Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (5): 790-796.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1581
Previous Articles Next Articles
Feasibility of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheet transplantation for wound healing
Chen Meihong, Dang Yini, Zhu Xudong, Li Xuan, Peng Lei, Yang Jiajia, Zhang Guoxin
- the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2018-11-07Online:2019-02-18Published:2019-02-18 -
Contact:Zhang Guoxin, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Chen Meihong, Master candidate, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Jiangsu Provincial Special Fund for Research and Development Project in 2015, No. BE2015716 (to ZGX); 2014 Fourth-Phase “333 Project” Research Funding Project of Jiangsu Province, No. BRA2014332 (to ZGX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Meihong, Dang Yini, Zhu Xudong, Li Xuan, Peng Lei, Yang Jiajia, Zhang Guoxin. Feasibility of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheet transplantation for wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 790-796.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
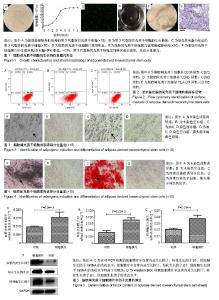
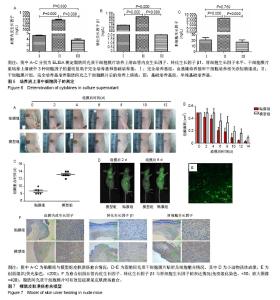
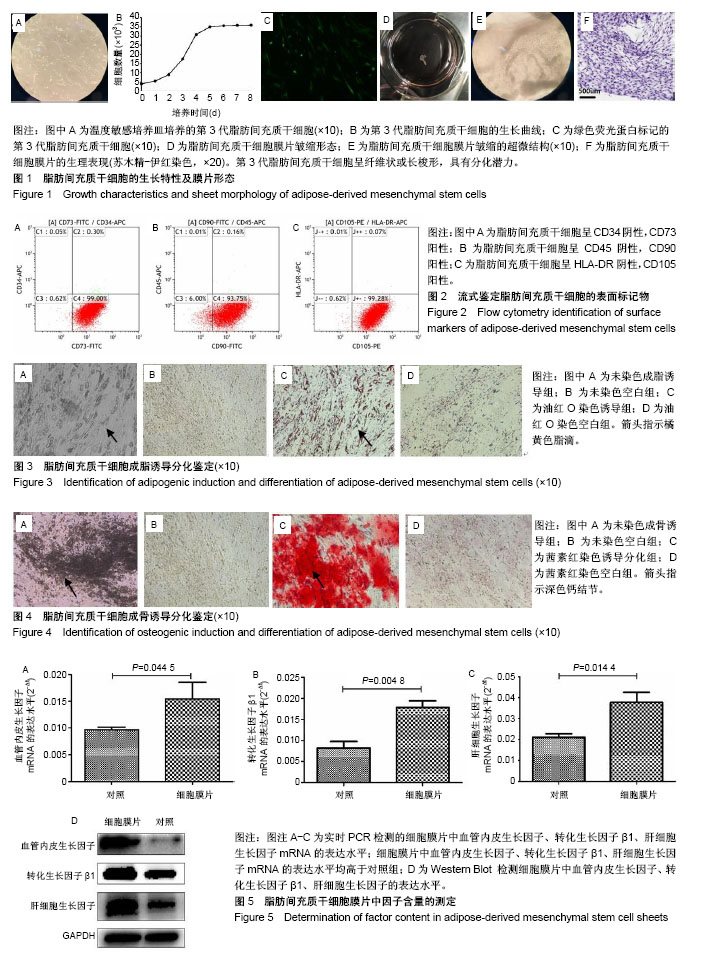
2.1 脂肪间充质干细胞的生长特性及膜片形态 第3代脂肪间充质干细胞接种于温度敏感培养皿24 h后,即可见细胞贴壁生长,呈纤维状或长梭形,见图1A;第3代细胞的生长曲线呈S形,前2 d细胞生长缓慢,至第3天进入对数生长期,第5天进入生长平台期,见图1B;荧光显微镜下可见约80%的脂肪间充质干细胞标记绿色荧光蛋白,见图1C;脂肪间充质干细胞连续培养1周后,培养皿底部出现半透明乳白色膜样物质,细胞膜片呈皱缩状,倒置显微镜及苏木精-伊红染色可见膜片中细胞含量较高,细胞外基质丰富,细胞间连接紧密,膜片结构致密且厚度均匀,见图1D-F。 2.2 脂肪间充质干细胞的干细胞特性 流式细胞仪检测第3代脂肪间充质干细胞有99.30%的细胞表面表达CD73、93.91%的细胞表达CD90、99.35%的细胞表达CD105,而仅有0.35%的细胞表达CD34、0.17%的细胞表达CD45、0.08%的细胞表达HLA-DR,这与原代干细胞高表达CD73、CD90、CD105,低表达CD34、CD45、HLA-DR特性一致[20-23],见图2;成脂诱导培养基诱导培养第18天,油红O染色可见细胞胞浆内存在大小不一的橘黄色脂滴,表明成脂分化阳性,见图3;成骨诱导培养基诱导培养第16天,茜素红染色显示细胞中后出现深色钙结节,表明成骨分化阳性,见图4。 2.3 脂肪间充质干细胞膜片中血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子β1、肝细胞生长因子基因及蛋白的表达水平 实时定量PCR结果显示:细胞膜片3种基因的表达水平均高于对照组(P < 0.05),见图5A-C;进一步Western blot验证了膜片中基因所对应的蛋白表达情况,与PCR检测结果一致,膜片血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子β1、肝细胞生长因子3种蛋白的表达水平均高于对照组,见图5D。 2.4 脂肪间充质干细胞膜片培养上清液中血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子β1、肝细胞生长因子的表达水平 ELISA结果显示,膜片移植前培养液生长因子含量显著高于干细胞专用完全培养基和基础培养基(P < 0.000),见图6,而基础培养基和干细胞专用完全培养基中3种因子的含量接近。 2.5 裸鼠皮肤溃疡愈合模型的验证 将脂肪间充质干细胞膜片移植至裸鼠人工皮肤溃疡创面,图7A-C显示贴膜组裸鼠皮肤溃疡愈合速度快于模型组,贴膜组裸鼠皮肤溃疡约于造模后第8天全部愈合,而模型组为造模后12 d,造模后1周时,贴膜组溃疡表面血痂基本脱落,而模型组稍晚于贴膜组,于第10天全部脱落;造模后第2天和第6天小动物活体成像及造模后1周组织切片荧光显微镜观察可见绿色荧光蛋白标记的脂肪间充质干细胞成功贴附并整合于创面组织,见图7D,E;待溃疡完全愈合后取其瘢痕组织行免疫组化,发现贴膜组的血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子β1、肝细胞生长因子表达水平高于模型组,见图7F。"
| [1] Fontijn RD, Favre J, Naaijkens BA, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stromal cells acquire endothelial-like features upon reprogramming with SOX18. Stem Cell Res. 2014;13(3 Pt A):367-378. [2] Okano T, Yamada N, Sakai H, et al. A novel recovery system for cultured cells using plasma-treated polystyrene dishes grafted with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;27(10):1243-1251. [3] Goodarzi P, Alavi-Moghadam S, Sarvari M, et al. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Cells for Wound Healing. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. doi: 10. 1007/5584_2018_220. [4] Han G, Ceilley R. Chronic Wound Healing: A Review of Current Management and Treatments. Adv Ther. 2017;34(3):599-610. [5] Johnston BR, Ha AY, Kwan D. Surgical Management of Chronic Wounds. R I Med J (2013). 2016;99(2):30-33. [6] Tsuji W, Rubin JP, Marra KG. Adipose-derived stem cells: Implications in tissue regeneration. World J Stem Cells. 2014;6(3):312-321. [7] Kato Y, Iwata T, Morikawa S, et al. Allogeneic Transplantation of an Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Sheet Combined With Artificial Skin Accelerates Wound Healing in a Rat Wound Model of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Diabetes. 2015;64(8):2723-2734. [8] Perrod G, Pidial L, Camilleri S, et al. ADSC-sheet Transplantation to Prevent Stricture after Extended Esophageal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. J Vis Exp. 2017;(120). [9] Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4(6):688-694. [10] Higuchi K, Tanabe S, Koizumi W, et al. Expansion of the indications for endoscopic mucosal resection in patients with superficial esophageal carcinoma. Endoscopy. 2007;39(1):36-40. [11] Lee HJ, Lee H, Park JC, et al. Treatment Strategy after Endoscopic Resection of Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Single Institution Experience. Gut Liver. 2015;9(6):714-719. [12] Ono S, Fujishiro M, Niimi K, et al. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70(5):860-866. [13] 张晓琦,吕瑛,钱铖,等.内镜下黏膜切除术后食管狭窄的危险因素分析[J].中华消化内镜杂志,2011,28(4):192-195.[14] 鞠辉,钟芸诗,姚礼庆,等.早期食管癌内镜黏膜下剥离术后食管狭窄的危险因素分析[J].中华消化内镜杂志,2013,30(6):310-314.[15] Oyama T. Prevention of stricture after large esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissections. Endoscopy. 2015;47(4):289-290. [16] Sato H, Inoue H, Kobayashi Y, et al. Control of severe strictures after circumferential endoscopic submucosal dissection for esophageal carcinoma: oral steroid therapy with balloon dilation or balloon dilation alone. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;78(2):250-257. [17] Pauli EM, Schomisch SJ, Furlan JP, et al. Biodegradable esophageal stent placement does not prevent high-grade stricture formation after circumferential mucosal resection in a porcine model. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26(12):3500-3508. [18] Hashimoto S, Kobayashi M, Takeuchi M, et al. The efficacy of endoscopic triamcinolone injection for the prevention of esophageal stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74(6):1389-1393. [19] [19] Ohki T, Yamato M, Ota M, et al. Prevention of esophageal stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection using tissue-engineered cell sheets. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):582-588.e2. [20] Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a source of human hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2007;46(1):219-228. [21] Okura H, Komoda H, Saga A, et al. Properties of hepatocyte-like cell clusters from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(4):761-770. [22] Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, et al. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1294-1301. [23] 张云巍,徐丽娟,王淑芳,等.人脂肪间充质干细胞体外分离、培养的方法研究[J].肝脏,2014,19(10):752-755.[24] Park SR, Kim JW, Jun HS, et al. Stem Cell Secretome and Its Effect on Cellular Mechanisms Relevant to Wound Healing. Mol Ther. 2018;26(2): 606-617. [25] Han CM, Wang XG. Tissue engineered skin and regenerative wound repair. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2013;29(2):122-125. [26] Cerqueira MT, Pirraco RP, Santos TC, et al. Human adipose stem cells cell sheet constructs impact epidermal morphogenesis in full-thickness excisional wounds. Biomacromolecules. 2013;14(11):3997-4008. [27] Huang SP, Hsu CC, Chang SC, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells seeded on acellular dermal matrix grafts enhance wound healing in a murine model of a full-thickness defect. Ann Plast Surg. 2012;69(6):656-662. [28] Cerqueira MT, Marques AP, Reis RL. Using stem cells in skin regeneration: possibilities and reality. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(8):1201-1214. [29] Ma T, Sun J, Zhao Z, et al. A brief review: adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):124. [30] Honda M, Nakamura T, Hori Y, et al. Process of healing of mucosal defects in the esophagus after endoscopic mucosal resection: histological evaluation in a dog model. Endoscopy. 2010;42(12):1092-1095. [31] Perrod G, Rahmi G, Pidial L, et al. Cell Sheet Transplantation for Esophageal Stricture Prevention after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in a Porcine Model. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0148249. [32] Abe S, Iyer PG, Oda I, et al. Approaches for stricture prevention after esophageal endoscopic resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86(5): 779-791. [33] Kobayashi S, Kanai N, Ohki T, et al. Prevention of esophageal strictures after endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20(41):15098-15109. [34] Honda M, Hori Y, Nakada A, et al. Use of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells for prevention of esophageal stricture after circumferential EMR in a canine model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(4):777-784. [35] Hirose M, Yamato M, Kwon OH, et al. Temperature-Responsive surface for novel co-culture systems of hepatocytes with endothelial cells: 2-D patterned and double layered co-cultures. Yonsei Med J. 2000;41(6): 803-813. [36] Lin YC, Grahovac T, Oh SJ, et al. Evaluation of a multi-layer adipose-derived stem cell sheet in a full-thickness wound healing model. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(2):5243-5250. [37] Muller D, Silva JP, Rambo CR, et al. Neuronal cells' behavior on polypyrrole coated bacterial nanocellulose three-dimensional (3D) scaffolds. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(11):1368-1377. [38] Yang J, Yamato M, Kohno C, et al. Cell sheet engineering: recreating tissues without biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2005;26(33): 6415-6422. [39] Yang Z, Jin F, Zhang X, et al. Tissue engineering of cementum/ periodontal-ligament complex using a novel three-dimensional pellet cultivation system for human periodontal ligament stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2009;15(4):571-581. [40] Choi JS, Kim JD, Yoon HS, et al. Full-thickness skin wound healing using human placenta-derived extracellular matrix containing bioactive molecules. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(3-4):329-339. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||