Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (24): 3803-3807.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2738
Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification of the hot sub-fields of tissue engineering and technological strength assessment based on patent analysis
Zhang Ting, Chen Juan, Lu Yan, Ouyang Zhaolian, Chi Hui
- Institute of Medical Information/Medical Library, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100020, China
-
Received:2019-12-04Revised:2019-12-06Accepted:2020-01-17Online:2020-08-28Published:2020-08-13 -
Contact:Ouyang Zhaolian, Associate Researcher, Institute of Medical Information/Medical Library, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100020, China -
About author:Zhang Ting, PhD, Associate Researcher, Master supervisor, Institute of Medical Information/Medical Library, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100020, China -
Supported by:the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. 2017PT63006; the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, No. 2016-I2M-2-004; the National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. 2016YFC0104805
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Ting, Chen Juan, Lu Yan, Ouyang Zhaolian, Chi Hui. Identification of the hot sub-fields of tissue engineering and technological strength assessment based on patent analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3803-3807.
share this article
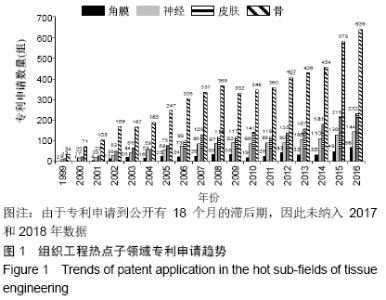
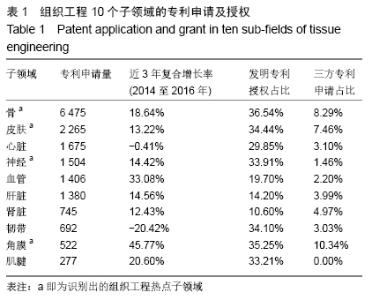
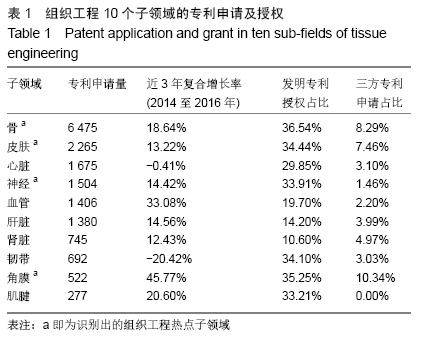
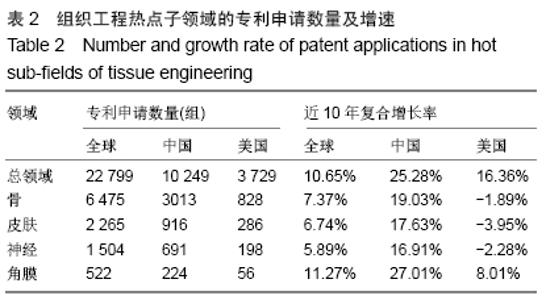
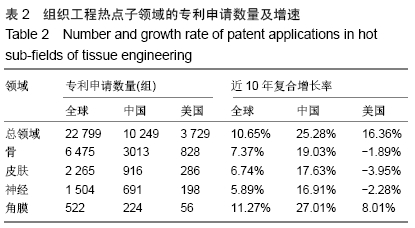
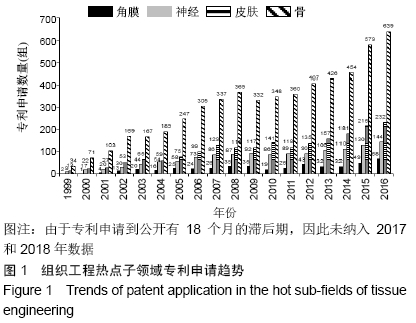
基于专利分析,借鉴既往研究工作中热点子领域、重点领域等的识别方法[9,11,16,19-20],对10个子领域的专利申请量、发明专利授权量、三方专利申请量进行了分析,结合专利申请近3年复合增长率(2014至2016年)、发明专利授权占比、三方专利申请占比3个角度的分析结果以此识别热点子领域。专利申请量的年复合增长率可以反映一个领域的技术增长潜力,近3年复合增长率能反映连续3年的增长情况,体现出持续发展态势[12,21-22]。并不是每个专利申请都能授权,尤其是发明专利,审查特别严格,发明专利的总体授权率还不到一半[23]。发明专利对技术的要求高,更加反映技术实力。发明专利授权占比是技术创新力的重要指标[24],一个领域的发明专利授权量越多则技术创新力越强。此次研究的三方专利(Triadic patent families)引用经济合作与发展组织(Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development,OECD)的定义,即同时向美国专利及商标局(United States Patent and Trademark Office,USPTO)、欧洲专利局(European Patent Office,EPO)和日本专利局(Japan Patent Office,JPO)均提出申请的同一组专利[25-26]。三方专利拥有量的规模可以反映一个领域的技术发明水平以及国际竞争力[27]。 因此,此次研究选择专利申请量的近3年复合增长率(2014至2016年)、发明专利授权占比、三方专利申请占比3个指标来识别组织工程热点子领域。专利申请量的近3年复合增长率为正值的表明该领域呈现持续增长态势,骨、皮肤、神经、血管、肝脏、肾脏、角膜、肌腱8个子领域的近3年复合增长率均为正值,表明这8个子领域专利申请量持续增长,技术开发持续活跃。计算10个子领域发明专利授权占比的平均值(28.18%),其中高于平均值的子领域有7个,分别是骨、皮肤、心脏、神经、韧带、角膜、肌腱,表明这7个领域技术创新力相对较高。一个领域有三方专利申请则有较高的技术水平和国际竞争力,除了肌腱组织工程,其他9个子领域均有三方专利申请,表明这9个子领域具有较强的国际竞争力。此次研究选择同时满足3个条件(专利申请量的近3年复合增长率为正值、发明专利授权占比高于10个子领域平均值、三方专利申请占比大于1%)的子领域为组织工程的热点子领域,热点子领域具有技术创新持续活跃、技术创新力强及国际竞争力较高的特点,共识别出4个热点子领域,分别是骨、皮肤、神经、角膜。 2.2 组织工程热点子领域的技术开发实力研究 2.2.1 专利申请趋势 专利是技术开发重要的成果表现形式,专利申请是为了有效保护发明创造成果,独占市场[27]。专利申请量是指专利机构受理技术发明申请专利的数量,反映技术发展活动是否活跃,以及发明人是否有谋求专利保护的积极性。专利申请数量越多,表示相关领域的创新能力越高,越有活力[27-28]。通过对骨、皮肤、神经、角膜组织工程领域的专利分析,可以揭示4个热点子领域的技术规模及增速。 骨、皮肤、神经、角膜组织工程领域专利申请数量和增速见图1和表2。4个热点子领域的技术开发规模各具特点,骨组织工程领域专利申请数量最多(6 475组),皮肤(2 265组)和神经(1 504组)组织工程领域规模相对有限,角膜组织工程专利申请数量最少(522组)。骨(7.37%)、皮肤(6.74%)、神经(5.89%)、角膜(11.27%)4个热点子领域的全球专利申请数量均呈现增长趋势,且角膜组织工程领域的增速高于总领域增速(10.65%)。骨组织工程创新活动最为活跃;角膜组织工程虽然规模最小,但增速最快。中国在4个热点子领域的专利申请数量和增速均远超过美国,且增速远高于全球平均水平,美国除了角膜组织工程领域,其他3个子领域呈现负增长。 "
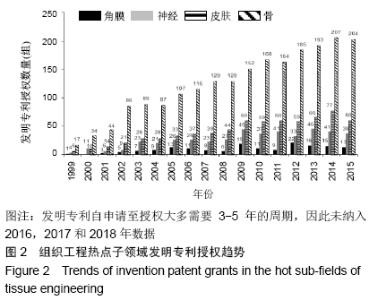
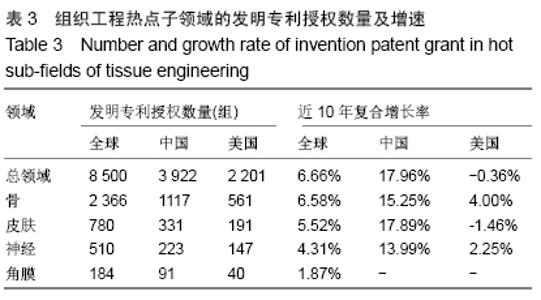
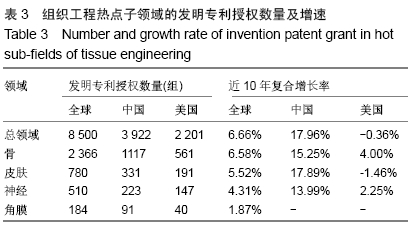
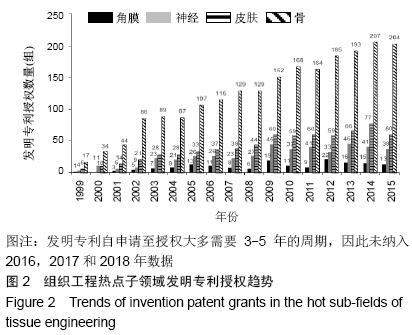
2.2.2 发明专利授权趋势 发明专利是初步的发明设计方案,授权发明专利是已经获得了知识产权部门的授权,拿到了授权通知书,就相当于这个技术已经成为发明专利。发明专利授权不仅表明专利权人获得了其发明技术的排他性产权,也意味着其发明技术转变为受法律保护的无形资产和竞争优势[29]。专利授权信息能反映各个国家/地区或不同专利权人在不同技术领域所持有专利权状况,进而能揭示专利权人凭借专利权对不同技术领域的控制状况[27,30-31]。通过热点子领域的发明专利授权分析,可以揭示骨、皮肤、神经、角膜组织工程领域的高质量成果布局及其竞争优势。 骨、皮肤、神经、角膜组织工程领域发明专利授权数量和增速见图2和表3。4个热点子领域发明专利授权与专利申请趋势基本一致,骨组织工程领域发明专利授权数量最多(2 366组,39.69%),皮肤(780组,37.30%)和(510组,35.94%)数量相对有限,角膜组织工程数量最少(184组,38.25%),4个热点子领域均有近4成的发明专利获得授权。骨(6.58%)、皮肤(5.52%)、神经(4.31%)、角膜(1.87%)4个热点子领域的全球发明专利授权数量均呈现增长趋势,但均低于总领域增速(6.66%)。全球角膜组织工程规模较小,发明专利授权数量也相对较少,中美两国发明专利授权数量也较少,呈现波动式发展,因此未计算中美两国的近10年复合增长率。中国在骨、皮肤、神经3个热点子领域的专利申请数量和增速均远超过美国,且增速远高于全球平均水平,一路保持快速增长,美国皮肤组织工程领域呈现负增长,骨和神经组织工程正增长。 "
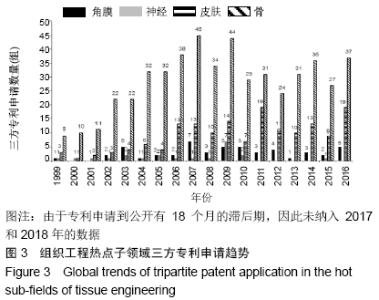
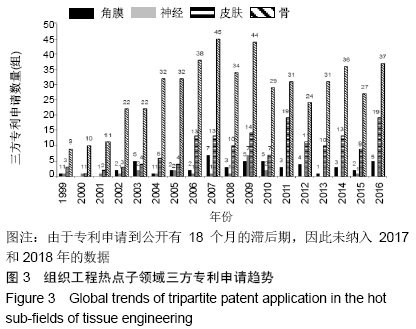
2.2.3 三方专利申请趋势 由于不同国家统计的发明专利数据具有不同程度的“本土优势”,这样在进行国际比较时就存在较大的不可比性,而三方专利很大程度上能消除这种不可比性。又由于三方专利在地理上囊括了美国、日本、欧洲这三个世界上科技水平和创新活力最高的国家/地区,同时在这三个国家/地区申请专利的费用昂贵,因此三方专利通常被认为具有较高的科技含量和经济价值[32-33]。三方专利拥有量的规模可以反映一个领域的技术发明水平以及在国际竞争力[27]。通过骨、皮肤、神经、角膜组织工程领域的三方专利申请分析,可以揭示其高市场价值成果的科技含量及其技术竞争力。 组织工程总领域共有三方专利申请1 536组,占该领域全球专利申请量的6.74%,骨、皮肤、神经、角膜4个热点子领域的全球三方专利申请均是发明专利,申请趋势见图3。骨(537组,8.29%)、皮肤(169组,7.46%)、角膜(54组,11.23%)3个子领域的三方专利申请占比均高于组织工程总领域的三方专利申请占比(6.74%)。神经组织工程领域全球三方专利申请数量相对较少,只有22组,仅占该领域专利申请的1.56%。从三方专利申请数量来看,骨、皮肤、角膜3个子领域的技术发明水平较高,具有较高的科技含量,且专利质量相对较高,而神经组织工程相对较低。 "

中国在组织工程领域的高市场价值成果与美国相比还存在较大差距。美国在组织工程4个热点子领域均有三方专利申请,中国仅在神经、角膜2个子领域有三方专利申请,其中南通大学在神经组织工程领域有1组、中国海洋大学在角膜组织工程领域有1组。南通大学这组三方专利在美国专利及商标局、欧洲专利局均拿到了授权,但在日本专利局被驳回;在中国国家知识产权局的同族专利(公开号:CN100382772C)于2008-04-23拿到授权,该专利是关于一种含蚕丝丝素的医用神经移植物及其制备方法,所用材料高纯度蚕丝丝素是天然可降解材料,与人体有着良好的生物相容性[34]。中国海洋大学的这组三方专利已经拿到三方授权,并且在美国专利及商标局、日本专利局的专利发生了权利转让,专利权转移给了发明人;在中国国家知识产权局的同族专利(公开号:CN101508971B)于2013-12-17拿到授权,并于2015-12-30发生权利转移,中国海洋大学将专利权转让给了青岛宇明生物技术有限公司。该专利涉及一种组织工程人角膜内皮的重建方法,所重建的组织工程人角膜内皮可用于批量生产,能够满足角膜移植治疗对组织工程人角膜内皮的大量需求,且组织工程人角膜内皮体外重建和临床治疗的成本低[35]。 "

| [1] 王佃亮.组织工程的诞生与发展——组织工程连载之一[J].中国生物工程杂志,2014,34(5):122-129. [2] 杜娟,王佃亮,张艳梅,等. 组织工程面临的技术挑战与发展趋势[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2011,31(6): 142-148. [3] XU C, WANG Y, YANG H, et al. Association between cancer incidence and mortality in web-based data in china: infodemiology study. J Med Int Res. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(1):e10677. [4] DU J, JIA X. Engineering nerve guidance conduits with three-dimenisonal bioprinting technology for long gap peripheral nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(12): 2073-2074. [5] FU X. Regenerative medicine in China: new advances and hopes. Sci China Life Sci. 2018;61(10):1135-1136. [6] TANG X, QIN H, GU X, et al. China's landscape in regenerative medicine. Biomaterials. 2017;124:78-94. [7] 曹雪飞,宋朋杰,乔永杰,等. 3D打印骨组织工程支架的研究与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(25):4076-4080. [8] QU J, LU J, HU Y. Research and development of anti-Parkinson's drugs: an analysis from the perspective of technology flows measured by patent citations. Exp Opin Ther Pat. 2019;29(2):127-135. [9] ZHANG T, CHEN J, OUYANG Z. Key fields and key technical points of pharmaceuticals: a perspective from patent analysis. BIBE 2018; International Conference on Biological Information and Biomedical Engineering.2018:1-13. [10] RODRIGUEZ-SALVADOR M, MARIA RIO-BELVER R, GARECHANA-ANACABE G. Scientometric and patentometric analyses to determine the knowledge landscape in innovative technologies: The case of 3D bioprinting. PLoS One.2017; 12:e01803756. [11] ZHANG T, CHEN J, JIA X. Identification of the key fields and their key technical points of oncology by patent analysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10(11): e0143573. [12] 张婷,陈娟,欧阳昭连,等.组织工程与再生医学领域的专利竞争态势[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(34):5479-5485. [13] 张婷,欧阳昭连.基于专利分析及可视化的抗肿瘤药竞争态势研究[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2018,27(20):2337-2345. [14] 张婷.基于专利分析和社会网络分析的天然抗肿瘤药研究[J].中国肿瘤, 2017,26(8):642-649. [15] 张婷,池慧,欧阳昭连.基于专利分析的手术机器人竞争态势研究[J].中国医学装备,2018,15(7):119-123. [16] 张婷, 欧阳昭连.中国肿瘤领域重点技术的识别研究[J].中国肿瘤, 2018, 27(5):393-400. [17] 张婷,池慧,欧阳昭连.基于专利分析及可视化的神经刺激器竞争态势研究[J].中国医疗设备,2018, 33(11): 33-36. [18] 赵晓宇.药物研发相关的专利策略研究[D]. 北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院,2007. [19] 张婷,陈娟,欧阳昭连.生物医药科技前沿领域的识别研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2019,19(2): 370-378. [20] 张婷,安嘉璐,曹敏军,等.基于专利分析的医学科技重点技术前沿领域的识别研究[J].现代生物医学进展, 2015,15(32):6371-6376. [21] 谭泽林.医药类上市公司价值评估方法的选择及估值差异研究[D].成都:西南交通大学, 2012. [22] 周博闻.美国健康服务业发展研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2018. [23] 张广安.专利质量综合评价指数构建及应用[M].北京:北京工业大学,2013. [24] 李自香.基于专利分析的企业自主创新效率评价研究[M].济南:山东大学, 2014. [25] 张克群,牛悾悾,夏伟伟.高被引专利质量的影响因素分析——以LED产业为例[J]. 情报杂志, 2018, 37(2): 81-87. [26] 刘辉锋. 从PCT申请和三方专利指标评价中国海外专利申请实力[J].科技和产业, 2017,17(7):146-149. [27] 张韵君.基于专利战略的企业技术创新研究[D].武汉:武汉大学, 2014. [28] 周磊.专利视角下企业技术合作竞争研究[D].武汉:武汉大学, 2013. [29] 郑永锋.药品专利侵权判定规则研究[D].北京:中国政法大学, 2008. [30] 王灿. 专利贸易壁垒及其应对研究[D].北京:北京邮电大学, 2013. [31] 方曙.基于专利信息分析的技术创新能力研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学, 2007. [32] 池慧.中国医疗器械创新力发展报告[M].北京: 科学出版社, 2018. [33] 张婷,陈娟,池慧,等.基于专利分析的医疗器械领域技术竞争态势研究[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2019, 34(5):107-113. [34] 顾晓松,杨宇民,丁斐,等.含蚕丝丝素的医用神经移植物的制备方法[P]: CN200510094683.2. 2005-09-28. [35] 樊廷俊,赵君,王晶,等.一种组织工程人角膜内皮的重建方法[P]: CN200910020034.6. 2009-03-23. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||