Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (24): 3857-3862.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0831
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory mechanism underlying testicular maintenance in a mouse model of Gata6 gene knockdown
Wang Shun-de, Li Jing, Wang Shu-hong
- Chongqing Three Gorges Central Hospital, Chongqing 404000, China
-
Received:2018-01-30 -
Contact:Wang Shu-hong, Master, Attending physician, Chongqing Three Gorges Central Hospital, Chongqing 404000, China -
About author:Wang Shun-de, Associate chief physician, Chongqing Three Gorges Central Hospital, Chongqing 404000, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology innovation Project of Social Programs and Strengthening Peasant’s Livelihood of Chongqing, No. cstc2016shmszx130028
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Shun-de, Li Jing, Wang Shu-hong. Regulatory mechanism underlying testicular maintenance in a mouse model of Gata6 gene knockdown[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(24): 3857-3862.
share this article
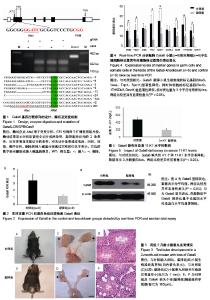
2.1 Gata6 敲降序列选择及突变检测 将靶序列选择在Gata6的第一个外显子上,靶序列为:GGC GCC TTC ATG CAC AGC GCG GG,酶切位点为AlwI。提取小鼠尾巴基因组DNA,扩增DNA片段,用AlwI限制性内切酶进行酶切。在对照组相比较,AlwI能切开成2明显的DNA条带,一条322 bp,另一条140 bp,而敲降组大部分条带未被切开。将敲降组未切开条带回收、测序,测序得到的序列与对照组相比较,结果显示在22个测序样品共有10个中出现2-103个碱基不同程度的缺失或者插入(图1)。 2.2 小鼠Gata6敲降后表达 通过实时定量PCR技术和 蛋白免疫印迹检测敲降组和对照组小鼠Gata6表达量,在敲降组中发现Gata6的表达量不论基因水平(图2A)还是蛋白水平(图2B)都显著性降低。 2.3 Gata6基因敲降影响睾丸的发育结果 与对照组睾丸相比,2月龄Gata6基因敲降阳性小鼠睾丸与肛门的距离更短(图3A,B);睾丸和相关生殖器官的大小显著性降低(图3C,D)。 组织学观察(苏木精-伊红染色)发现,敲降阳性小鼠个体的精巢发育不完整,出现明显的空腔,精原细胞明显减少(图3E,F)。 2.4 Gata6缺失对小鼠相关雄性相关信号通路中基因的影响 取2月龄雄性敲降小鼠和正常小鼠睾丸,提取RNA,反转录成cDNA,通过实时荧光定量PCR方法检测生殖细胞和体细胞相关基因变化情况。如图4所示,与正常对照组相比,敲降组小鼠睾丸中与减数分裂和精原细胞相关的标记基因表达量显著性降低(Stra8,Vasa,Tnp1,Spo11),同时,与体细胞相关的标记基因表达量也显著性降低(Sox9,17HSDb3,Dmrt1),但是Cx30.2和Dazl基因无显著性变化(图4)。 2.5 Gata6缺失对小鼠激素水平的影响 采用酶联免疫法(EIA)检测2月龄Gata6基因敲降阳性小鼠雄激素(11-KT)水平,结果显示,Gata6基因敲降阳性小鼠雄性个体雄激素水平与对照组雄性个体相比显著降低(图5)。"
| [1] Lee HY, Zhao S, Fields PA,et al.The extent to which relaxin promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of cervical epithelial and stromal cells is greatest during late pregnancy in rats. Endocrinology.2005;146(1):511-518.[2] 景彩霞,杨加周,艾庆燕,等. GATA家族与生殖[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2009, 15(10):932-936.[3] Cui X,Jing X,Wu X, et al. Protective effect of resveratrol on spermatozoa function in male infertility induced by excess weight and obesity. Mol Med Rep.2016; 14(5):4659-4665.[4] Hayashi S, Akiyama R, Wong J, et al. Gata6-Dependent GLI3 Repressor Function is Essential in Anterior Limb Progenitor Cells for Proper Limb Development.PLoS Genet.2016;12(6): e1006138.[5] Xuan S,Sussel L.GATA6 and GATA6 regulate pancreatic endoderm identity through inhibition of hedgehog signaling. Development.2016;143(5):780-786.[6] 岳文慧,张立广,于铁莉,等.GATA-6蛋白在喉鳞状细胞癌组织中的表达及意义[J].山东医药,2014,54(37):29-31.[7] Zito G, Naselli F, Saieva L, et al. Retinoic Acid affects Lung Adenocarcinoma growth by inducing differentiation via GATA6 activation and EGFR and Wnt inhibition.Sci Rep.2017;7(1): 4770.[8] 陈文博,张世能,庄燕妍,等.胰腺癌组织转录因子GATA-6表达及其意义的探讨[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2011, 18(14):1101-1104.[9] Zhang X, Wang H, Li M,et al.Isolation of doublesex- and mab-3-related transcription factor 6 and its involvement in spermatogenesis in tilapia.Biol Reprod.2014;91(6):136.[10] 宋强. 尼罗罗非鱼两种relaxin3基因的克隆、表达与功能研究[D].西南大学.[11] Sun H, Wang X, Liu K, et al.β-catenin coordinates with Jup and the TCF1/GATA6 axis to regulate human embryonic stem cell fate. Dev Biol.2017;431(2):272-281.[12] Maitra M,Schluterman MK,Nichols HA,et al.Interaction of Gata4 and Gata6 with Tbx5 is critical for normal cardiac development. Dev Biol.2009;362(2):368-377.[13] Convissar SM, Bennett J, Baumgarten SC,et al. GATA6 and GATA6 Knockdown During Luteinization Inhibits Progesterone Production and Gonadotropin Responsiveness in the Corpus Luteum of Female Mice.Biol Reprod.2015;96(6): 133.[14] 许细财,李奋,周万平,等. 单纯性房间隔缺损患儿GATA4 和GATA6 基因突变筛查[J].临床儿科杂志, 2015, 33(3):229-229.[15] Okumura T,Takeda K,Kuchiki M,et al.GATAe regulates intestinal stem cell maintenance and differentiation in Drosophila adult midgut.Dev Biol.2016;410(1):24-35.[16] Sozen B, Ozturk S, Yaba A, et al. The p38 MAPK signalling pathway is required for glucose metabolism, lineage specification and embryo survival during mouse preimplantation development. Mech Dev.2015;138(3): 375-398.[17] Shirazi R,Zarnani AH,Soleimani M,et al.Differentiation of bone marrow-derived stage-specific embryonic antigen 1 positive pluripotent stem cells into male germ cells. Microsc Res Tech. 2017;80(4):430-440.[18] 张龙波,苟欣,何卫阳,等. GATA6、ROR2和STAT3在膀胱移行细胞癌的表达及其意义[J], 重庆医科大学学报, 2011, 36(5): 535-538.[19] Fairchild MJ,Smendziuk CM,Tanentzapf G.A somatic permeability barrier around the germline is essential for Drosophila spermatogenesis.Development.2015;142(2):268-281.[20] Foster JW,Brennan FE,Hampikian GK,et al.Evolution of sex determination and the Y chromosome: SRY-related sequences in marsupials.Nature.1992;359(6395):531-533.[21] Froese N, Kattih B, Breitbart A, et al.GATA6 promotes angiogenic function and survival in endothelial cells by suppression of autocrine transforming growth factor beta/activin receptor-like kinase 5 signaling. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(7):5680-5690.[22] Rodríguez A, Allegrucci C, Alberio R.Modulation of pluripotency in the porcine embryo and iPS cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49079.[23] Visser JA,Themmen AP.Anti-Mullerian hormone and folliculogenesis.Mol Cell Endocrinol.2005;234(1-2):81-86.[24] Lee WY, Lee R, Song H,et al. Establishment of a surgically induced cryptorchidism canine recipient model for spermatogonial stem cell transplantation.Lab Anim Res. 2016;32(4):257-266.[25] Fisher JB,Pulakanti K,Rao S,et al. GATA6 is essential for endoderm formation from human pluripotent stem cells.Biol Open.2017;6(7):1084-1095.[26] Allen HL,Flanagan SE,Shaw-Smith C,et al.GATA6 haploinsufficiency causes pancreatic agenesis in humans.Nat Genet. 2011;44(1):20-22.[27] 才锦麟,阿力亚,何强.慢病毒介导的GATA6 基因沉默对肝癌Huh-7细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2015, 31(5): 938-942.[28] 龚春华,李爱国,赵庆顺,等.视黄酸对乙醇致斑马鱼胚胎心脏发育畸形的影响[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2010,25(1):53-56.[29] De Franco E, Shaw-Smith C, et al. GATA6 mutations cause a broad phenotypic spectrum of diabetes from pancreatic agenesis to adult-onset diabetes without exocrine insufficiency. Diabetes 2013, 62(3):993-997.[30] Rémond MC, Iaffaldano G,et al. GATA6 reporter gene reveals myocardial phenotypic heterogeneity that is related to variations in gap junction coupling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2011, 301(5):H1952-H1964.[31] Summers AF, Pohlmeier WE, Sargent KM. Altered theca and cumulus oocyte complex gene expression, follicular arrest and reduced fertility in cows with dominant follicle follicular fluid androgen excess. PLoS One. 2014;9(10): e110683.[32] Miyagi H, Nag K, Sultana N, Munakata K,et al. Characterization of the zebrafish cx36.7 gene promoter: Its regulation of cardiac-specific expression and skeletal muscle-specific repression. Gene. 2016;577(2):265-274.[33] Murphy SJ, Hart SN, Halling GC, et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas Reveals Genomic Rearrangement Events as Significant Drivers of Disease. Cancer Res. 2016; 76(3):749-761.[34] Convissar SM, Bennett J, Baumgarten SC, et al. GATA4 and GATA6 Knockdown During Luteinization Inhibits Progesterone Production and Gonadotropin Responsiveness in the Corpus Luteum of Female Mice. Biol Reprod. 2015; 93(6):133.[35] Jahromi MS, Tehrani FR, Noroozzadeh M, et al. Elevated expression of steroidogenesis pathway genes; CYP17, GATA6 and StAR in prenatally androgenized rats. Gene. 2016;593(1):167-171.[36] Porter JL, Bukey BR, Geyer AJ, et al. Immunohistochemical detection and regulation of α5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunits by FoxA2 during mouse lung organogenesis. Respir Res. 2011;12:82.[37] Bennett J, Baumgarten SC, Stocco C. GATA4 and GATA6 silencing in ovarian granulosa cells affects levels of mRNAs involved in steroidogenesis, extracellular structure organization, IGF-I activity, and apoptosis. Endocrinology. 2013;154(12):4845-4858.[38] Kee HJ, Park S, Kang W, et al. Piceatannol attenuates cardiac hypertrophy in an animal model through regulation of the expression and binding of the transcription factor GATA binding factor 6. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(9):1529-1536.[39] Deng SQ, Xu H, He Q,et al. Detecting the developmental toxicity of bFGF in the embryonic stem cell test using differential gene expression of differentiation-related genes. Toxicol Mech Methods. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2014;24(5): 323-331.[40] Orgeig S, McGillick EV, Botting KJ, et al. Increased lung prolyl hydroxylase and decreased glucocorticoid receptor are related to decreased surfactant protein in the growth-restricted sheep fetus. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015;309(1):L84-L97.[41] Geng Z, Li P, Tan L,et al. Targeted Knockdown of RNA-Binding Protein TIAR for Promoting Self-Renewal and Attenuating Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2015; 2015:657325.[42] Katsuyama M, Demura M, Katsuyama H, et al. Genistein and menaquinone-4 treatment-induced alterations in the expression of mRNAs and their products are beneficial to osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cell functions. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16(1):873-880. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [6] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [7] | Ma Zhijie, Li Jingyu, Cao Fang, Liu Rong, Zhao Dewei. Influencing factors and biological property of novel biomedical materials: porous silicon carbide coated with bioactive tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 558-563. |
| [8] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [9] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [10] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [11] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [12] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [13] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [14] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [15] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||