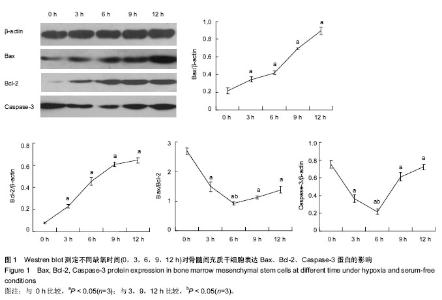
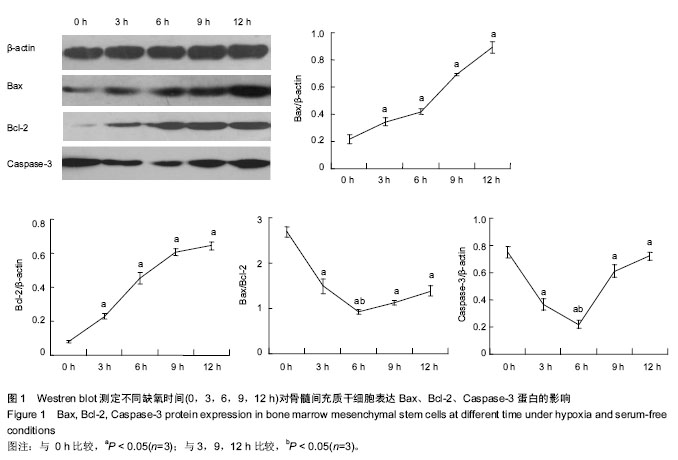
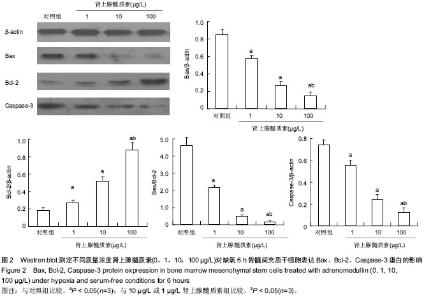
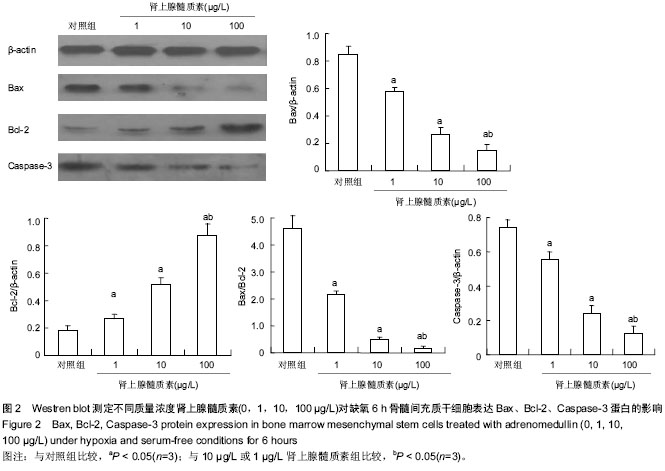
| [1] Mishra PK. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of heart failure: is it all paracrine actions and immunomodulation. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2008; 9(2):122-128.
[2] Toma C, Pittenger MF, Cahill KS, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart. Circulation. 2002 1;105(1):93-98.
[3] Nouguerède E, Berenguer C, Garcia S, et al. Expression of adrenomedullin in human colorectal tumors and its role in cell growth and invasion in vitro and in xenograft growth in vivo. Cancer Med. 2013;2(2):196-207.
[4] Kocemba KA, van Andel H, de Haan-Kramer A, et al. The hypoxia target adrenomedullin is aberrantly expressed in multiple myeloma and promotes angiogenesis. Leukemia. 2013;27(8):1729-1737.
[5] Okumura H, Nagaya N, Itoh T, et al. Adrenomedullin infusion attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. Circulation. 2004;109(2):242-248.
[6] 林茂海,苏津自,许昌声.肾上腺髓质素基因转染增强骨髓间充质干细胞移植对心肌梗死大鼠心室重构及心功能的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25(9):1692-1699.
[7] 苏津自,林茂海,林美萍.移植转染ADM或 HGF基因的骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠心肌梗死[J].基础医学与临床, 2010,30(2): 125-132.
[8] 蔡文钦,苏津自,俞登及.肾上腺髓质素基因转染改善缺氧培养骨髓间充质干细胞的抗凋亡能力[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(32):5913-5917.
[9] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[10] 陈华,苏津自.肾上腺髓质素基因病毒表达载体的构建及其对骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖影响[J].中国保健医学:研究版,2008, 16(20):867-870.
[11] 林茂海,苏津自,蔡文钦,等.携带肾上腺髓质素基因腺病毒体外转染骨髓间充质干细胞及其蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(23):4303-4306.
[12] Lee K, Majumdar MK, Buyaner D, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells maintain transgene expression during expansion and differentiation. Mol Ther. 2001;3(6):857-866.
[13] Nielsen LL, Gurnani M, Syed J, et al. Recombinant E1-deleted adenovirus-mediated gene therapy for cancer: efficacy studies with p53 tumor suppressor gene and liver histology in tumor xenograft models.Hum Gene Ther. 1998; 9(5):681-694.
[14] 王海英,陈恩乐,周琴,等.新辅助化疗对结肠癌细胞凋亡及相关调控蛋白表达的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(1):171-174.
[15] 田黎明,谢红付,李吉,等.β联蛋白对过氧化氢诱导人皮肤成纤维细胞增殖活性及凋亡相关基因Bcl-2、Bax表达的影响[J].中华皮肤科杂志,2015,48(2):112-115.
[16] 姜志云,刘义.原花青素对Ⅰ型糖尿病大鼠血管内皮功能、氧化性损伤和凋亡相关蛋白表达的影响[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2015, 23(3): 271-276.
[17] 刘日许,刁禹尧,苏珮茹,等.人参皂苷Rb1对低氧加无血清培养诱导的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡的影响[J].广东医学,2015, 26(8):1165-1169.
[18] 刘德胜,肖诗亮,王博,等.缺氧环境中胸腺素β4基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡率及Bax和Bcl-2的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(41):6573-6577.
[19] 邰文琳,董昭兴,徐益恒,等.骨髓间充质干细胞抗肺泡上皮细胞凋亡作用研究[J].昆明医科大学学报,2014,35(12):29-33.
[20] 张磊,赵学凌,李彪,等.二甲基乙二酰基甘氨酸对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞缺血清凋亡及Bcl-2/Bax蛋白表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(1):21-25.
[21] 周美玲,王爱玲,徐凤,等.低氧增强骨髓间充质干细胞对缺氧诱导心肌细胞凋亡的可能性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(6):955-958.
[22] Khan N, Adhami VM, Afaq F, et al. Butein induces apoptosis and inhibits prostate tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012;16(11):1195-1204.
[23] Quindry JC, Miller L, McGinnis G, et al. Ischemia reperfusion injury, KATP channels, and exercise-induced cardioprotection against apoptosis. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012;113(3):498-506.
[24] Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, et al. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(1):49-63.
[25] Sun X, Wu Y, Chen B, et al. Regulator of calcineurin 1 (RCAN1) facilitates neuronal apoptosis through caspase-3 activation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(11):9049-9062.
[26] Snigdha S, Smith ED, Prieto GA, et al. Caspase-3 activation as a bifurcation point between plasticity and cell death. Neurosci Bull. 2012;28(1):14-24.
|