Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (33): 5386-5392.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0674
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of stretch-activated ion channels in mechanotransduction of mesenchymal stem cells
Su Hao, Jia Xiao-ling
- Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Ministry of Education, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
-
Revised:2018-06-28Online:2018-11-28Published:2018-11-28 -
Contact:Jia Xiao-ling, MD, Associate professor, Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Ministry of Education, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China -
About author:Su Hao, Master candidate, Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Ministry of Education, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11372030
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Su Hao, Jia Xiao-ling. Mechanism of stretch-activated ion channels in mechanotransduction of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5386-5392.
share this article
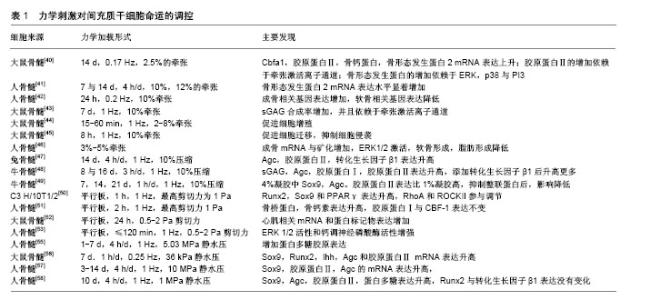
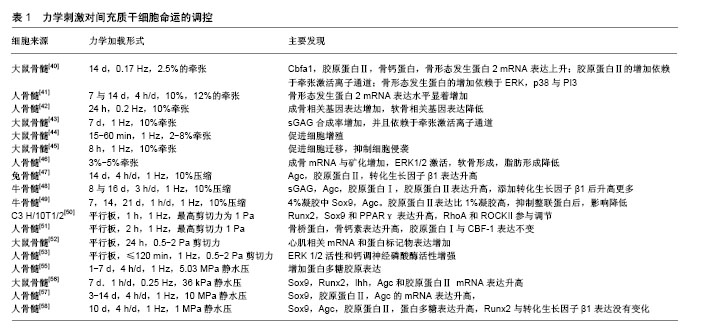
2.1 牵张激活通道简介 是一类开放概率随着细胞膜张力变化而变化的通道。Guharay等[12]第1次描述了鸡骨骼肌细胞中牵张激活通道的特征:在150 mmol/L外液K+和150 mmol/L内液Na+存在下,通道具有70 pS的电导,其中-50 mV到-140 mV之间,电流电压呈线性变化,翻转电位为30 mV,随后在细菌壁、草履虫膜、脊椎动物和哺乳动物细胞中都发现了牵张激活离子通道[13-16]。牵张激活通道几乎存在于所有细胞中,也参与很多重要的生理功能,如触觉刺激、疼痛、听觉、突触发生、细胞体积和心率调节等[17-20]。此外,牵张激活通道也与心律失常、肺动脉高压、肌营养不良、多囊肾、机械性异常性疼痛、贫血、外周感觉异常及肿瘤转移等多种疾病状态有关[21-24]。 目前真核生物中牵张激活通道的具体蛋白质结构依然是未知的,但是真核细胞中牵张激活通道有许多备选基因家族,候选者包括DEG/ENaC/ASIC 通道,TRP通道,弱内向整流性K+通道-K2P通道以及新发现的Piezo通道[25]。其中TRP通道是非选择性阳离子通道,有7个亚家族:TRPA,TRPC,TRPM,TRPML,TRPN,TRPP和TRPV,因为TRP通道在多种细胞内表现出机械敏感性,所以猜测TRP通道是牵张激活通道的研究较多[26-28]。在间充质干细胞中,TRPM7与TRPV4是两种研究比较多的TRP通道,有研究者发现TRPM7在剪切力诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨中发挥重要作用,TRPV4在剪切应力诱导的人骨髓间充质干细胞的早期成骨分化中起作用[31-34]。Piezo通道是新发现的一种通道,Coste等[35]已经证实纯化的Piezo蛋白重构的脂质双层可以形成钌红敏感的离子通道,并且Piezo的敲低降低了牵张激活通道的电流,而Piezo表达的增加升高了牵张激活通道的电流,他的发现让Piezo通道被认为是牵张激活通道最有希望的候选成员。 虽然牵张激活通道的具体结构是未知的,但是有两种阻断剂被确认可以阻断牵张激活通道电流。钆(Gd3+)是早期被发现的阳离子间充质干细胞抑制剂,1989年Yang等[36]发现Gd3+可以降低非洲爪蟾卵母细胞牵张激活通道通道的电流以及开放时间,但是Ermakov等[37]证实Gd3+不是特异性的,因为阴离子磷脂可以作为Gd3+的高亲和力受体产生数十mN/m的侧压力,这个压力足以改变通道的开放状态。GsMTx4是更为选择性的阳离子型牵张激活通道抑制剂,由Suchyna等[38]从蜘蛛的毒液中分离出来,在膜片钳实验中,GsMTx4对电压门控离子通道的电流没有影响,但减少了40%肿胀的大鼠星形胶质细胞电流。Gnanasambandam等[39]认为GsMTx4主要通过松弛磷脂双分子层外部区域降低膜拉伸的形变从而阻断牵张激活通道。虽然GsMTx4具有比较好的特异性,但是它不是一个通用的牵张激活通道抑制剂,因为它对K2P通道和其他可能的牵张激活通道没有影响,这可能是因为GsMTx4只作用于膜外层。 2.2 外部机械刺激对间充质干细胞的调控 目前,应用到间充质干细胞上的外部机械刺激大致可以分为牵张、压缩、流体剪切力与静水压力4种,下面将总结这4种力学刺激对间充质干细胞命运的影响,见表1。"
| [1] Becker AJ, Mcculloch EA, Till JE. Cytological demonstration of the clonal nature of spleen colonies derived from transplanted mouse marrow cells. Nature. 1963;197:452-454. [2] Fukumoto T, Sperling JW, Sanyal A, et al. Combined effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 and transforming growth factor-beta1 on periosteal mesenchymal cells during chondrogenesis in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003;11:55. [3] Mauney JR, Nguyen T, Gillen K, et al. Engineering adipose-like tissue in vitro and in vivo utilizing human bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with silk fibroin 3D scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2007;28:5280-5290. [4] Tsai MS, Lee JL, Chang YJ, et al. Isolation of human multipotentmesenchymal stem cells from second-trimester amniotic fluid using a novel two-stage culture protocol. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:1450. [5] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science.1999;284: 143-147. [6] Jankowski RJ, Deasy BM, Huard J. Muscle-derived stem cells. Gene Ther. 2002;9:642-647. [7] Fan X, Liu T, Yang L, et al. Optimization of primary culture condition for mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood with factorial design. BiotechnolProg. 2009;25:499-507. [8] Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W,et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2002;81:531. [9] Salinas Tejedor L, Skripuletz T,Stangel M,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells require the peripheral immune system for immunomodulating effects in animal models of multiple sclerosis.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(1):90-91.[10] Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhjan RK, Lalykina KS. The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell Tissue Kinet.1970;3(4):393-403. [11] Dominici M, Le BK, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotentmesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4): 315-317. [12] Guharay F, Sachs F. Stretch-activated single ion channel currents in tissue-cultured embryonic chick skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1984; 352:685-701. [13] Sukharev SI, Blount P,Martinac B, et al. A large-conductance mechanosensitive channel in E. coli encoded by mscL alone. Nature. 1994;368:265-268. [14] Zhou XL, Kung C. A mechanosensitive ion channel in Schizosaccharomycespombe.EMBO J. 1992;11(8):2869-2875. [15] Elinder F, Arhem P. Effects of gadolinium on ion channels in the myelinated axon of Xenopuslaevis: four sites of action. Biophys J. 1994;67(1):71-83. [16] Hamill OP. Foreword: mechanosensitive ion channels, Part B.Curr Top Membr. 2007;59:: xvii-xviii. [17] Gu Y, Gu C. Physiological and pathological functions of mechanosensitive ion channels. MolNeurobiol. 2014;50(2): 339-347. [18] Tyler WJ. The mechanobiology of brain function.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:867-878. [19] Takahashi K, Kakimoto Y, Toda K, et al. Mechanobiology in cardiac physiology and diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17: 225-232. [20] Woo SH, Ranade S, Weyer AD, et al. Piezo2 is required for Merkel-cell mechanotransduction. Nature. 2014;509:622-626. [21] Song S, Yamamura A, Yamamura H, et al. Flow shear stress enhances intracellular Ca2+ signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;307:C373. [22] Lolignier S, Eijkelkamp N, Wood JN. Mechanical allodynia. Pflugers Arch. 2015;467(1):133-139. [23] Chen YF, Chen YT, Chiu WT, et al. Remodeling of calcium signaling in tumor progression. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20:23. [24] Lennertz RC, Tsunozaki M, Bautista DM, et al. Physiological basis of tingling paresthesia evoked by hydroxy-alpha-sanshool.J Neurosci. 2010;30(12):4353-4361. [25] Árnadóttir J, O'Hagan R, Chen Y, et al. The DEG/ENaC protein MEC-10 regulates the transduction channel complex in C. elegans touch receptor neurons. J Neurosci. 2011;31:12695-12704. [26] Gottlieb P, Folgering J, Maroto R, et al. Revisiting TRPC1 and TRPC6 mechanosensitivity. Pflugers Arch. 2008;455(6): 1097-1103. [27] Corey DP, García-Añoveros J, Holt JR, et al. TRPA1 is a candidate for the mechanosensitive transduction channel of vertebrate hair cells. Nature. 2004;432:723-730. [28] Zhou X-L, Batiza AF, LoukinSH, et al. The Transient receptor potential channel on the yeast vacuole is mechanosensitive. ProcNatlAcadSci U S A. 2003;100(12):7105-7110. [29] Honoré E, Patel AJ, Chemin J, et al. Desensitization of mechano- gated K2P channels. ProcNatlAcadSci U S A. 2006;103(18): 6859-6864. [30] Bang H,Kim Y,Kim D.TREK-2, a new member of the mechanosensitive tandem-pore K+ channel family. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:17412. [31] Coste B, Mathur J, Schmidt M, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science. 2010;330:55-60. [32] Liu YS, Liu YA, Huang CJ, et al. Mechanosensitive TRPM7 mediates shear stress and modulates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells through Osterix pathway. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16522. [33] Xiao E, Yang H, Gan YH, et al. TRPM7 Senses Mechanical Stimulation Inducing Osteogenesis in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2015;33:615-621. [34] Hu K, Sun H, Gui B, Sui C. TRPV4 functions in flow shear stress induced early osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;91:841-848. [35] Coste B, Xiao B, Santos JS, et al. Piezos are pore-forming subunits of mechanically activated channels. Nature. 2012;483:176-181. [36] Yang XC, Sachs F. Block of stretch-activated ion channels in Xenopus oocytes by gadolinium and calcium ions. Science. 1989;243:1068-1071. [37] Ermakov YA, Kamaraju K, Sengupta K, et al. Gadolinium ions block mechanosensitive channels by altering the packing and lateral pressure of anionic lipids. Biophys J. 2010;98:1018-1027. [38] Suchyna TM, Johnson JH, Hamer K, et al. Identification of a Peptide Toxin from Grammostolaspatulata Spider Venom That Blocks Cation-Selective Stretch-Activated Channels. J Gen Physiol. 2000;115:583-598. [39] Gnanasambandam R, Ghatak C, Yasmann A, et al. GsMTx4: Mechanism of Inhibiting Mechanosensitive Ion Channels. Biophys J. 2017;112:31-45. [40] Kearney EM, Farrell EPrendergast PJ, et al. Tensile strain as a regulator of mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38:1767-1779. [41] Sumanasinghe RD, Bernacki SH, Loboa EG.Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in collagen matrices: effect of uniaxial cyclic tensile strain on bone morphogenetic protein (BMP-2) mRNA expression. Tissue Eng Part A. 2006;12:3459-3465. [42] Haudenschild AK, Hsieh AH, Kapila S, et al. Pressure and distortion regulate human mesenchymal stem cell gene expression. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009;37:492-502. [43] Mcmahon LA, Reid AJ, Campbell VA, et al. Regulatory Effects of Mechanical Strain on the Chondrogenic Differentiation of MSCs in a Collagen-GAG Scaffold: Experimental and Computational Analysis. Ann Biomed Eng. 2008;36:185-194. [44] Song G, Ju Y, Shen X, et al. Mechanical stretch promotes proliferation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2007;58:271-277. [45] Zhang B, Luo Q, Chen Z, et al. Cyclic mechanical stretching promotes migration but inhibits invasion of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2015;14(2):155-164. [46] Jr WD, Salasznyk RM, Klees RF, et al. Mechanical strain enhances extracellular matrix-induced gene focusing and promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells through an extracellular-related kinase-dependent pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2007;16(3):467-480. . [47] Huang CY, Hagar KL, Frost LE, et al. Effects of cyclic compressive loading on chondrogenesis of rabbit bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22:313-323. [48] Mouw JK, Connelly JT, Wilson CG, et al. Dynamic compression regulates the expression and synthesis of chondrocyte-specific matrix molecules in bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25:655-663. [49] Steward AJ, Wagner DR, Kelly DJ. Exploring the roles of integrin binding and cytoskeletal reorganization during mesenchymal stem cell mechanotransduction in soft and stiff hydrogels subjected to dynamic compression. J MechBehav Biomed Mater. 2014;38:174-182. [50] Arnsdorf EJ, Tummala P, Kwon RY, et al. Mechanically induced osteogenic differentiation--the role of RhoA, ROCKII and cytoskeletal dynamics. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:546-553.[51] Li YJ, Batra NN, You L, et al. Oscillatory fluid flow affects human marrow stromal cell proliferation and differentiation. J Orthop Res. 2004;22:1283-1289. [52] Huang Y, Jia X, Bai K, et al. Effect of fluid shear stress on cardiomyogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Arch Med Res. 2010;41:497-505. [53] Riddle RC, Taylor AF, Genetos DC, et al. MAP kinase and calcium signaling mediate fluid flow-induced human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;290:C776. [54] Xiao E, Yang H, Gan YH, et al. TRPM7 Senses Mechanical Stimulation Inducing Osteogenesis in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2015;33:615-621. [55] Angele P, Yoo JU, Smith C, et al. Cyclic hydrostatic pressure enhances the chondrogenic phenotype of human mesenchymal progenitor cells differentiated in vitro. J Orthop Res. 2003;21: 451-457. [56] Li J, Zhao Z, Yang J, et al. p38 MAPK mediated in compressive stress-induced chondrogenesis of rat bone marrow MSCs in 3D alginate scaffolds. J Cell Physiol. 2009;221:609. [57] Miyanishi K, Trindade MC, Lindsey DP, et al. Dose- and time-dependent effects of cyclic hydrostatic pressure on transforming growth factor-beta3-induced chondrogenesis by adult human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(8):2253-2262. [58] Wagner DR, Lindsey DP, Li KW, et al. Hydrostatic Pressure Enhances Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells in Osteochondrogenic Medium. Ann Biomed Eng. 2008;36(5):813-820. [59] Nam HY, BalajiRaghavendran HR, et al. Fate of tenogenic differentiation potential of human bone marrow stromal cells by uniaxial stretching affected by stretch-activated calcium channel agonist gadolinium.PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0178117. [60] Mcmahon LA, Campbell VA, Prendergast PJ. Involvement of stretch-activated ion channels in strain-regulated glycosaminoglycan synthesis in mesenchymal stem cell-seeded 3D scaffolds. J Biomech. 2008;41(9):2055-2059. [61] Martinac B, Adler J, Kung C. Mechanosensitive ion channels of E. coli activated by amphipaths. Nature. 1990;348:261-263. [62] Kung C. A possible unifying principle for mechanosensation. Nature. 2005;436:647-654. [63] Effertz T, Scharr AL, Ricci AJ. The how and why of identifying the hair cell mechano-electrical transduction channel.Pflugers Arch. 2015;467(1):73-84. [64] Brohawn SG, Su Z, Mackinnon R. Mechanosensitivity is mediated directly by the lipid membrane in TRAAK and TREK1 K+ channels. ProcNatlAcadSci U S A. 2014;111:3614-3619. [65] Kim TJ, Joo C, Seong J, et al. Distinct mechanisms regulating mechanical force-induced Ca²? signals at the plasma membrane and the ER in human MSCs. Elife. 2015;4:e04876. [66] Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin VI, Vasileva VY, Pugovkina NA, et al. Local calcium signalling is mediated by mechanosensitive ion channels in mesenchymal stem cells. BiochemBiophys Res Commun. 2016; 482(4):563-568. [67] Zhang YY, Yue J, Che H, et al. BK and hEag1 channels regulate cell proliferation and differentiation in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(2):202-212. [68] Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin VI, Negulyaev YA, Morachevskaya EA. Functional coupling of ion channels in cellular mechanotransduction. BiochemBiophys Res Commun. 2014;451(3):421-424. [69] Fakler B, Adelman JP. Control of K Channels by Calcium Nano/Microdomains.Neuron. 2008;59:873-881. [70] Sugimoto A, Miyazaki A, Kawarabayashi K. Piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 functions as a regulator of the cell fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):17696. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||