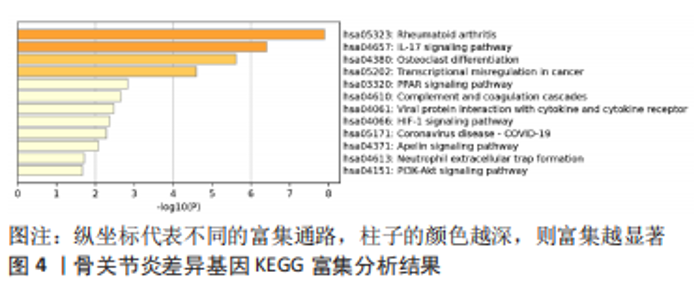
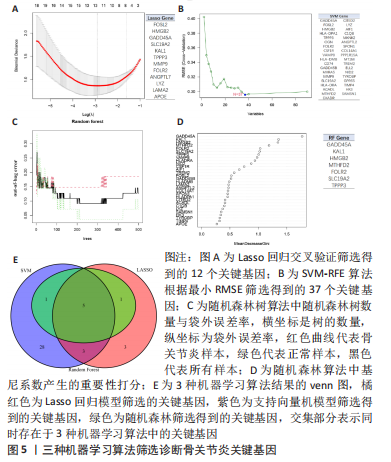
2.3 机器学习筛选骨关节炎关键基因结果 通过Lasso回归算法,得到10倍交叉验证误差最小的点对应的12个关键基因,见图5A。SVM-RFE算法中,关键基因筛选用“svmRadial”方法,抽样方法为“cv”,当交叉验证的标准误差(RMSE)最小为0.296时,共得到37个关键基因,见图5B。随机森林树算法中,首先计算1-500棵树的袋外误差率(OOB eror),选择错误率低、稳定性好的树的数目作为最优树数,结果显示当trees=200、mtry(为节点中二叉树的最佳变量数)=9时,误差值相对稳定,此时模型的袋外误差率最低为9.09%,Gini系数法计算每个基因的重要性得分,基因重要性评分> 2是随机森林常见的筛选条件[20],在此次研究中,由于得到的基因重要性评分均< 2,故选择重要性评分> 1作为筛选条件,见图5C,D。随后将3种机器学习算法得到的关键基因取交集,见图5E;最终得到5个具有代表性的骨关节炎关键基因,分别是HMGB2、GADD45A、SLC19A2、TPPP3、FOLR2。"
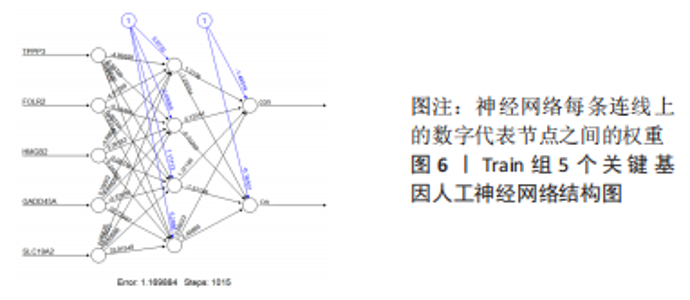
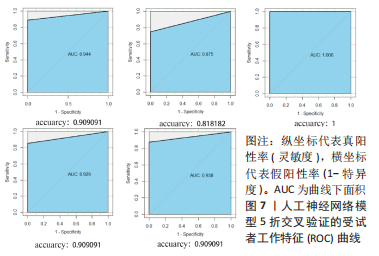
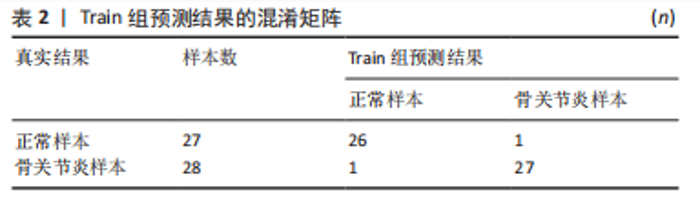
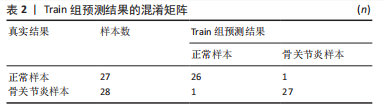
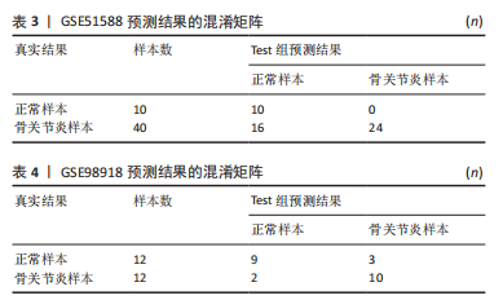
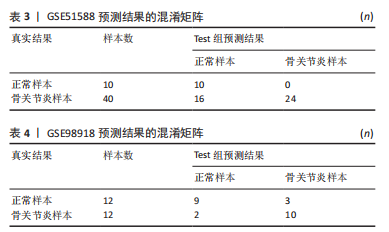
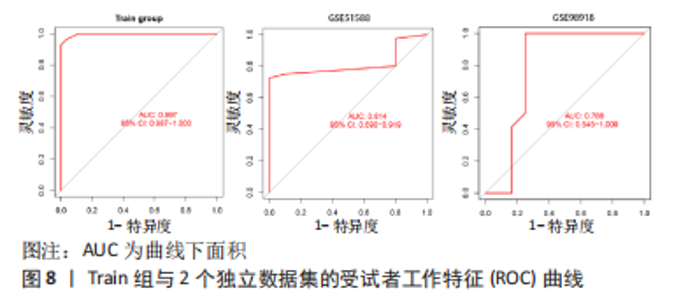
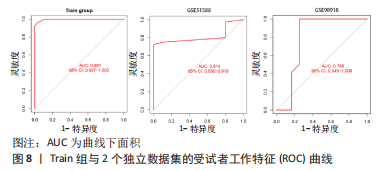
2.4 人工神经网络诊断骨关节炎模型的评价 通过Train组的5个关键基因建立的神经网络共执行了1 015步,终止条件为误差函数的绝对偏导数< 0.01,误差值为1.169 884,神经网络每条连线上的数字代表节点之间的权重,见图6。输出结果显示,模型的权重范围在-4.997-0.068,权重预测值-4.996 589(TPPP3),-4.912 893(FOLR2),-4.985 799 (HMGB2),0.290 0196(GADD45A),0.068 763 16(SLC19A2)。根据Train组的预测结果绘制混淆矩阵,Train组的准确率为96.36%,灵敏度为96.30%,特效度为96.42%,见表2。5折交叉验证显示其平均准确率与AUC值均>0.9,说明了模型的稳健性,见图7。"
| [1] JANG S, LEE K, JU J H. Recent updates of diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment on osteoarthritis of the knee. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2619. [2] WANG J, SUN Y, LIU J, et al. Roles of long non‑coding RNA in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(1):133. [3] LIANG Y, LIN F, HUANG Y. Identification of Biomarkers Associated with Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis Patients Based on Bioinformatics and Machine Learning. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:5600190. [4] XIE NN, WANG FF, ZHOU J, et al. Establishment and analysis of a combined diagnostic model of polycystic ovary syndrome with random forest and artificial neural network. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2613091. [5] MAMOSHINA P, VIEIRA A, PUTIN E, et al. Applications of deep learning in biomedicine. Mol Pharm. 2016;13(5):1445-1454. [6] WEI Q, FANG W, CHEN X, et al. Establishment and validation of a mathematical diagnosis model to distinguish benign pulmonary nodules from early non-small cell lung cancer in Chinese people. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020;9(5):1843-1852. [7] WANG C, ZHAO Y, JIN B, et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for coronary artery disease using machine learning. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021; 8:614204. [8] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553):436-444. [9] TIAN Y, YANG J, LAN M, et al. Construction and analysis of a joint diagnosis model of random forest and artificial neural network for heart failure. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):26221-26235. [10] SUN D, PENG H, WU Z. Establishment and analysis of a combined diagnostic model of alzheimer’s disease with random forest and artificial neural network. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:921906. [11] SHE J, SU D, DIAO R, et al. A Joint Model of Random Forest and Artificial Neural Network for the Diagnosis of Endometriosis. Front Genet. 2022;13:848116. [12] LAMBERT C, DUBUC JE, MONTELL E, et al. Gene expression pattern of cells from inflamed and normal areas of osteoarthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(4):960-968. [13] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84. [14] BROPHY RH, ZHANG B, CAI L, et al. Transcriptome comparison of meniscus from patients with and without osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3): 422-432. [15] CHOU CH, WU CC, SONG IW, et al. Genome-wide expression profiles of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R190. [16] LIU W, ZENG S, WU G, et al. Rice seed purity identification technology using hyperspectral image with LASSO logistic regression model. Sensors (Basel). 2021;21(13):4384. [17] HUANG ML, HUNG YH, LEE WM, et al. SVM-RFE based feature selection and Taguchi parameters optimization for multiclass SVM classifier. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:795624. [18] ACHARJEE A, LARKMAN J, XU Y, et al. A random forest based biomarker discovery and power analysis framework for diagnostics research. BMC Med Genomics. 2020;13(1):178. [19] XIANG J, HUANG W, HE Y, et al. Construction of artificial neural network diagnostic model and analysis of immune infiltration for periodontitis. Front Genet. 2022; 13:1041524. [20] WU Y, CHEN H, LI L, et al. Construction of novel gene signature-based predictive model for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction by combining random forest with artificial neural network. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:876543. [21] YE T, HAOYUAN Z, BEI Z, et al. Exploration of biomarkers in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(31):e26730. [22] 陈宗锐,孙洁,姜萍.骨关节炎软骨代谢相关生物标志物的研究进展[J].医学综述,2022,28(12):2351-2356 [23] KUO YY, HUANG ST, CHIU HW. Applying artificial neural network for early detection of sepsis with intentionally preserved highly missing real-world data for simulating clinical situation. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021;21(1):290. [24] BAXT WG. Application of artificial neural networks to clinical medicine. The lancet. 1995;346(8983):1135-1138. [25] TANIGUCHI N, CARAMÉS B, RONFANI L, et al. Aging-related loss of the chromatin protein HMGB2 in articular cartilage is linked to reduced cellularity and osteoarthritis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(4):1181-1186. [26] 谢春意,刘晓辉,谢获,等.膝骨关节炎患者滑液和血清中HMGB2的研究[J].放射免疫学杂志,2012,25(6):675-677 [27] WARMINK K, SIEBELT M, LOW PS, et al. Folate Receptor Expression by Human Monocyte–Derived Macrophage Subtypes and Effects of Corticosteroids. Cartilage. 2022;13(1):19476035221081469. [28] YI YS. Folate receptor-targeted diagnostics and therapeutics for inflammatory diseases. Immune Netw. 2016;16(6):337-343. [29] BLOM AB, VAN LENT PL, HOLTHUYSEN AE, et al. Synovial lining macrophages mediate osteophyte formation during experimental osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(8):627-635. [30] LI RN, LIN YZ, PAN YC, et al. GADD45a and GADD45b genes in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Clin Med. 2019;8(6):801. [31] ZHAN Q. Gadd45a, a p53-and BRCA1-regulated stress protein, in cellular response to DNA damage. Mutat Res. 2005;569(1-2):133-143. [32] HASHIMOTO S, NISHIYAMA T, HAYASHI S, et al. Role of p53 in human chondrocyte apoptosis in response to shear strain. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(8):2340-2349. [33] JANG HJ, YANG JH, HONG E, et al. Chelidonine induces apoptosis via GADD45a-p53 regulation in human pancreatic cancer cells. Integr Cancer Ther. 2021;20:15347354211006191. [34] JIN S, MAZZACURATI L, ZHU X, et al. Gadd45a contributes to p53 stabilization in response to DNA damage. Oncogene. 2003;22(52):8536-8540. [35] AMR K, PAWLIKOWSKA P, AOUFOUCHI S, et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies a new mutation in the SLC19A2 gene leading to thiamine‐responsive megaloblastic anemia in an Egyptian family. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019; 7(7):e00777. [36] LO PK, CHEN JY, TANG PP, et al. Identification of a mouse thiamine transporter gene as a direct transcriptional target for p53. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(40):37186-37193. [37] STAVEROSKY JA, PRYCE BA, WATSON SS, et al. Tubulin polymerization‐promoting protein family member 3, Tppp3, is a specific marker of the differentiating tendon sheath and synovial joints. Dev Dyn. 2009;238(3):685-692. |
| [1] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [2] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [3] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [4] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [5] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [6] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [7] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [8] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [9] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [10] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [11] | Maisituremu·Heilili, Zhang Wanxia, Nijiati·Nuermuhanmode, Maimaitituxun·Tuerdi. Effect of intraarticular injection of different concentrations of ozone on condylar histology of rats with early temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 505-509. |
| [12] | Qiao Hujun, Wang Guoxiang. Evaluation of rat osteoarthritis chondrocyte models induced by interleukin-1beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 516-521. |
| [13] | Liu Yuhan, Fan Yujiang, Wang Qiguang. Comparison of protocols for constructing animal models of early traumatic knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 542-549. |
| [14] | Zhang Yaru, Chen Yanjun, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Shenghua, Huang Wenhua. Effect of ferroptosis mediated by glutathione peroxidase 4 in the occurrence and progression of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 550-555. |
| [15] | Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||