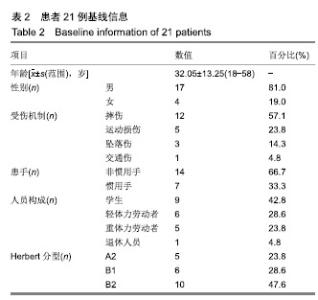
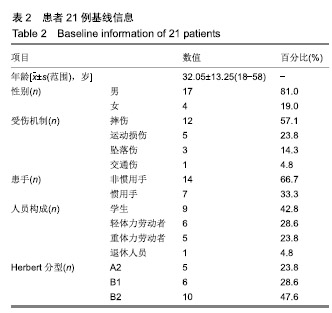
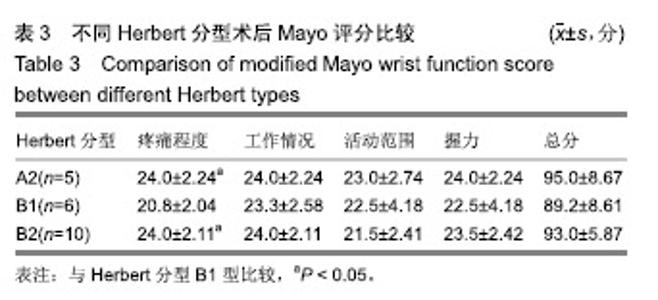
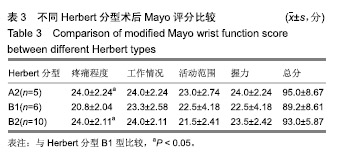
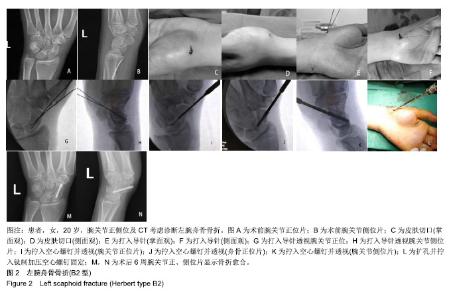
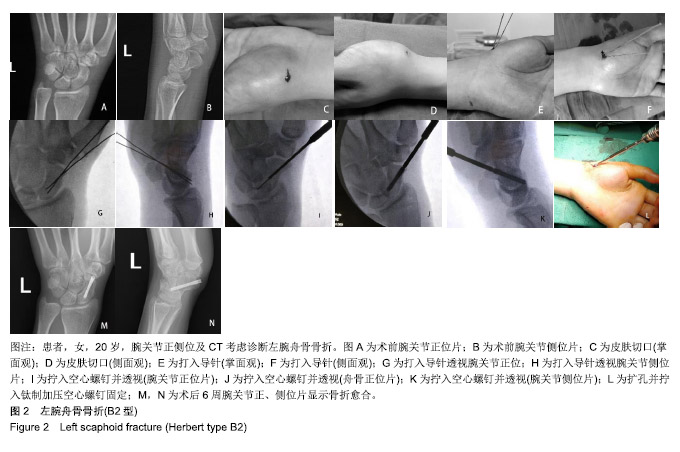
| [1]Sendher R, Ladd AL. The scaphoid. Orthop Clin North Am. 2013;44(1):107-120. [2]杨晨光,陈亮,胡韶楠.急性腕舟骨骨折的诊断治疗研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(4):507-510.[3]Kawamura K, Chung KC. Treatment of scaphoid fractures and nonunions. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(6):988-997. [4]Garcia RM, Ruch DS. Management of scaphoid fractures in the athlete: open and percutaneous fixation. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2014;22(1):22-28. [5]Unay K, Gokcen B, Ozkan K, et al. Examination tests predictive of bone injury in patients with clinically suspected occult scaphoid fracture. Injury. 2009;40(12):1265-1268. [6]Cooney WR, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Nonunion of the scaphoid: analysis of the results from bone grafting. J Hand Surg Am. 1980;5(4):343-354.[7]吴晓虎,王慧慧.研究腕舟骨骨不连患者运用显微外科手术治疗的临床疗效[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(21):69-70. [8]Klifto CS, Ramme AJ, Sapienza A, et al. Scaphoid nonunions. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2018;76(1):27-32. [9]Strauch RJ. Scapholunate advanced collapse and scaphoid nonunion advanced collapse arthritis-update on evaluation and treatment. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(4):729-735. [10]El TA, Smith H, Llewellyn C, et al. A systematic review of patients', parents' and healthcare professionals' adrenaline auto-injector administration techniques. Emerg Med J. 2017; 34(6):403-416. [11]陈美.石膏固定位置对腕舟骨骨折愈合和功能的影响[J].农家参谋,2019(1):255. [12]罗俊毅.不同石膏外固定位置对新鲜腕舟骨骨折治疗效果的影响[J].中医临床研究,2017,9(7):128-129. [13]吴宗明,白建忠.切开复位内固定手术治疗腕舟状骨骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2013,15(1):74. [14]牛海明.经皮微创Herbert螺钉内固定治疗新鲜腕舟骨骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2015,18(6):692. [15]Alshryda S, Shah A, Odak S, et al. Acute fractures of the scaphoid bone: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgeon. 2012;10(4):218-229. [16]Gilley E, Puri SK, Hearns KA, et al. Importance of computed tomography in determining displacement in scaphoid fractures. J Wrist Surg. 2018;7(1):38-42. [17]Cooney WP, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Fractures of the scaphoid: a rational approach to management. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;(149):90-97. [18]Adams JE, Steinmann SP. Acute scaphoid fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2007;38(2):229-235.[19]Dunn J, Kusnezov N, Fares A, et al. The scaphoid staple: a systematic review. Hand (N Y). 2017;12(3):236-241. [20]崔立舜.腕舟骨骨折与骨不连治疗现状[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(68):136-137. [21]Alnaeem H, Aldekhayel S, Kanevsky J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the differences between nonsurgical management and percutaneous fixation of minimally and nondisplaced scaphoid fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2016;41(12):1135-1144. [22]Al-Ajmi TA, Al-Faryan KH, Al-Kanaan NF, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing surgical versus conservative treatments for acute undisplaced or minimally-displaced scaphoid fractures. Clin Orthop Surg. 2018;10(1):64-73. [23]Mcqueen MM, Gelbke MK, Wakefield A, et al. Percutaneous screw fixation versus conservative treatment for fractures of the waist of the scaphoid: a prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(1):66-71. [24]Ahmed U, Malik S, David M, et al. The headless compression screw-technical challenges in scaphoid fracture fixation. J Orthop. 2015;12(Suppl 2):S211-S216. [25]张旭林,何晓清,徐永清.腕舟骨骨折固定物研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2017,38(6):345-348. [26]李磊,张基仁,齐勇,等.不同类型金属植入物内固定治疗腕舟骨骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(22): 4142-4145. [27]谢庆云,张波,魏萌,等. Acutrak空心无头加压螺钉治疗腕舟骨骨折早期疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(1):37-39. [28]黄成校,余化龙.螺旋CT扫描及其多平面重建技术在腕舟骨骨折诊断中应用[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2018,16(2):104-106. [29]Matson AP, Garcia RM, Richard MJ, et al. Percutaneous treatment of unstable scaphoid waist fractures. Hand (N Y). 2017;12(4):362-368. [30]杨顺.微创治疗桡骨远端骨折合并腕舟骨骨折12例疗效分析[Z].第七届全国中西医结合骨科微创学术年会,福建泉州.2017. |