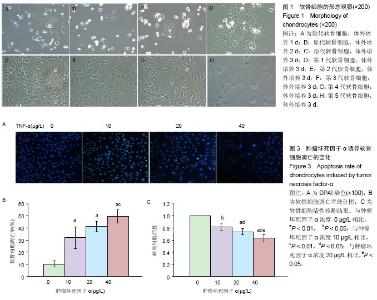
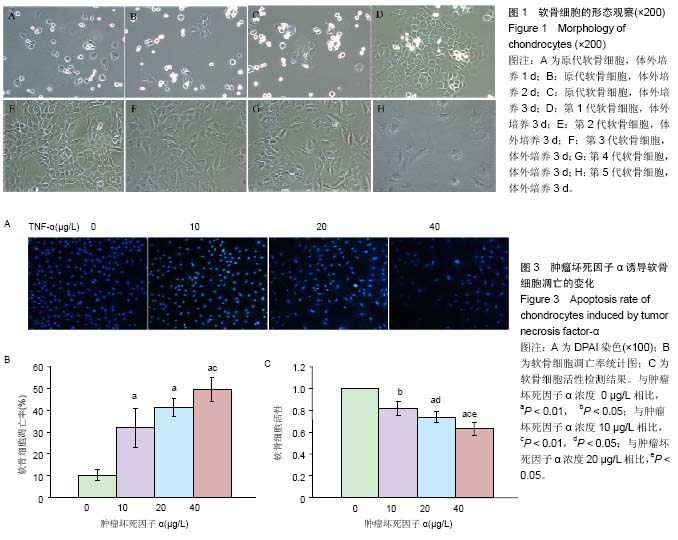
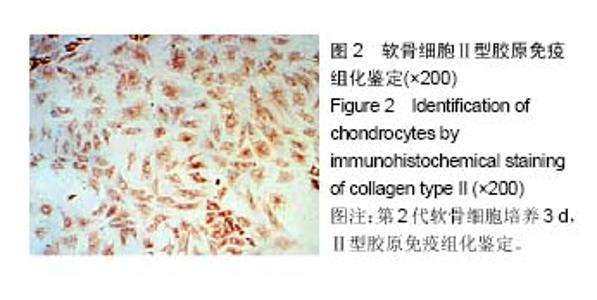
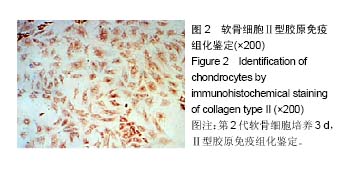
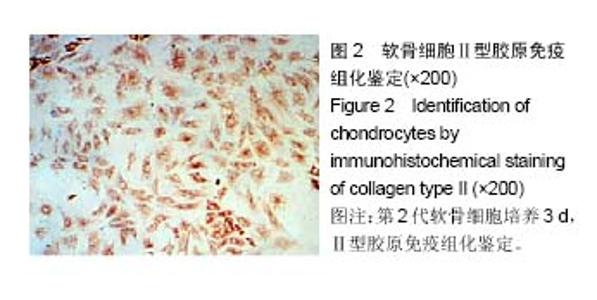
| [1] 李西海,梁文娜,软骨下骨骨重塑与骨关节炎的关系[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2007,28(01):35-37.[2] 陈后煌,邵翔,马玉环,等. 电针调节骨关节炎软骨细胞功能的机制探讨[J]. 风湿病与关炎,2015,4(6):37-41.[3] 叶锦霞,吴广文,李西海,等. 透骨消痛胶囊对凋亡软骨细胞Rac1和Cdc42表达的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(42): 6747-6751.[4] Liu F, Liu G, Liang W, et al. Duhuo Jisheng decoction treatment inhibits the sodium nitroprussiateinduced apoptosis of chondrocytes through the mitochondrial dependent signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med, 2014, 34(6):1573-1580.[5] Liu F, Weng X, Lin P, et al. Duhuo Jisheng decoction inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrocytes induced by tunicamycin through the downregulation of miR-34a. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(5):1311-1318. [6] Malemud CJ, Lewis AC, Wylie MA, et al. U0126, an Inhibitor of MEK1/2, Increases Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha-Induced Apoptosis, but not Interleukin-6 Induced Apoptosis in C-28/I2 Human Chondrocytes. J Autoimmune Disord. 2015;1(1). pii: 4. Epub 2015 Nov 7.[7] Lee SW, Rho JH, Lee SY, et al. Leptin protects rat articular chondrocytes from cytotoxicity induced by TNF-alpha in the presence of cyclohexamide. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015; 23(12):2269-2278.[8] 叶锦霞,王武炼,吴广文,等. 透骨消痛胶囊对TNF-α诱导关节软骨细胞Rho/Rock信号通路的影响[J]. 福建中医药大学学报, 2013,23(4):20-24.[9] Weng X, Lin P, Liu F, et al. Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides activate the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway to promote chondrocyte proliferation. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(4):1045-1050.[10] Yu S M, Kim S J. Salinomycin causes dedifferentiation via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway in rabbit articular chondrocytes. J Pharmacol Sci.2015;127(2): 196-202.[11] Yu F,Li X,Cai L,et al.Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides induce chondrocyte proliferation via the promotion of the G1/S cell cycle transition. Mol Med Rep.2013;7(3):935-940.[12] Li H, Li X, Liu G, et al. Bauhinia championi (Benth.) Benth. polysaccharides upregulate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med.2013;32(6):1329-1336.[13] Li X, Chen J, Liang W, et al. Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction promotes chondrocyte proliferation by stimulating cell cycle progression. Exp Ther Med.2015; 9(3):839-844.[14] Li X, Du M, Liu X, et al. Millimeter wave treatment inhibits NO-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes through the p38MAPK pathway.Int J Mol Med.2010;25(3):393-399.[15] Lin P, Weng X, Liu F, et al. Bushen Zhuangjin decoction inhibits TM-induced chondrocyte apoptosis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int J Mol Med.2015;36(6): 1519-1528.[16] 吴明霞,李西海,李俐,等.电针后血清对TNF-α诱导凋亡软骨细胞MAPK信号通路的影响[J]. 福建中医药,2011,42(6):43-45.[17] 史达,赵聪喆,柴惠斌,等. IL-1β诱导内质网应激增加人软骨细胞凋亡[J].基础医学与临床, 2015, 35(8): 1089-1093.[18] Genemaras AA, Ennis H, Kaplan L, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce specific time- and concentration- dependent microRNA release by chondrocytes, synoviocytes and meniscus cells. J Orthop Res. 2016, 34(5):779-790.[19] Ye J, Wu G, Li X, et al. Millimeter Wave Treatment Inhibits Apoptosis of Chondrocytes via Regulation Dynamic Equilibrium of Intracellular Free Ca (2+). Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2015;2015:464161. |