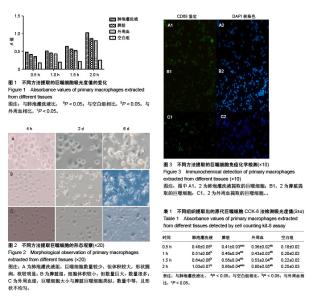
| [1] Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Pollard, Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature.2013;496 (7446):445-455.[2] Ginhoux F, Jung S. Monocytes and macrophages: developmental pathways and tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(6): 392-404.[3] Saidi H, Bérubé J, Laraba-Djebari F, et al. Involvement of alveolar macrophages and neutrophils in acute lung injury after scorpion envenomation:new pharmacological targets. Inflammation.2018.doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0731-9.[4] Morón-Calvente V, Romero-Pinedo S, Toribio-Castelló S, et al. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, NAIP, cIAP1 and cIAP2 expression during macrophage differentiation and M1/M2 polarization. PLoS One.2018;13(3):e0193643.[5] 翟涛,宫鹏涛,张西臣,等.新孢子虫感染小鼠巨噬细胞IFN,TN和IL6分泌的变化[J].中国病原生物学杂志,2017,(4): 350-352,358.[6] 刘华,田嘉铭,孙黎,等.正常小鼠巨噬细胞及外周血淋巴细胞亚群对防风多糖干预的反应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(18):3475-3478.[7] Kobayashi H, Kobayashi M, Heming, et al. TA Cytokine production by rabbit alveolar macrophages: differences between activated and suppressor cell phenotypes. Immunol Lett. 1999;69(3):339-346.[8] Savill J, Dransfield I, Gregory C, et al. A blast from the past: clearance of apoptotic cells regulates immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(12):965-975.[9] Gordon S, Taylor PR. Taylor, Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol.2005;5(12): 953-964.[10] Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008; 8(12): 958-969.[11] Sica A, Erreni M, Allavena P, et al. Macrophage polarization in pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci.2015;72(21):4111-4126.[12] Davies LC, Jenkins SJ, Allen JE, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2013;14(10):986-995.[13] 章述军,雷青松,李麟,等.两种PMA诱导方案对THP-1巨噬细胞M1和M2亚型相关基因表达的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2017,39(6): 765-771.[14] 翟纯刚,季晓平,王和峰,等.抑制PI3K/Akt/m TOR信号通路对兔原代巨噬细胞自体吞噬的影响及机制[J].中国动脉硬化杂志, 2014,1(3):7-12.[15] Epstein-Barash H, Gutman D, Markovsky E, et al. Physicochemical parameters affecting liposomal bisphosphonates bioactivity for restenosis therapy: Internalization, cell inhibition, activation of cytokines and complement, and mechanism of cell death. J Control Release. 2010;146(2):182-195.[16] Badaoui B, Rutigliano T, Anselmo A, et al. RNA-sequence analysis of primary alveolar macrophages after in vitro infection with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strains of differing virulence. PLoS One.2014; 9(3): e91918.[17] Li J, Yao ZY, She C, et al. Effects of low-dose X-ray irradiation on activated macrophages and their possible signal pathways. PLoS One.2017;12(10):e0185854.[18] Qiu W, Liu S, Chen J, et al. The primary culture of carp (Cyprinus carpio) macrophages and the verification of its phagocytosis activity. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.2015; 52(1): 10-19.[19] 杨琳,田蕾,谢杰施,等.一种简单的分离、培养及鉴定小鼠外周血单核巨噬细胞方法的建立[J].首都医科大学学报,2015,36(4): 610-613.[20] 关开泮,江仁, 徐雪,等.旋毛虫排泄分泌抗原53-ku重组蛋白上调M2型肺泡巨噬细胞减轻脓毒症小鼠急性肺损伤[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2017,38(5):670-675.[21] 何俊,徐文莉,曾思,等.大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞原代培养技术的改良措施[J].徐州医学院学报, 2010,30(5):325-327.[22] Qiu W, Liu S, Chen J, et al. The primary culture of carp (Cyprinus carpio) macrophages and the verification of its phagocytosis activity. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.2016; 52(1):10-19.[23] Farooque A, Afrin F, Adhikari JS, et al. Polarization of macrophages towards M1 phenotype by a combination of 2-deoxy-d-glucose and radiation: Implications for tumor therapy. Immunobiology.2016;221(2):269-281.[24] Takeshita S, Kaji K, Kudo A. Identification and Characterization of the new osteoclast progenitor with macrophage phenotypes being able to differentiate into mature osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res.2000;15:1477-1488.[25] 周龙,陈曦,罗宗平,等.C57BL/6小鼠骨髓单核细胞分离、培养、纯化及向破骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(6): 940-944.[26] 袁娜娜.Real-time PCR精确定量检测CD68阳性巨噬细胞在结直肠癌中的表达及意义[D]. 郑州大学.2012.[27] 刘志,黄允宁.生理状态下大鼠大网膜I型与II型乳斑内CD68、CD163阳性巨噬细胞数量对比研究[J].宁夏医学杂志, 2014, 36(2):139-140.[28] 尹国栋,倪斌,周风金,等.脊髓损伤局部表达NgR的巨噬细胞的体外分离培养[J].脊柱外科杂志,2009,7(4):198-200.[29] 陈龙,熊先智.巨噬细胞的极化分型在慢性阻塞性肺疾病中的研究进展[J].国际呼吸杂志,2014,34(21):1671-1676.[30] Jenkins SJ, Ruckerl D, Cook PC, et al. Local macrophage proliferation, rather than recruitment from the blood, is a signature of TH2 inflammation. Science. 2011;332(6035): 1284-1288. |