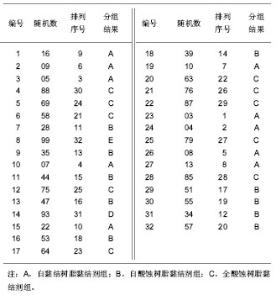
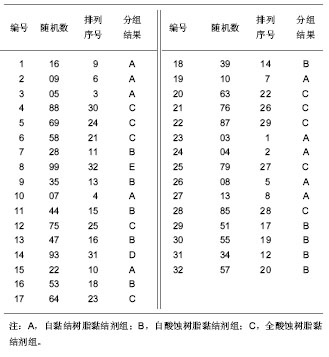
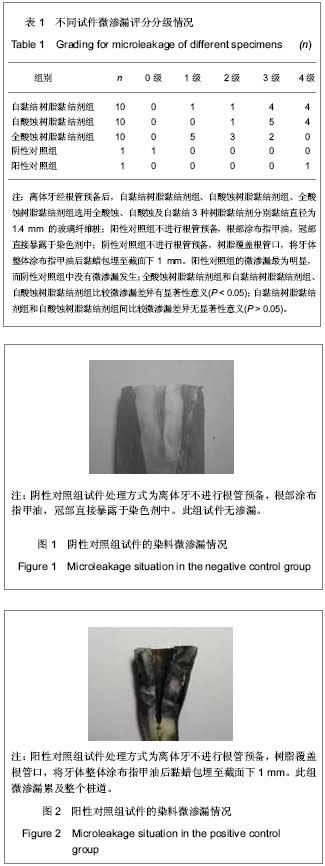
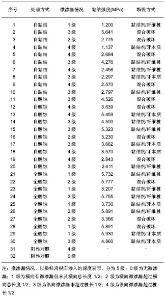
| [1] 陈亚琴,周峰,骆小平,等. 不同树脂粘接剂对纤维桩核微渗漏的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2011,29(5):461-468.
[2] 卫彦,杨小平,胡晓阳,等. 五种纤维桩/Panavia F粘接剂/牙本质之间微观机械固位研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2009,23(4): 392-394.
[3] Goracci C,Grandini S,Bossù M,et al.Laboratory assessment of the retentive potential of adhesive posts: A review.J Dent. 2007;35(11):827-835.
[4] 王宁,骆小平,俞长路,等.高强度纤维桩树脂核的临床应用研究[J]. 口腔医学研究,2005,25(3):149-151.
[5] 张雪晶,韦纪英,陈芳,等. 两种粘结剂对纤维桩与牙本质粘结强度的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2011,21(22):2707-2714.
[6] 全君杰,李永青,于青松,等.不同粘结系统对纤维桩粘结强度的对比分析[J].当代医学,2010,16(20):4-5.
[7] 冯云枝,陈梅,王压冲. 不同桩核和粘接系统冠向微渗漏的实验研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2009,25(4):482-485.
[8] 陈丽萍,黄林艳,张富强. 两种树脂粘结剂对纤维桩粘接强度测试及界面的激光扫描共聚焦显微镜观察[J].中国组织工程研究与临床修复,2009,13(47):9291-9294.
[9] 张文云,吴雨耘,杨立斗,等.不同粘固材料对纤维桩固位力的影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2009,10(2):106-108.
[10] 许诺,胡书海,杨洋,等.不同树脂粘结剂及硅烷偶联剂对玻璃纤维桩与牙本质粘结强度的影响[J].大连医科大学学报,2011,33(4): 321-329.
[11] 高宇,黄鹂,胡琳,等. 粘结剂使用方式对全酸蚀树脂水门汀与牙本质粘结性能影响的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2011,19(1):16-19.
[12] 黄鹂,陈吉华,张凌,等.四种双固化树脂粘结剂与根管牙本质间微渗漏的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2008,16(2):73-75.
[13] 周峰,聂蓉蓉,陈亚琴,等.不同桩核修复系统在长期水储存条件下的根管微渗漏表现[J].口腔医学研究,2011,27(5):419-421.
[14] Chong BS,Pitt Ford TR,Watson TF,et al.Sealing ability of potential retrograde root filling materials.Dent Traumatol. 2006; 11(6):264-269.
[15] 张文云,冯婷,杨立斗,等.根面处理方法对纤维桩核系统冠渗漏影响的初步研究[J].西南国防医药,2009,19(1):20-22.
[16] Francesca Z,Eduardo C,Jan DM,et al.Bonding effectiveness and sealing ability of fiber post bonding.Dent Mater.2008;24 (7):967-977.
[17] 雷慧云,陈蕾. 纤维桩核微渗漏的影响因素[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2011,25(5):379-381.
[18] 雷慧云,陈蕾,徐国富,等.两种树脂水门汀对纤维桩冠方微渗漏的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2011,27(2):109-112.
[19] 陈蕾,雷慧云,李继佳,等.3种黏固剂与根管牙本质粘接界面的扫描电镜观察[J].华西口腔医学,2010,28(2):132-138.
[20] Tay FR,Pashley DH,Yoshiyama M.Two modes of nanoleakage expression in single-step adhesives.J Dent Res.2002;81(7):472-476.
[21] 彭娟红,刘学恒,彭东,等. 纳米金刚石改性核树脂与纤维桩的微拉伸粘结强度研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2007,8(3):216-219.
[22] 李磊,李冉,刘江.不同树脂粘结系统对纤维桩粘结强度的实验研究[J].重庆医学,2012,41(7)694-695.
[23] Cantoro A,Goracci C,Papacchini F,et al.Effect of pre-cure temperature onthe bonding potential of self-etch and self-adhesive resin cements.Dent Mater.2008;24(5):577-583.
[24] 冯丽君,陈亚明,毛海燕. 纤维桩与根管不同处理后剪切粘结强度实验研究及电镜观察[J].口腔材料器械,2010,19(2):61-65.
[25] 刘莉,陈小冬.三种树脂黏结系统对纤维桩黏结强度的对比研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2011,4(9):532-535.
[26] 王林虎.自粘接型树脂水门汀粘接性能的研究[D].第四军医大学硕士学位论文,2008.
[27] 韩光政,熊正慧,陈亚明.离体牙经不同根管封闭剂充填后纤维桩剪切粘结强度的对比研究[J].口腔生物医学,2011,2(1):43-46.
[28] Baldissara P,Zicari F,Valandro LF,et al.Effect of root canal treatments on quartz fiber posts bonding to root dentin.J Endod.2006;32(10):985.
[29] 张晓,李津乐,冯晓伟.自粘结树脂水门汀与全酸蚀粘结系统对POPO和Para Post玻璃纤维桩在不同桩道深度剪切粘结强度的影响[J].郑州大学学报,2011,46(5):729-731.
[30] Bell AM,Lassila LV,Kangasniemi I,et al.Bonding of fibre-reinforced composite post to root canal dentin. J Dent. 2005;33(7): 533-539. |