Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (30): 4867-4872.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.30.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Performance characterization of bacterial cellulose reinforced polyvinyl alcohol/ polyacrylamide composite hydrogels
- 1Department of Emergency, Caoxian People’s Hospital, Caoxian 274400, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Bioengineering, Shanghai Institute of Technology, Shanghai 201418, China; 3Department of Neurosurgery, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital, Shanghai 200235, China
-
Received:2017-05-14Online:2017-10-28Published:2017-11-07 -
Contact:Chen Shi-wen, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Neurosurgery, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital, Shanghai 200235, China -
About author:Ma Biao, Attending physician, Department of Emergency, Caoxian People’s Hospital, Caoxian 274400, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Medicine Engineering Cross Fund of Shanghai Jian Tong University, No. YG2012MS34
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Biao, Dong Yan-yan, Chen Shi-wen.
share this article
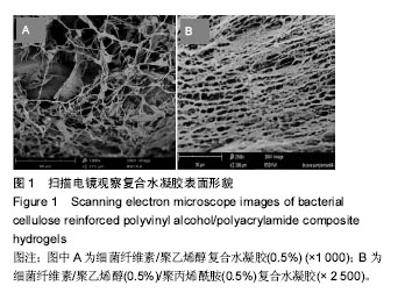
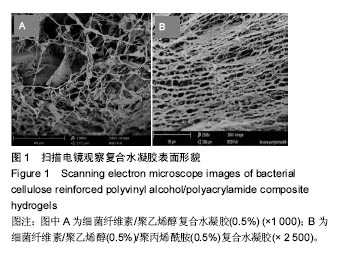
2.1 表面形貌表征及分析 图1A是放大1 000倍时的BC/PVA复合水凝胶的断面扫描电镜图,从图中可以看到纤维素丝带随意排列,并且有明显的大小不一的孔隙,而且呈现三维立体结构,单根细菌纤维素直径小于100 nm[33]。图1B为放大2 500倍时的BC/PAM/PVA复合水凝胶的截面扫描电镜图,从图中可以看到纤维素丝带随意排列,并且有明显的大小不一的孔隙,而且呈现三维立体结构,单根细菌纤维素直径小于100 nm,从图1B中可看到膜状物的聚乙烯醇和聚丙烯酰胺附着到细菌纤维素带上,同时没有破坏细菌纤维素的三维立体结构,并且可以看到纤维素丝带变粗,说明聚乙烯醇和聚丙烯酰胺结合到了细菌纤维素 上[34]。图1B与图1A比较发现图中纤维素丝带上附着的物质更浓密,孔隙较图1A更小,这是由于加入了聚丙烯酰胺进一步占据细菌纤维素的孔隙造成的[35]。"
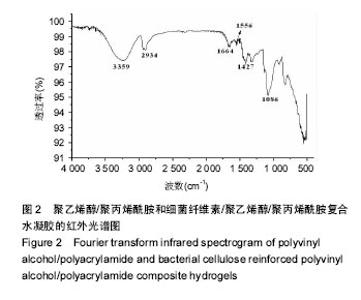
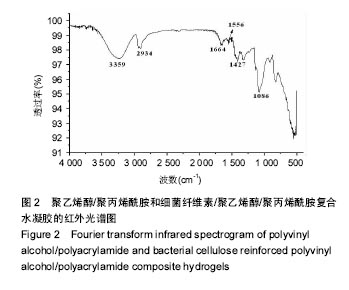
2.2 红外光谱分析 图2为PVA/PAM与BC/PVA/PAM水凝胶的红外光谱图,对于PVA/PAM而言,3 259 cm-1处的吸收峰是由-OH键伸缩振动引起的,表现为一个大的吸收带,峰型宽而强,2 924 cm-1和2 893 cm-1处的吸收峰是由-CH-伸缩振动引起的,1 664 cm-1处的吸收峰是由C=O振动引起的,1 556 cm-1处的吸收峰是由-NH2振动引起的,BC/PVA/PAM保留了PVA/PAM的特征吸收峰,而且细菌纤维素与聚乙烯醇和聚丙烯酰胺形成了新的氢键吸收峰位于3 352 cm-1,光吸收强度变大,1 067 cm-1处的吸收峰是由细菌纤维素中的C-O-C键伸缩振动引起的[36-37],说明制备出了BC/PVA/ PAM水凝胶[38]。"
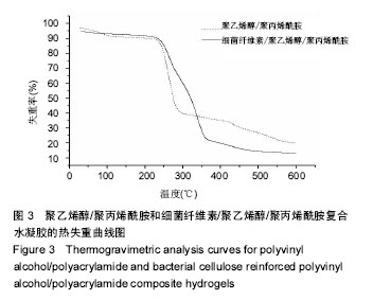
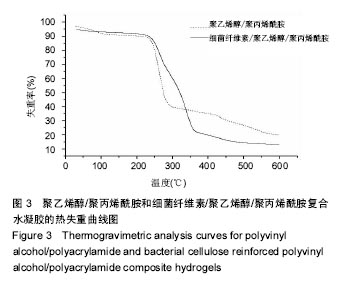
2.3 热重分析结果 取冻干后的细菌纤维素増强前的纯聚合物凝胶和细菌纤维素增强后的凝胶进行热重分析,在氮气气氛下进行热失重分析考察PVA/PAM水凝胶和复合凝胶的热分解行为。从图3中可以看出,PVA/PAM水凝胶经历4次分解过程,在48 ℃就开始第一次分解,在600 ℃趋于稳定,而BC/PVA/PAM水凝胶在241 ℃才有明显的质量变化,在300 ℃时,PVA/PAM与BC/PVA/PAM水凝胶的失重率分别为61%,41%,PVA/PAM水凝胶失重率达到50%所需要的温度为274 ℃,而BC/PVA/PAM水凝胶为362 ℃,对比发现复合水凝胶比PVA/PAM水凝胶的热稳定性明显提高[39-40]。"
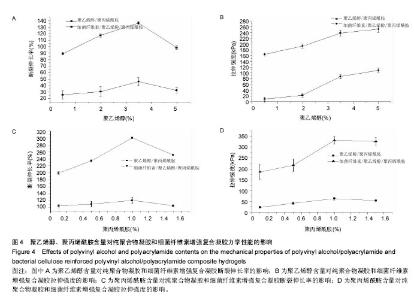
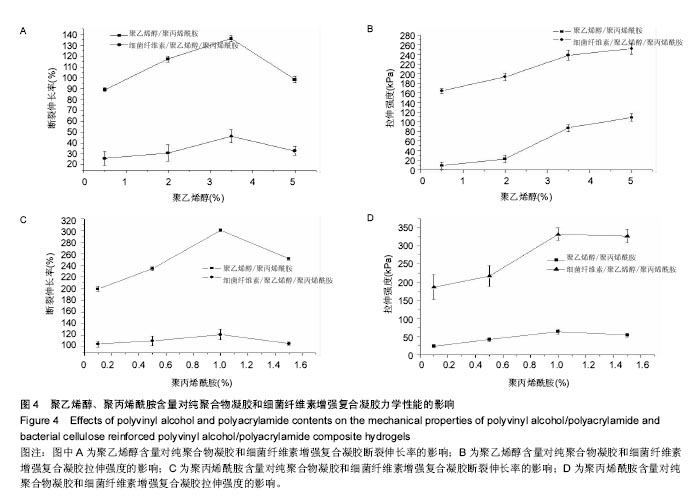
.4 力学性能分析结果 图4A和4B给出了聚乙烯醇含量对细菌纤维素増强前和细菌纤维素增强后的纯聚合物凝胶和细菌纤维素增强复合凝胶力学性能的影响。结果表明随着聚乙烯醇含量的增加,PVA/PAM和BC/PVA/PAM复合凝胶的拉伸强度呈增加趋势,这是由于聚乙烯醇的机械强度好及细菌纤维素本身的机械强度高,因此PVA/PAM复合膜体系引入细菌纤维素后的拉伸强度更高,而对于断裂伸长率而言,细菌纤维素增强复合凝胶断裂伸长率比纯聚合物凝胶明显降低,当聚乙烯醇含量为3.5%时,纯凝胶和增强后水凝胶的断裂伸长率均达到最大分别为136.09%,46.25%,而林建明等[41]采用水溶液聚合法得到的PVA/ PAM互穿网络水凝胶的最大断裂伸长率可达3 000%,本实验相比该数值较小,是因为两者的制备方法不同,主要是由于前者采用的是两步水溶液聚合法制备的,而本实验是用冷冻-解冻法制备的。对比引入细菌纤维素前后的复合凝胶可知,细菌纤维素的引入对PVA/PAM水凝胶起到明显的増强作用,说明BC/PVA/PAM复合水凝胶具有足够的韧性,可应用于伤口敷料方面。 图4C和4D是聚丙烯酰胺含量对细菌纤维素增强前和细菌纤维素增强后的纯聚合物凝胶和细菌纤维素增强复合凝胶力学性能的影响。结果显示加入少量聚丙烯酰胺 (< 1.0%)后,纯聚合物凝胶和细菌纤维素增强复合凝胶的拉伸强度随聚丙烯酰胺增加而增加,这是因为聚丙烯酰胺的力学性能差,而拉伸强度增加的主要原因是聚丙烯酰胺浓度提高,与聚乙烯醇形成的氨键数增多,当聚丙烯酰胺浓度为1.0%时细菌纤维素增强复合凝胶的拉伸强度达到最大为331.79 kPa,断裂伸长率为105.33%,但继续加入聚丙烯酰胺后,力学性能会趋于稳定或下降,这主要是由于少量聚丙烯酰胺对聚乙烯醇的结晶有促进作用,随着聚丙烯酰胺含量的增加,由聚丙烯酰胺形成的连续相区扩大,此时聚丙烯酰胺不仅难以起到增强作用,反而由于本身韧性较差,成为新的缺陷源[42-43]。断裂伸长率比増强前下降是由于细菌纤维素的引入限制了PVA/PVM网络的运动。"
| [1]Yudianti R, Indrarti L. Effect of Water Soluble Polymer on Structure and Mechanical Properties of Bacterial Cellulose Composites. J Applied Sci. 2008; 8(1):177-180.[2]Tercjak A, Gutierrez J, Barud HS, et al. Nano- and macroscale structural and mechanical properties of in situ synthesized bacterial cellulose/PEO-b-PPO-b-PEO biocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(7): 4142-4150.[3]Hutchens S. Synthesis and initial characterization of a calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite-bacterial cellulose composite. Knoxville: University of Tennessee, 2004.[4]Ul-Islam M, Khan T, Park JK. Water holding and release properties of bacterial cellulose obtained by in situ and ex situ modification. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2012;88(2):596-603.[5]Ul-Islam M, Khan T, Park JK. Nanoreinforced bacterial cellulose-montmorillonite composites for biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;89(4):1189-1197.[6]Xiao L, Mai Y, He F, et al. Bio-based green composites with high performance from poly(lactic acid) and surface-modified microcrystalline cellulose. J Materials Chemistry. 2012; 22(31):15732-15739. [7]Fu L, Zhang J, Yang G. Present status and applications of bacterial cellulose-based materials for skin tissue repair. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;92(2):1432-1442.[8]Kowalska-Ludwicka K, Cala J, Grobelski B, et al. Modified bacterial cellulose tubes for regeneration of damaged peripheral nerves. Arch Med Sci. 2013;9(3):527-534.[9]Leitao AF, Silva JP, Dourado F, et al. Production and Characterization of a New Bacterial Cellulose/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) .Nanocomposite.Materials. 2013; 6(5):1956-1966.[10]Martins NCT, Freire CSR, Neto CP, et al. Antibacterial paper based on composite coatings of nanofibrillated cellulose and ZnO. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects. 2013;417(417):111-119.[11]Oshima T, Taguchi S, Ohe K, et al. Phosphorylated bacterial cellulose for adsorption of proteins. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2011; 83(2):953-958.[12]Chen S, Teng Q. Quantitative Immobilization of Phthalocyanine onto Bacterial Cellulose for Construction of a High-Performance Catalytic Membrane Reactor. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(7): E846. [13]Khamrai M, Banerjee SL, Kundu PP. Modified bacterial cellulose based self-healable polyeloctrolyte film for wound dressing application. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;174:580-590.[14]Lee YJ, An SJ, Bae EB, et al. The Effect of Thickness of Resorbable Bacterial Cellulose Membrane on Guided Bone Regeneration. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(3): E320.[15]Lin WC, Lien CC, Yeh HJ, et al. Bacterial cellulose and bacterial cellulose-chitosan membranes for wound dressing applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;94(1):603-611.[16]Cao Z, Luo X, Zhang H, et al. A facile and green strategy for the preparation of porous chitosan-coated cellulose composite membranes for potential applications as wound dressing. Cellulose. 2016; 23(2):1349-1361.[17]Zhang J, Rong J, Li W, et al. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose/polyacrylamide hydrogel. Acta Polymerica Sinica. 2011;11(6):602-607.[18]Chang ST, Chen LC, Lin SB, et al. Nano-biomaterials application: Morphology and physical properties of bacterial cellulose/gelatin composites via crosslinking. Food Hydrocolloids. 2012;27(1):137-144.[19]Wan WK, Campbell G, Zhang ZF, et al. Optimizing the tensile properties of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel for the construction of a bioprosthetic heart valve stent. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002; 63(6):854-861.[20]Liu X, Wang X, Liu D. Recent development of the research on the structure effects and responsive mechanism of intelligent hydrogels. Chemistry. 2000;63(10):1-6.[21]Hassan CM, Peppas NA. Structure and applications of PVA hydrogels produced by conventional crosslinking or by freezing/thawing methods. Advance in Polymer Science. 2000;153:37-65.[22]Stauffer SR, Peppast NA. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by freezing-thawing cyclic processing.Polymer. 1992;33(18):3932-3936.[23]Stammen JA, Williams S, Ku DN, et al. Mechanical properties of a novel PVA hydrogel in shear and unconfined compression. Biomaterials. 2001;22(8):799-806.[24]Paradossi G, Cavalieri F, Chiessi E, et al. Poly(vinyl alcohol) as versatile biomaterial for potential biomedical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2003;14(8):687-691.[25]杨巍威. 聚丙烯酰胺及衍生物/三钛酸纳米片层复合水凝胶的光催化制备及其性能[D]. 泉州:华侨大学, 2015.[26]孙黛楠. 水凝胶纳米复合材料的增强机理研究[D]. 南京:南京师范大学, 2015.[27]Gonzalez JS, Maiolo AS, Hoppe CE, et al. Composite Gels Based on Poly (Vinyl alcohol) for Biomedical Uses. Procedia Materials Science. 2012; 1(1):483-490.[28]Li WD, Rong JH, Lin ZD, et al. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose reinforced pva/pvp hydrogels. Acta Polymerica Sinica. 2012; 12(4):357-364.[29]孙东平, 陈啸, 杨加志,等. 纳米细菌纤维素\聚乙烯醇\聚乙二醇多孔复合水凝胶:中国, CN105237925A[P]. 2016-01-13. [30]周玉惠. 细菌纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合材料的制备研究进展[J]. 胶体与聚合物, 2013,31(3):135-137.[31]Tang W, Jia S, Jia Y, et al. The influence of fermentation conditions and post-treatment methods on porosity of bacterial cellulose membrane. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2010; 26(1):125-131. [32]Tang WH, Ma X, Jia YY, et al. Bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum in static fed-batch culture. Food and Fermentation Industries. 2008; 34(2):21-23. [33]王彩霞, 洪枫. 细菌纤维素基复合水凝胶的制备及其评价[D]. 上海:东华大学,2013.[34]杜倩雯,陈琳,钟春燕,等. BC/PVA/PEG增强型复合水凝胶的制备及其表征[J]. 广东化工, 2014, 41(16):17-18.[35]Li WD, Rong JH, Lin ZD, et al. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose reinforced PVA/PVP hydrogels. Acta Polymerica Sinica. 2012; 12(4):357-364.[36]Shah N, Ha JH, Park JK. Effect of reactor surface on production of bacterial cellulose and water soluble oligosaccharides by Glu-conacetobacter hansenii PJK. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering. 2010; 15(1): 110-118.[37]Ha JH, Park JK. Improvement of bacterial cellulose production in Acetobacter xylinum, using byproduct produced by Gluconacetobacter hansenii. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering. 2012; 29(5):563-566.[38]翁诗甫.傅里叶变换红外光谱分析[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2010.[39]胥杰龙. 改性明胶/聚丙稀酰胺复合水凝胶及其用于软骨缺损修复的研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学, 2016.[40]Kloxin AM, Kasko AM, Salinas CN, et al. Photodegradable hydrogels for dynamic tuning of physical and chemical properties. Science. 2009;324(5923):59-63.[41]林建明, 唐群委, 吴季怀, 等.高强度PAM/PVA互穿网络水凝胶的合成[J].华侨大学学报,2010,31(1):41-48.[42]Ma RY, Xiong DS, Miao F, et al. Novel PVP/PVA hydrogelsfor articular cartilage replacement. Materials Science & Engineering C. 2009; 29(6):1979-1983.Shi Y, Xiong D. Microstructure and friction properties of PVA/PVP hydrogels for articular cartilage repair as function of polymerization degree and polymer concentration. Wear. 2013; 305(1-2):280-285. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [5] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [6] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [7] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [8] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [9] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [10] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [11] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [12] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [13] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||