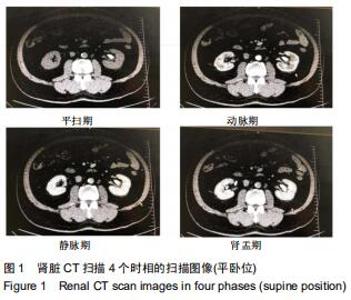
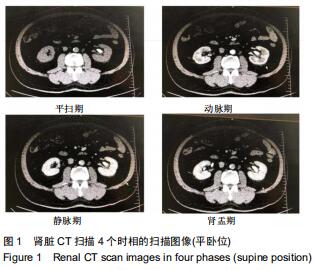
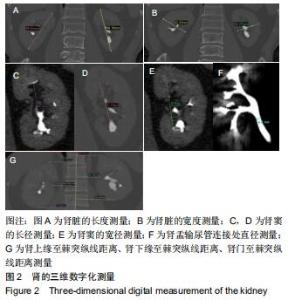
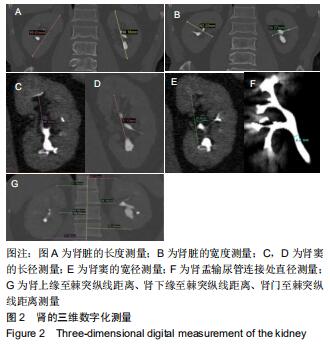
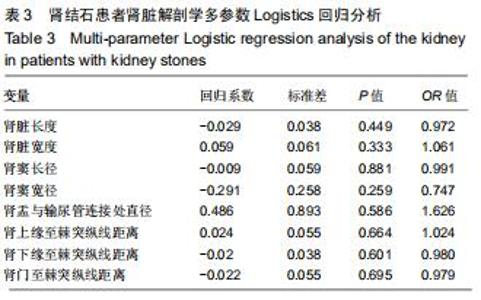
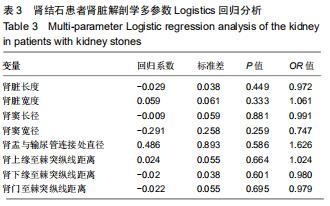
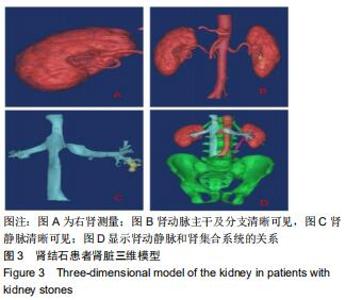
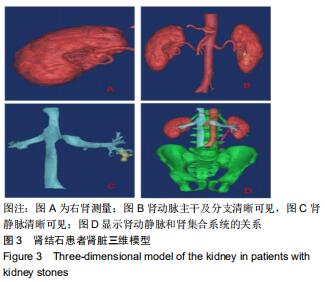
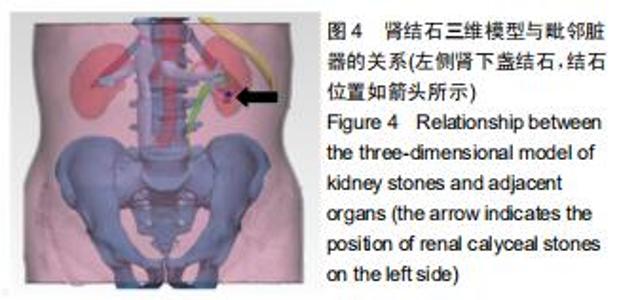
|
[1] EVAN AP, WORCESTER EM, COE FL, et al. Mechanisms of human kidney stone formation. Urolithiasis.2015;43(1):19-32.
[2] WORCESTER EM, COE FL. Clinical practice. Calcium kidney stones. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(10):954-963.
[3] 黄冠森,郑胜眉,蔡丽莉,等.达州宣汉县肾结石流行病学调查[J].生物技术世界,2016(1):207-208.
[4] 陈楠.重视肾结石的诊断及内科治疗[J].中华肾脏病杂志, 2004,20(5): 380-381.
[5] 张金,范海涛,张明,等.不完全性铸型肾结石18例临床分析[J].中国实验诊断学,2016,20(2):310-312.
[6] 颜昌智,唐猛,潘铁军,等.铸型肾结石伴复杂基础疾病1例报告[J].现代泌尿外科杂志,2017,22(11):90-91.
[7] 汤宗源,江顺建,李江,等.广西瑶族成年人肾结石流行病学调查[J].中国全科医学,2015(14):1691-1694.
[8] 陈厚传,杨正荣,刘学斌.农村地区肾结石发病的相关因素调查[J].中外健康文摘,2014(22):51-52.
[9] 金锡御,俞天麟.泌尿外科手术学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2004:97.
[10] 段中阳,李昕.肾结石形成解剖学因素研究[J].创伤与急危重病医学, 2018,6(1):12-17.
[11] 王猛,孔繁之.医学图像三维可视化技术及其新进展[J].医学影像学杂志, 2015,25(6):1095-1097.
[12] 袁小翠,吴禄慎,陈华伟.基于Otsu方法的钢轨图像分割[J].光学精密工程, 2016,24(7):1772-1781.
[13] MA J, SON JB, HAZLE JD. An improved region growing algorithm for phase correction in MRI.Magn Reson Med. 2016;76(2):519-529.
[14] ALELIGN T, PETROS B. Kidney Stone Disease: An Update on Current Concepts. Adv Urol. 2018;2018:3068365.
[15] PALSSON R, INDRIDASON OS, Edvardsson VO, et al. Genetics of common complex kidney stone disease: insights from genome-wide association studies. Urolithiasis. 2019;47(1):11-21.
[16] ASIAN GE, JEMIELITA T, GOLDFARB DS, et al. Oral Antibiotic Exposure and Kidney Stone Disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(6):1731-1740.
[17] AL-KAZWINI AT, AL-ATIF MS, ABU-MWEIS SS, et al. The relationship between kidney stones and dietary habits. Res Rep Urol. 2019;11: 201-214.
[18] PEERAPEN P, THONGBOONKERD V. Protective Cellular Mechanism of Estrogen Against Kidney Stone Formation: A Proteomics Approach and Functional Validation. Proteomics.2019;19(3):1-15.
[19] 亓鹏,胡亦新,曾丹,等.老年人肾脏相对长度的影响因素及临床意义[J].中国综合临床,2006, 22(1):46-48.
[20] 钟婷婷,刘艳君,张云飞,等.不同体位及部位对实时剪切波弹性成像技术对正常肾脏的影响[J].中国超声医学杂志,2016,32(10):911-913.
[21] 李刚.肾脏皮质厚度与年龄的关系[J].实用放射学杂志, 2009,25(6): 908-910.
[22] 王娜,刘荣波,孔维芳,等.成人活体肾脏CT/MRI测量指标分析及影响因素探讨[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2004,4(11):771-777.
[23] ELBAHNASY AM, SHALHAV AL, HOENIG DM, et al. Lower caliceal stone clearance after shock wave lithotripsy or ureteroscopy: the impact of lower pole radiographic anatomy. J Urol. 1998;159(3):676-682.
[24] VERMA A, TOMAR V, YADAV S. Complex multiple renal calculi: stone distribution, pelvicalyceal anatomy and site of puncture as predictors of PCNL outcome. Springerplus.2016;5(1):1356-1361.
[25] GANDHI KR, CHAVAN S. Revisiting the morphology of pelvicalyceal system in human cadaveric kidneys with a systematic review of literature. Asian J Urol. 2019;6(3):249-255.
|