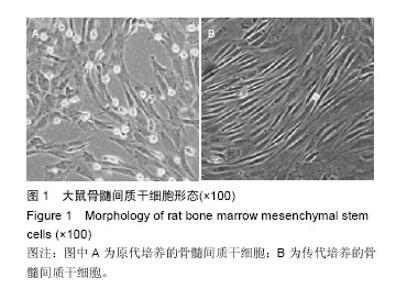
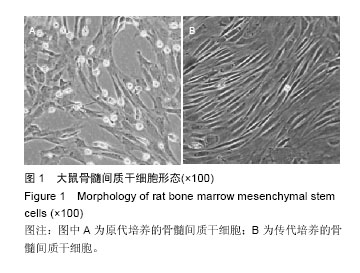
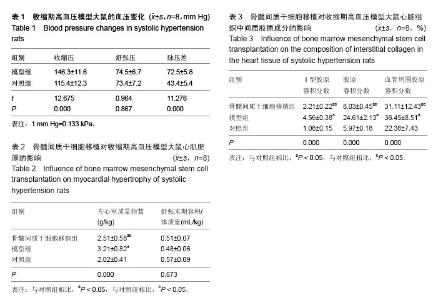
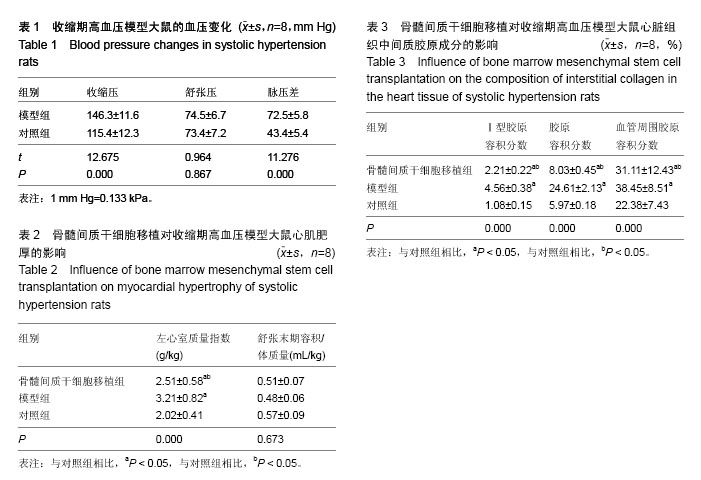
| [1] 吴寿岭,黄卫,戚长春,等.单纯收缩期高血压对老年人群心脑血管事件的影响[J].中华高血压杂志,2012,20(1): 67-71.[2] Martin JN Jr. Severe systolic hypertension and the search for safer motherhood. Semin Perinatol. 2016; 40(2):119-123. [3] 郭艺芳,刘琪.老年单纯收缩期高血压的治疗进展[J].心血管病学进展,2011,32(1):36-38.[4] Modesti PA, Omboni S, Taddei S, et al. Zofenopril or irbesartan plus hydrochlorothiazide in elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension untreated or uncontrolled by previous treatment: a double-blind, randomized study. J Hypertens. 2016;34(3):576-587; discussion 587. [5] 何杰.老年单纯收缩期高血压研究进展[J].心血管病学进展,2011,32(4):558-561.[6] 涂维,陈秀龙.老年单纯收缩期高血压中西医治疗进展[J].中国老年保健医学,2013,11(5):69-71.[7] 赵春美.老年单纯收缩期高血压治疗与靶器官保护探讨[J].实用中西医结合临床,2014,14(9):38-39.[8] Kim NR, Kim HC. Prevalence and Trends of Isolated Systolic Hypertension among Korean Adults: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1998-2012. Korean Circ J. 2015;45(6):492-499.[9] 范雯怡,武轶群,曹洋,等.降压0号治疗老年单纯收缩期高血压的疗效和安全性评价[J].现代预防医学,2012, 39(4): 1008-1010,1021.[10] Khanabdali R, Saadat A, Fazilah M, et al. Promoting effect of small molecules in cardiomyogenic and neurogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015; 10:81-91.[11] Pollock K, Dahlenburg H, Nelson H, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Genetically Engineered to Overexpress Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Improve Outcomes in Huntington's Disease Mouse Models. Mol Ther. 2016;24(5):965-977.[12] Parody R, Sureda A. Mesenchymal stromal cells for steroid-refractory acute GVHD. Lancet Haematol. 2016;3(1):e8-9.[13] 朱光照.单纯收缩期高血压动物模型建立及其早期干预的实验研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2008.[14] 童晓云.补肾活血方强化骨髓干细胞原位移植治疗急性心肌梗死的研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2008.[15] 雷建国,邹文淑,王剑峰,等.老年单纯收缩期高血压的发病机制及其优化治疗[J].实用医院临床杂志,2011, 8(1): 136-138.[16] 李迪,黄晓波,张娜,等.成都地区中老年人群单纯收缩期高血压流行特点及其影响因素[J].中华高血压杂志,2015, 23(2):174-177.[17] Bress AP, Tanner RM, Hess R, et al. Generalizability of SPRINT Results to the U.S. Adult Population. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(5):463-472.[18] Ihász F, Karsai I, Kaj M, et al. Characteristics of cardiorespiratory output determining factors among 11-19-year-old boys at rest and during maximal load: Its impact on systolic hypertension. Acta Physiol Hung. 2015;102(3):263-273.[19] 胡莹.老年单纯收缩期高血压综合干预研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2013.[20] 刘诗.天麻素缓释片治疗老年单纯收缩期高血压的临床试验研究[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2013.[21] Jung Y, Nolta JA. BMI1 Regulation of Self-Renewal and Multipotency in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(2):131-140.[22] Marti LC, Ribeiro AA, Hamerschlak N. Immunomodulatory effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2011;9(2):224-228.[23] Han S, Li YY, Chan BP. Extracellular Protease Inhibition Alters the Phenotype of Chondrogenically Differentiating Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in 3D Collagen Microspheres. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0146928.[24] Jiang Q, Yu T, Huang K, et al. Remote Ischemic Postconditioning Ameliorates the Mesenchymal Stem Cells Engraftment in Reperfused Myocardium. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0146074.[25] Wang C, Liu Y, Chang C, et al. Human fallopian tube proteome shows high coverage of mesenchymal stem cells associated proteins. Biosci Rep. 2016;36(1): e00297.[26] Skolekova S, Matuskova M, Bohac M, et al. Cisplatin-induced mesenchymal stromal cells-mediated mechanism contributing to decreased antitumor effect in breast cancer cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2016;14:4.[27] Kucerova L, Skolekova S, Matuskova M, et al. Altered features and increased chemosensitivity of human breast cancer cells mediated by adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. BMC Cancer. 2013;13: 535. [28] Kamat P, Schweizer R, Kaenel P, et al. Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells May Promote Breast Cancer Progression and Metastatic Spread. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136(1):76-84. [29] Seo KW, Lee HW, Oh YI, et al. Anti-tumor effects of canine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cell-based interferon-β gene therapy and cisplatin in a mouse melanoma model. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(8): 944-955. [30] Ahn Jo, Lee Hw, Seo Kw, et al. Anti-tumor effect of adipose tissue derived-mesenchymal stem cells expressing interferon-β and treatment with cisplatin in a xenograft mouse model for canine melanoma. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74897.[31] 朱希山,台卫平,施薇,等.骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导向内皮和上皮细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(40):7433-7436. |