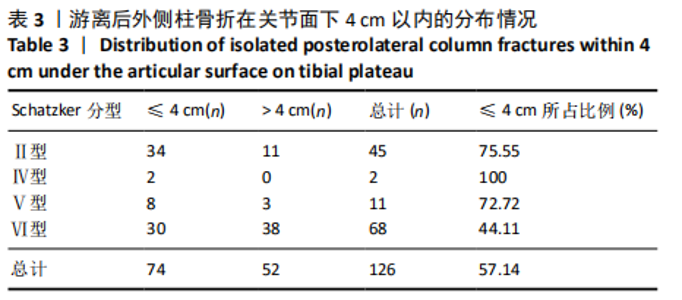
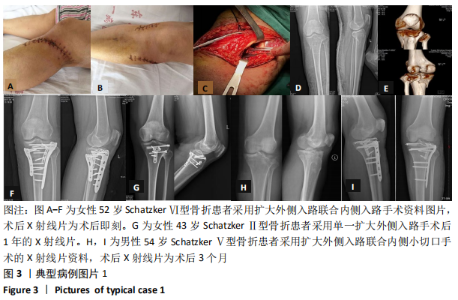
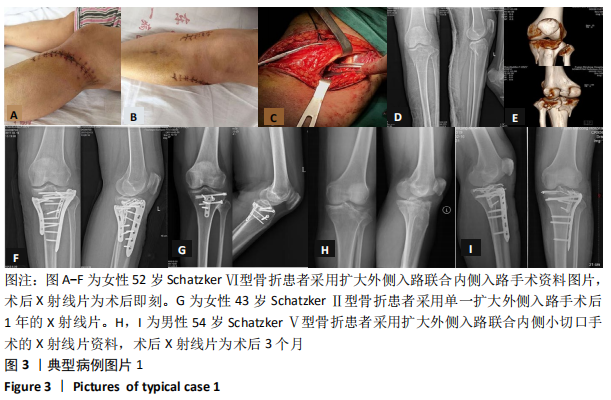
[1] SCHATZKER J, MCBROOM R, BRUCE D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968--1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;138: 94-104.
[2] 朱奕, 罗从风, 杨光, 等. 胫骨平台骨折三柱分型的可信度评价[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2012,32(3):254-259.
[3] YANG G, ZHAI Q, ZHU Y, et al. The incidence of posterior tibial plateau fracture: an investigation of 525 fractures by using a CT-based classification system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(7):929-934.
[4] ZHU Y, YANG G, LUO CF, et al. Computed tomography-based Three-Column Classification in tibial plateau fractures: introduction of its utility and assessment of its reproducibility. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(3):731-737.
[5] RASMUSSEN PS. Tibial condylar fractures. Impairment of knee joint stability as an indication for surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(7):1331-1350.
[6] 陈孝平,汪建平.外科学[M]. 8版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2013:635.
[7] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M]. 4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2012:464.
[8] 吴晓峰.改良Carlson膝关节后外侧入路治疗胫骨平台单纯后外侧柱骨折的解剖学研究及其应用[D].苏州:苏州大学,2016.
[9] 王松柏,陈春,刘东旭, 等.胫骨平台后外侧骨折三种入路的解剖学研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(10):874-879.
[10] ZHANG W, LUO CF, PUTNIS S, et al. Biomechanical analysis of four different fixations for the posterolateral shearing tibial plateau fracture. Knee. 2012;19(2):94-98.
[11] CARLSON DA. Bicondylar fracture of the posterior aspect of the tibial plateau. A case report and a modified operative approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(7):1049-1052.
[12] 罗从风,姜锐,仲飙,等.经后侧入路支撑钢板固定治疗胫骨平台后侧劈裂骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(1):6-9.
[13] HEIDARI N, LIDDER S, GRECHENIG W, et al. The risk of injury to the anterior tibial artery in the posterolateral approach to the tibia plateau:a cadaver study. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(4):221-225.
[14] SUN H, ZHAI QL, XU YF, et al. Combined approaches for fixation of Schatzker type II tibial plateau fractures involving the posterolateral column: a prospective observational cohort study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(2):209-221.
[15] FROSCH KH, BALCAREK P, WALDE T, et al. A new posterolateral approach without fibula osteotomy for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(8):515-520.
[16] 樊仕才,熊然,麦奇光, 等.外侧扩大切口入路治疗胫骨平台后侧及外侧粉碎性骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(1):34-37.
[17] 谢易,龚泰芳,李彬彬.改良扩大外侧切口入路治疗胫骨平台后外侧塌陷骨折的效果[J].广西医学,2019,41(1):116-118.
[18] 蒋广达,李晓斐,石亚雄, 等.外侧扩大入路联合内侧入路治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2019,4(4):236-238,250.
[19] 刘世杰,陈燕才,李树波.探讨改良扩大外侧切口入路治疗胫骨平台后外侧塌陷骨折的效果[J].中国医药科学,2020,10(2):257-259.
[20] 樊仕才,麦奇光,杨晓东,等.外侧扩大切口入路治疗胫骨平台后/外侧粉碎骨折的疗效分析[C].中华医学会.中华医学会第十七届骨科学术会议暨第十届COA国际学术大会论文集.2015.
[21] 张辉,薛锋,肖海军.改良前外侧入路治疗胫骨平台后外侧骨折的疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(3):358-361.
[22] ZHAO YW, XIE JB, DING GZ. Effects of expanded anterolateral approach for tibial plateau fractures involved the posterolateral column. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;98(5):352-356.
[23] YAO J, WANG H, QUAN S, et al. Posterior popliteal fossa S-shaped incision with double-window approach in treating posterior column of tibial plateau fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(5):574-578.
[24] SHEN QJ, ZHANG JL, XING GS, et al. Surgical Treatment of Lateral Tibial Plateau Fractures Involving the Posterolateral Column. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(6):1029-1038.
[25] CHO JW, KIM J, CHO WT, et al. Approaches and fixation of the posterolateral fracture fragment in tibial plateau fractures: a review with an emphasis on rim plating via modified anterolateral approach. Int Orthop. 2017;41(9):1887-1897.
[26] SUN H, ZHU Y, HE QF, et al. Reinforcement strategy for lateral rafting plate fixation in posterolateral column fractures of the tibial plateau: The magic screw technique.Injury. 2017;48(12):2814-2826.
[27] ZU B, WANG J, LIU J, et al. Application of modified anterolateral supra-fibular-head approach in treatment of tibial plateau fractures involving posterolateral column. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(6):702-706.
[28] ZHANG P, LIAN K, LUO D, et al. A combined approach for the treatment of lateral and posterolateral tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2016;47(10):2326-2330.
[29] FOSTER B, RODRIGUEZ-BUITRAGO A, OBREMSKEY WT. Prone Posteromedial Approach for Posterior Column Tibial Plateau Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34 Suppl 2:S35-S36.
[30] VAN DEN BERG J, STRUELENS B, NIJS S, et al. Value of three-dimensional computed tomography reconstruction in the treatment of posterior tibial plateau fractures. Knee. 2020;27(1):3-8.
[31] SOLOMON LB, STEVENSON AW, LEE YC, et al. Posterolateral and anterolateral approaches to unicondylar posterolateral tibial plateau fractures: a comparative study. Injury. 2013;44(11):1561-1568. |