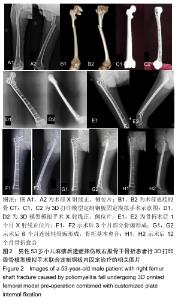
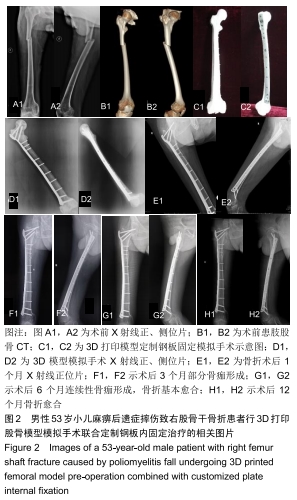
[1] GROCE NE, BANKS LM, STEIN MA. Surviving Poliomyelitismyelitis in a post-Poliomyelitismyelitis world. Soc Sci Med. 2014;107:171-178.
[2] MOHAMMAD AF, KHAN KA, GALVIN L, et al. High incidence of osteoporosis and fractures in an aging post-poliomyelitismyelitis population. Eur Neurol.2009;62(6): 369-374.
[3] ANOOP P, RICHARD D, MANOJ R, et al. Outcome of total knee arthroplasty in patients with poliomyelitis. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(6):358-362.
[4] GAN ZJ, PANG HN. Outcomes of total knee arthroplasty in patients with poliomyelitis. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(11): 2508-2513.
[5] BROGÅRDH C, LEXELL J. Falls, fear of falling, self-reported impairments, and walking limitations in persons with late effects of poliomyelitismyelitis. PMR. 2014;6(10):900-907.
[6] ROCHMAN T, SOEHARDJONO A, ZACOEB A. Simplification of failure-based composite design using general isotropic, linear fe softwares for classical lamination shell theory. Cureus. 2017; 9(12):496-507.
[7] WU CH, HUANG SW, LIN YN, et al. Adults with Poliomyelitismyelitis are at risk of hip fracturefrom middle age: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Injury. 2019; 50(3):738-743.
[8] GUPTA M, JAIN VK, UPADHYAYA GK, et al. Comprehensive review of challenges associated with management of lower limb fractures in Poliomyelitismyelitismyelitis patients. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2016;7(4):276-281.
[9] KHALIL ES. Locked plating for femoral fractures in Poliomyelitismyelitis patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(10):1299-1304.
[10] YAO C, JIN D, ZHANG C. Reverse Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) plating for proximal femur fractures in poliomyelitismye litismyelitis survivors: a report of two cases. Am J Case Rep. 2017;18:1209-1214.
[11] BAGARIA V, CHAUDHARY K. A paradigm shift in surgical planning and simulation using 3Dgraphy: Experience of first 50 surgeries done using 3D-printed biomodels. Injury. 2017; 48(11):2501-2508.
[12] PARK JH, LEE Y, SHON OJ, et al. Surgical tips of intramedullary nailing in severely bowed femurs in atypical femur fractures: Simulation with 3D printed model. Injury. 2016;47(6):1318-1324.
[13] 袁志根,付三清,蒋国安,等.3D打印技术在骨盆骨折前路微创手术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(2):117-119.
[14] 左睿,孙永建,吴毅,等.3D打印与虚拟手术设计在复杂胫骨平台骨折手术治疗中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(4): 369-372.
[15] 马立敏,周烨,周霞,等.3D打印技术辅助个性化定制钢板在膝关节周围骨肿瘤中的应用[J].中国数字医学,2019,14(2):5-8.
[16] 万永鲜,卓乃强,阳运康,等.数字化定制钢板治疗四肢复杂骨折的疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(4):402-405.
[17] RAWAL B, RIBEIRO R, MALHOTRA R, et al. Anthropometric measurements to design best-fit femoral stem for the Indian population. Indian J Orthop. 2012;46(1):46-53
|