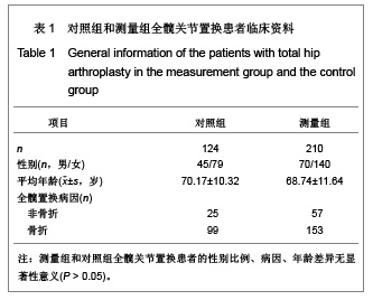
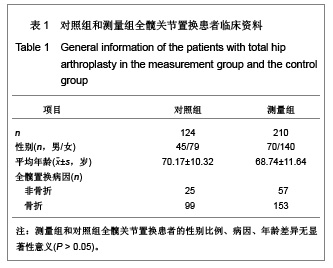
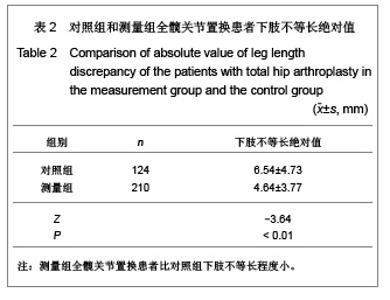
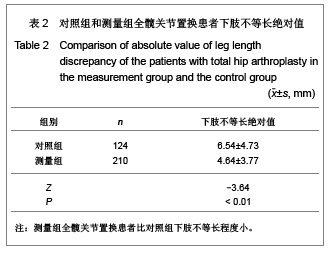
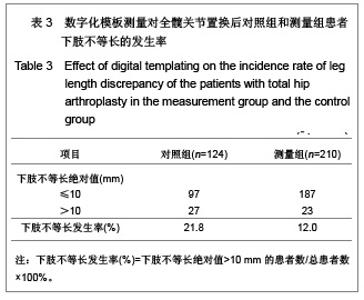
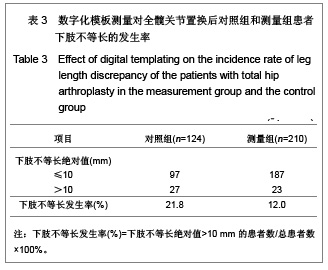
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (9): 1527-1534.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.09.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Digital templating alleviates leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty
Zhang Xue-jun, Wang Chen
- Department of Orthopedics, Zhongda Hospital of Southeast University, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2012-11-15Revised:2012-12-26Online:2013-02-26Published:2013-02-26 -
Contact:Wang Chen, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Zhongda Hospital Southeast University, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China wangchen@medmail.com.cn -
About author:Zhang Xue-jun★, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Zhongda Hospital Southeast University, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China zxjseu@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Xue-jun, Wang Chen. Digital templating alleviates leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1527-1534.
share this article
| [1] Liu SS, Della Valle AG, Besculides MC, et al. Trends in mortality, complications, and demographics for primary hip arthroplasty in the United States. Int Orthop. 2009;33(3): 643-651. [2] Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785.[3] Li GW, Dong MY, Zhang HF, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(22): 4061-4064. 李国威,董明岩,张海飞,等.全髋关节置换与双极人工股骨头置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(22):4061-4064.[4] Cao WY. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2006. 曹卫友.人工髋关节置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折的临床应用[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2006.[5] Sun LZ. Zhongguo Gu yu GUanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2008; 23(10):806-808. 孙立众.全髋关节置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折及其并发症分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2008,23(10):806-808.[6] Meermans G, Malik A, Witt J, et al. Preoperative radiographic assessment of limb-length discrepancy in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(6):1677- 1682. [7] Jin J, Chen B, Xu HG, et al. Shiyong Guke Zazhi. 2005;11(5): 398-401. 金今,陈宾,徐宏光,等.人工全髋关节置换术术前的模板测量与术后评估[J].实用骨科杂志, 2005,11(5):398-401.[8] Nie M. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2009. 聂茂.全髋关节置换术前模板测量的准确性分析[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2009.[9] Bai YJ, Sun WC, Li XL. Zhongguo Shangcan Yixue. 2010(6): 54-55. 白玉江,孙文才,李晓龙.模板测量在全髋关节置换术中的意义[J].中国伤残医学, 2010(6):54-55.[10] Clark CR, Huddleston HD, Schoch EP 3rd, et al. Leg-length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(1):38-45.[11] Konyves A, Bannister GC. The importance of leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(2):155-157.[12] Manzotti A, Cerveri P, De Momi E, et al. Does computer-assisted surgery benefit leg length restoration in total hip replacement? Navigation versus conventional freehand. Int Orthop. 2011;35(1):19-24. [13] Herman KA, Highcock AJ, Moorehead JD, et al. A comparison of leg length and femoral offset discrepancies in hip resurfacing, large head metal-on- metal and conventional total hip replacement: a case series. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6: 65. [14] McWilliams AB, Grainger AJ, O'Connor PJ, et al. A review of symptomatic leg length inequality following total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2013;23(1):6-14. [15] McWilliams AB, Grainger AJ, O'Connor PJ, et al. Assessing reproducibility for radiographic measurement of leg length inequality after total hip replacement. Hip Int. 2012;22(5): 539-544. [16] Röder C, Vogel R, Burri L, et al. Total hip arthroplasty: leg length inequality impairs functional outcomes and patient satisfaction. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:95. [17] Alazzawi S, Douglas SL, Haddad FS. A novel intra-operative technique to achieve accurate leg length and femoral offset during total hip replacement. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2012; 94(4):281-282. [18] Barbier O, Ollat D, Versier G. Interest of an intraoperative limb-length and offset measurement device in total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(4): 398-404. [19] Ito H, Tanino H, Yamanaka Y, et al. Long-term results of conventional varus half-wedge proximal femoral osteotomy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(3):308-314.[20] Chen GM, Ren WJ, Wang MJ, et al. Shiyong Zhenduan yu Zhiliao Zazhi. 2006;20(10):732-733. 陈明国,任文杰,王明君,等.人工髋关节置换术下肢不等长的预防处理[J].实用诊断与治疗杂志,2006,20(10):732-733.[21] Xu J, Liao GY, Bhandari PR, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(9): 1607-1610. 许杰,梁国彦,Prakash-Raj Bhandari,等.髋关节置换后双下肢不等长对功能影响的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(9):1607-1610.[22] Ren MA, Xu GH, Wang LH, et al. Zhejiang Chuangshang Waike. 2012;17(5):577-579. 任明安,徐国红,王利宏,等.术中测量股骨假体肩部与大转子顶点垂直高度预防全髋关节置换术后下肢不等长[J].浙江创伤外科,2012,17(5):577-579.[23] Sathappan SS, Ginat D, Patel V, et al. Effect of anesthesia type on limb length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(2):203-209. [24] Plaass C, Clauss M, Ochsner PE, et al. Influence of leg length discrepancy on clinical results after total hip arthroplasty-a prospective clinical trial. Hip Int. 2011;21(4):441-449. [25] Wylde V, Whitehouse SL, Taylor AH, et al. Prevalence and functional impact of patient-perceived leg length discrepancy after hip replacement. Int Orthop. 2009 ;33(4): 905-909. [26] Weng WJ, Wang F, Zhang HL, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2009; 22(12):906-908. 翁文杰,王锋,张海林,等.全髋关节置换术后双下肢不等长对功能和满意度影响的研究[J].中国骨伤,2009,22(12):906-908.[27] Rubash HE, Parvataneni HK. The pants too short, the leg too long: leg length inequality after THA. Orthopedics. 2007;30(9): 764-765.[28] Wu B, Yang L. Chongqing Yixue. 2006;35(12):1094-1096. 吴波,杨柳.全髋关节置换术模板测量法术前选择股骨假体型号的准确性分析[J].重庆医学, 2006,35(12):1094-1096.[29] Yang L. Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepo Xue Zazhi. 2006;24(2): 221-223. 杨磊.全髋关节置换术肢体不等长的原因和预防[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2006,24(2):221-223.[30] Zhang P, Huang Y, Wan LP, et al. Shandong Yiyao. 2008; 48(17):47-48. 张鹏,黄勇,万连平,等.数字模板测量法在髋关节置换术术前设计中的应用[J].山东医药, 2008,48(17):47-48.[31] Zhang XH, Yu ZS, Zhang YK, et al. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2008;23(10):809-811. 张星火,于振山,张亚奎,等.全髋关节置换术下肢长度均衡方法的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(10):809-811.[32] Knight JL, Atwater RD. Preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Quantitating its utility and precision. J Arthroplasty. 1992;7 Suppl:403-409.[33] Carter LW, Stovall DO, Young TR. Determination of accuracy of preoperative templating of noncemented femoral prostheses. J Arthroplasty. 1995;10(4):507-513.[34] Eggli S, Pisan M, Müller ME. The value of preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80(3):382-390.[35] González Della Valle A, Slullitel G, Piccaluga F, et al. The precision and usefulness of preoperative planning for cemented and hybrid primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(1):51-58.[36] Li SZ, Liu YP, Yuan F, et al. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2012;27(6):485-487. 李山珠,刘玉平,袁锋,等.人工全髋关节置换双下肢不等长的预防策略[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(6):485-487.[37] Davila JA, Kransdorf MJ, Duffy GP. Surgical planning of total hip arthroplasty: accuracy of computer-assisted EndoMap software in predicting component size. Skeletal Radiol. 2006; 35(6):390-393. [38] Bertz A, Indrekvam K, Ahmed M, et al. Validity and reliability of preoperative templating in total hip arthroplasty using a digital templating system. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41(10): 1245-1249. [39] Huang H. Taiyuan: Shanxi Medical University, 2008. 黄海.躯体X线测量系统在人工髋关节置换术后下肢长度测量中的应用[D].太原:山西医科大学,2008.[40] Zhao C, Jin LB, Yang QS. Guji Guke Xue Zazhi. 2006;27(4): 205-207. 赵晨,金礼斌,杨泉森.全髋关节置换术下肢长度测量及术后不等长处理[J].国际骨科学杂志,2006,27(4):205-207.[41] Zhang ZH, Liu YT. Zhongguo ZUzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(43):8465-8468. 张振华,刘永涛.髋关节置换股骨偏心距和下肢长度重建方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(43):8465-8468.[42] Zhou CS, Du YL, Xu WY, et al. Shengwu Guke Cailiao yu Linchuang Yanjiu. 2005;2(4):12-15. 周才胜,杜远立,许维亚,等.全髋关节置换术均衡双下肢长度的探讨[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2005,2(4):12-15.[43] Li LX, Zhou B, Wei Z, et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepo Xue Zazhi. 2011(4):452-455. 李利昕,周兵,魏振,等.股骨偏心距重建对人工全髋关节置换术后功能的影响[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2011(4):452-455.[44] Mao BY, Ying ZZ, Hu YT. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2002;9(6):550-553. 毛宾尧,应忠追,胡裕桐.人工全髋关节置换术下肢不等长的预防和处理[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2002,9(6):550-553.[45] Lin Z, Qin J, Wang XL, et al. Guangzhou Yiyao. 2012; 43(2): 3-5. 林竹,覃健,王新亮,等.膝关节表面置换术前高精度数字化模板测量的临床应用[J].广州医药,2012,43(2):3-5.[46] Jassim SS, Ingham C, Keeling M, et al. Digital templating facilitates accurate leg length correction in total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Belg. 2012;78(3):344-349. [47] Hsu AR, Kim JD, Bhatia S, et al. Effect of training level on accuracy of digital templating in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2012;35(2):e179-183. [48] Hossain M, Lewis J, Sinha A. Digital pre-operative templating is more accurate in total hip replacement compared to analogue templating. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2008; 18(8):577-580.[49] Lewis J, Hossain M, Mustafa A, et al. Comparison of digital and plain radiography preoperative templating in total knee arthroplasty. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2008;18(5): 357-360.[50] Specht LM, Levitz S, Iorio R, et al. A comparison of acetate and digital templating for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;464:179-183.[51] Iorio R, Siegel J, Specht LM, et al. A comparison of acetate vs digital templating for preoperative planning of total hip arthroplasty: is digital templating accurate and safe? J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(2):175-179.[52] The B, Verdonschot N, van Horn JR, et al. Digital versus analogue preoperative planning of total hip arthroplasties: a randomized clinical trial of 210 total hip arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(6):866-870. |
| [1] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [2] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [3] | Kong Lingbao, Lü Xin. Effect of implant selection and approach on support in the operation of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 942-947. |
| [4] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [5] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [6] | Liu Gang, Zhang Baolu, Shi Jie, Bao Dingsu, Zeng Shengqiang, Deng Kai, Liu Yang, Wang Guoyou, Fu Shijie. Difference between proximal humeral locking plate and cannulated screw fixation in the treatment of Mutch type II fracture of greater tuberosity of humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2863-2868. |
| [7] | Ji Qi, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Problems and trends of technique and clinical application of metallic biomaterials prepared by three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2597-2604. |
| [8] | Liu Pengran, Jiao Rui, Tao Jin, Chen Hui, Dai Jihang, Yan Lianqi. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty with different interface prostheses in the treatment of elderly hip diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2347-2351. |
| [9] | Liu Zige, Liu Xinrui, Li Yan, Song Guorui, Zhang Chen, Chen Desheng. In vitro experiment of tetrandrine on the model of osteolysis induced by wear particles around the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2358-2363. |
| [10] | Li Yonghe, Wang Xiankang, Meng Yu, Liu Lu, Zhang Chunqiu, Ye Jinduo . Mechanical analysis on the position difference of short-stemmed prosthesis in hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2394-2399. |
| [11] | Zhou Chen, Xing Wenhua. Application advantages of three-dimensional printing technology and finite element analysis in scoliosis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1898-1903. |
| [12] | Milalimmu•Multiza, Zhao Wei, Varesjiang•Nyyaz, Yuan Hong, Wang Li. Direct anterior approach versus anterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: comparison of early postoperative patient’s perception [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1318-1323. |
| [13] | Zhou Qi, Gao Yi, Wei Kang, Li Jun, Xu Jianda, Jiang Yang, Qu Yuxing. Total knee arthroplasty for rheumatoid arthritis: knee function and biochemical index changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1337-1341. |
| [14] | Huang Hetao, Pan Jianke, Yang Weiyi, Zeng Lingfeng, Liang Guihong, Liu Jun. Systematic evaluation of the efficacy and safety of collum femoris preserving prosthesis in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 962-967. |
| [15] | Wu Yeke, Gao Ranran, Zuo Yuling, Yu Jianfeng, Zhao Lixing, Nie Wenhan, Zheng Tao, Ai Huangping, Yan Hang. Factors affecting the clinical success rate of miniscrew implants for orthodontic treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 538-543. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||