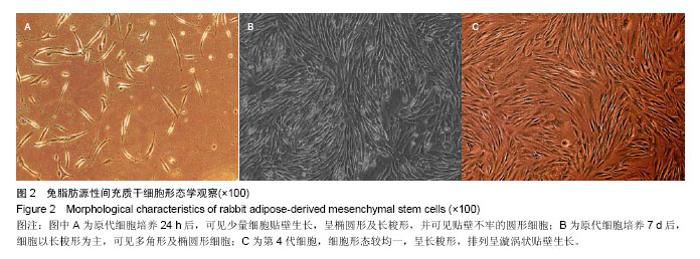
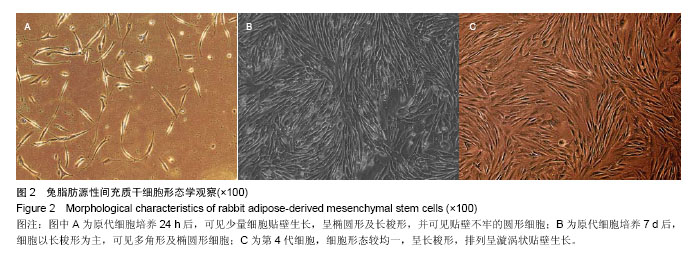
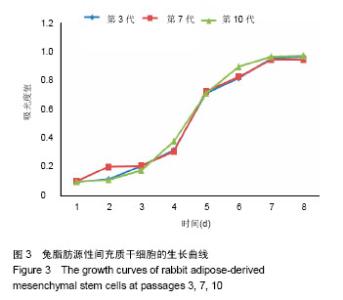
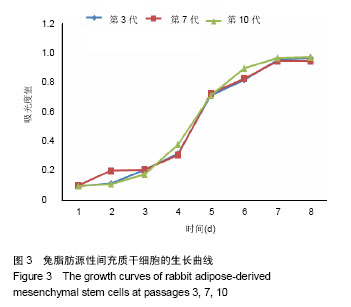
| [1] Gregory CA, Prockop DJ, Spees JL.Non-hematopoietic bone marrow stem cells: molecular control of expansion and differentiation.Exp Cell Res. 2005;306(2):330-335.
[2] Dragoo JL, Choi JY, Lieberman JR,et al.Bone induction by BMP-2 transduced stem cells derived from human fat.J Orthop Res. 2003;21(4):622-629.
[3] Nakao N, Nakayama T, Yahata T,et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells facilitate hematopoiesis in vitro and in vivo: advantages over bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Am J Pathol. 2010;177(2):547-554.
[4] 王之发,翁雁鸣,刘彦普,等.兔骨髓干细胞和脂肪干细胞增殖和分化能力的比较[J].现代生物医学进展, 2013,13(11):2026-2030.
[5] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H,et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.
[6] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P,et al.Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2002; 13(12): 4279-4295.
[7] Shigemura N, Okumura M, Mizuno S,et al. Autologous transplantation of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells ameliorates pulmonary emphysema.Am J Transplant. 2006; 6(11):2592-2600.
[8] Morizono K, De Ugarte DA, Zhu M,et al. Multilineage cells from adipose tissue as gene delivery vehicles.Hum Gene Ther. 2003;14(1):59-66.
[9] 余方圆,卢世璧,赵斌,等.脂肪干细胞与骨髓干细胞生物学性状的比较[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2009,26(3):396.
[10] 陈亮,吴柏霖,吴明珑,等.解剖部位差异对脂肪干细胞生物学行为及成骨分化能力的影响[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2013, 42(5):564-568.
[11] Toyoda M, Matsubara Y, Lin K,et al. Characterization and comparison of adipose tissue-derived cells from human subcutaneous and omental adipose tissues.Cell Biochem Funct. 2009;27(7):440-447.
[12] 李玲慧,丁道芳,龚浩,等.大鼠腹腔脂肪干细胞的分离培养及诱导成骨[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(23):4232-4239.
[13] Lee RH, Kim B, Choi I,et al.Characterization and expression analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2004; 14(4-6):311-324.
[14] 田方.大鼠脂肪来源干细胞的分离、培养及不同诱导液对其细胞状态的影响[D].遵义:遵义医学院, 2012.
[15] 宋小飞,傅强.纯化取材脂肪提高实验中干细胞培养的纯度[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(40):7529-7532.
[16] Rada T, Gomes ME, Reis RL.A novel method for the isolation of subpopulations of rat adipose stem cells with different proliferation and osteogenic differentiation potentials.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(8):655-664.
[17] Rada T, Reis RL, Gomes ME. Novel method for the isolation of adipose stem cells (ASCs).J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2009; 3(2):158-159.
[18] 李俊宪,孙恒赟,袁捷,等.式细胞仪分选纯化人脂肪干细胞体外成骨活性的实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2010,6(6): 311-314.
[19] Liu Y, Zhao Y, Zhang X,et al. Flow cytometric cell sorting and in vitro pre-osteoinduction are not requirements for in vivo bone formation by human adipose-derived stromal cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56002.
[20] Sterodimas A, de Faria J, Nicaretta B,et al.Tissue engineering with adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs): current and future applications.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63(11): 1886-1892.
[21] De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A,et al. Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow.Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(3):101-109.
[22] Miyazaki M, Zuk PA, Zou J,et al.Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue and bone marrow for ex vivo gene therapy in rat spinal fusion model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(8):863-869.
[23] Han C, Zhang L, Song L,et al.Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a better cell source for nervous system regeneration.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(2): 329-337.
[24] Gronthos S, Zannettino AC, Hay SJ,et al. Molecular and cellular characterisation of highly purified stromal stem cells derived from human bone marrow.J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 9): 1827-1835.
[25] Zhu Y, Liu T, Song K,et al. Adipose-derived stem cell: a better stem cell than BMSC.Cell Biochem Funct. 2008;26(6):664- 675.
[26] 谢泽飞.不同年龄段、不同取材部位大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞生物学特性的对比研究[D].汕头:汕头大学医学院, 2013.
[27] 毕晓娟,马艳,江明.大鼠腹股沟脂肪间充质干细胞的分离、培养、鉴定及活体标记[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(14): 2512-2516.
[28] 雷蕙嘉,孙建军,彭本刚,等.大鼠脂肪干细胞的分离培养及鉴定的初步研究[J].中国实验诊断学, 2011,15(8):1245-1248.
[29] Vieira NM, Brandalise V, Zucconi E, et al. Isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential of canine adipose-derived stem cells.Cell Transplant. 2010;19(3): 279-289.
[30] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[31] 方小魁,李光早.种子细胞在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].中华全科医学, 2012,10(4):608-609.
[32] Zanetti AS, Sabliov C, Gimble JM,et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells and three-dimensional scaffold constructs: a review of the biomaterials and models currently used for bone regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(1):187-199. |