Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (35): 5583-5588.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.35.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Simultaneous bilateral versus unilateral total knee arthroplasty in treatment of knee osteoarthritis
Ye Chuan1, Liu Ri-guang1, Tang Jin1, Li Jiang-wei1, Zhang Tao2, Ren Hou-xiang1, Sun Qi1, Wu Cheng1, Zhao Bao-ping1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guiyang Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
2Department of Orthopedics, the 117 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Hangzhou 310013, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Revised:2014-07-28Online:2014-08-27Published:2014-08-27 -
About author:Ye Chuan, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guiyang Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the International Science and Technology Cooperation Project in Guizhou Province, No. Qiankehewai G 2010-7; the Social Development Jointly Foundation of Guizhou Province Science and Technology Department, No. Qiankehe 20103166; the Guizhou Province Science and Technology Agency-Funded project, No. LG2012008; the Project of Affiliated Hospital of Guiyang Medical University, No. 1-2012-18
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ye Chuan, Liu Ri-guang, Tang Jin, Li Jiang-wei, Zhang Tao, Ren Hou-xiang, Sun Qi, Wu Cheng, Zhao Bao-ping . Simultaneous bilateral versus unilateral total knee arthroplasty in treatment of knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(35): 5583-5588.
share this article
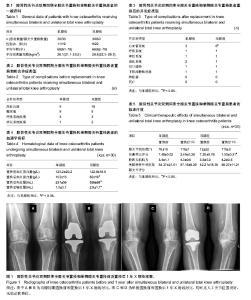
2.1 膝骨性关节炎双侧同期全膝关节置换和单侧膝关节置换患者的数量分析及一般资料 所有患者均获随访,随访12-24个月。双膝组与单膝组患者年龄、性别和体质量指数比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05;表1)。 2.2 膝骨性关节炎双侧同期全膝关节置换和单侧膝关节置换患者置换前后合并症变化 在60例患者中,有33例(55%)存在合并一种或多种内科疾病,其中单膝组16例(27%),双膝组17例(28%),2组患者置换前合并症患病率的比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05;表2)。 共有20例患者出现置换后并发症,其中单膝组9例(30%),双膝组11例(37%),2组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。但单膝组患者置换后出现心血管系统疾病的占10%,而双膝组则高达20%,明显高于单膝组(P < 0.05)。2组患者置换后出现呼吸系统、神经系统、消化系统、泌尿系统、切口感染、下肢深静脉栓塞、肺栓塞、死亡的比例差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05;表3)。 2.3 膝骨性关节炎双侧同期全膝关节置换和单侧膝关节置换患者血液学指标的差异 2组患者置换前血红蛋白水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但双膝组患者置换后血红蛋白水平、失血量和输血量均高于单膝组(P < 0.05,表4)。 2.4 膝骨性关节炎双侧同期全膝关节置换和单侧膝关节置换患者的临床疗效 2组患者置换后1年随访时的膝关节活动度、目测类比评分、股四头肌肌力和美国特种外科医院膝关节评分较置换前均有明显改善(P < 0.05),而2组患者膝关节活动度、股四头肌肌力和美国特种外科医院膝关节评分的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但单膝组患者目测类比评分明显高于双膝组(P < 0.05;表5)。影像学检查显示2组患者均未出现假体松动和移位(图1)。"
| [1] Murphy L, Schwartz TA, Helmick CG, et al. Lifetime risk of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(9): 1207-1213. [2] Hootman JM, Helmick CG. Projections of US prevalence of arthritis and associated activity limitations. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(1):226-229. [3] McMahon M, Block JA. The risk of contralateral total knee arthroplasty after knee replacement for osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(8):1822-1824. [4] Cohen RG, Forrest CJ, Benjamin JB. Safety and efficacy of bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12(5): 497-502. [5] Ritter MA, Harty LD, Davis KE, et al. Simultaneous bilateral, staged bilateral, and unilateral total knee arthroplasty. A survival analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(8):1532-1537. [6] Kim YH, Kim DY, Kim JS. Simultaneous mobile- and fixed-bearing total knee replacement in the same patients. A prospective comparison of mid-term outcomes using a similar design of prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(7): 904-910. [7] Kim YH, Yoon SH, Kim JS. The long-term results of simultaneous fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing total knee replacements performed in the same patient. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(10):1317-1323. [8] Fabi DW, Mohan V, Goldstein WM, et al. Unilateral vs bilateral total knee arthroplasty risk factors increasing morbidity. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(5):668-673. [9] Bini SA, Khatod M, Inacio MC, et al. Same-day versus staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty poses no increase in complications in 6672 primary procedures. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(4):694-697. [10] Niki Y, Katsuyama E, Takeda Y, et al. Comparison of postoperative morbidity between simultaneous bilateral and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasties: serological perspective and clinical consequences. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(3):504-509. [11] Gurunathan U. Perioperative considerations of bilateral total knee replacement: a review. J Clin Anesth. 2013;25(3):232- 239. [12] 中华医学会.临床诊疗指南——骨科学分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2008. [13] Lombardi AV, Mallory TH, Fada RA, et al. Simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasties: who decides? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(392):319-329. [14] Bullock DP, Sporer SM, Shirreffs TG Jr. Comparison of simultaneous bilateral with unilateral total knee arthroplasty in terms of perioperative complications. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(10):1981-1986. [15] Restrepo C, Parvizi J, Dietrich T, et al. Safety of simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(6):1220-1226. [16] Oakes DA, Hanssen AD. Bilateral total knee replacement using the same anesthetic is not justified by assessment of the risks. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(428):87-91. [17] Leonard L, Williamson DM, Ivory JP, et al. An evaluation of the safety and efficacy of simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(8):972-978. [18] Lombardi AV, Mallory TH, Fada RA, et al. Simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasties: who decides? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(392):319-329. [19] Kim YH, Choi YW, Kim JS. Simultaneous bilateral sequential total knee replacement is as safe as unilateral total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(1):64-68. [20] 李彪,龚跃昆,李世和,等.同期双侧人工全膝关节置换术治疗双膝骨性关节炎[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(2):151-152. [21] Dorr LD, Udomkiat P, Szenohradszky J, et al. Intraoperative monitoring for safety of bilateral total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(396):142-151. [22] Trojani C, Bugnas B, Blay M, et al. Bilateral total knee arthroplasty in a one-stage surgical procedure. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(8):857-862. [23] Yeager AM, Ruel AV, Westrich GH. Are bilateral total joint arthroplasty patients at a higher risk of developing pulmonary embolism following total hip and knee surgery? J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(5):900-902. [24] Ekinci Y, Oner M, Karaman I, et al. Comparison of simultaneous bilateral with unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(2):127-135. [25] Memtsoudis SG, Mantilla CB, Parvizi J, et al. Have bilateral total knee arthroplasties become safer? A population-based trend analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):17-25. [26] Memtsoudis SG, Ma Y, Chiu YL, et al. Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: risk factors for major morbidity and mortality. Anesth Analg. 2011;113(4):784-790. [27] Peskun C, Mayne I, Malempati H, et al. Cardiovascular disease predicts complications following bilateral total knee arthroplasty under a single anesthetic. Knee. 2012;19(5): 580-584. [28] Spicer E, Thomas GR, Rumble EJ. Comparison of the major intraoperative and postoperative complications between unilateral and sequential bilateral total knee arthroplasty in a high-volume community hospital. Can J Surg. 2013; 56(5): 311-317. [29] Bong MR, Patel V, Chang E, et al. Risks associated with blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(3):281-287. [30] Maniar RN, Baviskar JV, Singhi T, et al. Influence of bilateral sequential total knee arthroplasty on functional recovery. Indian J Orthop. 2013;47(1):23-30. [31] 王文浩,田少奇,张才龙,等.同期双侧与单侧全膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(7):598- 602. [32] 方锐,梁治权,孟庆才.同期双侧全膝关节置换与选择性单侧全膝关节置换后的早期功能恢复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(9):1549-1552. [33] 方锐,梁治权,孟庆才.一期双膝关节与单膝关节置换的早期评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):599-603. [34] Huotari K, Lyytikäinen O, Seitsalo S, et al. Patient outcomes after simultaneous bilateral total hip and knee joint replacements. J Hosp Infect. 2007;65(3):219-225. [35] Fu D, Li G, Chen K, et al. Comparison of clinical outcome between simultaneous-bilateral and staged-bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of retrospective studies. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(7):1141-1147. [36] Memtsoudis SG, Ma Y, González Della Valle A, et al. Perioperative outcomes after unilateral and bilateral total knee arthroplasty. Anesthesiology. 2009;111(6):1206-1216. [37] Odum SM, Troyer JL, Kelly MP, et al. A cost-utility analysis comparing the cost-effectiveness of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95(16):1441-1449. [38] Kim MH, Nahm FS, Kim TK, et al. Comparison of postoperative pain in the first and second knee in staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty: clinical evidence of enhanced pain sensitivity after surgical injury. Pain. 2014; 155(1):22-27. [39] Poultsides LA, Ghomrawi HM, Lyman S, et al. Change in preoperative expectations in patients undergoing staged bilateral primary total knee or total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(9):1609-1615.e1. [40] Haanstra TM, van den Berg T, Ostelo RW, et al. Systematic review: do patient expectations influence treatment outcomes in total knee and total hip arthroplasty? Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2012;10:152. [41] Ethgen O, Bruyère O, Richy F, et al. Health-related quality of life in total hip and total knee arthroplasty. A qualitative and systematic review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A(5):963-974. [42] Ravi B, Croxford R, Reichmann WM, et al. The changing demographics of total joint arthroplasty recipients in the United States and Ontario from 2001 to 2007. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012;26(5):637-647. [43] 加亨,梁治权,方锐,等.双膝骨性关节炎患者未行二期膝关节置换的影响因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(52):9707- 9711. |
| [1] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [4] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [5] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [6] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [7] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [8] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [9] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [10] | Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Hu Weifan, Tang Jinlong, Zhao Fengchao. Risk assessment of contralateral knee arthroplasty after unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 374-379. |
| [11] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [12] | Luo Anyu, Liu Hanlin, Xie Xiaofei, Huang Chen. Effect of antioxidant mixture on structural degeneration of an osteoarthritis rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3625-3629. |
| [13] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [14] | Liu Jinfu, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Fan Siqi, Feng Chengqin, Huang Jiaxing. Integrative analysis of biomarkers and therapeutic targets in synovium of patients with osteoarthritis by multiple microarrays [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3690-3696. |
| [15] | Chen Feng, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Liao Jianzhao, Li Jiajun, Song Shilei, Lai Yu. Molecular mechanism of anhydroicaritin in the treatment of osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3704-3710. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||