Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (13): 2012-2019.doi: 10.12307/2022.326
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells secreting tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulating gene-6 protein on conversion of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophage subtypes
Zhao Jiling, Peng Yi, Peng Zhiyong, Yu Guolong
- Department of Cardiology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2020-03-06Revised:2020-03-12Accepted:2020-12-14Online:2022-05-08Published:2021-12-20 -
Contact:Yu Guolong, MD, Professor, Department of Cardiology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Zhao Jiling, Master, Physician, Department of Cardiology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81570266 (to YGL); Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation Key Project, No. 2015SK2025 (to YGL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Jiling, Peng Yi, Peng Zhiyong, Yu Guolong. Effects of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells secreting tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulating gene-6 protein on conversion of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophage subtypes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2012-2019.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
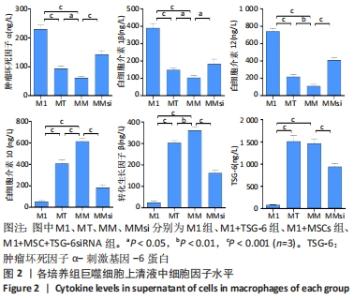
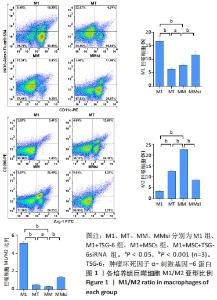
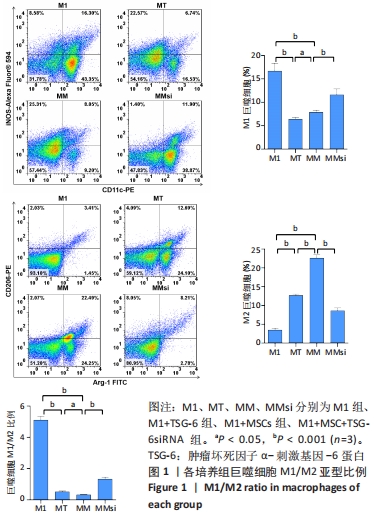
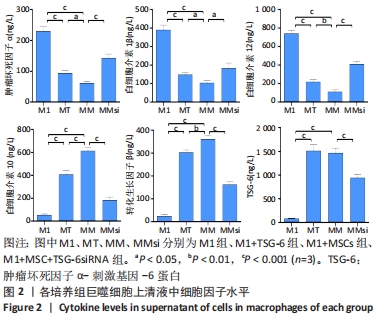
2.2 炎症因子变化 促炎症细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素12水平在M1+TSG-6组及M1+MSC组低于M1组(P < 0.001),且M1+MSC组低于M1+TSG-6组(P < 0.05),M1+MSC+TSG-6siRNA组促炎细胞因子水平高于M1+MSC组(P < 0.05);抗炎症细胞因子白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β1、TSG-6水平在M1+TSG-6组及M1+MSC组高于M1组(P < 0.001),与M1+TSG-6组相比,M1+MSC组白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β1水平较高(P < 0.05),TSG-6水平无明显差异(P > 0.05);M1+MSC+TSG-6siRNA组抗炎因子水平低于M1+MSC组(P < 0.05),见图2。"
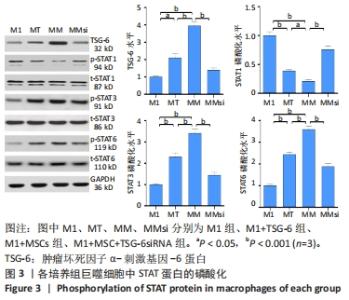
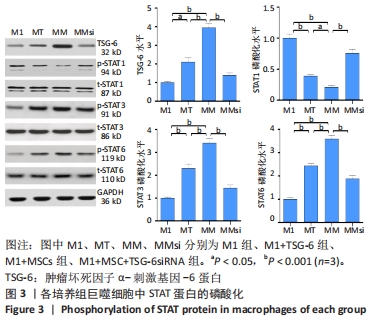
2.3 通道蛋白磷酸化 M1+MSC组和M1+TSG-6组巨噬细胞TSG-6水平高于M1组(P < 0.01),其中M1+MSC组较M1+TSG-6组亦有增加(P < 0.001),而M1+MSC+TSG-6siRNA组TSG-6水平低于M1+MSC组(P < 0.001)。与M1组比较,M1+MSC组和M1+TSG-6组巨噬细胞p/t-STAT1水平降低(P < 0.001)、p/t-STAT3/6水平升高(P < 0.001);与M1+TSG-6组比较,M1+MSC组巨噬细胞p/t-STAT1水平降低(P < 0.001)、p/t-STAT3/6水平升高(P < 0.001);与M1+MSC组比较,M1+MSC+TSG-6siRNA组p/t-STAT 1水平升高(P < 0.001)、p/t-STAT 3/6水平降低(P < 0.001),见图3。"
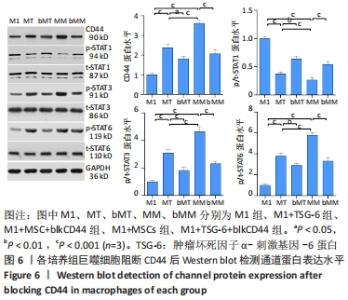
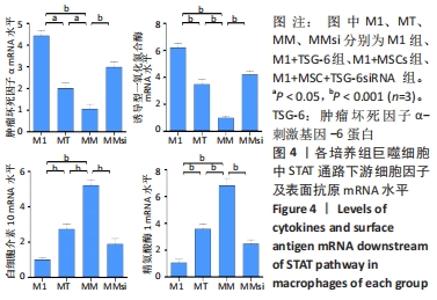
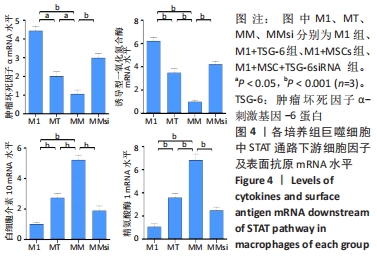
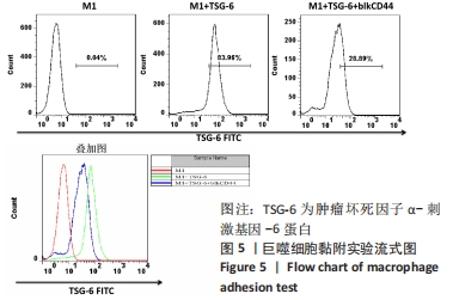
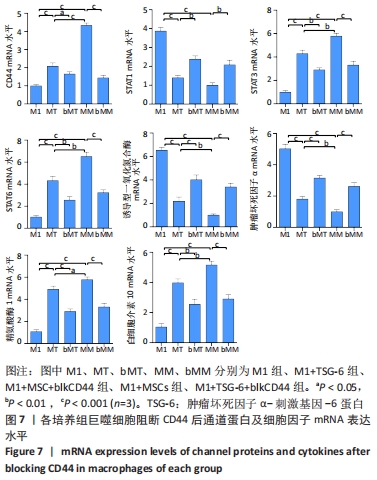
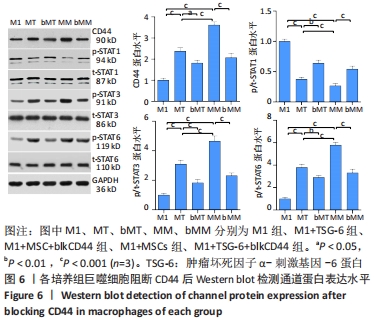
与M1组比较,M1+MSC组和M1+TSG-6组细胞表面CD44表达较高、CD44 mRNA表达增加(P < 0.001),且M1+MSC组较M1+TSG-6组高(P < 0.001);M1+MSC+blkCD44组与M1+MSC组、M1+TSG-6+blkCD44组与M1+TSG-6组比较,细胞表面CD44表达及CD44 mRNA表达较低(P < 0.01);M1+MSC+blkCD44组的CD44表达高于M1+TSG-6+blkCD44组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。与M1组比较,M1+MSC组和M1+TSG-6组p/t-STAT1及STAT1 mRNA水平降低(P < 0.01),p/t-STAT3/6及STAT3/6 mRNA水平下降(P < 0.001),下游肿瘤坏死因子α及诱导型一氧化氮合酶mRNA降低,白细胞介素10及精氨酸酶1 mRNA上升(P < 0.01);与M1+TSG-6组比较,M1+MSC组p/t-STAT1下降,p/t-STAT3/6升高(P < 0.001),STAT3/6 mRNA水平升高(P < 0.01),M1+TSG-6组STAT1 mRNA表达高于M1+MSC组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),肿瘤坏死因子α及诱导型一氧化氮合酶 mRNA降低(P < 0.01),白细胞介素10及精氨酸酶1 mRNA上升(P < 0.05);M1+MSC+blkCD44组与M1+MSC组、M1+TSG-6+blkCD44组与M1+TSG-6组比较,p/t-STAT1及STAT1 mRNA水平升高(P < 0.01),p/t-STAT3及STAT3 mRNA水平下降(P < 0.01),p/t-STAT6及STAT6 mRNA水平下降(P < 0.001),肿瘤坏死因子α及诱导型一氧化氮合酶 mRNA水平升高、白细胞介素10及精氨酸酶1 mRNA水平下降(P < 0.01);而接受CD44阻断剂的两组之间比较,通道蛋白活化及mRNA表达无明显差异(P > 0.05),见图6,7。"
| [1] VAN DER VORST EPC, WEBER C. Novel Features of Monocytes and Macrophages in Cardiovascular Biology and Disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(2):e30-e37. [2] MCNELIS JC, OLEFSKY JM. Macrophages, immunity, and metabolic disease. Immunity. 2014;41(1):36-48. [3] MUNSHI NV. Resident Macrophages: Near and Dear to Your Heart. Cell. 2017;169(3):376-377. [4] FRODERMANN V, NAHRENDORF M. Macrophages and Cardiovascular Health. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(4):2523-2569. [5] DAS A, SINHA M, DATTA S, et al. Monocyte and macrophage plasticity in tissue repair and regeneration. Am J Pathol. 2015;185(10):2596-2606. [6] WYNN TA, VANNELLA KM. Macrophages in Tissue Repair, Regeneration, and Fibrosis. Immunity. 2016;44(3):450-462. [7] BEN-MORDECHAI T, HOLBOVA R, LANDA-ROUBEN N, et al. Macrophage subpopulations are essential for infarct repair with and without stem cell therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(20):1890-1901. [8] FRANTZ S, NAHRENDORF M. Cardiac macrophages and their role in ischaemic heart disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;102(2):240-248. [9] SWIRSKI FK, ROBBINS CS, NAHRENDORF M. Development and Function of Arterial and Cardiac Macrophages. Trends Immunol. 2016;37(1):32-40. [10] FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Inflammation in cardiac injury, repair and regeneration. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2015;30(3):240-245. [11] WILLIAMS JW, GIANNARELLI C, RAHMAN A, et al. Macrophage Biology, Classification, and Phenotype in Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Macrophage in CVD Series (Part 1). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(18): 2166-2180. [12] MOORE KJ, KOPLEV S, FISHER EA, et al. Macrophage Trafficking, Inflammatory Resolution, and Genomics in Atherosclerosis: JACC Macrophage in CVD Series (Part 2). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(18): 2181-2197. [13] FAYAD ZA, SWIRSKI FK, CALCAGNO C, et al. Monocyte and Macrophage Dynamics in the Cardiovascular System: JACC Macrophage in CVD Series (Part 3). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(18):2198-2212. [14] DEBERGE M, SHAH SJ, WILSBACHER L, et al. Macrophages in Heart Failure with Reduced versus Preserved Ejection Fraction. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25(4):328-340. [15] DE COUTO G, LIU W, TSELIOU E, et al. Macrophages mediate cardioprotective cellular postconditioning in acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(8):3147-3162. [16] PAPAGEORGIOU N, TOUSOULIS D. Healing of Myocardial Infarction//Myocardial Preservation. Cham: Springer, 2019:151-169. [17] HULSMANS M, SAM F, NAHRENDORF M. Monocyte and macrophage contributions to cardiac remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;93:149-155. [18] GOMBOZHAPOVA A, ROGOVSKAYA Y, SHURUPOV V, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization in post-infarction cardiac remodeling. J Biomed Sci. 2017;24(1):13. [19] SHI Y, SU J, ROBERTS AI, et al. How mesenchymal stem cells interact with tissue immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2012;33(3):136-143. [20] LIU W, ZHANG S, GU S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages to alleviate experimental colitis through TGFβ1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(3):858-865. [21] WANG N, SHAO Y, MEI Y, et al. Novel mechanism for mesenchymal stem cells in attenuating peritoneal adhesion: accumulating in the lung and secreting tumor necrosis factor α-stimulating gene-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(6):51. [22] BERNARDO ME, FIBBE WE. Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(4):392-402. [23] PENG Y, CHEN B, ZHAO J, et al. Effect of intravenous transplantation of hUCB-MSCs on M1/M2 subtype conversion in monocyte/macrophages of AMI mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;111:624-630. [24] UM S, KIM HY, LEE JH, et al. TSG-6 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells suppresses immune reactions influenced by BMP-2 through p38 and MEK mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;368(3):551-561. [25] LEE RH, PULIN AA, SEO MJ, et al. Intravenous hMSCs improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(1):54-63. [26] DAY AJ, MILNER CM. TSG-6: A multifunctional protein with anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective properties. Matrix Biol. 2019;78-79:60-83. [27] CHOI H, LEE RH, BAZHANOV N, et al. Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by activated MSCs attenuates zymosan-induced mouse peritonitis by decreasing TLR2/NF-κB signaling in resident macrophages. Blood. 2011;118(2):330-338. [28] SONG WJ, LI Q, RYU MO, et al. TSG-6 released from intraperitoneally injected canine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate inflammatory bowel disease by inducing M2 macrophage switch in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):91. [29] LIU L, SONG H, DUAN H, et al. TSG-6 secreted by human umbilical cord-MSCs attenuates severe burn-induced excessive inflammation via inhibiting activations of P38 and JNK signaling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30121. [30] LI R, LIU W, YIN J, et al. TSG-6 attenuates inflammation-induced brain injury via modulation of microglial polarization in SAH rats through the SOCS3/STAT3 pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):231. [31] LEE JL, WANG MJ, CHEN JY. Acetylation and activation of STAT3 mediated by nuclear translocation of CD44. J Cell Biol. 2009;185(6):949-957. [32] YAN D, WANG HW, BOWMAN RL, et al. STAT3 and STAT6 Signaling Pathways Synergize to Promote Cathepsin Secretion from Macrophages via IRE1α Activation. Cell Rep. 2016;16(11):2914-2927. [33] BOURGUIGNON LY, BIKLE D. Selective Hyaluronan-CD44 Signaling Promotes miRNA-21 Expression and Interacts with Vitamin D Function during Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinomas Progression Following UV Irradiation. Front Immunol. 2015;6:224. [34] CHANG SH, YEH YH, LEE JL, et al. Transforming growth factor-β-mediated CD44/STAT3 signaling contributes to the development of atrial fibrosis and fibrillation. Basic Res Cardiol. 2017;112(5):58. [35] PONTA H, SHERMAN L, HERRLICH PA. CD44: from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(1):33-45. [36] FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Cardiac fibrosis: Cell biological mechanisms, molecular pathways and therapeutic opportunities. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;65:70-99. [37] ANZAI A, ANZAI T, NAGAI S, et al. Regulatory role of dendritic cells in postinfarction healing and left ventricular remodeling. Circulation. 2012;125(10):1234-1245. [38] SHORTMAN K, LIU YJ. Mouse and human dendritic cell subtypes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(3):151-161. [39] HIRATA Y, TABATA M, KUROBE H, et al. Coronary atherosclerosis is associated with macrophage polarization in epicardial adipose tissue. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(3):248-255. [40] WYNN TA, CHAWLA A, POLLARD JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496(7446):445-455. |
| [1] | Xu Xinzhong, Wu Zhonghan, Yu Shuisheng, Zhao Yao, Xu Chungui, Zhang Xin, Zheng Meige, Jing Juehua. Biomechanical analysis of different ways of inserting Steinmann Pins into the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [3] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [4] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [5] | Liu Tongbin, Lin Peng, Zhang Xiaoming, Dong Xiling, Cao Fei, Wang Le, Guo Xinxing. Optimization of preparation method of atorvastatin calcium sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 535-539. |
| [6] | Li Anan, Jiang Tao, Zhan Min, Cai Yuning, Song Min, Li Congcong, Lin Wenzheng, Zhang Jiayuan, Liu Wengang. Pharmacological mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 197-204. |
| [7] | Guo Junfu, Li Xiangnan, Ma Tianchi, Miao Lanying. Effects of miR-7-5p on stem cell-like properties of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3030-3035. |
| [8] | Zou Wanghui, Qian Nannan, Zhang Meng, Pang Qiming, Yang Yichun, Zhang Tao. Implications of preclinical research on mesenchymal stem cells: relationship between cell function of mesenchymal stem cells and the JAK/STAT signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3048-3055. |
| [9] | Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Zhao Wanhua, Lin Yushi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Important role of exosomes-mediated hypoxia-related signaling pathways in the occurrence and progression of diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3065-3070. |
| [10] | Min Keting, Zhang Yiguo, Yang Hao, Lü Xin. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on negative regulation of immune response of myeloid-derived suppressor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3084-3089. |
| [11] | Yang Qin, Wang Min. Constructing a mouse model of periodontitis with occlusal trauma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2667-2672. |
| [12] | Liu Xiaolin, Liu Shutai, Han Xiaoqian, Mu Xinyue. Topical simvastatin administration in the treatment of periodontitis: effect of loading on sustained drug release system or biomaterial scaffold system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2596-2601. |
| [13] | Liu Xiaojun, Xu Yuyin, Liu Kangbo, Zhou Jing, Han Ying, Xiong Yue, Tian Yuan. Preparation and properties of carboxymethylated cotton linters hemostatic gauze [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2473-2479. |
| [14] | Wang Hujun, Wang Yingpeng, Fang Boyan, Jin Zhaohui, Qi Lin, Zhang Qiaorong, Wang Congxiao, Qie Shuyan. Effect of forearm weight-bearing on spatiotemporal parameters and joint angles of the lower limbs in patients with Parkinson’s disease during walking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2307-2311. |
| [15] | Liu Jie, Wang Min. Changes in programmed necrosis pathway in the occurrence and development of periapical periodontitis in a mouse model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2179-2183. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||