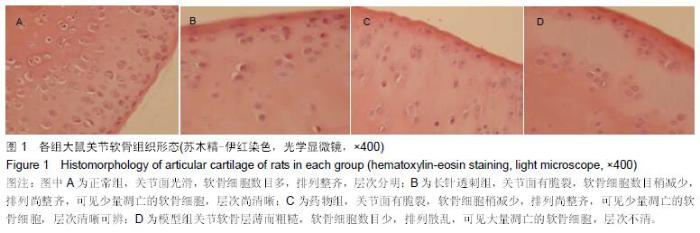
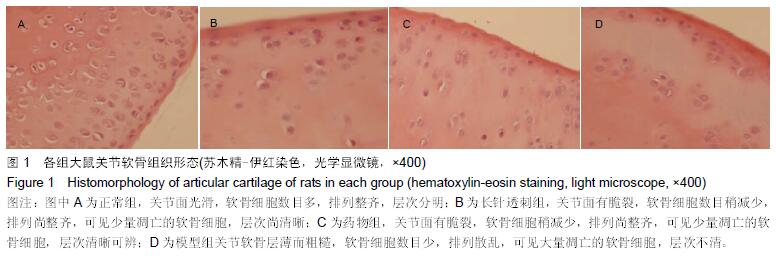
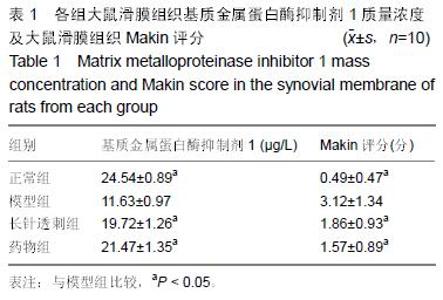
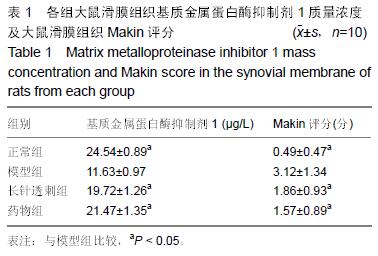
| [1] Creamer P, Hochberg MC. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 1997;350(9076):503-508. [2] Jain A, Nanchahal J, Troeberg L, et al. Production of cytokines,vascular endothelial growth factors, matrix metalloproteinases, and tissue in-hibitors of metalloproteinases-1 by ten-osynovium demonstrates its potential for tendon destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1754-1760. [3] Bramono DS, Richmond JC, Weitzel PP, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and their clinical applications in orthopaedics. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(428): 272-285. [4] Dean DD, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, et al. Evidence for metalloproteinase and metalloproteinase inhibitor imbalance in human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1989;84(2):678-685. [5] Tetlow LC, Adlam DJ, Woolley DE. Matrix metalloproteinase and proinflammatory cytokine production by chondrocytes of human osteoarthritic cartilage associations with degenerative changes. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(3):585-594. [6] Lijnen HR. Matrix metalloproteinases and cellular fibrinolytic activity. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2002;67(1): 92-98. [7] Fukui N, Zhu Y, Maloney WJ. Stimulation of BMP-2 expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and TNF-alpha in normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A (Suppl 3):59-66. [8] 卫小春.关节软骨[M].北京:科学出版社,2007. [9] Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707. [10] 高亮,陈默,岳萍,等.温针灸对膝骨关节炎兔膝关节软骨转化生长因子β1和胰岛素生长因子1水平的影响[J].针刺研究,2015,40(3):229-232. [11] 张必萌,吴耀持,沈健.长针透刺治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J].中国针灸,2004,24(9):613-614. [12] Oltariz ZA, Milliman C, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 heterodimers in vivo with a conserved homolog bax that accelerates programmed cell death. Nural Cell. 1993;74(4):609-619. [13] Visse R, Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 2003;92:827-839. [14] Pelletier JP, Jovanovic D, Fernandes JC, et al. Reduced rogression of experimental osteoarthritis in vivo by selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(7):1275-1286. [15] 中国国家标准化管理委员会.针灸技术操作规范第20部分:毫针基本刺法[M].北京:中国标准出版社,2009. [16] Close DR. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60(Suppl 3):62-67. [17] 李本杨,王峰.基质金属蛋白酶家族与膝骨关节炎成因机制相关性研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志,2014,26(5): 545-547. [18] 陈松.骨性关节炎患者基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)水平的变化[J].江西医学检验,2004,22(5):442-443. [19] 包飞,孙华,吴志宏,等.针刺对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨基质金属蛋白酶及其抑制剂表达的影响[J].中国针灸, 2011, 31(3):241-246. [20] Kevorkian L, Young DA, Darrah C, et al. Expression profiling of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(1):131-141. [21] 张仁.实用独特针刺法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1997. [22] 刘汗银.实用针灸大全[M].北京:北京出版社,1992. |