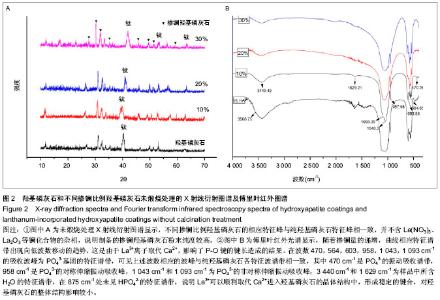
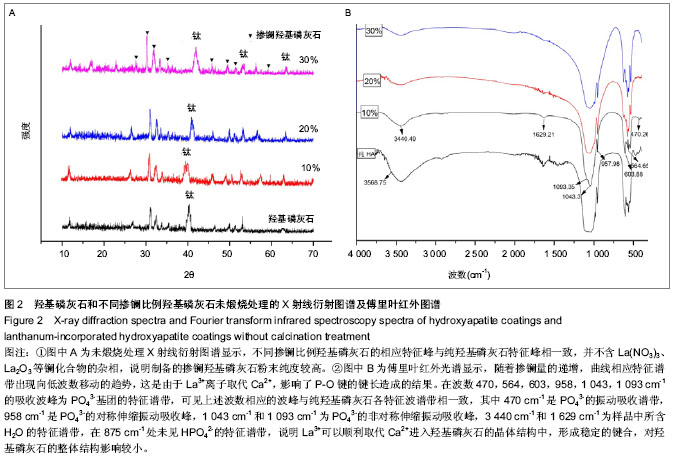
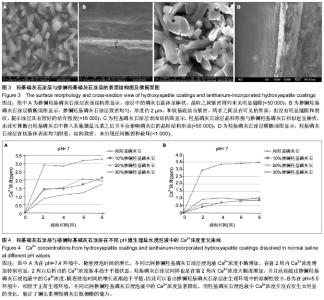
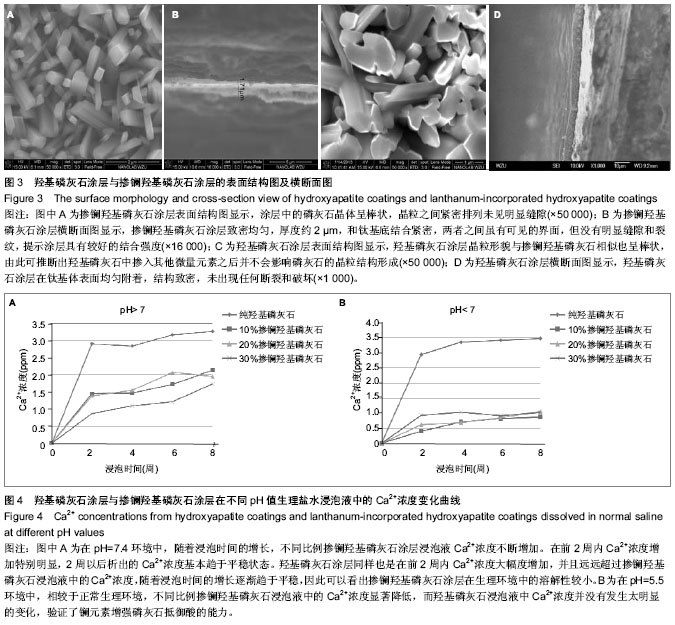
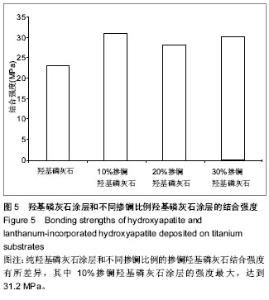
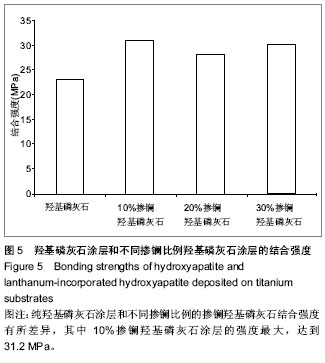
| [1] 崔阳,刘一,陈学思,等.改性羟基磷灰石骨修复纳米复合材料的制备及生物学评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(26): 5074-5077.[2] 王云,王青山.纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合材料在口腔医学中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(8):1426-1428.[3] Koch KA,Brave DG.Bioceramics,Part 2: The clinician's viewpoint. Dent Today.2012;31(2):118-120.[4] Vallet-Regi M,Izquierdo-Barba I,Colilla M.Structure and functionalization of mesoporous bioceramics for bone tissue regeneration and local drug delivery. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci.2012;370(1963):1400-1421.[5] Zheng X,He J.Effect evaluation of medical calcium sulfate-OsteoSet in repairing jaw bone defect.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2012;26(1):87-90.[6] Lang L,Wu D,Xu Z.Controllable fabrication of TiO(2) 1D- nano/ micro structures: solid, hollow, and tube- in- tube fibers by electrospinning and the photocatalytic performance.Chemistry.2012;18(34):10661-10668.[7] Dinda GP,Shin J,Mazumder J. Pulsed laser deposition of hydroxyapatite thin films on Ti6Al4V:effect of heat treatment on structure and properties.Acta B iomater.2009;5(5):1821- 1830.[8] Saju KK, Reshmi R,Jayadas NH,et al.Polycrystalline coating of hydroxyapatite on TiAl6V4 implant material grown at lower substrate temperatures by hydrothermal annealing after pulsed laser deposition.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2009;223(8): 1049-1057.[9] Rau JV,Generosi A,Laureti S,et al.Physicochemical investigation of pulsed laser deposited carbonated hydroxyapatite films on titanium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2009;1(8):1813-1820.[10] Huang J,Best SM,Bonfield W,et al.Development and characterization of titanium-containing hydroxyapatite for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(1):241- 249.[11] Yang GL,He FM,Hu JA,et al.Effects of biomimetically and electrochemically deposited nano-hydroxyapatite coatings on osseointegration of porous titanium implants. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2009;107(6): 782-789.[12] Meirelles L,Albrektsson T,K jell in P,e t al.Bone reaction to nano hydroxyapatite modified titanium implants placed in a gap-healing model.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;87(3):624-631.[13] Canullo L,Sisti A.Early implant loading after vertical ridge augmentation(VRA)using e-PTFE titanium-reinforced membrane and nano-structured hydroxyapatite:2-year prospective study. Eur J Oral Implantology.2010;3(7): 56-59.[14] Heimann RB,Wirth R.Formation and transformation of amorphous calcium phosphates on titanium alloy surfaces during atmospheric plasma spraying and their subsequent in vitro performance.Biomaterials. 2006;27(6):823-831.[15] Vidigal GM Jr,Groisman M,deSena LA,et al.Surface characterization of dental implants coated with hydroxyapatite by plasma spray and biomimetic process.Implant Dent.2009; 18(4):353-361.[16] Kim HW,Koh YH,Li LH,et al.Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate with titania buffer layer processed by sol-gel method.Biomaterials.2004;25(13)2533-2538.[17] Lewandowski JA, Johnson CM.Structural failure of osseointegrated implants at the time of restoration.J Prosthet Dent.1989;62(2):127-129.[18] 严杰,曹聪,董宇启.钛及钛合金表面生物活性改性及效果评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(21):3921-3924.[19] LeGeros RZ. Calcium phosphates in oral biology and medicine. Monogr Oral Sci.1991;15:1-201.[20] Blake GM,Zivanovic MA,Mcewan AJ.Sr-89 therapy strontium kinetics in metastatic bone disease.J Nucl Med.1986;279(9): 1030-1035.[21] Blake GM,Zivanovic MA,Mcewan AJ.Sr-89 strontium kinetics in disseminated carcinoma of the prostate.Eur J Nucl Med. 1986; 12(9):447-451.[22] Naveau B.Strontium: a new treatment for osteoporosis.Joint Bone Spine. 2004;71(4):261-263.[23] Chen DM, Fu YF, Gu GZ. Preparation and solubility of the solid solution of strontium substituted hydroxyapatite.Chin J Biomed Eng.2003;20:278-282.[24] 陈德敏,傅远飞.不同含锶量的掺锶羟磷灰石固溶体机械性能评价[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2001,10(4):178-183.[25] Guo D,Xu K,Zhao XY, et al. Development of a strontium containing hydroxyapatite bone cement. Biomaterials.2005; 26(19):4073-4083.[26] 郭大刚,徐可为,岳进,等.含锶磷灰石骨水泥浆体的pH值及其固化体的体外细胞毒性评价[J].无机材料学报,2005,20(5):1159- 1166.[27] Dagang G, Kewei X,Yong H. The influence of Sr doses on the in vitro biocompatibility and in vivo degradability of single-phase Sr-incorporated HAP cement.J Biomed Mater Res A.2008;86(4):947-958.[28] Yang H,Zhang L,Xu KW.The microstructure and specific properties of La/HAP composite powder and its coating.Appl Surf Sci.2007;254(2):425-430.[29] Femandez-Gavarron F, Huque T, Rabinowita J L, et al. Incorparation of 140-lanthanum into bones,teeth and Hydroxyapatite.Bone Miner.1988;3(4):283-291.[30] Fresa R, Contantini A,Buri A,et al.Apatite formation on (2-x)CaO•x/3M2O3•2SiO2 glasses (M=La,Y; 0<x<0.6) in a simulated body fluid. Biomaterials.1995;16:1249-1253.[31] Huang J,Zhang TL,Xu SJ,et al.Effects of lanthanum on composition, crystal size, and lattice structure femur bone mineral of Wistar rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006;78(4): 241- 247.[32] 刘天建,王友法,李世普.溶胶凝胶法制备纳米掺镧磷灰石及性能表征[J].武汉理工大学学报,2009,31(20):8-10.[33] Ji X, Lou W, Wang Q,et al. Sol-Gel-Derived Hydroxyapatite-Carbon Nanotube/Titania Coatings on titanium Substrates.Int J Mol Sci. 012;13(4):5242-5253.[34] 尚渤程,黎一苇.人体常见的pH值[J].生物学教学,2009,34(12): 66.[35] Ramay HR, Zhang M.Preparation pf porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds by combination of the gel-casting and polymersponge methods. Biomaterials.2003;24:3293-3302 |