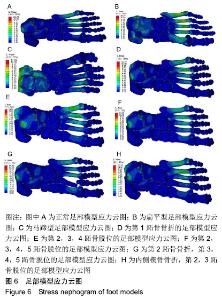
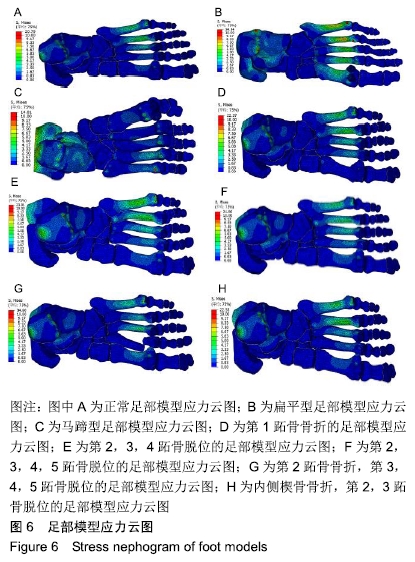
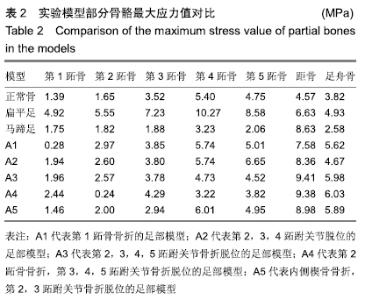
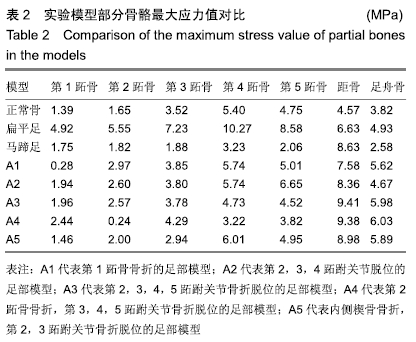
[1] 卢昌怀.距骨数值仿真模型的建立及有限元分析[D].广州:南方医科大学,2011.
[2] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317.
[3] 刘敏,周晓赛,王俊诚,等.不同方法治疗不稳定骨盆骨折中前环损伤的有限元分析[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(2):156-160.
[4] 张兴飞,王文成,许亚军.数字化技术在平足研究中的应用:三维模型构建与生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(20): 3242-3247.
[5] 张家豪,任爽,邵嘉艺,等.前交叉韧带生物力学止点重建的解剖学与有限元分析[J/OL].北京大学学报(医学版),2019,51(3): 586-590.
[6] 张宏,范雅丽,杨东浩,等.足部有限元模型模拟碾压伤的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(12):1903-1907.
[7] 钟环,欧阳汉斌,魏波,等.桡骨远端骨折锁定钢板的拓扑优化及有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(23):2189-2194.
[8] 祝永刚,孙旗,陈江等.退变椎间盘生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(15):1400-1404.
[9] 金乾坤,何盛为,何飞熊,等.足踝部三维有限元仿真模型的构建及验证[J].中国数字医学,2016,11(4):83-86.
[10] LEDOUX W, CAMACHO D, CHING R, et al.The Development and Validntion of a Computational Foot and Ankle Model. Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (Cat. No.00CH37143).Chicago,USA,2000.
[11] 卢昌怀,余斌,陈辉强,等.正常步态下距骨三维有限元模型的建立及应力分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(10):2273-2276.
[12] BANDAK FA,TANNOUS RE,TORIDIS T. On the development of an os seo-ligamentous finite element model of the human ankle joint. International Journal of Solids and Structures. 2001;38(10-13):1681-1697.
[13] CHEN G, WU FY, LIU ZC, et al. Comparisons of node-based and element-based approaches of assigning bone material properties onto subject-specific finite element models. Med Eng Phys. 2015;37(8):808-812.
[14] CHEUNG JT, AN KN, ZHANG M. Consequences of partial and total plantar fascia release: a finite element study. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(2):125-132.
[15] 李云婷,陶凯,王冬梅,等.足底软组织硬化对足部生物力学性能影响的三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2009,24(3):169-173.
[16] SOWMIANARAYANAN S, CHANDRASEKARAN A, KUMAR RK. Finite element analysis of a subtrochanteric fractured femur with dynamic hip screw, dynamic condylar screw, and proximal femur nail implants--a comparative study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(1):117-127.
[17] SHARKEY NA, HAMEL AJ. A dynamic cadaver model of the stance phase of gait: performance characteristics and kinetic validation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1998;13(6):420-433.
[18] 陶凯.人体足踝系统建模与相关力学问题研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2010.
[19] 张琳琳,朱明,沈凌,等.肱骨外旋运动中人工肱骨头与肩胛盂表面的接触分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2014,31(1):120-123.
[20] CHEUNG JT, ZHANG M, LEUNG AK, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the foot during standing--a material sensitivity study. J Biomech.2005;38(5): 1045-1054.
[21] 吴立军,李宇婷,王亭,等.无症状扁平足与正常足生物力学差异的数字化研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2015,34(6):763-767.
[22] 夏域昆.青少年扁平足与正常足的足底压力特征比较分析[D].长春:吉林大学,2018.
[23] KIDO M, IKOMA K, IMAI K, et al. Load response of the tarsal bones in patients with flatfoot deformity: in vivo 3D study. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32(11):1017-1022.
[24] 管仲良,李战春,王丹,等.先天性马蹄内翻足的三维有限元分析在临床手术中的应用[J].浙江创伤外科,2012,17(6):760-761.
[25] 杨璇,张菁,陈珽,等.手法复位先天性马蹄内翻足过程中的力学变化[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(3):323-326.
[26] KOTWICK JE. Biomechanics of the foot and ankle. Clin Sports Med. 1982;1(1):19-34.
[27] 谢强,王智慧,刘文一,等.踝关节融合三维有限元模型的初步建立及验证[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(6):645-646.
[28] 徐翔燕.基于解剖学参数的踝关节假体的设计及力学仿真[D].上海:上海交通大学,2015.
[29] 何正言.锁定钢板固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ型跟骨骨折有限元模型分析[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2016,26(13):130-131.
[30] 徐世明,蔡慧,邓子文,等.Suture Endobutton与跖肌腱重建Lisfranc韧带的生物力学对比研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2018,36(2):211-215.
[31] 赵宏谋,李毅,梁晓军,等.不同内固定方法治疗踝关节后侧骨-韧带损伤的生物力学研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(6): 613-616.
[32] 钟世镇.数字医学在不同学科中的探索应用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2018,34(6):前插2.
[33] OKA K, MURASE T, MORITOMO H, et al. Accuracy of corrective osteotomy using a custom-designed device based on a novel computer simulation system. J Orthop Sci. 2011; 16(1):85-92.
[34] 杜明昌,柳椰,翟良全,等.定制3D打印截骨导板辅助双膝关节同期置换的临床疗效观察[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2018, 12(1):18-23.
[35] 张占阅,董乐乐,左强,等.有限元分析法在拇外翻生物力学研究中的应用:可靠性与提升空间[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11): 1762-1767.
|