Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (29): 4613-4619.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2811
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immunoinflammatory mechanism of Panax notoginseng in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on network pharmacology
Nong Jiao1, Zeng Ping2, Li Juan2, Liu Jinfu1, Li Jinyi2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-08-27Revised:2019-09-06Accepted:2019-10-26Online:2020-10-18Published:2020-09-11 -
Contact:Zeng Ping, MD, Professor, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Nong Jiao, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Master’s Degree Graduate Innovation Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. YCSW2019172
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Nong Jiao, Zeng Ping, Li Juan, Liu Jinfu, Li Jinyi. Immunoinflammatory mechanism of Panax notoginseng in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4613-4619.
share this article
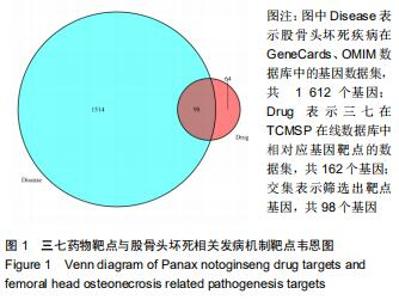
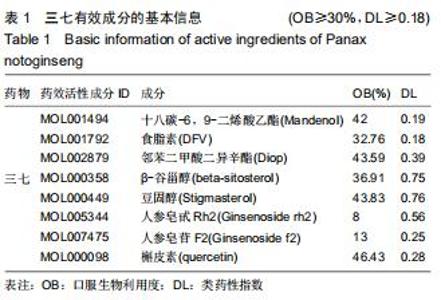
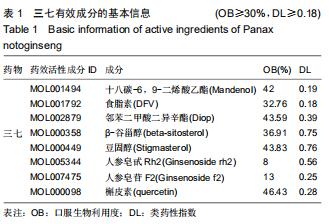
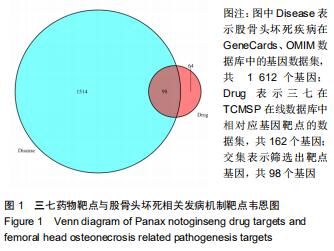
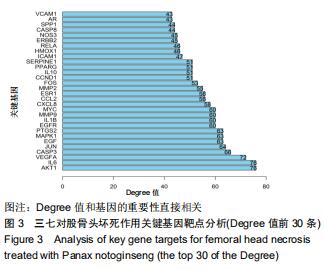
2.2 股骨头坏死相关“活性成分-靶点网络”构建和分析 通过GeneCards、OMIM数据库共筛选出1 612个基因与股骨头坏死相关。通过对三七靶点与股骨头坏死疾病发病机制靶点进行统计,并利用R软件绘制三七药物潜在靶点与股骨头坏死发病机制靶点韦恩图,见图1,共筛选出98个作用靶蛋白,其中包括丝氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶(AKT1)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)、胱天蛋白酶3(CASP3)、氨基末端激酶(JUN)、表皮细胞生长因子(EGF)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK1)、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶(PTGS2)、表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)等。运用cytoscape3.7.1将药物、药物成分以及疾病作用靶蛋白绘制成三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络关系,见图2,应用R软件绘制三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的PPI网络核心靶点柱状图,见图3,运用cytoscape3.7.1进行三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络的拓扑学分析,经插件CytoHubba分析网络拓扑学属性发现,该PPI网络中 ClusteringCoefficient为0.657,Betweenness为66.680,Radiality在2.146-2.792之间,Closeness在45.333-86之间,Degree最大值为76。研究发现,一个蛋白的Degree值和基因的重要性直接相关,也就是说具有高Degree的蛋白更倾向于是关键蛋白,在三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的拓扑学分析中,如丝氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶、白细胞介素6、血管内皮生长因子A、胱天蛋白酶3、氨基末端激酶、表皮细胞生长因子、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶、表皮生长因子受体、白细胞介素1β等蛋白Degree值在43-76之间,说明在三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络的拓扑学分析中起到关键蛋白作用。 "
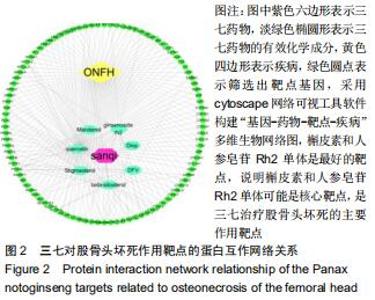
2.2 股骨头坏死相关“活性成分-靶点网络”构建和分析 通过GeneCards、OMIM数据库共筛选出1 612个基因与股骨头坏死相关。通过对三七靶点与股骨头坏死疾病发病机制靶点进行统计,并利用R软件绘制三七药物潜在靶点与股骨头坏死发病机制靶点韦恩图,见图1,共筛选出98个作用靶蛋白,其中包括丝氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶(AKT1)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)、胱天蛋白酶3(CASP3)、氨基末端激酶(JUN)、表皮细胞生长因子(EGF)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK1)、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶(PTGS2)、表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)等。运用cytoscape3.7.1将药物、药物成分以及疾病作用靶蛋白绘制成三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络关系,见图2,应用R软件绘制三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的PPI网络核心靶点柱状图,见图3,运用cytoscape3.7.1进行三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络的拓扑学分析,经插件CytoHubba分析网络拓扑学属性发现,该PPI网络中 ClusteringCoefficient为0.657,Betweenness为66.680,Radiality在2.146-2.792之间,Closeness在45.333-86之间,Degree最大值为76。研究发现,一个蛋白的Degree值和基因的重要性直接相关,也就是说具有高Degree的蛋白更倾向于是关键蛋白,在三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的拓扑学分析中,如丝氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶、白细胞介素6、血管内皮生长因子A、胱天蛋白酶3、氨基末端激酶、表皮细胞生长因子、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶、表皮生长因子受体、白细胞介素1β等蛋白Degree值在43-76之间,说明在三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络的拓扑学分析中起到关键蛋白作用。 "
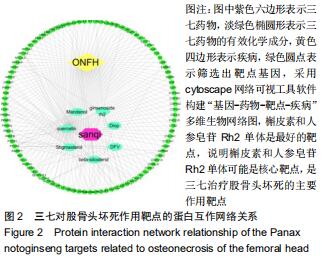
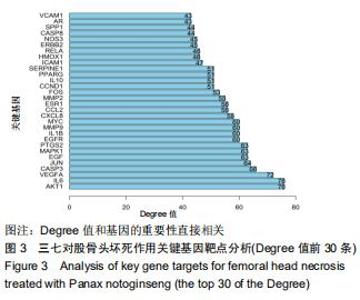
2.2 股骨头坏死相关“活性成分-靶点网络”构建和分析 通过GeneCards、OMIM数据库共筛选出1 612个基因与股骨头坏死相关。通过对三七靶点与股骨头坏死疾病发病机制靶点进行统计,并利用R软件绘制三七药物潜在靶点与股骨头坏死发病机制靶点韦恩图,见图1,共筛选出98个作用靶蛋白,其中包括丝氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶(AKT1)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)、胱天蛋白酶3(CASP3)、氨基末端激酶(JUN)、表皮细胞生长因子(EGF)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK1)、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶(PTGS2)、表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)等。运用cytoscape3.7.1将药物、药物成分以及疾病作用靶蛋白绘制成三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络关系,见图2,应用R软件绘制三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的PPI网络核心靶点柱状图,见图3,运用cytoscape3.7.1进行三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络的拓扑学分析,经插件CytoHubba分析网络拓扑学属性发现,该PPI网络中 ClusteringCoefficient为0.657,Betweenness为66.680,Radiality在2.146-2.792之间,Closeness在45.333-86之间,Degree最大值为76。研究发现,一个蛋白的Degree值和基因的重要性直接相关,也就是说具有高Degree的蛋白更倾向于是关键蛋白,在三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的拓扑学分析中,如丝氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶、白细胞介素6、血管内皮生长因子A、胱天蛋白酶3、氨基末端激酶、表皮细胞生长因子、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶、表皮生长因子受体、白细胞介素1β等蛋白Degree值在43-76之间,说明在三七对股骨头坏死作用靶点的蛋白互作网络的拓扑学分析中起到关键蛋白作用。 "
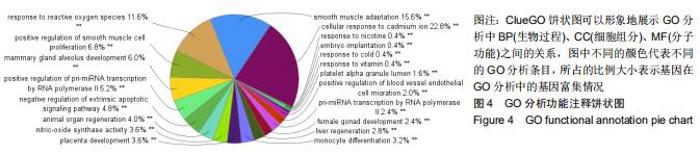
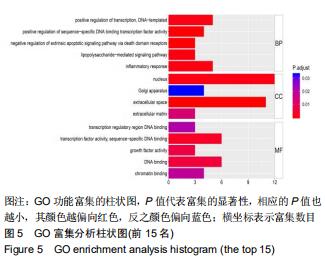
2.3 靶点生物学功能分析 将“图1”疾病基因-药物靶点导入Protein name进行注释,注释结果导入David数据库,在DAVID数据库Functional Annotation Tool的Upload中粘贴筛选出关键基因,以人类全基因组为背景和参照,分析结果设置阈值EASE< 0.05,Count≥4,FDR< 0.01,P < 0.05,获得显著性较高的生物过程和通路富集的结果,点击通路名称可以链接到KEGG数据库查看通路图及详情,分析得出12个生物过程(biological process,BP):包括炎症反应、免疫反应、脂多糖介导的信号通路、通过死亡域受体对外源性凋亡信号通路的负调节等;4个细胞组分(cellular component,CC):包括细胞外间隙、细胞外基质、细胞核、高尔基体;8个分子功能(molecular function,MF):包括转录因子活性、序列特异性DNA结合、生长因子活性等,见图4;经R语言运行后共得到105个功能,做前15个功能的GO功能富集的柱状图,P 值代表富集的显著性,相应的P 值也越小,其颜色越偏向红色,反之颜色偏向蓝色;横坐标表示富集数目,见图5。由结果可知GO功能富集后富集数目较多的有DNA结合转录激活活性、受体配体活性(receptor ligand activity)、细胞因子受体结合转录因子活性(cytokine receptor binding、transcription factor activity)、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ近端启动子序列特异性DNA结合(RNA polymerase II proximal promoter sequence- specific DNA binding)、DNA结合转录激活因子活性(DNA-binding transcription activator activity)、RNA聚合酶II特异性(RNA polymerase II-specific)、细胞因子活性(cytokine activity)等。 "
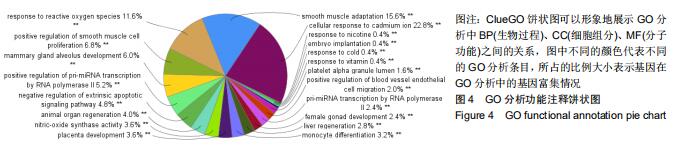
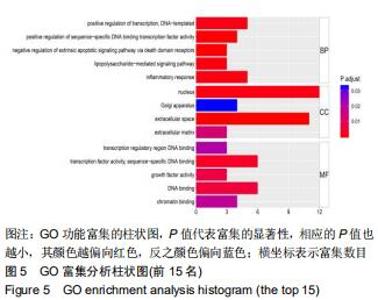
2.3 靶点生物学功能分析 将“图1”疾病基因-药物靶点导入Protein name进行注释,注释结果导入David数据库,在DAVID数据库Functional Annotation Tool的Upload中粘贴筛选出关键基因,以人类全基因组为背景和参照,分析结果设置阈值EASE< 0.05,Count≥4,FDR< 0.01,P < 0.05,获得显著性较高的生物过程和通路富集的结果,点击通路名称可以链接到KEGG数据库查看通路图及详情,分析得出12个生物过程(biological process,BP):包括炎症反应、免疫反应、脂多糖介导的信号通路、通过死亡域受体对外源性凋亡信号通路的负调节等;4个细胞组分(cellular component,CC):包括细胞外间隙、细胞外基质、细胞核、高尔基体;8个分子功能(molecular function,MF):包括转录因子活性、序列特异性DNA结合、生长因子活性等,见图4;经R语言运行后共得到105个功能,做前15个功能的GO功能富集的柱状图,P 值代表富集的显著性,相应的P 值也越小,其颜色越偏向红色,反之颜色偏向蓝色;横坐标表示富集数目,见图5。由结果可知GO功能富集后富集数目较多的有DNA结合转录激活活性、受体配体活性(receptor ligand activity)、细胞因子受体结合转录因子活性(cytokine receptor binding、transcription factor activity)、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ近端启动子序列特异性DNA结合(RNA polymerase II proximal promoter sequence- specific DNA binding)、DNA结合转录激活因子活性(DNA-binding transcription activator activity)、RNA聚合酶II特异性(RNA polymerase II-specific)、细胞因子活性(cytokine activity)等。 "
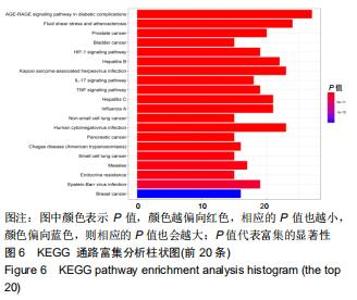
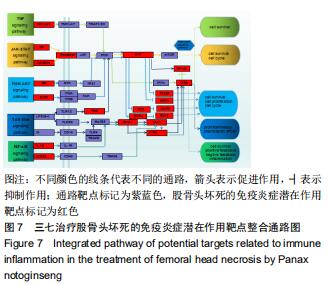
2.4 KEGG靶点通路分析 使用R语言程序将所得的98个共作靶点进行KEGG通路富集分析,运行R程序后得到76条信号转导通路,将靶点富集最多的前20的信号通路经R程序绘制KEGG通路富集分析柱状图,见图6,P 值代表富集的显著性,相应的P值也越小,其颜色越偏向红色,反之颜色偏向蓝色;富集分析结果显示,三七治疗股骨头坏死除涉及到糖尿病并发症中的糖化终末产物及其受体信号通路(AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications)、流体剪切力及动脉硬化(Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis)、卡波西肉瘤相关疱疹病毒感染(Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection)、甲型流感(Influenza A)、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路(PI3K-Akt signaling pathway)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路(MAPK signaling pathway)等通路比较明显外,另外还得到肿瘤坏死因子信号通路(TNF signaling pathway)、核转录因子κB信号通路(NF-κB signaling pathway)、单磷酸腺苷活化蛋白激酶信号通路(AMPK signaling pathway)、Toll样受体信号通路(Toll-like receptor signaling pathway)等与细胞免疫炎症有关的通路。通过上述提到的有关免疫炎症的信号通路图,筛选出基因靶点富集靠前的5条通路并进行整合绘制最终的通路图,见图7。图中以不同颜色箭头代表不同的通路,其中箭头表示促进作用,┤表示抑制作用。通路靶点标记为紫蓝色,三七治疗股骨头坏死的免疫炎症潜在作用靶点标记为红色。图中显示出了磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、核转录因子κB信号通路、Toll样受体信号通路,涉及21个三七抗免疫炎症靶点,占三七治疗股骨头坏死的免疫炎症潜蛋白靶点的40%,提示三七抗免疫炎症靶点分散于这5条信号通路中,通过调节其中的几个环节发挥作用,绝大多数靶点分散在多条通路中发挥作用,如丝氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶、核转录因子κB、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素1受体。 "
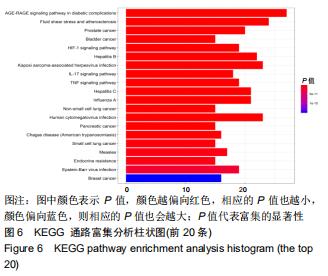
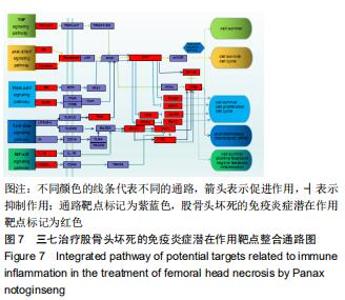
2.4 KEGG靶点通路分析 使用R语言程序将所得的98个共作靶点进行KEGG通路富集分析,运行R程序后得到76条信号转导通路,将靶点富集最多的前20的信号通路经R程序绘制KEGG通路富集分析柱状图,见图6,P 值代表富集的显著性,相应的P值也越小,其颜色越偏向红色,反之颜色偏向蓝色;富集分析结果显示,三七治疗股骨头坏死除涉及到糖尿病并发症中的糖化终末产物及其受体信号通路(AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications)、流体剪切力及动脉硬化(Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis)、卡波西肉瘤相关疱疹病毒感染(Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection)、甲型流感(Influenza A)、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路(PI3K-Akt signaling pathway)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路(MAPK signaling pathway)等通路比较明显外,另外还得到肿瘤坏死因子信号通路(TNF signaling pathway)、核转录因子κB信号通路(NF-κB signaling pathway)、单磷酸腺苷活化蛋白激酶信号通路(AMPK signaling pathway)、Toll样受体信号通路(Toll-like receptor signaling pathway)等与细胞免疫炎症有关的通路。通过上述提到的有关免疫炎症的信号通路图,筛选出基因靶点富集靠前的5条通路并进行整合绘制最终的通路图,见图7。图中以不同颜色箭头代表不同的通路,其中箭头表示促进作用,┤表示抑制作用。通路靶点标记为紫蓝色,三七治疗股骨头坏死的免疫炎症潜在作用靶点标记为红色。图中显示出了磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、核转录因子κB信号通路、Toll样受体信号通路,涉及21个三七抗免疫炎症靶点,占三七治疗股骨头坏死的免疫炎症潜蛋白靶点的40%,提示三七抗免疫炎症靶点分散于这5条信号通路中,通过调节其中的几个环节发挥作用,绝大多数靶点分散在多条通路中发挥作用,如丝氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶、核转录因子κB、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素1受体。 "
|
[1] WANG C, PENG J, LU S. Summary of the various treatments for osteonecrosis of the femoral head by mechanism: A review. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(3):700-706.
[2] MOYA-ANGELER J, GIANAKOS AL, VILLA JC, et al. Current concepts on osteonecrosis of the femoral head. World J Orthop. 2015;6(8): 590-601.
[3] LI W, YE Z, WANG W, et al. Clinical effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the treatment of femoral head necrosis : A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthopade. 2017;46(5):440-446.
[4] BOSCO G, VEZZANI G, MRAKIC SPOSTA S, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy ameliorates osteonecrosis in patients by modulating inflammation and oxidative stress. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2018; 33(1):1501-1505.
[5] SUN ZB, WANG JW, XIAO H, et al. Icariin may benefit the mesenchymal stem cells of patients with steroid-associated osteonecrosis by ABCB1-promoter demethylation: a preliminary study. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(1):187-197.
[6] VAN GIEZEN JJ, JANSEN JW. Correlation of in vitro and in vivo decreased fibrinolytic activity caused by dexamethasone. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;667:199-201.
[7] ZHANG C, ZOU YL, MA J, et al. Apoptosis associated with Wnt/β-catenin pathway leads to steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:132.
[8] MARKER DR, SEYLER TM, ULRICH SD, et al. Do modern techniques improve core decompression outcomes for hip osteonecrosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(5):1093-1103.
[9] LIU ZH, GUO WS, LI ZR, et al. Porous tantalum rods for treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(4): 8342-8352.
[10] CAO L, GUO C, CHEN J, et al. Free Vascularized Fibular Grafting Improves Vascularity Compared With Core Decompression in Femoral Head Osteonecrosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(9):2230-2240.
[11] LIGH CA, NELSON JA, FISCHER JP, et al. The Effectiveness of Free Vascularized Fibular Flaps in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head and Neck: A Systematic Review. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2017;33(3):163-172.
[12] LI R, LIN QX, LIANG XZ, et al. Stem cell therapy for treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head: From clinical applications to related basic research. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):291.
[13] 左荣台,关俊杰,康庆林.激素性股骨头坏死治疗研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2019,40(3):160-164.
[14] 梅丹.个性化心理护理对人工髋关节置换围手术期患者心理状态及并发症的影响研究[J].中国医药指南, 2017,15(26):207-208.
[15] 刘敬锋,冯建民.多孔钽金属棒治疗早期股骨头无菌性坏死:应用与问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(52):9062-9068.
[16] 费腾,阎作勤.激素性股骨头坏死发病机制的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2011,5(4):504-508.
[17] 清·黄元御.《玉楸药解》释义[M].太原:山西科学技术出版社,2009.
[18] 陈卫衡.股骨头坏死“痰瘀同治”的理论基础[J].江苏中医药,2008,40(5): 3-4.
[19] 吴惠斌,史宝明.三七总皂苷对兔酒精性股骨头坏死模型组织形态学的影响[J].甘肃中医学院学报,2012,29(6):4-7.
[20] 韩杰,陈跃平,莫坚,等.三七总皂苷干预激素性股骨头缺血坏死模型兔的超微结构评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(7):1035-1039.
[21] 陈杰,张堃,孔令俊,等.三七总皂苷通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路减轻家兔股骨头坏死[J].中药药理与临床,2019,35(4):95-99.
[22] PAINE MF, SHEN DD, KUNZE KL, et al. First-pass metabolism of midazolam by the human intestine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1996;60(1): 14-24.
[23] WALTERS WP, MURCKO MA. Prediction of 'drug-likeness'. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54(3):255-271.
[24] 姚雨.基于深度学习网络的剪接位点及蛋白质相互作用预测方法研究[D].合肥:安徽大学,2019.
[25] 吴毓苗.三七不同生育期皂苷积累状况研究[D].昆明:云南中医学院,2018.
[26] 林飞,王阶,郭丽丽,等.《中华人民共和国药典》收载治疗冠心病心绞痛中成药配伍规律分析[J].中医杂志, 2013,54(18):1596-1599.
[27] 曹满,张洁,赵阳,等.人参皂苷Rh2及其衍生物的研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2012,14(6):2205-2211.
[28] 许丹,律颖,朱小语,等.小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞(RAW264.7)的培养及其在诱导破骨细胞中的应用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2016,22(10): 1355-1360.
[29] 毕文岩,付本懂,宋舟,等.人参皂苷Rh2硫酸化衍生物抗炎作用的分子机制[J].中国兽医学报, 2012, 32(1):115-119.
[30] 吴永祥,吴丽萍,胡长玉,等.桑白皮中sanggenon B对脂多糖诱导RAW264.7细胞炎症反应的影响[J].天然产物研究与开发, 2018, 30(7):1132-1137.
[31] MILADPOUR B, RASTI M, OWJI AA, et al. Quercetin potentiates transdifferentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into the beta cells in vitro. J Endocrinol Invest. 2017;40(5):513-521.
[32] FARR JN, XU M, WEIVODA MM, et al. Targeting cellular senescence prevents age-related bone loss in mice. Nat Med. 2017;23(9): 1072-1079.
[33] YUAN Z, MIN J, ZHAO Y, et al. Quercetin rescued TNF-alpha-induced impairments in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and improved osteoporosis in rats. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(12):4313-4321.
[34] PANG XG, CONG Y, BAO NR, et al. Quercetin Stimulates Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation through an Estrogen Receptor-Mediated Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:4178021.
[35] 丁玉文.三七总皂苷对A549细胞上皮间质转化的干预作用及对P38MAPK信号通路的影响[D].郑州:河南中医药大学, 2017.
[36] 宋奕,丁道芳,李玲慧,等.细胞凋亡在激素性股骨头坏死机制中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21 (21) :2163-2165.
[37] 牛增强.三七总皂甙对急性胰腺炎大鼠血清炎性因子TNF-α和IL-1β的影响[J].中外医疗,2008, 27(31):83.
[38] YANG T, MARTIN P, FOGARTY B, et al. Exosome delivered anticancer drugs across the blood-brain barrier for brain cancer therapy in Danio rerio. Pharm Res. 2015;32(6):2003-2014.
[39] ATRETKHANY KN, DRUTSKAYA MS, NEDOSPASOV SA, et al. Chemokines, cytokines and exosomes help tumors to shape inflammatory microenvironment. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;168:98-112.
[40] LEE DK, SONG SU. Immunomodulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic applications. Cell Immunol. 2018;326: 68-76.
[41] ADAPALA NS, YAMAGUCHI R, PHIPPS M, et al. Necrotic Bone Stimulates Proinflammatory Responses in Macrophages through the Activation of Toll-Like Receptor 4. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(11): 2987-2999.
[42] YUAN L, LI W, TIAN ZB, et al. Predictive role of cytokines IL-10, IL-12 and TNF-α gene polymorphisms for the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in the Chinese Han population. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017;63(9):144-149. |
| [1] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [2] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [5] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [6] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [7] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [8] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [9] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [10] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [11] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [12] | Chen Feng, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Liao Jianzhao, Li Jiajun, Song Shilei, Lai Yu. Molecular mechanism of anhydroicaritin in the treatment of osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3704-3710. |
| [13] | Zhang Haitao, Chen Jinlun, Zhu Xingyang, Zeng Huiliang, Li Jie, Sun Xiaobo, Qi Xinyu, Zeng Jianchun, Zeng Yirong. Effect and molecular mechanism of Honeysuckle-Rhizoma coptidis in the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection based on molecular docking and network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3360-3367. |
| [14] | Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi. Potential molecular mechanism of Wuling powder in treating osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3185-3193. |
| [15] | Zhong Yuanming, He Bingkun, Wu Zhuotan, Wu Sixian, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng. An exploration on the mechanism of Shaoyao Gancao Decoction in treating early pain of lumbar disc herniation based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3194-3201. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||