Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (16): 2473-2479.doi: 10.12307/2022.243
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and properties of carboxymethylated cotton linters hemostatic gauze
Liu Xiaojun1, Xu Yuyin1, Liu Kangbo1, Zhou Jing1, Han Ying1, Xiong Yue1, Tian Yuan2
- 1Henan Medical Equipment Inspection Institute (Henan Medical Equipment Inspection and Testing Engineering Technology Research Center), Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Nanyang Jiukang Medical Device Co., Ltd., Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-19Revised:2020-10-22Accepted:2020-11-19Online:2022-06-08Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Zhou Jing, Master, Senior engineer, Henan Medical Equipment Inspection Institute (Henan Medical Equipment Inspection and Testing Engineering Technology Research Center), Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Liu Xiaojun, Master, Engineer, Henan Medical Equipment Inspection Institute (Henan Medical Equipment Inspection and Testing Engineering Technology Research Center), Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China Xu Yuyin, Master, Senior engineer, Henan Medical Equipment Inspection Institute (Henan Medical Equipment Inspection and Testing Engineering Technology Research Center), Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Scientific and Technological Project in Henan Province, No. 202102310467 (to LXJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Xiaojun, Xu Yuyin, Liu Kangbo, Zhou Jing, Han Ying, Xiong Yue, Tian Yuan. Preparation and properties of carboxymethylated cotton linters hemostatic gauze[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2473-2479.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
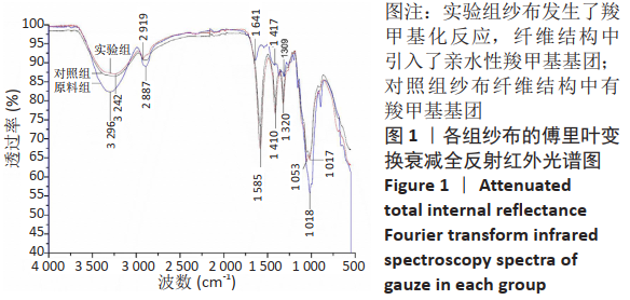
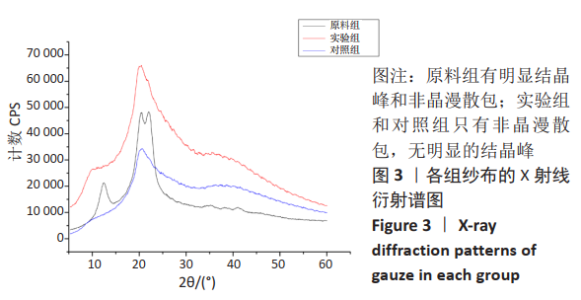
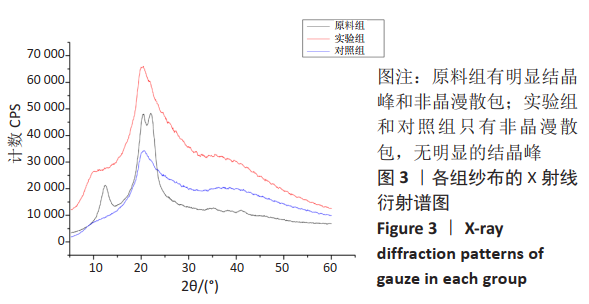
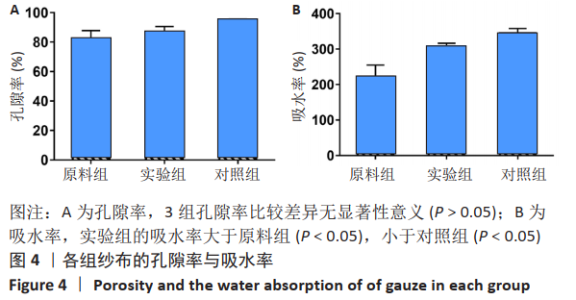
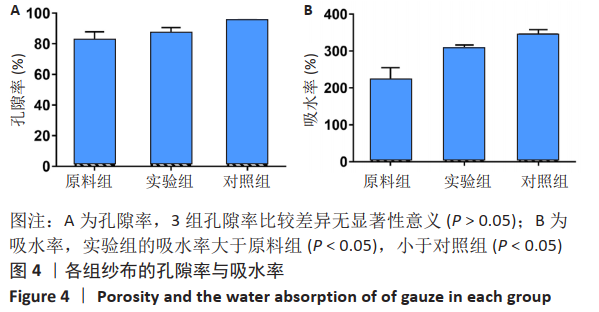
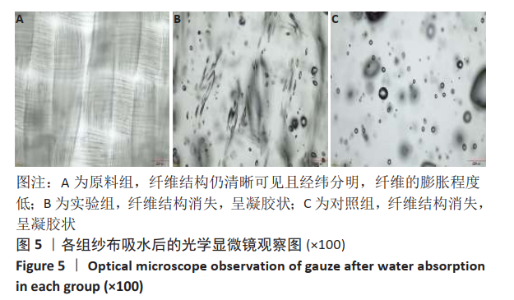
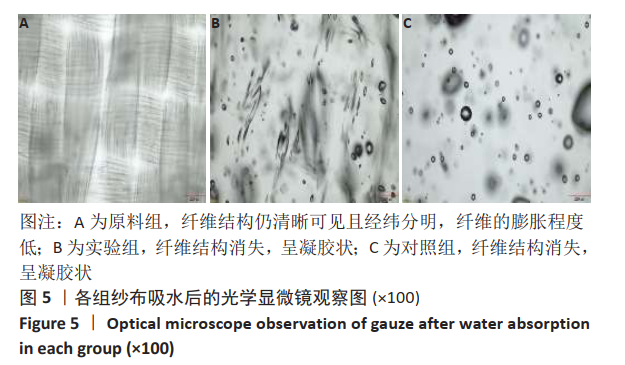
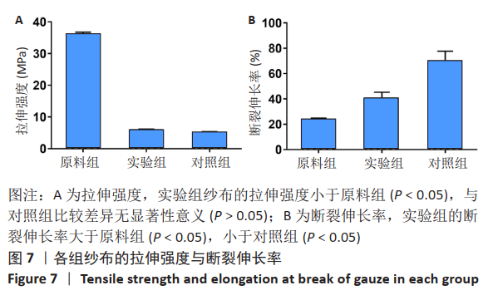
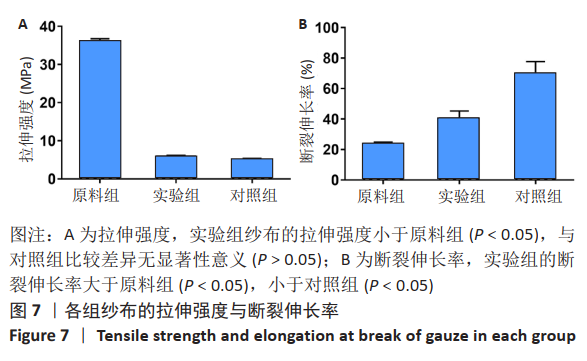
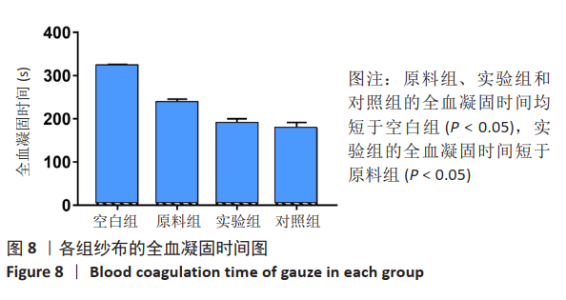
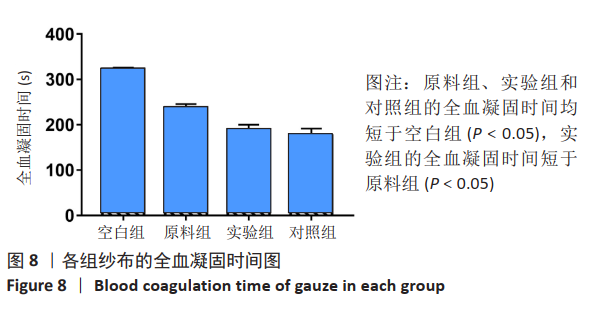
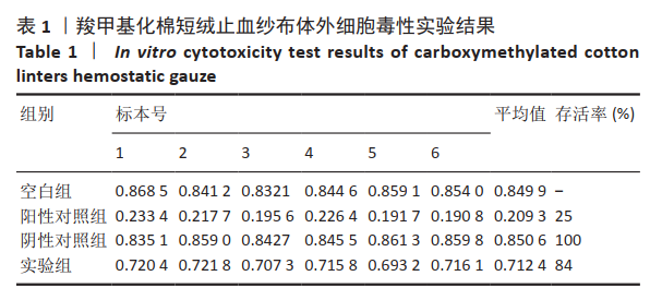
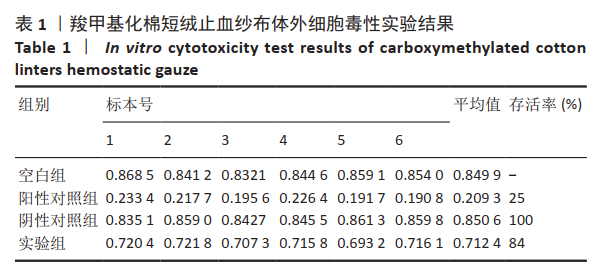
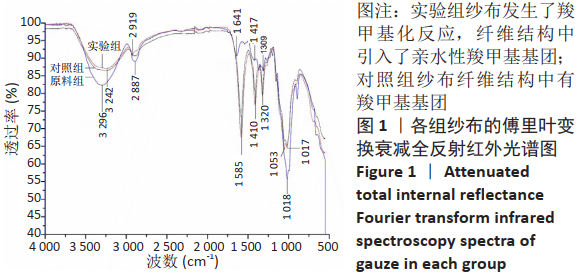
2.1 各组纱布红外光谱分析结果 图1是傅里叶变换红外光谱测定各组纱布的主要官能团分布。从图可以看出,原料组纱布在波长3 700-3 200 cm-1处呈现强而尖锐的羟基(-OH)伸缩振动形成的特征吸收峰;改性后的实验组纱布由于部分羟基被取代,在该处的特征吸收峰明显变弱。实验组纱布在波数1 585 cm-1处出现-COOH的特征吸收峰,在波数1 410 cm-1 处出现-CH2形成的特征吸收峰,在波数1 320 cm-1处出现-OH形成的特征吸收峰,由此可见,实验组纱布发生了羧甲基化反应,纤维结构中引入了亲水性羧甲基基团。与原料组纱布相比,对照组纱布在波长3 700-3 200 cm-1处的羟基(-OH)伸缩振动形成的特征吸收峰也明显变弱,而且在波数1 585,1 410,1 320 cm-1处也分别出现-COOH、-CH2和-OH形成的特征吸收峰,由此可见,对照组纱布纤维结构中有羧甲基基团。"
| [1] 刘梦媛,荆妙蕾,关静,等.N-己烷壳聚糖的制备、细胞毒性与凝血性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(22):3520-3526. [2] 韦加娜,陈锦涛抗菌止血纱布的制备及性能研究[J].广东化工,2019, 46(13):26-27. [3] 李丽娟,邢克飞,刁天喜.美军止血材料研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志, 2018,34(3):242-245. [4] BEHRENS AM, SIKORSKI MJ, KOFINAS P. Hemostatic strategies for traumatic and surgical bleeding. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2014; 102(11):4182-4194. [5] DAVIS JS, SATAHOO SS, BUTLER FK, et al. An analysis of prehospital deaths: Who can we save? J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;77(2): 213-218. [6] ZHU NW, SHI CH, SHANG R, et al. Immobilization of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on cotton gauze for biological oxidation of ferrous ions in a batch bioreactor .Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2017;64(5):727-734. [7] KITTINAOVARAT S, HENGPRAPAKRON N, JANVIKUL W. Comparative multifunctional properties of partially carboxymethylated cotton gauze treated by the exhaustion or pad-dry-cure methods. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;87(1):16-23. [8] 周本丽.刍议医用棉纱布层结构设计及其定向吸液能力[J].纺织报告,2020(2):94-95. [9] GRABER JJ, TABAR V, BRENNAN C, et al. Acute inflammatory reactions to hemostatic materials mimicking post-operative intracranial abscess. Inter Neuro Adv Tech Case Manage. 2014;1(1):5-7. [10] FRIBERG L, BENSON L, LIP GY. Balancing stroke and bleeding risks in patients with atrial fibrillation and renal failure: the Swedish Atrial Fibrillation Cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(5):297-306. [11] 崔智慧,张雅菲,田田,等.国产氧化纤维素可吸收止血纱布对大鼠皮肤伤口愈合影响的机制研究[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2019, 40(10):1193-1196+1241. [12] 白忠祥,但年华,但卫华,等.双醛羧甲基纤维素-胶原复合止血材料的研制[J].材料导报,2018,32(20):3628-3633. [13] 熊绪琼,梅昕,马凤森.多糖类可吸收止血材料的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(6):571-574. [14] COSERI S, BILIUTA G, SIMIONESCU BC, et al. Oxidized cellulose-Survey of the most recent achievements. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;93(1): 207-215. [15] KUCINSKA LJ, GUBANSKA I, JANIK H. Bacterial cellulose in the field of wound healing and regenerative medicine of skin: recent trends and future prospectives. Polym Bull (Berl). 2015;72(9):2399-2419. [16] 李伟,王玲爽,孙伟庆.纤维素类止血材料的临床应用及作用机制的研究[J].当代医药论丛,2019,17(22):21-23. [17] 石长灿,赵瑾,刘雯,等.可吸收止血材料的研究与应用进展[J].高分子通报,2018(5):1-13. [18] CHIA PL, FOO D. Use of oxidized regenerated cellulose to prevent pocket hematomas after cardiac electronic device implantation in patients on anticoagulants or dual antiplatelet therapy. Int J Cardiol. 2013;4(168):4406-4407. [19] 王剑平.医用纤维素敷料的改性与性能研究[D].青岛:青岛大学, 2015. [20] CAO S, DONG T, XU G, et al. Cyclic filtration behavior of structured cattail fiber assembly for oils removal from waste water. Environ Technol. 2018;39(14):1833-1840. [21] 魏玉君,夏朝阳,徐丽丽,等.棉短绒非织造布吸油性能测试与评价[J].上海纺织科技,2018,46(8):52-54. [22] 冯晓宁,丁成立,刘月娥.棉短绒纤维素基复合材料的制备及吸油性能[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2019,35(7):25-30. [23] CUI Y, XU G, LIU Y. Oil sorption mechanism and capability of cattail fiber assembly. J Ind Text. 2014;43(3):330-337. [24] LIKON M, REMSKAR M, DUCMAN V, et al. Populus seed fibers as a natural source for production of oil super absorbents. J Environ Manage. 2013;114(JAN.15):158-167. [25] 黄伟,徐小慧,郭利萍.三维结构和氧化度对C6位氧化再生纤维素止血材料性能影响[J].高分子通报,2017,(9):71-78. [26] 钟红荣,张岩,包红,等.丝素/明胶/壳聚糖支架材料的构建及表征[J].材料导报,2018,32(22):3954-3960. [27] 石敏,陶思洁,李丹,等.面向组织工程应用的再生丝素/海藻酸钙海绵:制备、表征及体内、体外性能研究[J].材料导报,2020, 34(4):4158-4165. [28] GB/T 16886.5-2017,医疗器械生物学评价第5部分:体外细胞毒性试验[S]. [29] 历雪,王思颖,丁雪,等.壳聚糖/迷迭香多孔干凝胶抗菌止血作用的研究[J].长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,42(4): 120-124+128. [30] GE TC, XING N, CHEN J, et al. Comparison among several foam dressings in the properties of water-absorption, water-locking and air permeability. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2012;28(5):349-352. [31] 钱璐敏,张斌.可溶性止血医用棉纱布的制备及其性能[J].纺织学报,2019,40(5):102-106. [32] 戴海玲.高吸水性医用棉纱布的制备及性能研究[D].上海:东华大学,2014. [33] KANOKPANONT S, DAMRONGSAKKUL S, RATANAVARAPORN J, et al. An innovative bi-layered wound dressing made of silk and gelatin for accelerated wound healing. Int J Pharm. 2012;436(1/2):141-153. [34] 何越,侯增淼,李晓颖,等.重组胶原蛋白海绵的制备及性状表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(6):912-916. [35] 韩玎玎,贺曾,钟锐,等.一种可止血的富血小板血浆壳聚糖/丝素蛋白多孔伤口敷料的制备及性能表征[J].生物工程学报,2020, 36(2):332-340. [36] 张楠楠,赵瑾朝,张传杰,等.医用棉纱布的羧甲基化改性[J].武汉纺织大学学报,2012,25(3):12-16. [37] 钱璐敏,张斌,张亚军.高吸液性医用纱布制备工艺的优化[J].东华大学学报(自然科学版),2018,44(5):719-723. [38] NIE W, YUAN X, ZHAO J, et al. Rapidly in situ forming chitosan/epsilon-polylysine hydrogels for adhesive sealants and hemostatic materials. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;96(1):342-348. [39] 陈晓松,张建,李建新.一种新型活组织材料的组织学及力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(34):6110-6115. [40] 张世明,陶树清.评价医疗器械体外细胞毒性的常用方法概述[J].现代医学,2020,48(1):146-150. [41] 汪芳, 陈云平, 苏香萍. 抗菌止血壳聚糖/黄连素多孔干凝胶的制备及其表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):899-905. |
| [1] | Li Huo, Wang Peng, Gao Jianming, Jiang Haoran, Lu Xiaobo, Peng Jiang. Relationship between revascularization and internal microstructure changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [2] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [3] | Shen Song, Xu Bin. Diffuse distribution of bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty reduces the incidence of refracture of adjacent vertebral bodies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 499-503. |
| [4] | Hou Wanxing, Li Hongwei, Zheng Xin, Zhu Xianren. Correlation between preoperative magnetic resonance imaging findings and bone cement leakage after percutaneous vertebral augmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 504-509. |
| [5] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| [6] | Le Guoping, Zhang Ming, Xi Licheng, Luo Hanwen. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of vancomycin hydrochloride@polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer-chitosan-hyaluronic acid composite sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 528-534. |
| [7] | Liu Tongbin, Lin Peng, Zhang Xiaoming, Dong Xiling, Cao Fei, Wang Le, Guo Xinxing. Optimization of preparation method of atorvastatin calcium sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 535-539. |
| [8] | Qiu Peng, Fu Qilin, Liu Min, Lan Yuyan, Wang Pin. Comparison of oral micro-adhesion on polyetheretherketone, zirconium dioxide, and pure titanium abutment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 540-545. |
| [9] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [10] | Wang Can, Gu Weiping, Jiang Yubin, Zhu Lin, Chen Gang. Finite element analysis of the influence of different implant designs on the stress of mandibular edentulous jaw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 573-578. |
| [11] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [12] | Zhang Jianguo, Chen Chen, Hu Fengling, Huang Daoyu, Song Liang. Design and biomechanical properties of dental implant pore structure based on three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 585-590. |
| [13] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [14] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [15] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||