Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (36): 5325-5331.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.36.001
Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Li Jie-mei, Wang Huai-gao, Deng Da-shi, Lu Fang, Zhang Chen-chen, Liu Guo-zeng, Zhou Yan-fang
- Department of Pathophysiology, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 525808, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2016-06-24Online:2016-09-02Published:2016-09-02 -
Contact:Zhou Yan-fang, M.D., Department of Pathophysiology, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 525808, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Jie-mei, Master, Department of Pathophysiology, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 525808, Guangdong Province, China Wang Huai-gao, Master, Lecturer, Department of Pathophysiology, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 525808, Guangdong Province, China Li Jie-mei and Wang Hai-gao contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Plan for Social Development of Guangdong Province, No. 2013B021800073; the Scientific Research Project of Dongguan Science and Technology Department, No. 2014108101049
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jie-mei, Wang Huai-gao, Deng Da-shi, Lu Fang, Zhang Chen-chen, Liu Guo-zeng, Zhou Yan-fang. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(36): 5325-5331.
share this article
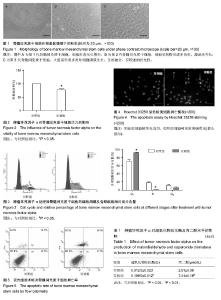
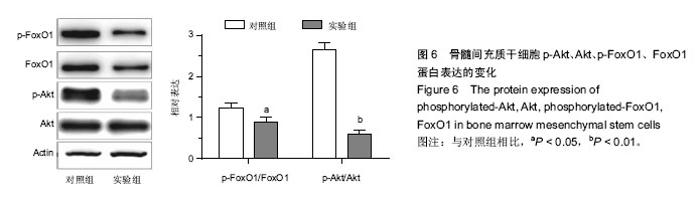
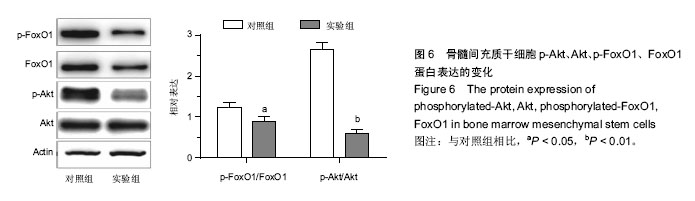
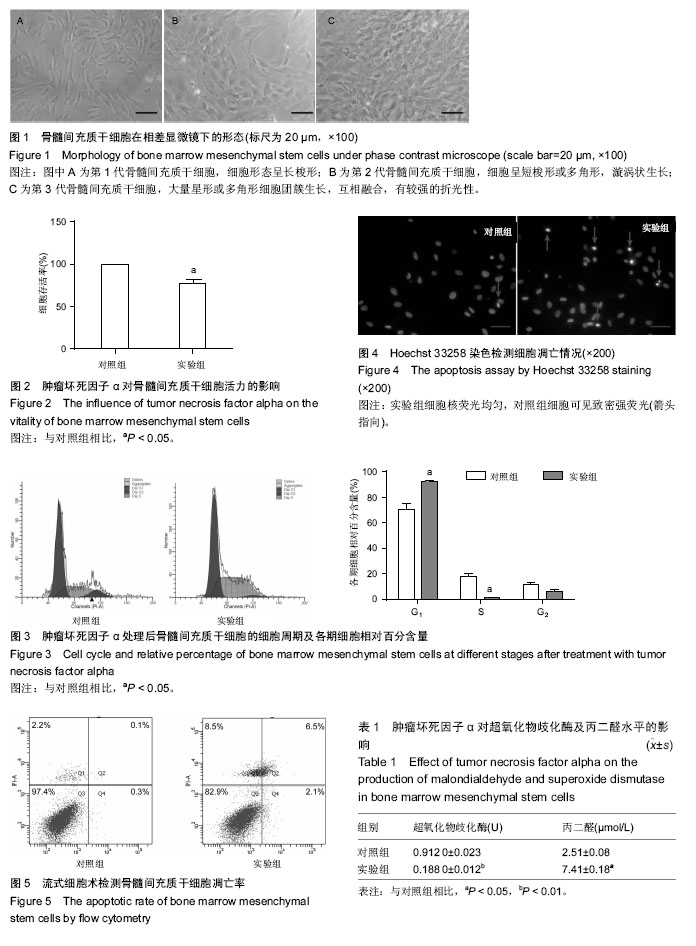
2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞的分离、培养及形态学观察结果 原代培养48 h后首次换液,可见有少许细胞集落及已贴壁的圆形和短梭形的散在单个细胞,72 h后细胞增殖加快,呈团簇集落样生长,细胞形态呈长梭形或多角形,有较强的折光性,1周后细胞铺满瓶底达到融合状态,漩涡状生长,见图1。 2.2 肿瘤坏死因子α对骨髓间充质干细胞活力的影响 200 μg/L肿瘤坏死因子α作用6 h后,细胞存活率降低,与对照组相比,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2。 2.3 流式细胞术测定肿瘤坏死因子α对骨髓间充质干细胞周期的影响 肿瘤坏死因子α作用后,流式细胞仪检测细胞周期发现:S期、G2期细胞比例有所下降,G1期细胞比例增加,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明肿瘤坏死因子α能抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖,将细胞阻滞在G1期(图3)。 2.4 荧光显微镜骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡的形态 荧光显微镜下观察,对照组细胞核荧光均匀,实验组细胞可见致密强荧光,细胞核变小皱缩,染色质高度凝聚,边缘化,可见核裂解为碎块的凋亡小体(图4)。 2.5 流式细胞仪检测肿瘤坏死因子α对骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡的影响 肿瘤坏死因子α作用后,细胞凋亡率为8.6%,较对照组细胞凋亡率0.4%有明显增高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明缺血微环境中肿瘤坏死因子α可促进骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡(图5)。 2.6 肿瘤坏死因子α对p-Akt的及p-FoxO1的下调作用 Western blot结果表示,正常骨髓间充质干细胞内有一定水平p-Akt及p-FoxO1的表达。200 μg/L肿瘤坏死因子α处理骨髓间充质干细胞6 h可明显下调p-Akt及其下游p-FoxO1表达水平,与对照组比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),见图6。 2.7 肿瘤坏死因子α引起骨髓间充质干细胞内超氧化物歧化酶生成减少,丙二醛生成增加 200 μg/L肿瘤坏死因子α处理骨髓间充质干细胞6 h后,胞内超氧化物歧化酶水平明显降低(P < 0.01),丙二醛水平明显升高(P < 0.05),与对照组比较,差异有显著性意义。实验结果说明,缺血微环境中肿瘤坏死因子α能促进细胞的氧化应激水平,增强细胞损伤(表1)。"
| [1] Ding Y, Clark JC. Cerebrovascular injury in stroke. Neurol Res. 2006;28(1):3-10. [2] Schippers EF, van't Veer C, van Voorden S, et al. TNF-alpha promoter, Nod2 and toll-like receptor-4 polymorphisms and the in vivo and ex vivo response to endotoxin. Cytokine. 2004;26(1):16-24. [3] El-Obeid A, Hassib A, Pontén F, et al. Effect of herbal melanin on IL-8: a possible role of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;344(4): 1200-1206. [4] Jin Z, Liang J, Wang J, et al. MCP-induced protein 1 mediates the minocycline-induced neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in vitro and in vivo. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:39. [5] Hong SQ, Zhang HT, You J, et al. Comparison of transdifferentiated and untransdifferentiated human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells in rats after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Res. 2011;36(12): 2391-2400. [6] Jeong CH, Kim SM, Lim JY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic stroke model. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:129145. [7] Mahmood A, Lu D, Qu C, et al. Treatment of traumatic brain injury with a combination therapy of marrow stromal cells and atorvastatin in rats. Neurosurgery. 2007;60(3):546-553. [8] Rao RR, Peterson AW, Ceccarelli J, et al. Matrix composition regulates three-dimensional network formation by endothelial cells and mesenchymal stem cells in collagen/fibrin materials. Angiogenesis. 2012; 15(2):253-264. [9] Sheikh AM, Nagai A, Wakabayashi K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation modulates neuroinflammation in focal cerebral ischemia: contribution of fractalkine and IL-5. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;41(3):717-724. [10] Lee EJ, Park HW, Jeon HJ, et al. Potentiated therapeutic angiogenesis by primed human mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of hindlimb ischemia. Regen Med. 2013;8(3):283-293. [11] Wang H, Nagai A, Sheikh AM, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation changes proinflammatory gene expression through a nuclear factor-κB-dependent pathway in a rat focal cerebral ischemic model. J Neurosci Res. 2013;91(11): 1440-1449. [12] Xue Q, Luan XY, Gu YZ, et al. The negative co-signaling molecule b7-h4 is expressed by human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and mediates its T-cell modulatory activity. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(1):27-38. [13] Parr AM, Tator CH, Keating A. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for the repair of central nervous system injury. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007; 40(7):609-619. [14] Merson TD, Bourne JA. Endogenous neurogenesis following ischaemic brain injury: insights for therapeutic strategies. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;56:4-19. [15] Nadri S, Soleimani M, Mobarra Z, et al. Expression of dopamine-associated genes on conjunctiva stromal-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;377(2):423-428. [16] Xu YX, Chen L, Hou WK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells treated with rat pancreatic extract secrete cytokines that improve the glycometabolism of diabetic rats. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(5):1878-1884. [17] Han EY, Chun MH, Kim ST, et al. Injection time-dependent effect of adult human bone marrow stromal cell transplantation in a rat model of severe traumatic brain injury. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013; 8(2):172-181. [18] Walker PA, Shah SK, Jimenez F, et al. Bone marrow-derived stromal cell therapy for traumatic brain injury is neuroprotective via stimulation of non-neurologic organ systems. Surgery. 2012;152(5): 790-793. [19] Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Semin Immunol. 2007; 19(1):24-32. [20] Xu JW, Ikeda K, Yamori Y. Inhibitory effect of polyphenol cyanidin on TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis through multiple signaling pathways in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2007;193(2):299-308. [21] 余科科,汪思应.TNF-α诱导肝干细胞凋亡及信号转导途径的改变[J].世界华人消化杂志,2010,18(7):707-710. [22] Qiao L, Yacoub A, Studer E, et al. Inhibition of the MAPK and PI3K pathways enhances UDCA-induced apoptosis in primary rodent hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2002;35(4):779-789. [23] Basak S, Hoffmann A. Crosstalk via the NF-kappaB signaling system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008; 19(3-4):187-197. [24] Wang L, Zhao Y, Liu Y, et al. IFN-γ and TNF-α synergistically induce mesenchymal stem cell impairment and tumorigenesis via NFκB signaling. Stem Cells. 2013;31(7):1383-1395. [25] 张玉龙. TNF-α抑制骨髓间充质干细胞参与糖尿病创面愈合的机制研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2013. [26] Erceg S, Ronaghi M, Oria M, et al. Transplanted oligodendrocytes and motoneuron progenitors generated from human embryonic stem cells promote locomotor recovery after spinal cord transection. Stem Cells. 2010;28(9):1541-1549. [27] Zheng Z, Yenari MA. Post-ischemic inflammation: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neurol Res. 2004;26(8):884-892. [28] Xian YF, Lin ZX, Mao QQ, et al. Isorhynchophylline Protects PC12 Cells Against Beta-Amyloid-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:163057. [29] Kops GJ, Dansen TB, Polderman PE, et al. Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a protects quiescent cells from oxidative stress. Nature. 2002;419(6904): 316-321. [30] Furukawa-Hibi Y, Yoshida-Araki K, Ohta T, et al. FOXO forkhead transcription factors induce G(2)-M checkpoint in response to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(30):26729-26732. [31] Medema RH, Kops GJ, Bos JL, et al. AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature. 2000;404(6779):782-787. [32] Fukunaga K, Ishigami T, Kawano T. Transcriptional regulation of neuronal genes and its effect on neural functions: expression and function of forkhead transcription factors in neurons. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;98(3):205-211. [33] Okada T, Liew CW, Hu J, et al. Insulin receptors in beta-cells are critical for islet compensatory growth response to insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(21):8977-8982. [34] Nakae J, Kitamura T, Kitamura Y, et al. The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 regulates adipocyte differentiation. Dev Cell. 2003;4(1):119-129. [35] Nemoto S, Finkel T. Redox regulation of forkhead proteins through a p66shc-dependent signaling pathway. Science. 2002;295(5564):2450-2452. [36] Storz P. Forkhead homeobox type O transcription factors in the responses to oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14(4):593-605. [37] Biggs WH 3rd, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, et al. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(13): 7421-7426. [38] Medema RH, Kops GJ, Bos JL, et al. AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature. 2000;404(6779):782-787. [39] Huang H, Tindall DJ. Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(Pt 15):2479-2487. [40] Katayama K, Nakamura A, Sugimoto Y, et al. FOXO transcription factor-dependent p15(INK4b) and p19(INK4d) expression. Oncogene. 2008;27(12): 1677-1686. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||