Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (1): 113-118.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0420
Previous Articles Next Articles
An in vitro study of enhancing tendon-bone healing by human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells co-modified with hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and Scleraxis gene
Zhu Xi-zhong1, Liu Zi-ming2, Liu Yi1, Xiong Hua-zhang1, Yang Ji-bin1, Li Yu-wan1, Jin Ying1, Wu Shu-hong1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopaedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400000, China
-
Revised:2017-11-20Online:2018-01-08Published:2018-01-08 -
Contact:Wu Shu-hong, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhu Xi-zhong, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Joint Foundation of Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. (2012)172, [2016]7477; [2017]2882
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Xi-zhong, Liu Zi-ming, Liu Yi, Xiong Hua-zhang, Yang Ji-bin, Li Yu-wan, Jin Ying, Wu Shu-hong. An in vitro study of enhancing tendon-bone healing by human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells co-modified with hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and Scleraxis gene[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(1): 113-118.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
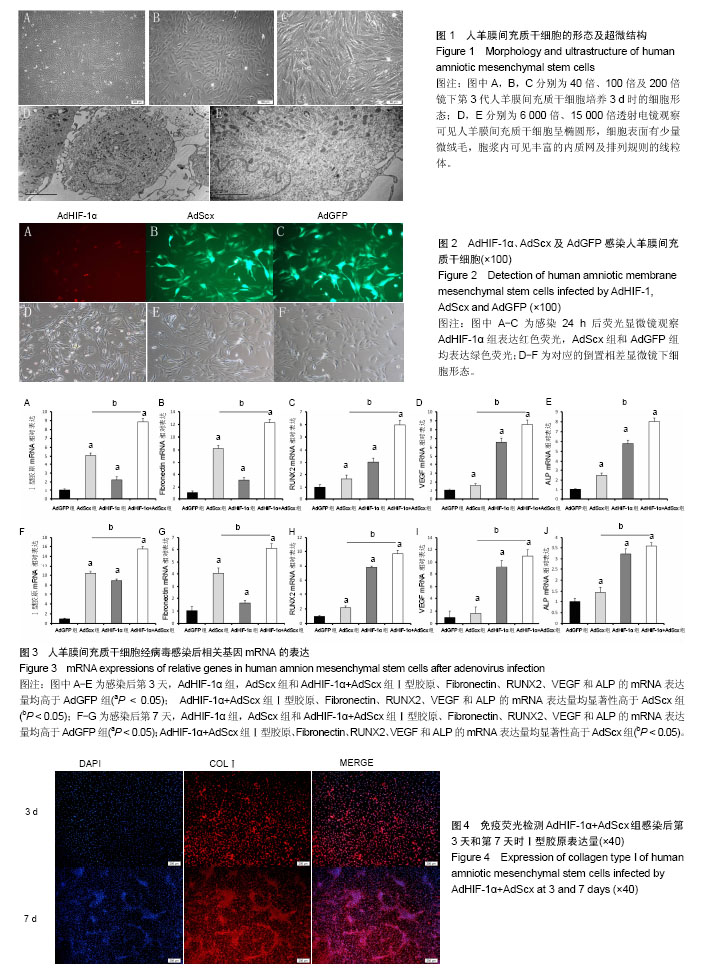
2.1 人羊膜间充质干细胞的形态 倒置相差显微镜显示:40倍镜下第3代人羊膜间充质干细胞呈长梭形贴壁生长,可见漩涡形成(图1A);100倍镜下可见细胞接触紧密,类似于三角形或长菱形(图1B);200倍镜下观察细胞长梭状明显,细胞间相互黏附(图1C)。透射电镜观察可见人羊膜间充质干细胞呈椭圆形,结构清晰,细胞表面有少量微绒毛,染色质分布均匀,胞浆内可见丰富的内质网及排列规则的线粒体(图1D,E)。 2.2 病毒感染人羊膜间充质干细胞 倒置相差显微镜显示:AdHIF-1α组,AdScx组和AdGFP组细胞贴壁生长,呈长梭状,与正常细胞相比无明显形态异常;荧光显微镜观察显示:转染24 h后,AdHIF-1α组表达红色荧光,荧光表达量约为50%,AdScx组和AdGFP组均表达绿色荧光,荧光表达量约为70%(图2)。 2.3 实时荧光定量PCR检测结果 感染第3天和第7天时,AdHIF-1α组,AdScx组和AdHIF-1α+AdScx组Ⅰ型胶原、Fibronectin、RUNX2、VEGF和ALP的mRNA表达量均高于AdGFP组(P < 0.05);感染第3天和第7天时,AdHIF-1α+AdScx组Ⅰ型胶原、Fibronectin、RUNX2、VEGF和ALP的mRNA表达量均显著性高于AdScx组(P < 0.05),见图3。 2.4 荧光免疫组化分析 AdHIF-1α+AdScx组感染后第7天时Ⅰ型胶原表达量高于AdHIF-1α+AdScx组感染后第3天时表达量(图4)。"
| [1] Chen T, Zhang P, Chen J, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Using Either Synthetics With Remnant Preservation or Hamstring Autografts: A 10-Year Longitudinal Study. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(12):2739-2750.[2] Park SH, Choi YJ, Moon SW, et al. Three-Dimensional Bio-printed Scaffold Sleeves With Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Enhancement of Tendon-to-Bone Healing in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Using Soft-Tissue Tendon Graft. Arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(1):166-179. [3] Kato Y, Ingham SJ, Kramer S, et al. Effect of tunnel position for anatomic single-bundle ACL reconstruction on knee biomechanics in a porcine model. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2010;18(1): 2-10.[4] Xu Y, Liu J, Kramer S, et al. Comparison of in situ forces and knee kinematics in anteromedial and high anteromedial bundle augmentation for partially ruptured anterior cruciate ligament. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(2):272-278.[5] 金瑛,李豫皖,张承昊,等.体外诱导人羊膜间充质干细胞向韧带细胞分化的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(2):237-244.[6] 李豫皖,朱喜忠,金瑛,等. 体外定向诱导人羊膜间充质干细胞向骨、软骨及脂肪细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(1):122-127.[7] Ilancheran S, Moodley Y, Manuelpillai U. Human fetal membranes: a source of stem cells for tissue regeneration and repair. Placenta. 2009;30(1):2-10.[8] Choudhry H, Harris AL. Advances in Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Biology. Cell Metab. 2017 Nov 8. [Epub ahead of print][9] Hu K, Olsen BR. Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):509-526.[10] Zhou N, Hu N, Liao JY, et al. HIF-1a as a Regulator of BMP2-Induced Chondrogenic Differentiation, Osteogenic Differentiation, and Endochondral Ossification in Stem Cells. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2015;36(1):44-60.[11] Lampert FM, Kütscher C, Stark GB, et al. Overexpression of Hif-1α in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Affects Cell-Autonomous Angiogenic and Osteogenic Parameters. J Cell Biochem. 2016;117(3):760-768.[12] Alberton P, Popov C, Prägert M, et al. Conversion of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into tendon progenitor cells by ectopic expression of scleraxis. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(6): 846-858.[13] Yoshimoto Y, Takimoto A, Watanabe H, et al. Scleraxis is required for maturation of tissue domains for proper integration of the musculoskeletal system. Sci Rep. 2017;7:45010.[14] Gulotta LV, Kovacevic D, Ying L, et al. Augmentation of tendon-to-bone healing with a magnesium-based bone adhesive. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36(7):1290-1297.[15] Hettrich CM, Gasinu S, Beamer BS, et al. The effect of mechanical load on tendon-to-bone healing in a rat model. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(5):1233-1241.[16] Levy BA, Dajani KA, Morgan JA, et al. Repair versus reconstruction of the fibular collateral ligament and posterolateral corner in the multiligament-injured knee. Am J Sports Med. 2010; 38(4):804-809.[17] Tashjian RZ, Hollins AM, Kim HM, et al. Factors affecting healing rates after arthroscopic double-row rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(12):2435-2442.[18] Jang KM, Lim HC, Jung WY, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of a Rabbit Model: New Strategy to Enhance Tendon Graft Healing. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(8):1530-1539.[19] Nguyen VT, Cancedda R, Descalzi F. et al. Platelet lysate activates quiescent cell proliferation and reprogramming in human articular cartilage: involvement of Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017 Oct 19. [Epub ahead of print][20] Li H, Huang L, Xie Q, et al. Study on the effects of gradient mechanical pressures on the proliferation, apoptosis, chondrogenesis and hypertrophy of mandibular condylar chondrocytes in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 2017;73:186-192.[21] Maes C. Signaling pathways effecting crosstalk between cartilage and adjacent tissues: Seminars in cell and developmental biology: The biology and pathology of cartilage. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017; 62:16-33.[22] Johnson RW, Schipani E, Giaccia AJ. HIF targets in bone remodeling and metastatic disease. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;150:169-177.[23] 王国祥,刘殿玉,刘晓莉,等. 肌腱周围炎大鼠模型建立与针刺干预作用的实验研究[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2011,38(12):2310-2313.[24] Bavin EP, Atkinson F, Barsby T, et al. Scleraxis Is Essential for Tendon Differentiation by Equine Embryonic Stem Cells and in Equine Fetal Tenocytes. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26(6):441-450.[25] Murchison ND, Price BA, Conner DA, et al. Regulation of tendon differentiation by scleraxis distinguishes force-transmitting tendons from muscle-anchoring tendons. Development. 2007; 134(14):2697-2708.[26] Li Y, Ramcharan M, Zhou Z, et al. The Role of Scleraxis in Fate Determination of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tenocyte Differentiation. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13149.[27] 方宁,张路,宋秀军,等. 人羊膜间充质干细胞的分离、培养及鉴定[J]. 遵义医学院学报, 2009,32(3):234-236.[28] Niwa H, Masui S, Chambers I, et al. Phenotypic complementation establishes requirements for specific POU domain and generic transactivation function of Oct-3/4 in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(5):1526-1536.[29] Fu Y, Liu S, Cui SJ, et al. Surface Chemistry of Nanoscale Mineralized Collagen Regulates Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell Fate. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(25):15958-15966.[30] Federer AE, Steele JR, Dekker TJ, et al. Tendonitis and Tendinopathy: What Are They and How Do They Evolve. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017;22(4):665-676.[31] Krstic J, Trivanovic D, Obradovic H, et al. Regulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation by Transforming Growth Factor Beta Superfamily. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017 Nov 16. [Epub ahead of print][32] Zhang JC, Song ZC, Xia YR, et al. Extracellular matrix derived from periodontal ligament cells maintains their stemness and enhances redifferentiation via the wnt pathway. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017 Sep 7. [Epub ahead of print][33] Otabe K, Nakahara H, Hasegawa A, et al. Transcription factor Mohawk controls tenogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. J Orthop Res. 2015; 33(1):1-8.[34] Branco-Price C, Evans CE, Johnson RS. Endothelial hypoxic metabolism in carcinogenesis and dissemination: HIF-A isoforms are a NO metastatic phenomenon. Oncotarget. 2013;4(12):2567-2576.[35] Chen J, Yang L, Guo L, et al. Sodium hyaluronate as a drug-release system for VEGF 165 improves graft revascularization in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a rabbit model. Exp Ther Med. 2012;4(3):430-434.[36] Ai C, Sheng D, Chen J, et al. Surface modification of vascular endothelial growth factor-loaded silk fibroin to improve biological performance of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene via promoting angiogenesis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:7737-7750.[37] Jensen T, Baas J, Dolathshahi-Pirouz A, et al. Osteopontin functionalization of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in a PDLLA matrix promotes bone formation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011; 99(1):94-101.[38] Jiang L, Tang Z. Expression and regulation of the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in periodontal tissue remodeling of orthodontic tooth movement. Mol Med Rep. 2017 Nov 10. [Epub ahead of print][39] Bottini M, Mebarek S, Anderson KL, et al. Matrix vesicles from chondrocytes and osteoblasts: Their biogenesis, properties, functions and biomimetic models.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017 Nov 3. [Epub ahead of print] |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||