Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (49): 7397-7403.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.49.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jaw bone and periodontal capillary casting in a Wistar rat model of occlusal trauma
Bi Zhen-yu1, Liu Yang2, Wu Bin2, Xie Chun2, Yang Yu-chao1, Ouyang Jun1
- 1Department of Anatomy of Southern Medical University, Medical Biomechanics Key Laboratory of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Stamatology, People’s Hospital of Longhua New District of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518109, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2016-09-03Online:2016-11-30Published:2016-11-30 -
Contact:Ouyang Jun, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Anatomy of Southern Medical University, Medical Biomechanics Key Laboratory of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Bi Zhen-yu, M.D., Lecturer, Department of Anatomy of Southern Medical University, Medical Biomechanics Key Laboratory of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31170903; the Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Shenzhen, No. 201506088
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bi Zhen-yu, Liu Yang, Wu Bin, Xie Chun, Yang Yu-chao, Ouyang Jun. Jaw bone and periodontal capillary casting in a Wistar rat model of occlusal trauma[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7397-7403.
share this article
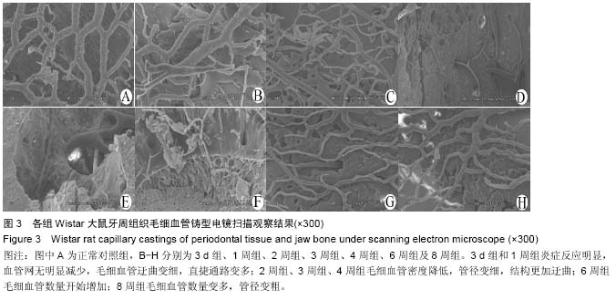
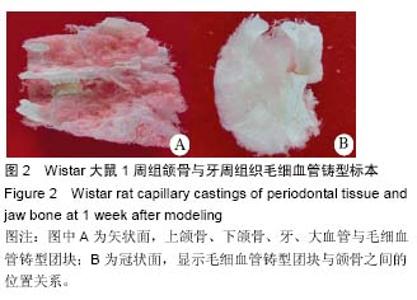
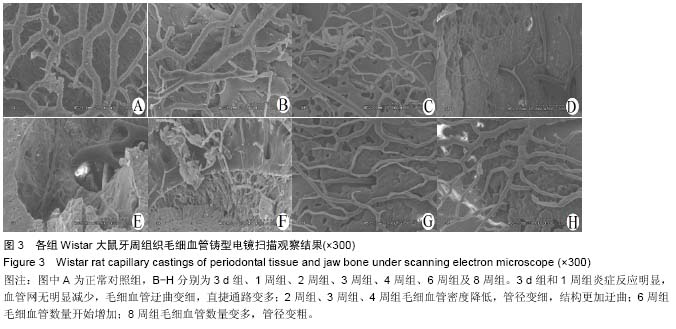
2.1 实验动物数量分析 48只大鼠均进入结果分析。 2.2 大鼠颌骨牙周毛细血管铸型宏观发现 所有大鼠均成功制作包含颌骨与牙周毛细血管铸型标本,清晰地显示上颌骨、下颌骨、上下颌磨牙及制作咬合创伤的树脂材料高点,直径较大的血管结构与走形清晰可见,直径细微的血管呈现棉絮状团块;支架性能良好,连续性好,铸型稳定,表面无杂物附着,见图2。 3 d组和1周组标本牙槽骨无明显吸收;2周、3周、4周组标本牙槽骨逐渐吸收明显,牙略有松动;5周、6周组标本牙槽骨吸收没有明显加重。 2.3 牙周组织毛细血管铸型电镜发现 扫描电镜可以显示牙周和根尖部位的血管网结构,小动脉发出细微动脉,再发出毛细血管,构成了立体的毛细血管网,同时也可以观察到较粗动静脉之间的短路结构及直捷通路等结构。 3 d组和1周组炎症反应明显,血管网无明显减少,毛细血管迂曲变细,直捷通路变多;2周组、3周组、4周组毛细血管密度降低,管径变细,结构更加迂曲;6周组毛细血管数量开始增加;8周组毛细血管数量变多,管径变粗,见图3。"
| [1] de Oliveira Diniz CK,Corrêa MG,Casati MZ,et al.Diabetes mellitus may increase bone loss after occlusal trauma and experimental periodontitis.J Periodontol.2012; 83(10):1297-1303. [2] Cakmak F,Turk T,Karadeniz EI,et al.Physical properties of root cementum: part 24. Root resorption of the first premolars after 4 weeks of occlusal trauma.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014; 145(5): 617-625. [3] Foz AM,Artese HP,Horliana AC,et al.Occlusal adjustment associated with periodontal therapy--a systematic review.J Dent.2012;40(12):1025-1035. [4] Takaya T,Mimura H,Matsuda S,et al.Cytological Kinetics of Periodontal Ligament in an Experimental Occlusal Trauma Model.Int J Med Sci.2015;12(7): 544-551. [5] Chai H.On crack growth in molar teeth from contact on the inclined occlusal surface.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2015;44:76-84. [6] Sims MR.Endothelin-1 expression in the microvasculature of normal and 3-hour continuously loaded rat molar periodontal ligament. Eur J Orthod. 2001;23(6):647-662. [7] Pau M,Reinbacher KE,Feichtinger M,et al.The mandibular symphysis as a starting point for the occlusal-level reconstruction of panfacial fractures with bicondylar fractures and interruption of the maxillary and mandibular arches: report of two cases. J Craniomaxillofac Surg.2014;42(4):e51-56. [8] Kolk A,Neff A.Long-term results of ORIF of condylar head fractures of the mandible: A prospective 5-year follow-up study of small-fragment positional-screw osteosynthesis (SFPSO).J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;43(4):452-461. [9] Kvinnsland I,Heyeraas KJ.Effect of traumatic occlusion on CGRP and SP immunoreactive nerve fibre morphology in rat molar pulp and periodontium. Histochemistry.1992;97(2):111-120. [10] Byers MR,Taylor PE.Effect of sensory denervation on the response of rat molar pulp to exposure injury.J Dent Res.1993;72(3):613-618. [11] Song ZC,Zhou W,Shu R,et al.Hypoxia induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death in human periodontal ligament cells through HIF-1α pathway.Cell Prolif.2012;45(3):239-248. [12] Varga R,Janovszky Á,Szabó A,et al.A novel method for in vivo visualization of the microcirculation of the mandibular periosteum in rats.Microcirculation.2014; 21(6):524-531 [13] Molcho S,Peer A,Berg T,et al.Diabetes microvascular disease and the risk for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: a single center study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2013;98(11):E1807-1812. [14] Kantola R,Sivén M,Kurunmäki H,et al.Laser Doppler imaging of skin microcirculation under fiber-reinforced composite framework of facial prosthesis.Acta Odontol Scand. 2014;72(2):106-112 [15] Müller S,Gosau M,Strobel D,et al.Assessment of bone microcirculation by contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and [18F]-positron emission tomography/computed tomography in free osseous and osseocutaneus flaps for mandibular reconstruction: preliminary results.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc.2011; 49(1-4):115-128. [16] 毕振宇,刘阳,孙培栋,等.Wistar大鼠口腔颌面部微血管铸型制作[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2015,33(5):604-606. [17] Kajiwara N, Masaki C,Mukaibo T,et al. Soft tissue biological response to zirconia and metal implant abutments compared with natural tooth: microcirculation monitoring as a novel bioindicator. Implant Dent.2015;24(1):37-41. [18] Parlange LM,Sims MR.A T.E.M. stereological analysis of blood vessels and nerves in marmoset periodontal ligament following endodontics and magnetic incisor extrusion. Eur J Orthod.1993;15(1):33-44. [19] Wise GE,King GJ.Mechanisms of tooth eruption and orthodontic tooth movement.J Dent Res.2008;87(5): 414-434. [20] Agrawal N,Kundu D,Agrawal K,et al.Comparison of longitudinal changes in clinical periodontal parameters of canines and first molars treated with fixed orthodontic appliances.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2016;149(3):325-330. [21] Xie Y,Zhao Q,Tan Z,et al.Orthodontic treatment in a periodontal patient with pathologic migration of anterior teeth.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2014;145(5): 685-693. [22] Park KN,Oh SM,Lee CY,et al.Design and application of hybrid maxillomandibular fixation for facial bone fractures.J Craniofac Surg.2013;24(5):1801-185. [23] Sugawara Y,Sawada T,Inoue S, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of elastin, fibrillins and microfibril-associated glycoprotein-1 in the developing periodontal ligament of the rat molar.J Periodontal Res.2010;45(1):52-59. [24] Toms A,Gannon B,Carati C.The immunohistochemical response of the rat periodontal ligament endothelium to an inflammatory stimulus.Aust Orthod J.2000;16(2): 61-68. [25] Cousley RR,Gibbons AJ.Correction of the occlusal and functional sequelae of mandibular condyle fractures using orthodontic mini-implant molar intrusion. J Orthod. 2014;41(3):245-253. [26] Inoue K,Hara Y,Sato T. Development of the oxytalan fiber system in the rat molar periodontal ligament evaluated by light- and electron-microscopic analyses. Ann Anat.2012;194(5):482-488. [27] Cheung AT,Miller JW,Miguelino MG,et al.Exchange transfusion therapy and its effects on real-time microcirculation in pediatric sickle cell anemia patients: an intravital microscopy study.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012;34(3):169-174. [28] 吴琳,韩丹.猫恒前磨牙牙周膜微血管构筑的实验研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2006, 35(1):43-44. [29] 何玲,徐军,邓燕.牙周膜微血管构筑对水平外力反应的实验研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 1998,33(5):309-311. [30] 周书敏,何明之,张延宏.用三维有限法对健康牙周膜在11种载荷下应力分布的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 1989, 6(24):334. [31] Galvao MP,Chapper A,Rosing CK,et al.Methodological considerations on descriptive studies of induced periodontal diseases in rats.Pesqui Odontol Bras. 2003;17(1):56-62. [32] Goncalves PF,Nogueira FilhoGda R,Sallum EA,et al.Immunosuppressant therapy and bone loss in ligature-induced periodontitis -a study in rats.Pesqui Odontol Bras. 2003;17(1):46-50. [33] Schreiner HC,Sinatra K,Kaplan JB,et al.Tight- adherence genes of Actinobacillusactinomycetemcomitansarerequired for virulence in a rat model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003; 100(12):7295-7300. [34] Dumitrescu AL,Abd-El-Aleem S,Morales-Aza B,et al.A model of periodontitis in the rat: effect of lipopolysaccharide on bone resorption, osteoclastactivity, and local peptidergic innervation.J Clin Periodontol.2004;31(8):596-603. [35] Liu H,Jiang H,Wang Y.The biological effects of occlusal trauma on the stomatognathic system-a focus on animal studies.J Oral Rehabil.2013;40(2):130-138. [36] Hamanaka EF,Poi WR,Salzedas LM,et al. A method for the geometric standardization of intraoral radiographs for long-term follow up of replanted teeth: a case report. Dent Traumatol.2013;29(2):121-126. [37] Caviedes-Bucheli J,Azuero-Holguin MM,Correa-Ortiz JA,et al.Effect of experimentally induced occlusal trauma on substance p expression in human dental pulp and periodontal ligament.J Endod. 2011;37(5): 627-630. [38] Bai H,Wang D,Delattre B,et al. Biomimetic gradient scaffold from ice-templating for self-seeding of cells with capillary effect.Acta Biomater.2015;20:113-119. [39] Belle J,Ysasi A,Bennett RD,et al.Stretch-induced intussuceptive and sprouting angiogenesis in the chick chorioallantoic membrane.Microvasc Res. 2014;95: 60-67. [40] Stoppato M,Carletti E,Maniglio D,et al.Functional role of scaffold geometries as a template for physiological ECM formation: evaluation of collagen 3D assembly. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2013;7(2):161-168. |
| [1] | Fan Jiabing, Zhang Junmei. Morphological measurement and analysis of the mandible in adult females with different vertical skeletal types [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1177-1183. |
| [2] | Cheng Bingkun, Liang Jianfei, Qin Dongze, Cheng Zixu, Zhao Yunzhuan. Isolation, culture and biological characteristics of high-purity orofacial-bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells of the rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 67-72. |
| [3] | Dong Wenjie, Zhang Shiyang, Zhao Lei, Wang Yukun. Icariin deproteinized inorganic bovine bone composite and deproteinized inorganic bovine bone material in repairing mandibular defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5467-5472. |
| [4] | Zhou Pengfei, Lin Jing, Chen Yuying, Lin Minkui. Canine dental pulp stem cells-polyglycolic acid scaffold complex for canine periodontal tissue defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5526-5531. |
| [5] | Wu Min1, Li Xue1, Gao Jie1, Yang Shuai1, Cai Yizhi2, Wang Mingguo1 . Micro-CT changes and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in reconstructed mandibular condylar cartilage under continuous mandibular advancement in growing and adult rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1001-1006. |
| [6] | Luo Dongyuan1, Zhou Niangou2, Chen Yiyang1, Wang Hongtao1, Li Fan1, Wu Wenli1, Liu Jiayu1, Hao Jiansuo1. Body weight changes in children with Pierre Robin syndrome after distraction osteogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4927-4931. |
| [7] | Zhou Yang, Zhou Libin, Piao Zhengguo. Prospects and application of curvilinear distraction osteogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2436-2442. |
| [8] | Li Yi-dan, Xu Nuo, Li Yue-ling, Yu Ming, Chen Jie, Li Xiao-jie. Implanting two kinds of bone substitutes into the sockets after wisdom tooth extraction to recover alveolar bone height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(6): 846-851. |
| [9] | Yu Hedong, Leng Weidong, Chen Yongji, Ni Xiaobing, Ai Jun, Tan Yaqin, Luo Jie. Repair of mandibular defects with polyetheretherketone/biphase bioceramic composites [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5452-5457. |
| [10] | Wang Jing, Wang Mengyang, Feng Qiaoqiao, Sun Jijun, Ci Haosu. Perforation of the pulp chamber floor: repair with mineral trioxide aggregate, light-cured glass ionomer cement and light-cured calcium hydroxide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5458-5463. |
| [11] | Du Guo-qing, Sun Jian, Li Ya-li, Chen Li-qiang, Chen Chen, Deng Nan, Wu Yu-tong, Li Li, Wang Zhi-hao . Reconstruction of mandibular defects with tissue-engineered bone using 3D bionic printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(18): 2813-2819. |
| [12] | Li Dong-mei, Liu Xin-hui, Li Qing-xing. Constructing nanosized cell-type tissue-engineered bone for repair of mandibular bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(14): 2146-2151. |
| [13] | Chen Hui-hong, Wei Song-guan, Pang Bo, Wang Ling-fei, Qin Yuan, Xie Liu-rong, Liao Hong-bing. Socket shield technique for peri-implant tissue preservation in esthetics zone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(10): 1605-1610. |
| [14] | Zhou He-jie, Xu Xiao-mei, Mao Jie, Zhou Yi-fei. Fixed bite plate combined with intermaxillary traction screw for free fibula flap repair of mandibular defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(8): 1215-1220. |
| [15] | Huang Ying1, Zhang Hui1, Cai Yue1, Zeng Fan-gang2, Guo Ling1. Bone mineral density of cancellous bone in edentulous areas: quantitative CT measurement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(36): 5775-5780. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||