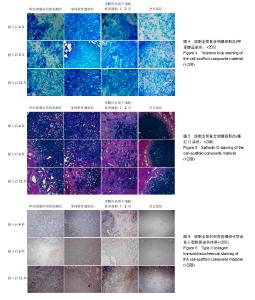
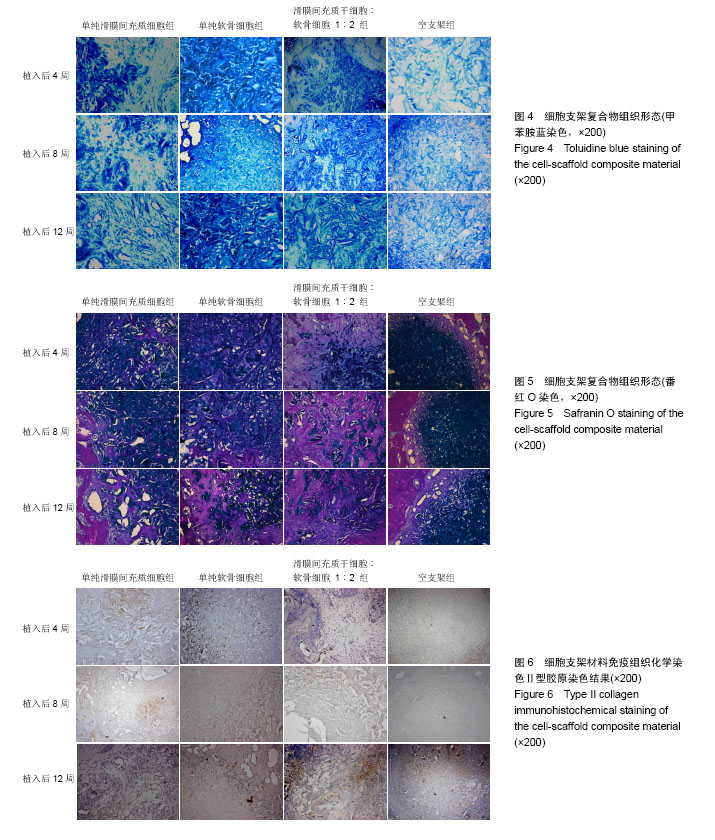
| [1] Nishioka M, Ioi H, Matsumoto R, et al. TMJ osteoarthritis/ osteoarthrosis and immune system factors in a Japanese sample. Angle Orthod. 2008;78(5):793-798. [2] Zhang S, Yap AU, Toh WS. Stem Cells for Temporomandibular Joint Repair and Regeneration. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(5): 728-742. [3] Steinert A F, Ghivizzani SC, Rethwilm A, et al. Major biological obstacles for persistent cell-based regeneration of articular cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(3):213.[4] Sakaguchi Y, Sekiya I, Yagishita K, et al. Comparison of human stem cells derived from various mesenchymal tissues:superiority of synovium as a cell source. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(8):2521-2529.[5] Fu P, Cong R, Chen S, Zhang L, et al. Conditions of synovial mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into fibrocartilage cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015;29(1):81-91. [6] Koga H, Engebretsen L, Brinchmann J E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for cartilage repair: a review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17(11):1289-1297.[7] Shapiro F, Koide S, Glimcher MJ. Cell origin and differentiation in the repair of full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(4):532-553.[8] 宁晓婷,邵博,龚忠诚,等.滑膜间充质干细胞与软骨细胞三维条件下混合培养向软骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(34):5434-5440.[9] 龚忠诚,魏丽丽,吴杨,等.滑膜间充质干细胞软骨分化能力的实验研究[J]. 新疆医科大学学报,2010,33(1):22-25.[10] 邵博,龚忠诚,刘慧,等.大鼠来源滑膜间充质干细胞的成软骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(15):2338-2344.[11] 龚忠诚,龙星,林兆全,等.壳聚糖/Ⅰ型胶原复合支架材料制备及其性能的研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2009,32(12):1670-1674.[12] Ahmed TA, Hincke MT. Mesenchymal stem cell-based tissue engineering strategies for repair of articular cartilage. Histol Histopathol. 2014;29(6):669-689.[13] De Bari C, Dell’Accio F, Tylzanowski P, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from adult human synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheum, 2001;44(8):1928-1942.[14] Pei M. Optimization of an in vitro three-dimensional microenvironment to reprogram synovium-derived stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011; 17(5-6):703-712.[15] Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Regeneration of articular cartilage of the knee. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33(4):837-845.[16] Kurth TB, Dell'accio F, Crouch V, et al. Functional mesenchymal stem cell niches in adult mouse knee joint synovium in vivo. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(5):1289-1300.[17] Miyamoto A, Deie M, Yamasaki T, et al. The role of the synovium in repairing cartilage defects. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15(9):1083-1093.[18] 杨萌,邵博,龚忠诚,等.三维环境下软骨细胞诱导滑膜间充质干细胞向软骨样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(11): 1544-1550.[19] Jones E, Churchman SM, English A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in rheumatoid synovium: enumeration and functional assessment in relation to synovial inflammation level. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(2):450-457.[20] Yoshimura H, Muneta T, Nimura A, et al. Comparison of rat mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, synovium, periosteum, adipose tissue, and muscle. Cell Tissue Res. 2007;327(3):449-462. |