Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (34): 5526-5517.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0649
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of needle puncture versus abnormal mechanical compression on the biological properties of annulus fibrosus: a preliminary study at nano-scale
Li Haitao1, Liang Ting2, Shao Yijie1, Chen Xi2, Yang Huilin1, Luo Zongping2
- 1The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Institute of Orthopaedics at Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2018-07-03Online:2018-12-08Published:2018-12-08 -
Contact:Yang Huilin, Chief physician, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Li Haitao, Master candidate, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81320108018, 31570943, 31270995
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Haitao, Liang Ting, Shao Yijie, Chen Xi, Yang Huilin, Luo Zongping. Influence of needle puncture versus abnormal mechanical compression on the biological properties of annulus fibrosus: a preliminary study at nano-scale[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5526-5517.
share this article

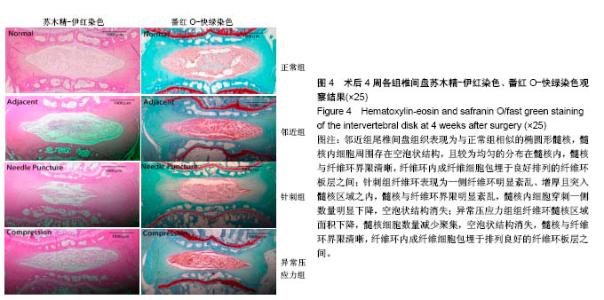
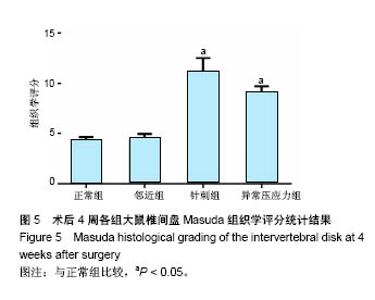
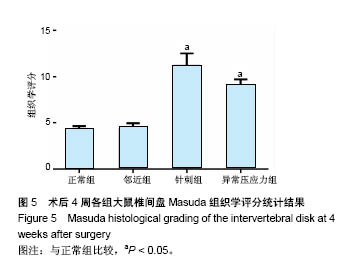
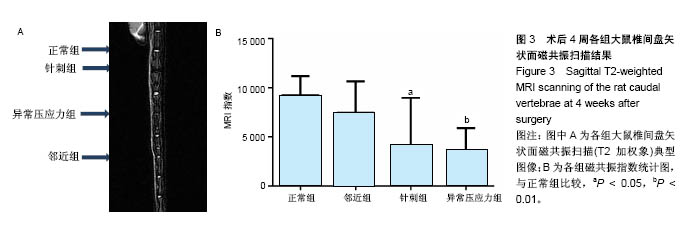
2.1 实验动物数量分析 所有8只大鼠手术耐受良好,均存活过4周实验期。大鼠平均体质量由最初的(405±20) g增长至(445±15) g,外固定支架(约5.0 g)对大鼠日常活动影响不明显,未发现感染、皮肤坏死或支架滑脱现象。 2.2 磁共振结果评估 典型的各组正中矢状面T2加权像尾椎间盘图像见图3A,依据Sobajima S评价法所得磁共振指数见图3B。结果显示,针刺组与异常压应力组大鼠椎间盘髓核含水量与正常组相比显著下降(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),表现为T2加权像低信号;邻近组Co10-Co11椎间盘含水量与正常组比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.207),针刺组与异常压应力组间椎间盘髓核含水量比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.745 6)。"

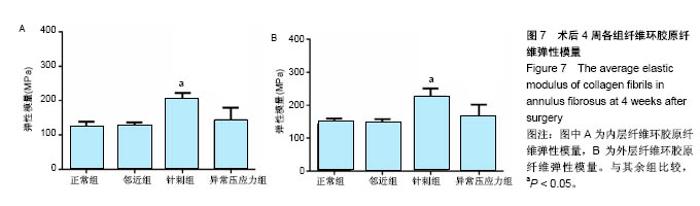
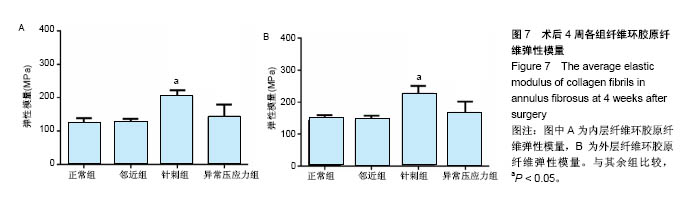
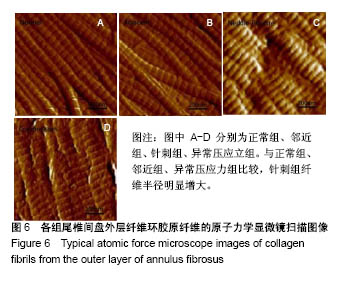
2.4 原子力显微镜分析结果 各组典型外层纤维环胶原纤维原子力显微镜下高清图像(1 μm×1 μm)如图6,各组纤维环内外层胶原纤维弹性模量统计值见图7,可知纤维环内外区域及诱导椎间盘退变的不同机制对大鼠椎间盘纤维环胶原纤维弹性模量有明显影响。各组大鼠椎间盘纤维环胶原纤维弹性模量均表现为外层高于内层(P < 0.05)。邻近组椎间盘内层、外层胶原纤维弹性模量均与正常组相比差异均无显著性意义(P=0.913 1);针刺组内(P < 0.01)、外层胶原纤维弹性模量较正常组明显增大(P < 0.01);异常压应力组内层(P=0.134 1)、外层(P=0.065 2)胶原纤维弹性模量与正常组相比差异无显著性意义;针刺组内外层胶原纤维弹性模量均显著高于异常压应力组(P < 0.01)。"
| [1] Driscoll T,Jacklyn G,Orchard J,et al.The global burden of occupationally related low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study.Ann Rheum Dis.2014;73(6):975-981.[2] Luoma K,Riihimäki H,Luukkonen R,et al.Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2000;25(4):487-492.[3] Hughes SP,Freemont AJ,Hukins DW,et al.The pathogenesis of degeneration of the intervertebral disc and emerging therapies in the management of back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(10): 1298-1304.[4] Daly C,Ghosh P,Jenkin G,et al.A Review of Animal Models of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Pathophysiology, Regeneration, and Translation to the Clinic.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016: 5952165.[5] Iatridis JC,Mente PL,Stokes IA,et al.Compression-induced changes in intervertebral disc properties in a rat tail model.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(10):996-1002.[6] Lipson SJ,Muir H.1980 Volvo award in basic science. Proteoglycans in experimental intervertebral disc degeneration.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1981;6(3):194-210.[7] Kroeber MW,Unglaub F,Wang H,et al.New in vivo animal model to create intervertebral disc degeneration and to investigate the effects of therapeutic strategies to stimulate disc regeneration.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(23):2684-2690.[8] Yoon SH,Miyazaki M,Hong SW,et al.A porcine model of intervertebral disc degeneration induced by annular injury characterized with magnetic resonance imaging and histopathological findings. Laboratory investigation.J Neurosurg Spine.2008;8(5):450-457.[9] Rousseau MA,Ulrich JA,Bass EC,et al.Stab incision for inducing intervertebral disc degeneration in the rat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007; 32(1):17-24.[10] Masuda K,Aota Y,Muehleman C,et al.A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):5-14.[11] Moskowitz RW,Ziv I,Denko CW,et al.Spondylosis in sand rats: a model of intervertebral disc degeneration and hyperostosis.J Orthop Res. 1990;8(3):401-411.[12] Gruber HE,Johnson T,Norton HJ,et al.The sand rat model for disc degeneration: radiologic characterization of age-related changes: cross-sectional and prospective analyses. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2002; 27(3):230-234.[13] Hoogendoorn RJ,Helder MN, Kroeze RJ,et al.Reproducible long-term disc degeneration in a large animal model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(9):949-954.[14] Oda H,Matsuzaki H,Tokuhashi Y,et al.Degeneration of intervertebral discs due to smoking: experimental assessment in a rat-smoking model.J Orthop Sci.2004;9(2):135-141.[15] Li CG,Liang QQ,Zhou Q,et al.A continuous observation of the degenerative process in the intervertebral disc of Smad3 gene knock-out mice.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(13):1363-1369.[16] Yurube T,Nishida K,Suzuki T,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 gene up-regulation in a rat tail compression loading-induced disc degeneration model.J Orthop Res. 2010;28(8):1026-1032.[17] Holzapfel GA,Schulze-Bauer CAJ,Feigl G,et al.Single lamellar mechanics of the human lumbar anulus fibrosus.Biomech Model Mechanobiol.2005;3(3):125-140.[18] Roughley PJ.Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2004; 29(23):2691-2699.[19] Iatridis JC,MacLean JJ,Roughley PJ,et al.Effects of mechanical loading on intervertebral disc metabolism in vivo.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006;88 Suppl 2:41-46.[20] Setton LA,Chen J.Mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc and relevance to disc degeneration.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:52-57.[21] Hayes AJ,Benjamin M,Ralphs JR.Role of actin stress fibres in the development of the intervertebral disc: cytoskeletal control of extracellular matrix assembly.Dev Dyn. 1999;215(3):179-189.[22] Hughes PC,Tanner JM.The assessment of skeletal maturity in the growing rat.J Anat. 1970;106(Pt 2):371-402.[23] Lotz JC,Colliou OK,Chin JR,et al.Compression-induced degeneration of the intervertebral disc: an in vivo mouse model and finite-element study.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(23):2493-2506.[24] Yurube T,Takada T,Suzuki T,et al.Rat tail static compression model mimics extracellular matrix metabolic imbalances of matrix metalloproteinases,aggrecanases, and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(2):R51.[25] Sobajima S,Kompel JF,Kim JS,et al.A slowly progressive and reproducible animal model of intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by MRI, X-ray, and histology.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2005; 30(1):15-24.[26] Liang T,Zhang LL,Xia W,et al.Individual Collagen Fibril Thickening and Stiffening of Annulus Fibrosus in Degenerative Intervertebral Disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(19):E1104-E1111.[27] Iatridis JC,Mente PL,Stokes IA,et al.Compression-induced changes in intervertebral disc properties in a rat tail model.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(10):996-1002.[28] Modic MT,Masaryk TJ,Ross JS,et al.Imaging of degenerative disk disease.Radiology.1988;168(1):177-186.[29] Pearce RH,Thompson JP,Bebault GM,et al.Magnetic resonance imaging reflects the chemical changes of aging degeneration in the human intervertebral disk.J Rheumatol Suppl.1991;27:42-43.[30] Modic MT,Herfkens RJ.Intervertebral disk: normal age-related changes in MR signal intensity.Radiology. 1990;177(2):332-333.[31] Pfirrmann CW,Metzdorf A,Zanetti M,et al.Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(17):1873.[32] Anderson DG,Izzo MW,Hall DJ,et al.Comparative gene expression profiling of normal and degenerative discs: analysis of a rabbit annular laceration model.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2002;27(12):1291-1296.[33] Eyre DR,Muir H.Types I and II collagens in intervertebral disc. Interchanging radial distributions in annulus fibrosus.Biochem J. 1976;157(1):267-270.[34] Gruber HE,Hanley EN Jr.Ultrastructure of the human intervertebral disc during aging and degeneration: comparison of surgical and control specimens.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2002;27(8): 798-805.[35] Adams MA,Hutton WC.Gradual disc prolapse.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10(6):524.[36] Gregory DE,Bae WC,Sah RL,et al.Disc degeneration reduces the delamination strength of the annulus fibrosus in the rabbit annular disc puncture model.Spine J.2014;14(7):1265-1271.[37] Yu J,Fairbank JC,Roberts S,et al.The elastic fiber network of the anulus fibrosus of the normal and scoliotic human intervertebral disc.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(16):1815-1820.[38] Adams MA,Green TP.Tensile properties of the annulus fibrosus. I. The contribution of fibre-matrix interactions to tensile stiffness and strength.Eur Spine J.1993;2(4): 203-208.[39] Schollum ML,Robertson PA,Broom ND.ISSLS prize winner: microstructure and mechanical disruption of the lumbar disc annulus: part I: a microscopic investigation of the translamellar bridging network.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(25):2702-2710.[40] Wagner DR,Lotz JC.Theoretical model and experimental results for the nonlinear elastic behavior of human annulus fibrosus.J Orthop Res.2004;22(4):901-909.[41] Elliott DM,Setton LA.Anisotropic and inhomogeneous tensile behavior of the human anulus fibrosus: experimental measurement and material model predictions.J Biomech Eng. 2001;123(3):256-263.[42] Martin JT,Gorth DJ,Beattie EE,et al.Needle puncture injury causes acute and long-term mechanical deficiency in a mouse model of intervertebral disc degeneration.J Orthop Res.2013;31(8):1276-1282.[43] Attia M,Santerre JP,Kandel RA.The response of annulus fibrosus cell to fibronectin-coated nanofibrous polyurethane-anionic dihydroxyoligomer scaffolds. Biomaterials.2011;32(2):450-460.[44] Benallaoua M,Richette P,François M,et al.Modulation of proteoglycan production by cyclic tensile stretch in intervertebral disc cells through a post-translational mechanism. Biorheology.2006;43(3,4): 303-310.[45] Nerurkar NL,Elliott DM,Mauck RL.Mechanics of oriented electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for annulus fibrosus tissue engineering.J Orthop Res.2007;25(8):1018-1028.[46] Elliott DM,Yerramalli CS,Beckstein JC,et al.The effect of relative needle diameter in puncture and sham injection animal models of degeneration.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(6):588-596.[47] Hu MH,Yang KC,Chen YJ,et al.Optimization of puncture injury to rat caudal disc for mimicking early degeneration of intervertebral disc.J Orthop Res.2018;36(1):202-211.[48] Michalek AJ,Buckley MR,Bonassar LJ,et al.The effects of needle puncture injury on microscale shear strain in the intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus.Spine J. 2010;10(12):1098-1105.[49] Cuellar JM,Stauff MP,Herzog RJ,et al.Does provocative discography cause clinically important injury to the lumbar intervertebral disc? A 10-year matched cohort study.Spine J. 2016;16(3):273-280.[50] Erwin WM,Inman RD.Notochord cells regulate intervertebral disc chondrocyte proteoglycan production and cell proliferation.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2006;31(10):1094-1099.[51] Hunter CJ,Matyas JR,Duncan NA.Cytomorphology of notochordal and chondrocytic cells from the nucleus pulposus: a species comparison.J Anat.2004;205(5):357-362. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||