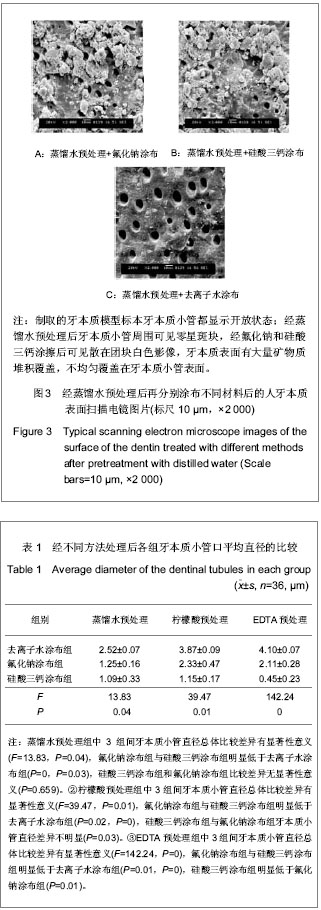
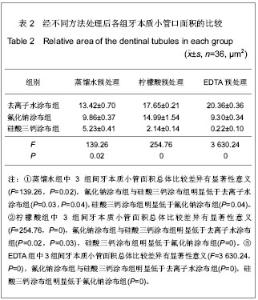
| [1] 中华口腔医学会牙本质敏感专家组.牙本质敏感的诊断和防治指南[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2009,44(3):132-134.
[2] PaesLeme AF,dosSantos JC,Giannini M,et al.Occlusion of dentin tubles by desensitizing agents.Am J Dent.2004;17(5): 3682372.
[3] Al-Sabbagh M,Andreana S,Ciancio SG.Dentinal hypersensitivity: review of aetiology,differential diagnosis, prevalence,and mechanism.J IntAcad Periodontol. 2004;6(1): 8212.
[4] 樊明文.牙体牙髓病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2003:134-137.
[5] 孙卫斌,袁留平,俞未一,等.复方高良姜糊剂牙本质小管堵塞作用的实验研究(Ⅱ)[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,1996,6(3):139-141.
[6] Hirvonen TJ,Närhi MVO,Hakumaki MOK.The excitability of dog pulp nerves in relation to the condition of dentine surface. J Endod.1984;10:294-298.
[7] Uchida A,Ishikawa Y,Ishida H.Transmission electron microscopic characterization of hypersensitive human radicular dentin. J Dent Res.1990;69:1293.
[8] 郑麟藩,张震康,俞光岩.实用口腔科学[M].2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2000:34-36.
[9] American Dental Association.Survey of consumer attitudes and behaviors regarding dental issues.Chicago:American Dental Association,1997.
[10] Dederich DN,Bushick RD.Laser in dentistry separating science from hype. J Am Dent Assoc.2004;135(2):204-212.
[11] 刘颖婷, 高辉.氟保护漆治疗牙本质敏感症临床疗效观察[J].中国误诊学杂志,2007,7(2):256.
[12] 周红文,陈亚明,祁惠兰,等.氟离子导入治疗牙本质敏感症的临床研究[J].口腔医学,2007,27(10):523-524.
[13] Itota T,Torii Y,Nakabo S,et al.Effect of fluoride-re-leasing adhesive system on decalcified dentin.J Oral Rehabil. 2003; 30(2):178-183.
[14] Suge T,Kawasaki A,Ishikawa K,et al.Ammonium hexafluorosilicate elicits calcium phosphate precipitation and shows continuous dentin tubule occlusion Dent Mater.2008; 24(2):192-198.
[15] 王晓虹,常江,孙宏晨.硅酸三钙阻塞牙本质小管的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(2): 176-178.
[16] Pashley DH.Dentin permeability,dentin sensitivity,and treatment through tubule occlusion.J Endod.1986;12(10): 465-467.
[17] 熊伯刚,熊世江.牙本质过敏症治疗的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2008,35(3):292-294.
[18] 梁登忠,关淑妮.牙本质过敏症治疗进展[J].广东牙病防治,2001, 9(4): 313-314.
[19] 周红文,陈亚明,祁惠兰,等.氟离子导入治疗牙本质敏感症的临床研究[J].口腔医学,2007,27(10):523-524.
[20] 李玉晶,李建英,杨玉琴.氟化氨银抑制牙本质龋机制的探讨[J].北京口腔医学,1997,42 (4):18-20.
[21] Sauro S,Gandolfi MG,Prati C,et al.Oxalate-containing phytocomplexes as dentine desensitisers:An in vitrostudy. Arch Oral Biol. 2006;51(8):655-664.
[22] Dragolich WE,Pashley DH,Brennan WA,et al.An in vitro study ofdentinal tubule occlusion by ferric oxalate. J Periodontol. 1993;64:1045-1051.
[23] Pereira JC,Angela D.Effect of desensitizing agents on the hydraulic conductance ofhuman dentin subjected to different surface pre-treatments-an invitro study. Dent Mater.2005; 21:129-138.
[24] Imai Y,Akimoto T.A new method of treatment for dentin hypersensitivity by precipitation of calcium phosphate in situ. Dent Mater J.1990;9:167-172.
[25] Ishikawa K,Suge T,Yoshiyama M,et al.Occlusion of dentinal tubules with calcium phosphate using acidic calcium phosphate solution followed byneutralization.J Dent Res. 1994;73(6):1197-1204.
[26] Gillam DG,Tang JY,Mordan NJ,et al.The effects of a novel bioglass? dentifrice on dentine sensitivity: a scanning electron microscopy investigation.J Ora Reha.2002;29:305-313.
[27] Zhao WY,Wang JY,Zhai WY,et al.The self-setting properties and in vitro bioactivity of tricalcium silicate. Biomaterials. 2005;26(31):6113-6121.
[28] Siriphannon P,Kameshima Y,Yasumori A,et al.Formation of hydroxyapatite onCaSiO3 powders in simulated body fluid.J Euro Ceram Soc.2002;22:511-520.
[29] Kokubo T,Kushitani C,Ohtsuki C,et al.Process of formation of bone-like apatite layer on silica gel.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1993; 4:127-131.
[30] Cho SB,Miyaji F,Kokubo T,et al.Apatite-forming ability of silicate ion dissolved from silica gels. J Biomed Mater Res. 1996;32(3):375-381.
[31] Torabinejad M,Hong CU,Pitt Ford TR,et al.Cytotoxicity of four root-end filling materials.J Endod.1995;21(8):489-492.
[32] 张向宇,孙志滢.深龋综合治疗法的疗效[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2003,13(11):621. |