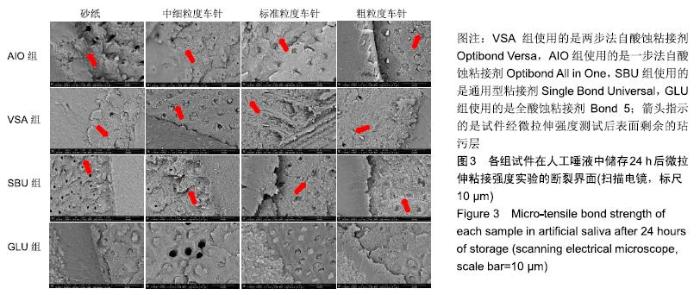
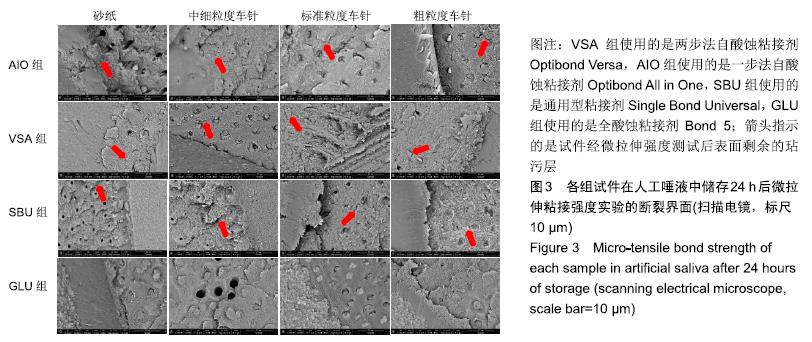
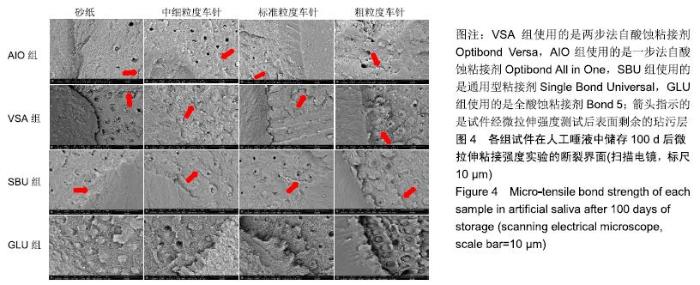
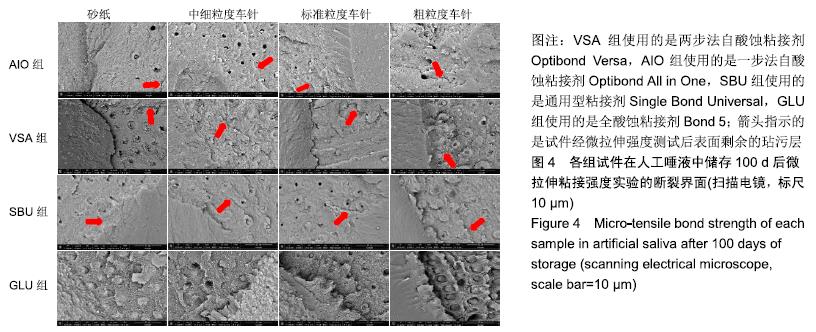
[1] FU J, KAKUDA S, PAN F, et al.Bonding performance of a newly developed step-less all-in-one system on dentin. Dent Mater J.2013;32(2):203-211.
[2] ARGOLO S, MATHIAS P, AGUIAR T, et al.Effect of agitation and storage temperature on water sorption and solubility of adhesive systems.Dent Mater J.2015;34(1):1-6.
[3] 梁乙然,郭斌,罗强,等.人工唾液条件下3种自酸蚀粘接剂与牙本质粘接耐久性研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2018,11(5): 286-290.
[4] 伊哲,朱琳琳,李柯檬.四种自酸蚀粘接剂的粘接强度耐久性实验研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2015,8(6):358-362.
[5] TAKAMIZAWA T, BARKMEIER WW, SAI K, et al.Influence of different smear layers on bond durability of self-etch adhesives. Dent Mater.2018;34(2):246-259.
[6] SAIKAEW P, CHOWDHURY AF, FUKUYAMA M, et al.The effect of dentine surface preparation and reduced application time of adhesive on bonding strength.J Dent.2016;47:63-70.
[7] AYAD MF.Effects of rotary instrumentation and different etchants on removal of smear layer on human dentin. J Prosthet Dent.2001;85(1):67-72.
[8] INOUE H, INOUE S, UNO S, et al.Microtensile bond strength of two single-step adhesive systems to bur-prepared dentin. J Adhes Dent.2001;3(2):129-136.
[9] TAY FR, SANO H, CARVALHO R, et al.An ultrastructural study of the influence of acidity of self-etching primers and smear layer thickness on bonding to intact dentin. J Adhes Dent. 2000;2(2):83-98.
[10] TAY FR, CARVALHO R, SANO H, et al.Effect of smear layers on the bonding of a self-etching primer to dentin.J Adhes Dent. 2000;2(2):99-116.
[11] DIAS WR, PEREIRA PN, SWIFT EJ JR. Effect of bur type on microtensile bond strengths of self-etching systems to human dentin.J Adhes Dent.2004;6(3):195-203.
[12] ERMIS RB, DE MUNCK J, CARDOSO MV, et al.Bond strength of self-etch adhesives to dentin prepared with three different diamond burs. Dent Mater.2008;24(7):978-985.
[13] 邢春霞,聂蓉蓉,孟翔峰,等.不同牙体预备车针所致玷污层对自粘接型树脂水门汀粘接强度的影响[J].口腔医学, 2019,39(5): 423-426.
[14] WATANABE I, NAKABAYASHI N, PASHLEY DH. Bonding to ground dentin by a phenyl-P self-etching primer.J Dent Res. 1994;73(6):1212-1220.
[15] ZABEU GS, MAENOSSONO RM, SCARCELLA CR, et al. Effect of diode laser irradiation on the bond strength of polymerized non-simplified adhesive systems after 12 months of water storage.J Appl Oral Sci.2018;27:e20180126.
[16] KANZOW P, BAXTER S, RIZK M, et al.Effectiveness of a universal adhesive for repair bonding to composite and amalgam.J Oral Sci.2019;61(2):343-350.
[17] VAN LANDUYT KL, SNAUWAERT J, PEUMANS M, et al.The role of HEMA in one-step self-etch adhesives.Dent Mater. 2008;24(10):1412-1419.
[18] SIA CF, LEVEY C.HEMA-free or HEMA-containing adhesive systems for non-carious cervical lesions.Evid Based Dent. 2018;19(4):114-115.
[19] MINE A, DE MUNCK J, CARDOSO MV, et al.Dentin-smear remains at self-etch adhesive interface. Dent Mater. 2014. 30(10):1147-1153.
[20] YOSHIHARA K, NAGAOKA N, OKIHARA T, et al.Functional monomer impurity affects adhesive performance.Dent Mater. 2015;31(12):1493-1501.
[21] 徐婧秋.新型底涂冲洗剂提高自酸蚀粘接剂的牙本质粘接持久性的研究[J].杭州:浙江大学,2016.
[22] WANG R, SHI Y, LI T, et al.Adhesive interfacial characteristics and the related bonding performance of four self-etching adhesives with different functional monomers applied to dentin. J Dent.2017;62:72-80.
[23] VAN LANDUYT KL, YOSHIDA Y, HIRATA I, et al.Influence of the chemical structure of functional monomers on their adhesive performance.J Dent Res.2008;87(8):757-761.
[24] FEITOSA VP, OGLIARI FA, VAN MEERBEEK B, et al.Can the hydrophilicity of functional monomers affect chemical interaction.J Dent Res.2014;93(2):201-216.
[25] ZHANG Z, WANG X, ZHANG L, et al.The contribution of chemical bonding to the short- and long-term enamel bond strengths.Dent Mater.2013;29(7):e103-112.
[26] YOSHIHARA K, YOSHIDA Y, NAGAOKA N, et al. Nano-controlled molecular interaction at adhesive interfaces for hard tissue reconstruction.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(9): 3573-3582.
[27] 汪嘉.不同粘结剂不同涂布次数对牙本质粘接强度的影响[D].长沙:中南大学,2009.
[28] LIU KL, ZHANG XF, WEI X.Influence of different acid etching modes on bond strengths to non-carious sclerotic dentin. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue.2016;25(1):38-41.
[29] 傅柏平.牙本质粘接持久性的影响因素及解决对策[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2013,22(1):5-6.
[30] SHONO Y, TERASHITA M, SHIMADA J, et al.Durability of resin-dentin bonds.J Adhes Dent.1999;1(3):211-218.
[31] DAVIDSON CL, DE GEE AJ, FEILZER A.The competition between the composite-dentin bond strength and the polymerization contraction stress.J Dent Res. 1984;63(12): 1396-1399.
|