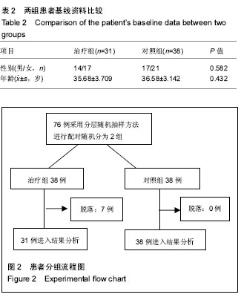
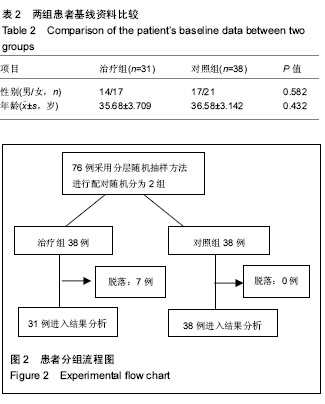
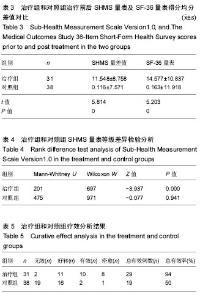
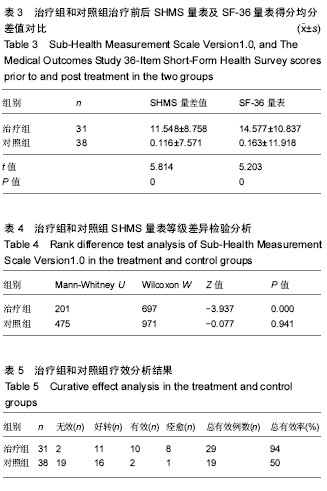
| [1] |
Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong.
Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382.
|
| [2] |
An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu.
Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong.
Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118.
|
| [4] |
Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun.
Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596.
|
| [5] |
Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao.
Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603.
|
| [6] |
Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong.
Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji.
Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625.
|
| [8] |
Li Hui, Chen Lianglong.
Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630.
|
| [9] |
Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi.
Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642.
|
| [10] |
Liu Tongbin, Lin Peng, Zhang Xiaoming, Dong Xiling, Cao Fei, Wang Le, Guo Xinxing.
Optimization of preparation method of atorvastatin calcium sustained-release microspheres
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 535-539.
|
| [11] |
He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping.
Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559.
|
| [12] |
He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li.
Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566.
|
| [13] |
Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong.
Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455.
|
| [14] |
Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen.
Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617.
|
| [15] |
Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi .
Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606.
|