Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (33): 5407-5412.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.33.025
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation by different pathways and stem cell tracing by bioluminescence imaging in the treatment of ischemic brain injury
Wang Li-xin, Li Hui-ping
- Chinese Traditional Medicine Hospital of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2017-08-21Online:2017-11-28Published:2017-12-01 -
About author:Wang Li-xin, M.D., Chief physician, Chinese Traditional Medicine Hospital of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81373569
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Li-xin, Li Hui-ping. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation by different pathways and stem cell tracing by bioluminescence imaging in the treatment of ischemic brain injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(33): 5407-5412.
share this article
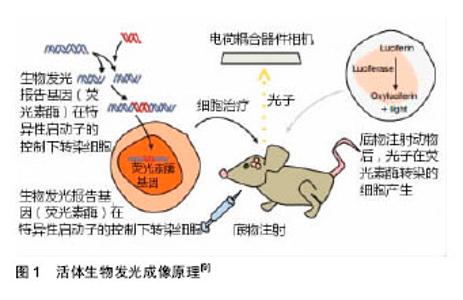
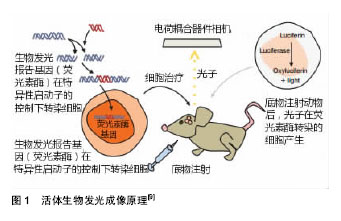
2.1.1 静脉移植 近年多项研究将HUCMSCs经尾静脉注入到大脑中动脉缺血再灌注大鼠体内[24,26-27],结果发现大鼠神经功能得到改善,脑水肿、梗死体积显著下降,通过调控免疫炎性反应发挥神经保护作用,包括降低促炎性因子,升高抗炎性因子,上调免疫炎性反应初期Foxp3 mRNA表达。Li等[5]证实经尾静脉移植HUCMSCs可改善脑缺血小鼠神经功能,缩小梗死区,促进内源性神经再生,并抑制星形胶质细胞活化。张培培等[25]结果表明人脐带间充质干细胞经尾静脉途径移植可以在宿主脑内存活,通过生成神经元样细胞和神经胶质样细胞、促进新生血管形成并分泌神经营养因子等因素促进大鼠神经功能恢复,且未发现明显免疫排斥反应及异常分化细胞,具有较高的安全性。 Guan等[28]选择将HUCMSCs经股静脉注入模型体内,其能够改善脑缺血小鼠神经功能,神经代谢产物变化较大,N-乙酰天冬氨酸(NAA)/磷酸肌酸(Cr)和胆固醇(Cho)/磷酸肌酸(Cr)比值明显升高,乳酸(Lac)/磷酸肌酸(Cr)比值明显降低,提示股静脉移植HUCMSCs可能通过影响缺血区的神经代谢产物而减轻缺血性脑损伤。Zhu等[29]将5×106个HUCMSCs经股静脉注入脑缺血再灌注兔模型体内,发现移植HUCMSCs抑制了早期脑缺血诱导的血清白细胞介素1β,白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平的增加,并显著降低缺血区周围凋亡细胞的百分比,说明HUCMSCs可能通过抑制脑缺血诱导的早期炎症反应及神经细胞凋亡来发挥作用。 以上实验研究证实不论是经尾静脉还是股静脉对于HUCMSCs移植治疗缺血性脑损伤都是安全的,可以通过调控免疫炎性反应、重塑神经环路、内源性血管再生、调控神经代谢产物、表达一些内源性营养因子、抑制脑缺血诱导的神经细胞凋亡等多个途径来发挥作用。 2.1.2 颈动脉移植 Karlupia等[30]经颈动脉将脐血单个核细胞、脐血间充质干细胞、脐带基质间充质干细胞分别注入至大脑中动脉闭塞大鼠体内,移植后2周,与假手术组相比,所有3种细胞组和PBS组的缺血半球均观察到脑源性神经营养因子mRNA的表达显著降低,脐血单个核细胞组降低最少。脐血间充质干细胞组观察到白细胞介素2 mRNA和白细胞介素6 mRNA的表达明显降低。该研究证实经颈动脉移植HUCMSCs治疗缺血性脑损伤的安全性和有效性,其在基因水平调控炎症反应从而发挥作用。 2.1.3 经脑立体定向移植 国内刘慧纯等[21]将HUCMSCs立体定向移植至大脑中动脉闭塞大鼠损伤侧纹状体,结果显示,HUCMSCs移植后第7天,移植组mNSS评分显著低于PBS组和模型组,提示经脑立体定向移植HUCMSCs早期即可促进损伤脑组织修复,实验中还发现PBS组在损伤后第14天(即移植操作后第7天)mNSS评分较前略有下降,仍高于对照组,说明移植操作可以加重脑组织损伤,而这种损伤随着时间推移可恢复。通过Brdu标记HUCMSCs,发现移植组大鼠损伤中心及周围均可见Brdu染色阳性细胞及Nestin、微管结合蛋白 2、胶原纤维酸性蛋白、Ⅷ因子、血管内皮生长因子免疫组织化学双染阳性细胞,推测HUCMSCs发挥作用的机制可能与分泌神经营养因子、内源性血管再生有关。其他也有研究发现其机制与神经发生、内源性血管再生、调控免疫炎性反应相关[31-33]。 2.1.4 侧脑室移植 Kim等[34]将1×105个HUCMSCs经侧脑室移植至大脑中动脉闭塞幼鼠损伤侧,通过MRI评价梗死病变体积,圆筒实验和旋转实验评价大鼠神经行为学,结果发现,移植组脑缺血体积缩小,神经功能改善。在缺血半暗带中观察到脱氧核糖核苷酸末端转移酶(TUNEL)、反应性小胶质细胞(ED-1)和胶质纤维酸性蛋白(GFAP)标记的细胞显著增加,这表明HUCMSCs可经神经血管发生及神经保护途径来发挥作用。 2.1.5 不同移植途径比较 对HUCMSCs经不同移植途径治疗缺血性脑损伤进行比较,如Lim等[23]分别将1×106、5×105两个剂量HUCMSCs经尾静脉、腰椎穿刺分别注入大脑中动脉闭塞大鼠缺血损伤侧,通过TTC染色和MRI评价梗死病变体积,旋转试验和移除黏附物能力测试评价大鼠神经行为学,结果表明两种移植方式注射1×106个HUCMSCs均可有效改善神经功能,5×105个HUCMSCs鞘内给药显著减少了缺血性损伤,但在静脉注射治疗组中没有显著效果。而经腰椎穿刺移植的HUCMSCs存活时间更长,迁移范围更广泛,并可分化为神经细胞和星形胶质细胞。 现有的多项研究支持HUCMSCs经不同移植途径治疗缺血性脑损伤的安全性及有效性。经脑立体定向移植操作可以加重脑损伤,是由于其可能影响梗死灶周围的血供或直接损害脑组织还是其他原因并未阐明;经静脉及腰椎途径移植对比可发现后者存活时间及迁移范围皆优于前者,可能是因为移植的HUCMSCs可以随脑脊液循环迁移到整个大脑和脊髓。 目前尚不能明确HUCMSCs治疗缺血性脑损伤的机制,且HUCMSCs各种移植途径之间缺少对比,因此,迫切需要能够活体内动态监测移植干细胞增殖、分化、迁移及作用机制的成像技术。 2.2 活体生物发光成像技术在干细胞治疗缺血性脑损伤中的应用 目前BLI可用于监测干细胞移植后的迁移、分布、生存时间,追踪不同因子如营养因子及免疫炎性因子的动态变化,以了解干细胞发挥作用的机制等(图1),在干细胞治疗缺血性脑损伤领域中广泛应用。"
| [1] Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095-2128.[2] Sullivan R, Duncan K, Dailey T, et al. A possible new focus for stroke treatment - migrating stem cells. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(7): 949-958.[3] Liu X, Ye R, Yan T, et al. Cell based therapies for ischemic stroke: from basic science to bedside. Prog Neurobiol. 2014;115:92-115.[4] Tang YH, Ma YY, Zhang ZJ, et al. Opportunities and challenges: stem cell-based therapy for the treatment of ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015;21(4):337-347.[5] Li D, Zhang M, Zhang Q, et al. Functional recovery after acute intravenous administration of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2015;4(2):98-104.[6] Kim JY, Jeon HB, Yang YS, et al. Application of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in disease models. World J Stem Cells. 2010;2(2):34-38.[7] 朱尧, 汪青松, 黄海丽, 等. 脐带血间充质干细胞改善兔脑梗死神经生长因子和神经元凋亡的研究[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2013, 15(12):1316-1320. [8] Aswendt M, Adamczak J, Tennstaedt A. A review of novel optical imaging strategies of the stroke pathology and stem cell therapy in stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:226.[9] Gavins FN, Smith HK. Cell tracking technologies for acute ischemic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35(7):1090-1099.[10] Tennstaedt A, Aswendt M, Adamczak J, et al. Noninvasive multimodal imaging of stem cell transplants in the brain using bioluminescence imaging and magnetic resonance imaging. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1052:153-166.[11] Couillard-Despres S, Vreys R, Aigner L, et al. In vivo monitoring of adult neurogenesis in health and disease. Front Neurosci. 2011;5:67.[12] Cool SK, Breyne K, Meyer E, et al. Comparison of in vivo optical systems for bioluminescence and fluorescence imaging. J Fluoresc. 2013;23(5):909-920.[13] Bakhsheshian J, Wei BR, Chang KE, et al. Bioluminescent imaging of drug efflux at the blood-brain barrier mediated by the transporter ABCG2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(51):20801-20806.[14] Kormann MS, Hasenpusch G, Aneja MK, et al. Expression of therapeutic proteins after delivery of chemically modified mRNA in mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(2):154-157.[15] Huang NF, Okogbaa J, Babakhanyan A, et al. Bioluminescence imaging of stem cell-based therapeutics for vascular regeneration. Theranostics. 2012;2(4):346-354.[16] Wang W, Jiang Q, Zhang H, et al. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells is safe for the lung in a chronic myocardial infarction model. Regen Med. 2011;6(2):179-190.[17] Pendharkar AV, Chua JY, Andres RH, et al. Biodistribution of neural stem cells after intravascular therapy for hypoxic-ischemia. Stroke. 2010;41(9):2064-2070.[18] Jiang Y, Zhu W, Zhu J, et al. Feasibility of delivering mesenchymal stem cells via catheter to the proximal end of the lesion artery in patients with stroke in the territory of the middle cerebral artery. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(12):2291-2298.[19] 魏建强. 不同途径移植骨髓间充质干细胞促进创伤性脑损伤大鼠功能恢复和神经再生的研究[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学, 2013.[20] De Keyser J. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann Neurol. 2005;58(4):653-654.[21] 刘慧纯, 张培培, 王世民,等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑缺血损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(19):3471-3475. [22] 郭燕宁, 王雪笠. 不同干细胞移植途径治疗脑缺血的示踪及效果评定[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志, 2013, 21(4):316-318.[23] Lim JY, Jeong CH, Jun JA, et al. Therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells after intrathecal administration by lumbar puncture in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011;2(5):38.[24] Cheng Q, Zhang Z, Zhang S, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischemic brain injury in mouse by regulating peripheral immunoinflammation. Brain Res. 2015;1594:293-304.[25] 张培培, 刘慧纯, 阎晓玲, 等. 脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠尾静脉移植脐带间充质干细胞的安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(14): 2581-2584. [26] 周晶晶, 徐芳, 俞明明, 等. 人脐带血间充质干细胞改善大鼠脑梗死免疫炎性反应的研究[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2016, 18(1):81-84.[27] 侯亮,徐芳,刘学春,汪青松. 人脐带血间充质干细胞移植对脑梗死大鼠外周血Foxp3表达的影响[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志,2016,33(12): 1060-1063. [28] Guan YM, Zhu Y, Liu XC, et al. Effect of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on neuronal metabolites in ischemic rabbits. BMC Neurosci. 2014;15:41.[29] Zhu Y, Guan YM, Huang HL, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell transplantation suppresses inflammatory responses and neuronal apoptosis during early stage of focal cerebral ischemia in rabbits. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014;35(5):585-591.[30] Karlupia N, Manley NC, Prasad K, et al. Intraarterial transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells is more efficacious and safer compared with umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells in a rodent stroke model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(2):45.[31] Park HW, Chang JW, Yang YS, et al. The Effect of Donor-Dependent Administration of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells following Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Exp Neurobiol. 2015;24(4):358-365.[32] Lin YC, Ko TL, Shih YH, et al. Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells promote recovery after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2011;42(7): 2045-2053.[33] Park HW, Moon HE, Kim HS, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve functional recovery through thrombospondin1, pantraxin3, and vascular endothelial growth factor in the ischemic rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 2015;93(12): 1814-1825.[34] Kim ES, Ahn SY, Im GH, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation attenuates severe brain injury by permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in newborn rats. Pediatr Res. 2012;72(3):277-284.[35] Rosenblum S, Smith TN, Wang N, et al. BDNF Pretreatment of Human Embryonic-Derived Neural Stem Cells Improves Cell Survival and Functional Recovery After Transplantation in Hypoxic-Ischemic Stroke. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(12):2449-2461.[36] Andres RH, Choi R, Pendharkar AV, et al. The CCR2/CCL2 interaction mediates the transendothelial recruitment of intravascularly delivered neural stem cells to the ischemic brain. Stroke. 2011;42(10):2923-2931.[37] Rosenblum S, Wang N, Smith TN, et al. Timing of intra-arterial neural stem cell transplantation after hypoxia-ischemia influences cell engraftment, survival, and differentiation. Stroke. 2012;43(6): 1624-1631.[38] Boehm-Sturm P, Aswendt M, Minassian A, et al. A multi-modality platform to image stem cell graft survival in the naïve and stroke-damaged mouse brain. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2218-2226. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [6] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [7] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [8] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [9] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [10] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [13] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [14] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [15] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||