Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (18): 2872-2876.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0862
Previous Articles Next Articles
An in vivo and in vitro study on the effect of tooth liquid polish sealant on the bond strength of orthodontic brackets
Lin Bao-shan, Li Ting
- Shenzhen Stomatological Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen 518001, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2018-04-06Online:2018-06-28Published:2018-06-28 -
Contact:Li Ting, Attending physician, Shenzhen Stomatological Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen 518001, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Lin Bao-shan, Attending physician, Shenzhen Stomatological Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen 518001, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. B2014058
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Bao-shan, Li Ting. An in vivo and in vitro study on the effect of tooth liquid polish sealant on the bond strength of orthodontic brackets[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(18): 2872-2876.
share this article
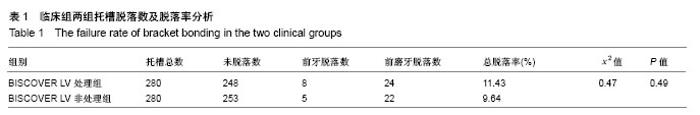
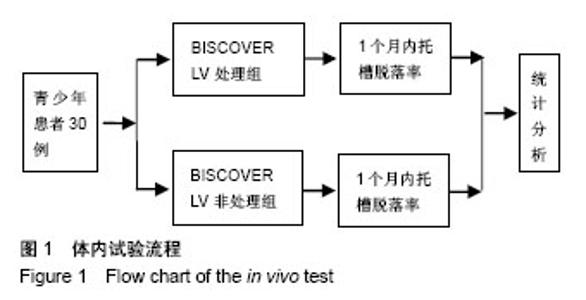
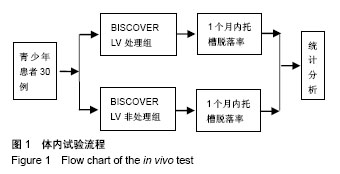
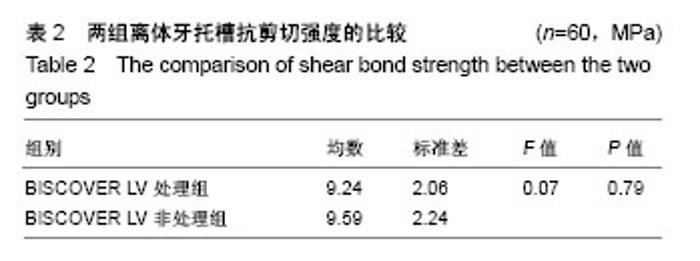
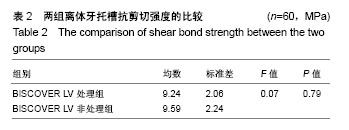
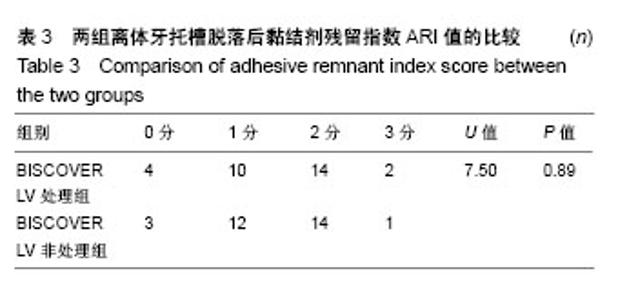
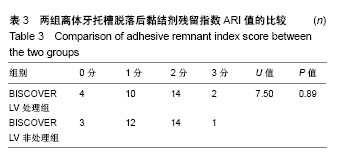
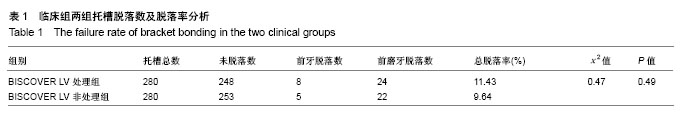
2.2 体内试验结果 由表1可见,患者左右两侧两组托槽脱落率都在10%左右,卡方检验显示两组托槽脱落率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);可以看到,患者托槽脱落的牙位以前磨牙居多,这个可能是因为在第一次托槽粘接后临床医生都会交代患者注意事项,要求患者前牙不能咬太硬或者大块的食物,因此患者的咬合力一般都集中于后牙区,这可能是造成患者前磨牙区托槽脱落频率较高的原因。 2.3 体外实验结果 表2显示,两组离体牙托槽的抗剪切强度比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。表3为两组离体牙托槽脱落后不同黏结剂残留指数ARI值所对应的牙齿数量,Mann-Whitney U检验表明者差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.4 不良反应 体内试验中,所有患者均未出现与正畸材料相关的不良反应。"
| [1] 陈万军,王晨齐,殷忠平,等.氟保护漆预防正畸治疗中牙釉质脱矿的临床研究[J].广东牙病防治,2015, 23(1):41-43.[2] Mehta A,Paramshivam G,Chugh VK,et al.Effect of light-curable fluoride varnish on enamel demineralization adjacent to orthodontic brackets: An in-vivo study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2015;148(5): 814-820.[3] Paschos E,Geiger FJ,Malyk Y,et al.Efficacy of four preventive measures against enamel demineralization at the bracket periphery-comparison of microhardness and confocal laser microscopy analysis.Clin Oral Investig.2016;20(6):1355-1366. [4] 林宝山,周媛,胡飚,等.液体抛光剂和护牙素预防托槽周围釉质脱矿效果的体外研究[J].口腔疾病防治,2017,25(9):565-568.[5] 舒丹,江蓉.玻璃离子水门汀与牙釉质粘结剂对青少年正畸后脱矿率、托槽脱落率的比较及对炎症因子影响的研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2016, 13(13):1315-1318.[6] 温兴涛,蔡少彬,李东健,等.自酸蚀光固化托槽粘结剂随机对照试验的临床评价[J].现代医院, 2015,15(8):36-38.[7] Krishnan S,Pandian S,Rajagopal R,et al.Six-month bracket failure rate with a flowable composite: A split-mouth randomized controlled trial. Dental Press J Orthod. 2017;22(2):69-76.[8] Tan ZM,Zhang J.Clinical study of light cured flowable resin in bonding orthodontic brackets. Clin Res Pract.2017.[9] 牟胤赫,杨陆一,吴嫣然,等.不同条件下3种正畸粘接剂粘结强度的比较及其意义[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2016,42(3):512-516.[10] Bezerra GL,Torres CR,Tonetto MR,et al.Shear Bond Strength of Orthodontic Brackets Fixed with Remineralizing Adhesive Systems after Simulating One Year of Orthodontic Treatment. ScientificWorld Journal.2015;2015:903451. [11] Bakhadher W,Halawany H,Talic N,et al.Factors Affecting the Shear Bond Strength of Orthodontic Brackets - a Review of In Vitro Studies. Acta Medica.2015;58(2):43.[12] Cossellu G,Lanteri V,Butera A,et al.Effects of six different preventive treatments on the shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets:in vitrostudy.Acta Biomater Odontol Scand. 2015;1(1):13-17. [13] Cao D,Gakunga GT,Hatch JP,et al.Prevention of Enamel Demineralization Around Orthodontic Brackets with BisCover LV[C]// Aadr Meeting.2010.[14] Clark TJ.The efficacy of ProSeal™, SeLECT Defense™, OrthoCoat™, and Biscover LV™ resin sealants on the prevention of enamel demineralization and white spot lesion formation. University of Iowa,2010.[15] O'Reilly MT,De Jesús Viñas J,Hatch JP.Effectiveness of a sealant compared with no sealant in preventing enamel demineralization in patients with fixed orthodontic appliances: a prospective clinical trial.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2013;143(6):837-844.[16] Sayinsu K,Isik F,Sezen S,et al.New protective Polish effects on shear bond strength of brackets.Angle Orthod. 2006;76(2):306-309.[17] 王聪,韩大江.液体封闭剂对托槽剪切强度的影响[J].四川医学, 2014, 35(8):960-962.[18] 郑闱颖,林军,叶衡峰,等.6种正畸粘结剂粘结强度的比较研究[J].口腔医学, 2014,34(6):447-449.[19] Chalipa J,Akhondi MS,Arab S,et al.Evaluation of shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets bonded with nano-filled composites.J Dent. 2013;10(5):461-465.[20] Sharma S,Tandon P,Nagar A,et al.A comparison of shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets bonded with four different orthodontic adhesives.J Orthod Sci.2014;3(2):29-33.[21] Mirzakouchaki B,Shirazi S,Sharghi R,et al.Shear bond strength and debonding characteristics of metal and ceramic brackets bonded with conventional acid-etch and self-etch primer systems: An in-vivo study.J Clin Exp Dent. 2016;8(1):e38.[22] Romano FL,Valério RA,Gomes-Silva JM,et al.Clinical evaluation of the failure rate of metallic brackets bonded with orthodontic composites. Braz Dent J.2012;23(4):399-402.[23] 李向东,宋然,白玉兴.三种粘结剂在唇侧间接粘结技术中的临床应用[J].北京口腔医学,2017, 25(4):226-228.[24] Mohammed-Salih HS.The Effect of Thermocycling and Debonding Time on the Shear Bond Strength of Different Orthodontic Brackets Bonded with Light - Emitting Diode Adhesive: In Vitro Study. JBCD. 2013.[25] Lee JY,Kim JS,Hwang CJ.Comparison of shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets using various zirconia primers.Korean J Orthod. 2015;45(4):164-170.[26] Nandhra SS,Littlewood SJ,Houghton N,et al.Do we need primer for orthodontic bonding? A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Orthod. 2015;37(2):147-55.[27] Jung-Hwan L,Milim L,Kyoung-Nam K,et al.Resin bonding of metal brackets to glazed zirconia with a porcelain primer. Korean J Orthod. 2015;45(6):299-307.[28] Arash V,Naghipour F,Ravadgar M,et al.Shear bond strength of ceramic and metallic orthodontic brackets bonded with self-etching primer and conventional bonding adhesives. Electron Physician. 2017;9(1): 3584-3591.[29] Bakhadher W,Halawany H,Talic N,et al.Factors Affecting the Shear Bond Strength of Orthodontic Brackets - a Review of In Vitro Studies. Acta Medica(Hradec Kralove).2015;58(2):43-48.[30] Bishara SE,Olsen ME,Damon P,et al.Evaluation of a new light-cured orthodontic bonding adhesive.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1998; 114(1):80-87.[31] Guzman UA,Jerrold L,Vig PS,et al.Comparison of shear bond strength and adhesive remnant index between precoated and conventionally bonded orthodontic brackets.Prog Orthod. 2013;14:39. [32] Kechagia A,Zinelis S,Pandis N,et al.The effect of orthodontic adhesive and bracket-base design in adhesive remnant index on enamel.J World Fed Orthod.2015;4(1):18-22.[33] Pham D,Bollu P,Chaudhry K,et al.Comparative evaluation of orthodontic bracket base shapes on shear bond strength and adhesive remnant index: An in vitro study.J Clin Exp Dent. 2017;9(7):e848-e854.[34] 卢小妹,牛胜德,安志毅.浅析正畸托槽脱落原因[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2004,20(6):778-778.[35] 舒绍兵,罗金英,钟建鑫,等.正畸托槽脱落原因的相关因素研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2015, 37(2):170-172.[36] 张春鹏.正畸托槽脱落原因的临床观察[J].大家健康(学术版), 2015,31(5): 275-276.[37] 何丽,王军强,曹伟靖.GC正畸玻璃离子粘接剂不同酸蚀时间对体外氟斑牙面与金属托槽粘接强度的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 38(1):154-156.[38] 董晶.不同氟斑牙程度及临床处理方法对正畸托槽脱落率的影响研究[J].中国美容医学,2015, 24(18):58-61.[39] Hooman ZN,Vahid M,Atefeh K,et al.The Effect of Four Surface Treatment Methods on the Shear Bond Strength of Metallic Brackets to the Fluorosed Enamel.J Dent(Shiraz). 2015;16(3 Suppl):251-259.[40] Gungor AY,Turkkahraman H,Adanir N,et al.Effects of fluorosis and self etching primers on shear bond strengths of orthodontic brackets.Eur J Dent.2009;3(3):173. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||