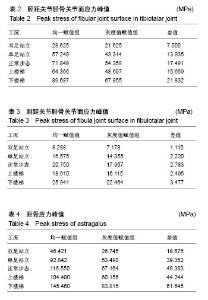
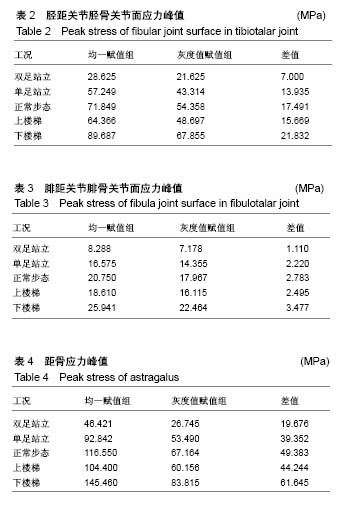
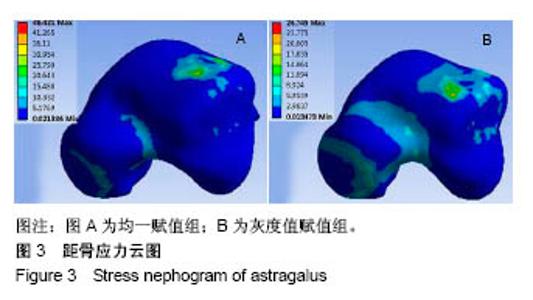
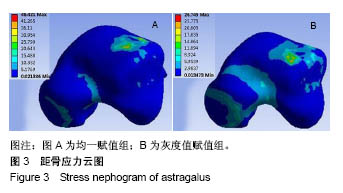
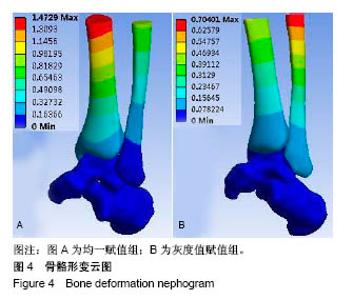
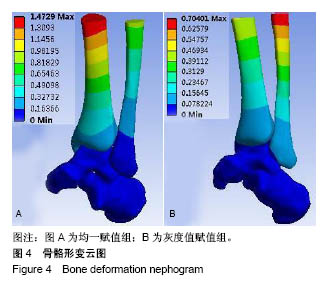
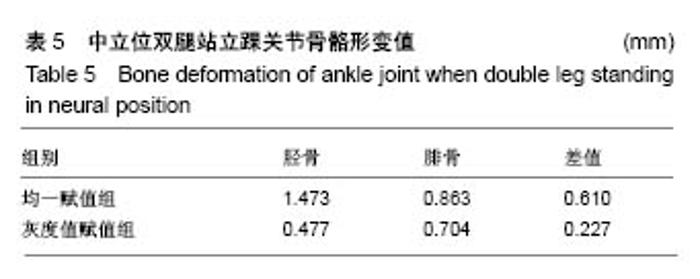
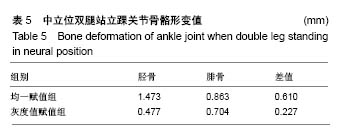
| [1]马信龙. 踝关节骨折的损伤机制[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2013, 33(4): 429-432.[2]关国平,孟强,牛文鑫,等. 踝关节扭伤防护及其康复研究进展[J]. 医用生物力学, 2016, 31(1):78-82.[3]曾茂兰,王静. 踝关节运动损伤应急处理及其康复治疗[J]. 甘肃医药, 2017, 36(1):25-26.[4]张琳琳. 人体上肢生物力学建模和典型运动的生物力学研究[D]. 上海:上海交通大学, 2009.[5]唐刚. 人体典型运动生物力学仿真分析[D].上海:上海交通大学, 2011.[6]王博文. 标本含湿率及加载方式对骨微观力学特性测试的影响研究[D].西安:第四军医大学, 2014.[7]郑海峰. 髂骨新月形骨折伴骶髂关节脱位两种内固定方法的生物力学研究[D].大连:大连医科大学, 2016.[8]何旅洋,张志强,郑百林. 外骨骼框架生物力学设计及强度分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2014,29(6):504-510.[9]尹峰,王晓东,梁炜,等. 建立锁骨个性化锁定接骨板模型及有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(35):5244-5249.[10]Zhou EC, Tang P, Zhu CY, et al. Finite element analysis on the effect of lateral wedge insole intervention on the contact characteristics of the subtalar joint. Chin J Orthop Traumatol. 2017;30(1):38.[11]Wang X, Sanyal A, Cawthon PM, et al. Prediction of new clinical vertebral fractures in elderly men using finite element analysis of CT scans. J Bone Mineral Res. 2012;27(4):808-816.[12]欧阳汉斌,谢普生,邓羽平,等. 基于CT灰度赋值的有限元模型建立及其在截骨矫形中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(7): 979-983.[13]Dall'Ara E, Luisier B, Schmidt R, et al. A nonlinear QCT-based finite element model validation study for the human femur tested in two configurations in vitro. Bone. 2013;52(1):27-38.[14]李瑜,邓双城,杜程,等. 中立位踝关节生物力学有限元仿真[J]. 北京石油化工学院学报, 2017,25(4):51-58.[15]张宏宁,朱永展,李雪,等. 踝关节骨折中外踝移位对胫距关节接触影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2017, 19(9):769-774.[16]郭国新,郭继涛,李伟,等. 基于有限元模型的踝关节生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3056-3060.[17]刘清华,马建兵,姚建锋. 不同载荷对正常踝关节影响的有限元研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013,15(8):704-708.[18]李瑜,邓双城,杜程,等.中立位踝关节生物力学有限元仿真中立位踝关节生物力学有限元仿真[J].北京石油化工学院学报, 2017,25(4): 51-58.[19]Chen G, Wu FY, Liu ZC, et al. Comparisons of node-based and element-based approaches of assigning bone material properties onto subject-specific finite element models. Med Eng Phys. 2015; 37(8):808.[20]徐志才,胡广洪,黄振宇,等. 胫骨模型对膝关节有限元分析结果影响的探讨[J]. 中国数字医学,2014,9(4):69-72.[21]谢亮文. 不同属性建模方法对股骨近端有限元分析影响的研究[D]. 福州:福建医科大学, 2015.[22]Rho JY, Hobatho MC, Ashman RB. Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys. 1995;17(5):347-355. [23]秦林林,马海波,张卫,等. 中国北方汉族健康人骨密度正常值[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2002, 8(2):110-111.[24]Cheung JT, An KN, Zhang M. Consequences of partial and total plantar fascia release: a finite element study. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(2):125.[25]Simon SR, Paul IL, Mansour J, et al. Peak dynamic force in human gait. J Biomech. 1981;14(12):817,821-819,822.[26]Stacoff A, Diezi C, Luder G, et al. Ground reaction forces on stairs: effects of stair nclination and age. Gait Posture. 2005;21(1):24.[27]Anderson DD, Goldsworthy JK, Li W, et al. Physical validation of a patient-specific contact finite element model of the ankle. J Biomech. 2007; 40(8):1662-1669.[28]唐勇涛,魏思奇,程刚,等. 基于两种不同建模方式的胫骨有限元对比分析[J]. 中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2016, 8(1):26-32.[29]尚禹,彭亮,刘加成,等. 均匀材料和基于CT灰度值材料的股骨、胫骨有限元分析[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2008, 27(5):722-727. |